Development
1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
List the key events of animal development
gamete formation
fertilization
cleavage
gastrulation
organogenesis
growth
Gamete Fromation
mature sperm and eggs form
Fertilization
egg and sperm fuse
cleavage
zygote subdivides determinantes partitioned in blastomeres
gastrulation
formation of germ layers
organogenesis
body organs form, cells interact, and differentiate
growth
organs increase in size until the adult body form is attained.
How do eggs prevent polyspermy?
This is prevented when a sperm break through the zone pellucid and then binds to a receptor the cortical granule release and hardens the vitelline layer. This prevents other sperm from entering the jelly coat and binding.
Why does egg type influence cleavage and blastula formation?
The yolk is difficult to divide. This determines the cleavage pattern.
What are the three types of cleavage patterns?
Isolecithal egg, mesolecithal egg, and telolecithal egg
Isolecithal egg
sparse evenly distributed yolk common in mammals which is rotational blastula and echinoderms which is radial blastula formation
Mesolecithal egg
moderate amount of yolk common in amphibians which is radial blastula formation
Telolecithal egg
dense yolk that is concentrated at one end which are found in birds and reptiles which both have discoidal blastula formation
Determinate cleavage
Fate of cells determined early on in embryo development. if a blastomere is removed blastula may fail
Indeterminant cleavage
fate of cells are not determined early on in embryo development. Blastomeres retain the ability to make a whole embryo
Which type of cleavage leads to twins?
indeterminate cleavage
Deuterostome
blastopore becomes anus first. Mammals
Protostomes
Blastopore becomes mouth first. Echinoderms
What are the three germ layers?
Endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm
Ectoderm
outer layer, develops epidermis of skin and its derivatives, produces nervous and sensory systems
Mesoderm
Middle layer. Develops skeletal and muscular systems and develops the circulatory and lymphatic systems
Endoderm
inner layer. Epithelial lining of digestive tract and associated organs. Also the lining of respiratory, excretory and reproductive tracts and ducts.
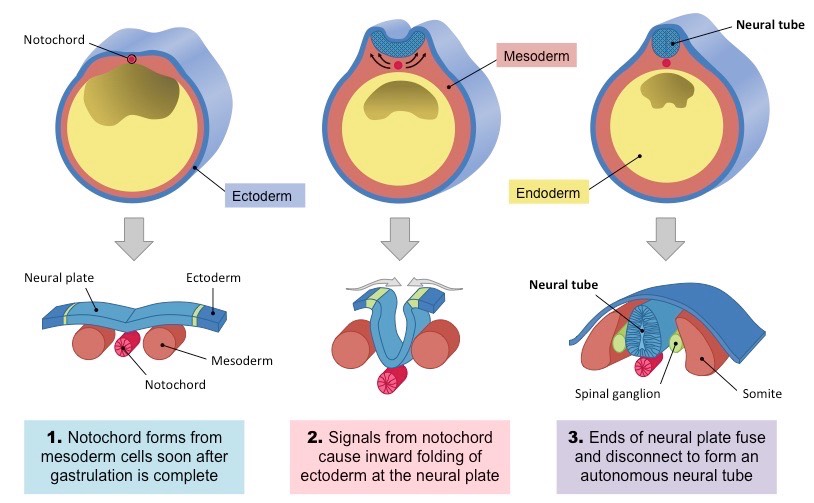
neurulation
formation of spinal chord and brain
Describe neurulation
Dorsal membrane forms → notochord signals ectoderm above to form neural plate → neural plate curves inwards forming the neural tube → neural tube becomes DHNC brain and spinal chord → neural crest cells become part of the peripheral nervous system parts of teeth and skull