Predator-Prey Relationships
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What is predation?
The hunting and comsuption of one species by another.
Predator-prey population graph
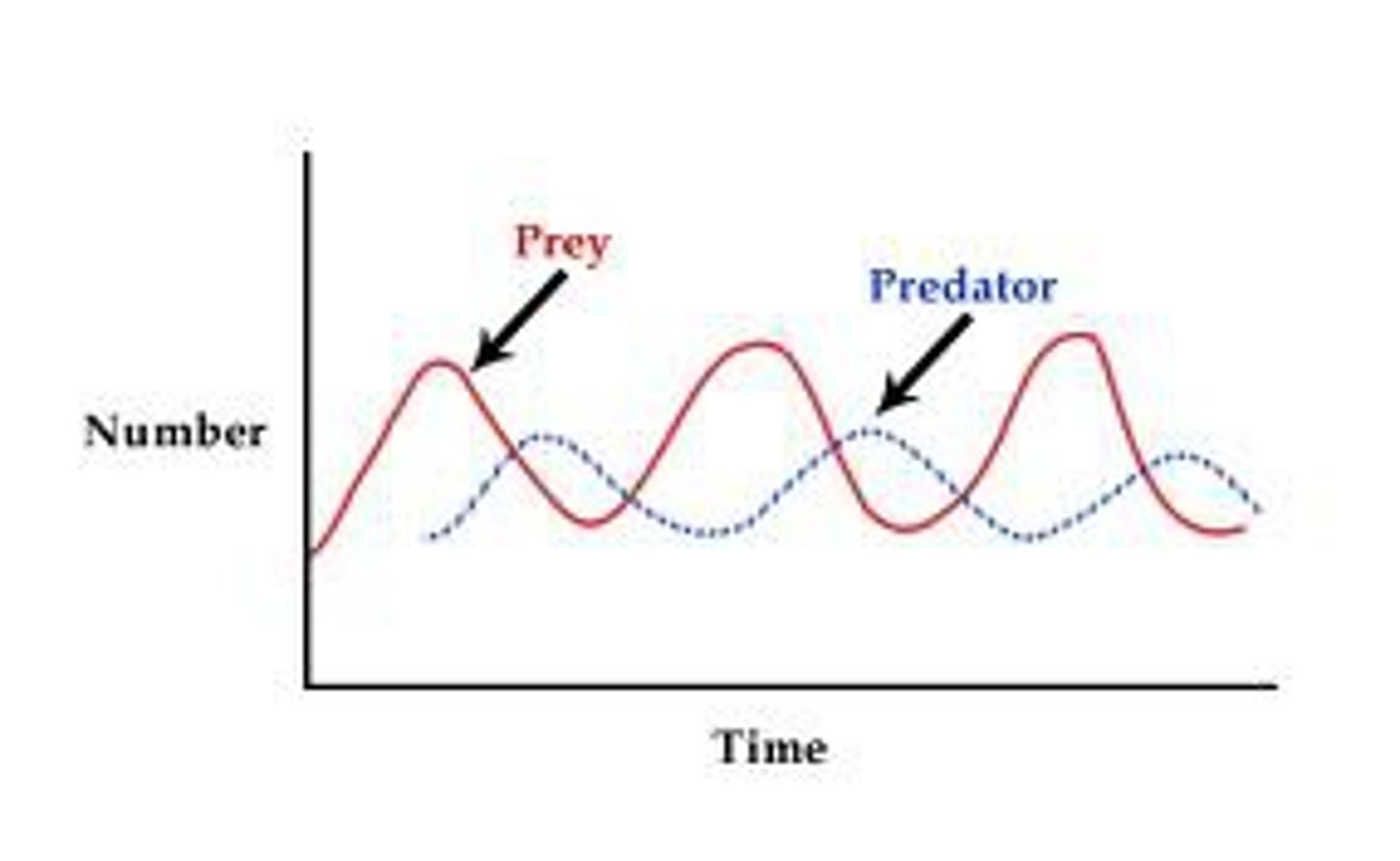
How many stages are there to the predator-prey population graph?
Four
What happens to the predator population when the prey population increases?
It increases because more food is provided for them which allows them to survive and reproduce.
What does an increase in predator population cause?
More predation which decreases the prey population.
What does a reduced prey population cause?
More intraspecific competition in the predator population which causes it to decrease.
What does a reduced predator population result in?
Less predation means more prey is able to survive and reproduce successfully, causing the population to increase.
Why is there a lag between the peak population sizes of predators and their prey?
Ecological response times.
Why are ecological response times so important?
They are vital for the balance of ecosystems.
Why are ecological response times vital for predator-prey populations?
There is a lag between peaks because if predators responded instantly to an increase in prey, they could hunt and wipe out the prey entirely and then end up starving themselves.
What does the predator-prey dynamic exert?
Selection pressure on both groups.
What happens to prey that are more effective at evading predators?
They survive and reproduce more, meaning the adaptations they used to avoid predation can be passed down.
What hapens to predators when prey adapt to avoid them more?
They also adapt methods that hunt prey more efficiently.
What are some examples of predator adaptations?
- Sudden bursts of speed
- Stealth
- Camouflage
- Better prey detection: forward facing eyes with sharp vision.
What are some adaptations of prey adaptations?
- Mimicry
- Protective features (e.g. spines)
- Camouflage
- Better predator detection: side facing eyes for broader field of vision