Eye as a receptor and nervous system
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
what is a synapse
a junction between two neurones
role of neurotransmitters
when an electrical impulse travels to the end of the presynaptic neurone
triggers the release of neurotransmitters
these travel/diffuse through the synaptic cleft
bind to the postsynaptic neurone
triggers new impulse
impulse=travels one way ONLY
what are neurotransmitters
chemicals that carry signals across the synaptic cleft between neurones
simple reflex arc illustrated by withdrawal of finger from a hot object
stimulus received (heat)
receptor detects
signal sent to CNS which consists of spinal cord and brain via sensory neuron
impulse crosses sensory neuron to motor neuron
motor neuron sends signal to effector e.g. muscle in this case to withdraw hand
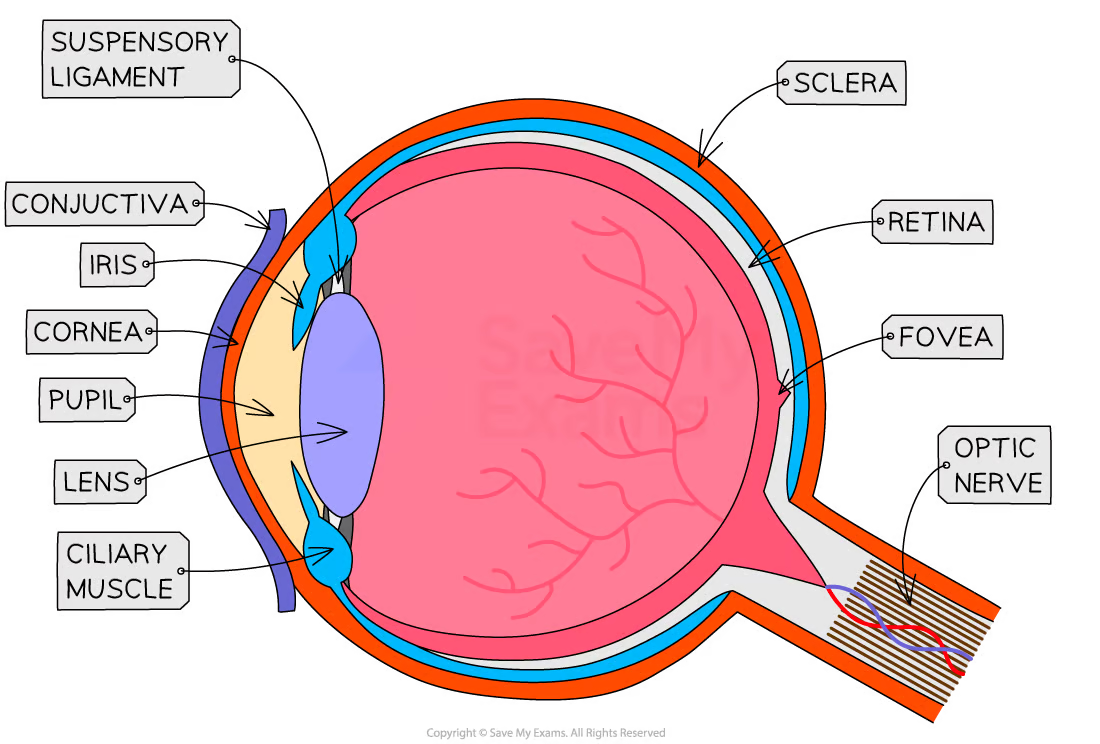
what is the purpose of the cornea
refracts light as it enters the eye to help focus it
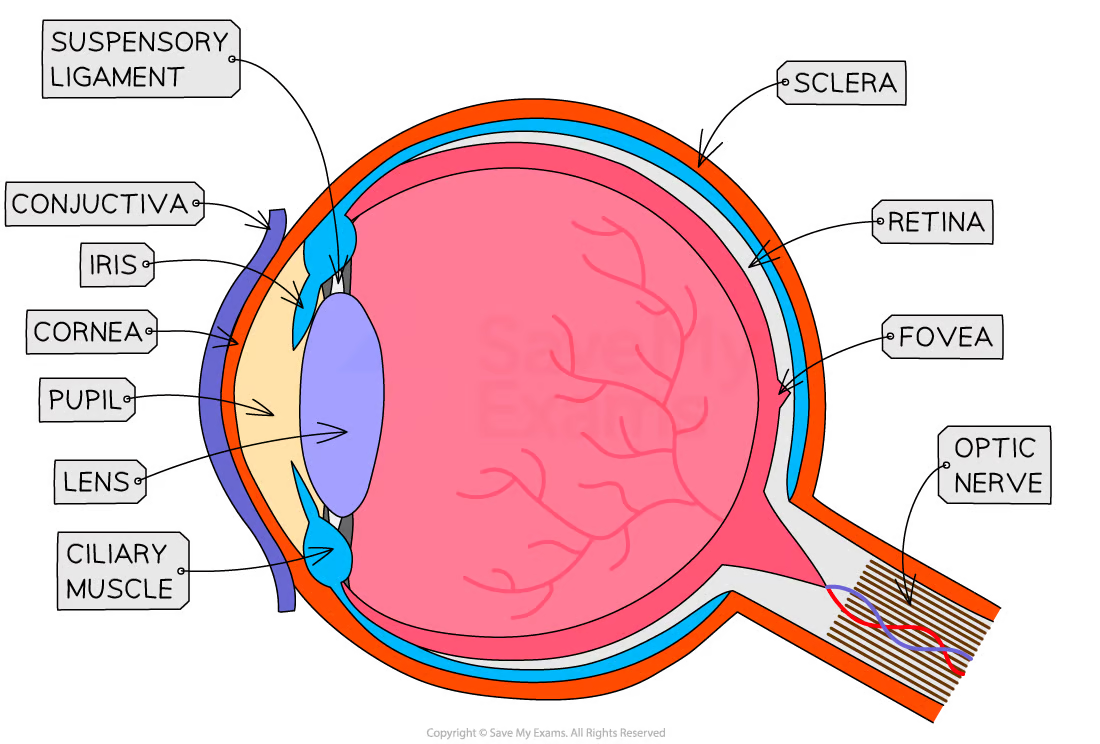
purpose of iris
controls the SIZE of pupil —> how much light enters your eye
in BRIGHT light —> constricts/gets smaller
in DARK —> dilate/get bigger to take in more light
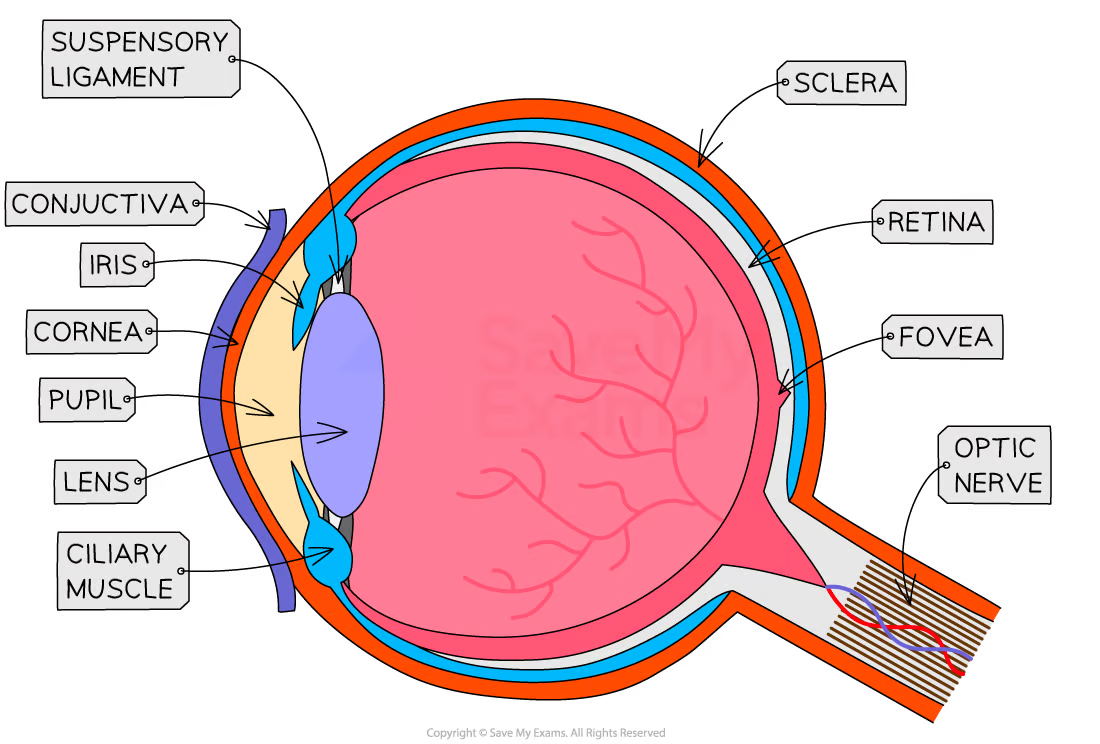
purpose of lens
changes shape to focus light on the retina
NEAR —> thicker
FAR —> thinner
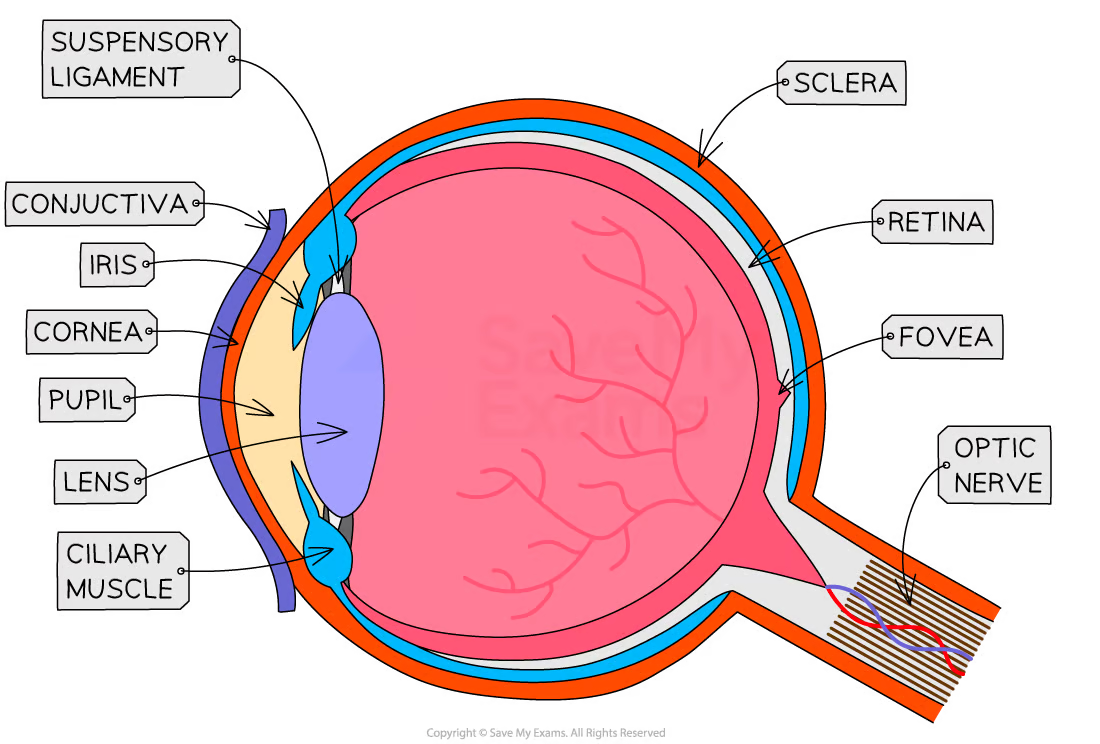
purpose of retina
contains photoreceptor cells:
cone cells —> colour and work in bright light
rod cells —> dim light BUT no colour
converts light into electrical impulses
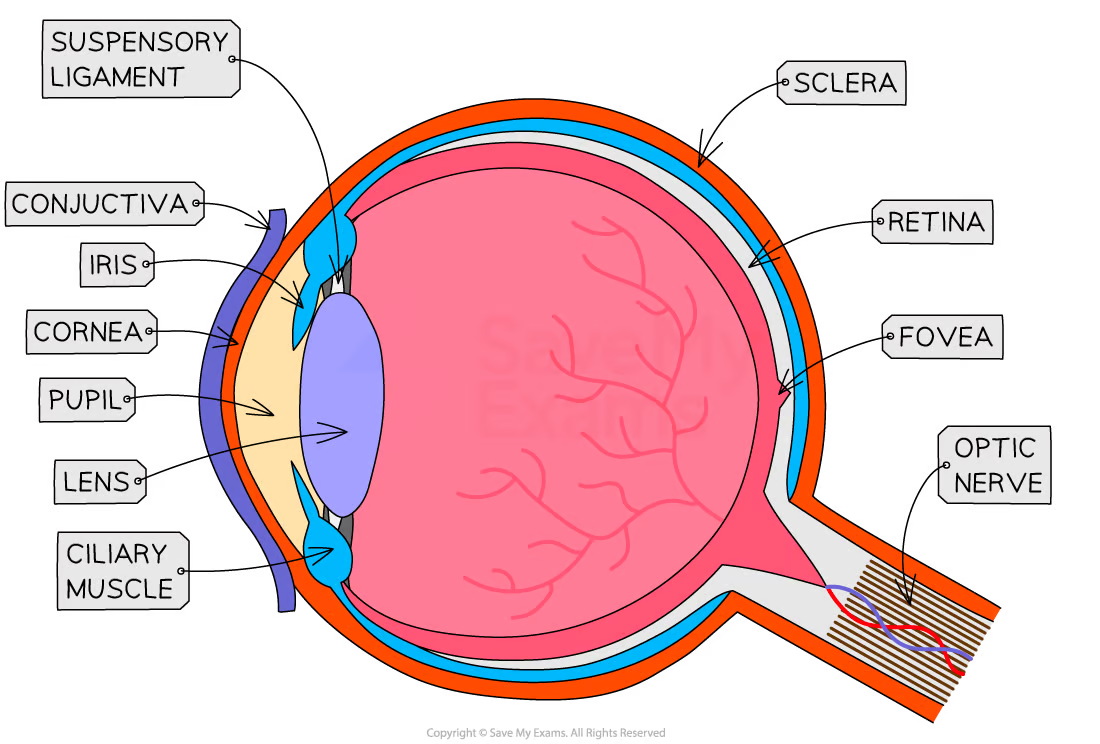
purpose of optic nerve
carries electrical impulses from retina to brain —> image is processed
what is the eye’s response to distant objects
ciliary muscles relax
suspensory ligaments tighten
lens get thinner
less bending of light needed
what is the eye’s response to close object
ciliary muscles contract
suspensory ligaments relax
lens is more curved
more bending of light needed
eye’s response to dim light
circular muscles contract
radial relax
pupils dilate
eye’s response to bright light
circular muscles relax
radial muscles contract
pupils constrict