anatomy exam 3
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Movement:
The contraction of the skeletal muscle is responsible for overall movement.
Maintain Posture:
skeletal muscle constantly maintains posture
Production of body heat:
Skeletal muscle contractions help maintain body temperature
Communication:
Skeletal muscles are responsible for speaking, writing, typing, gesturing, and facial expressions.
Glycemic control:
skeletal muscle absorbs, stores, and uses a large amount of glucose, thus regulating/stabilizing glucose concentration.
Contractibility:
ability to contract/shorten.
Excitability:
the capacity of muscle cells to respond to stimuli
Conductivity:
electrical changes trigger a wave of excitation
The extensibility
muscle can be stretched beyond its normal resting length and still be able to contract.
Elasticity
the ability of a muscle to return to its original length
Skeletal muscle:
attached to the skeletal system.
Contain long, threat-like cells that are multinucleated (located peripherally/edges)
Striations present (light and dark bands)
Under voluntary control (manual contraction)
Function of skeletal muscle
body movement, posture, body heat
Smooth muscle:
long, thin cells that taper at the end
Single, centrally located nucleus
Under involuntary control
No striations
Function of smooth muscle
makeup and function of visceral internal organs, such as digestion, emptying of bladder//both involuntary and voluntary control, and regulation of blood vessels.
Cardiac muscle:
cells are called cardiocytes, short, branched cells
Single, centrally located nucleus
Striations present
Involuntary control Autonomic (cardiac): self-excitable and able to generate an action potential without external stimulation by nerve cells
Intercalated discs (cardiac):
gap junctions and mechanical junctions (desmosomes) that join cardiocytes
Belly:
enlarged fleshy body of muscle located between the slender points of attachment
Fascia:
layers of tough connective tissue
Epimysium:
outer layer of fascia that can extend to the bone and form tendons
Perimysium:
connective tissue layer that surrounds fascicles (bundles of muscle fibers)
Endomysium:
connective tissue layer around individual muscle fibers (located in fascicles)
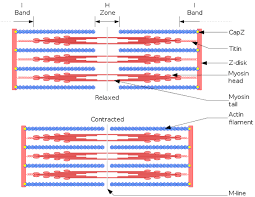
Sarcomere:
contractile units that make up myofibrils; the smallest portion of muscle that can contract, contains myofilaments
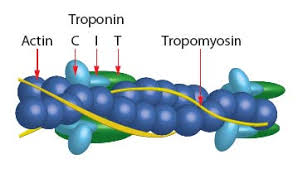
Actin (thin):
composed of 3 separate proteins
Tropomysin:
a long fibrous protein that lies in the groove along the actin strand. COvers the “attachment/active site” in relaxed muscles. (muscles can't contract until tropomyosin moves away from the active site) NERDS ROPE
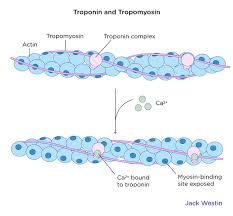
Troponin:
a protein with 3 parts
Anchor troponin to actin
Prevents tropomyosin from uncovering the actin attachment site in a relaxed muscle
Binds calcium ions
Myosin (thick):
composed of elongated myosin molecules shaped like golf clubs
Rod portion:
lying parallel to the myosin molecule
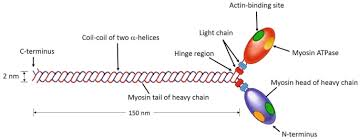
Myosin heads:
2 structures that extend laterally (stick out to the side).
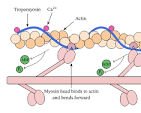
Myosin heads have 3 important functions:
Heads bind to the active site on actin to form a cross-bridge
Heads are attached to the rod with a hinge region that bends and straightens during contraction
Heads break down ATP, releasing energy
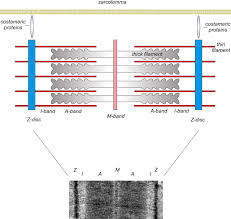
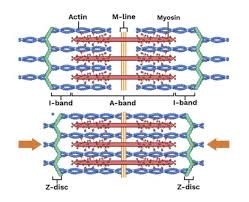
Sarcomere structure
Sarcomeres join end to end, forming myofibrils
Arrangement of actin and myosin gives muscles their striated appearance
Z discs:
stationary anchors for actin myofilaments. Creates the boundary for the sarcomere.
I bands:
two light-staining regions. contains only actin. Includes Z disks (anchors) and extends to myosin
A band:
a darker staining band in the center of each sarcomere. Contains both actin and myosin
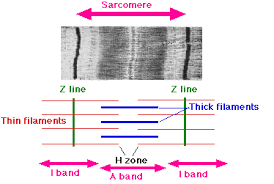
H zone:
center of A band (middle), contains only myosin
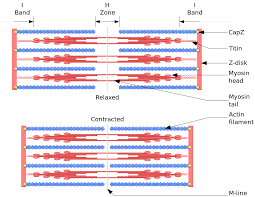
M-line:
middle of H zone. Consists of protein filaments that hold myosin in place
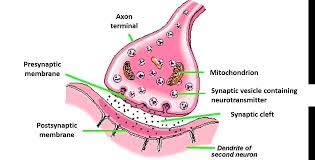
Neuromuscular junction (synapse):
point of contact between a motor neuron axon and muscle fiber. Consists 5 things
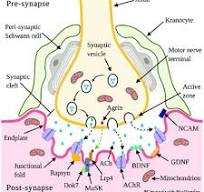
The presynaptic terminal/synaptic knob:
enlarged axon terminals
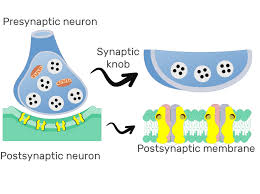
Synaptic vesicles:
small spherical sacs that contains acetylocholine (neurotransmitter)
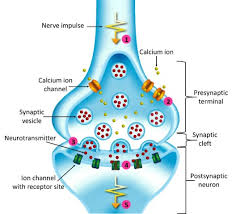
Synaptic cleft:
space between presynaptic terminal and muscle
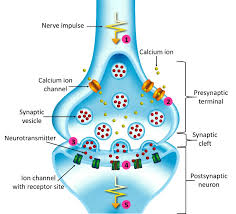
Postsynaptic membrane (motor end plate/junctional folds):
a portion of the sarcolemma of muscle fiber
It Contains high concentration of ACh receptors (transmembrane proteins)
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE):
enzyme that degrades ACh and stop stimulation of muscle fibers.
the first step of muscle contraction
Excitation
action potential in nerve fiber leads to action potential in muscle fiber
the second step of muscle contraction
Excitation-Contraction Coupling:
events that connect the action potential of the sarcolemma to activation of myofilaments
the third step of muscle contraction
contraction
muscle fiber shortens by the sliding filament theory (explains muscle contraction as the result of actin and myosin filaments sliding past each other, shortening the sarcomere, the basic unit of muscle contraction)
the fourth and final step of muscle contraction
Relaxation:
nerve fibers stop stimulating a muscle fiber, and the muscle fiber returns to its resting length
Electrical potential/voltage:
difference in electrical charges from one point to another. (inside of cell vs outside)
Polarized:
separation of charges between the inside of the cell and the outside
Resting membrane potential for sarcolemma
higher negative charges inside the cell as compared to outside the cell.
~ due to the high concentration of K+ in ICF and high Na+ in ECF (maintained by the SODIUM POTASSIUM PUMP)
Depolarization:
change in the membrane potential; for muscles, this occurs at the site of the receptors as the interior of the cell becomes slightly positive (less neg) than before. SODIUM RUSHES IN
~ influx of Na+ into cells
Repolarization:
the interior membrane returns to a negative charge. POTASSIUM RUSHES OUT
~ influx of K+ out of cells
Action potential:
quick up and down shift in voltage that spreads along the sarcolemma
Excitation STEPS
step 1
A nerve signal arrives at the synaptic knob and it opens voltage gated calcium channels and ca+ ions eneter from extracellular fluid.
excitation steps
2
Calcium stimulates vesicles to release acetylcholine into the synaptic cleft via exocytosis.
excitation steps
3
ACh (acetylcholine) diffuses across the cleft and binds to ACh receptors on the carcolemma
excitation step
4
Receptors open, allowing Na+ to quickly flow into the cell and K+ to flow out of the cell, causing the sarcolemma to reverse polarity and return to its original resting state. Forms and end plate potential (EPP) rapid change in polarity at the motor end plate. THE MUSCLE IS POTENTIALLY CHARGED
excitation step 5
Action potential created from Na+ moving into and K+ moving out of areas near the EPP.. A muscle fiber is now excited!
Excitation, contracting, coupling steps!
step 1
A wave of action potentials spreads down into the cell interior via T-tubules
Excitation, contracting, coupling steps!
2
An action potential opens voltage-gated channels in the terminal cisternae, which causes SR to diffuse Ca+ into the cytosol
Excitation, contracting, coupling steps!
3
Calcium binds to troponin
Excitation, contracting, coupling steps!
4
Troponin-tropomyosin complex changes its shape and exposes the active site on actin
Sliding filament theory steps
1
Myosin must have ATP bound to it to initiate the connection. Myosin ATPase hydrolyzes this ATP to ADP and phosphate. Energy released activated the head to “cock” into high energy position (extended). ADP and phosphate still bound to the head
Sliding filament theory steps
2
Extend myosin binds to the active site on actin, forming cross-bridge
Sliding filament theory steps
3
Myosin releases ADP and phosphate, flexes into a bent (low energy) position, tugging the thin filament along with it, called the power stroke
Sliding filament theory steps
4
ATP binds to myosin and destabilizes the myosin/actin bond, breaking the cross-bridge. Myosin repeats the whole process and performs a recovery stroke (myosin attaches to a new actin site further down the thin filament)
Relaxation steps!
1
Nerve signals stop arriving at the neuromuscular junction, and ACh is no longer released.
Relaxation steps!
2
ACh (acetylcholine) dissociates from receptors, AChE breaks it down into fragments. Synaptic knob reabsorbs the fragments for recycling.
~ This is also done while the muscle is being stimulated, but it increases when the nerve signal stops
Relaxation steps!
3
Ca+ release stops in the SR ( circoplasmic reticulum), and Ca+ reabsorption increases. In SR, calcium binds to the protein calsequestrin, allowing SR to store large amounts of calcium without forming salts
Relaxation steps!
4
Levels of free Ca+ decrease in the cytosol because of S.R. reabsorption. Ca+ dissociates from troponin
Relaxation steps!
5
Tropomyosin moves back to its resting location, blocking the active site. Myosin can no longer attach to actin.
cord of collegen fibers that attaches muscle to bone
epimysium
series of contractile units that make up each myofibrils
sarcomere
connective tissue that surrounds muscle fibers
endomysium
extension of the cell membrane that penetrates into the interior of the muscle
transverse (t) tubules
connective tissue unsheathing the fascicles
perimysium
actin or myosin containing structure
myofibrils
calcium stores in this structure in the relaxed muscle
sarcoplasmic reticulum
connective tissue that surrounds the whole skeletal muscle
fascia
muscle cell is
a muscle fiber
the gap between a motor neuron axon and muscle cell membrane
synaptic cleft
swelling at the end of each nerve fiber in a synapse
synaptic knob
pre synapse that contains this neurotransmitter
acetylcholine (ach)
the point where a nerve fiber meets a muscle fiber
neuromuscular junction
increases surface area of ach-sensitive membranes
neuromuscular junction