02. Human Nutrition
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Balanced diet definition
Diet consisting of the all dietary requirements needed in the right proportions
Carbohydrates
Made up of simple sugars
CHO - carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
Carbs → glucose, maltose → glycogen, starch
Protein
Made up of amino acids
CHON - carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
Lipids
Made up of fatty acids & glycerol
CHO - carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
Carbohydrates function
Provide energy
Protein function
Growth & repair of tissues
Lipids functions (3)
Provide energy
Energy store
Provide energy in emergencies
Insulation
Vitamin A function (3)
Improve vision
Keep skin & hair healthy
Promote resistance of disease
Vitamin C function (3)
Heal wounds
Rebuild new tissue
Prevent scurvy
Vitamin D function (3)
Maintain level of calcium in blood to form strong bones & teeth
Calcium absorption
Made by the body when skin is exposed to sunlight
Iodine function
Make thyroxine in the thyroid gland
Iron function
Make haemoglobin for blood to transport oxygen
Calcium functions (4)
Make bones & teeth
Control muscle contraction
Production of milk
Clotting of blood
Water (4)
Solvent
Transport medium
Substrate in digestive reactions
Lubrication (tears)
Dietary fibre (2)
Provide some energy
Aid movement of food through gut + prevent constipation
Source of starch (3)
Potatoes
Rice
Pasta
Source of sugar (3)
Sweets
Cakes
Fruits
Source of protein (4)
Meat
Fish
Eggs
Legumes
Source of lipids (3)
Butter
Cheese
Milk
Source of Vitamin A (2)
Carrots
Liver
Source of Vitamin C (3)
Citrus fruits [oranges]
Berries
Peppers
Source of Vitamin D (3)
Eggs
Fish liver oils
Fatty fish
Source of iodine (2)
Seaweed
Fish
Source of iron (3)
Red meat
Liver
Beans
Source of calcium (2)
Milk
Cheese
Source of water
Drinks & Foods
Source of dietary fibre (2)
Wholemeal bread
Nuts
Too much refined sugar
Tooth decay
Bacteria in mouth convert sugar to acid & damages tooth enamel
Too much saturated fats & cholesterol
Heart diseases
Plaque build-up blocks arteries
Prevents glucose & oxygen from reaching heart muscle
Too much salt (3)
Cause water retention
Rise in blood pressure
Arteries blocked / burst - stroke
Fibre deficiency
Constipation + Colon cancer
Gut muscles become inefficient → faeces remain in the gut
Too high energy content (2)
Excess energy stored in unlimited amounts of fat - obesity
Extra mass & volume cause:
Joint damage
Increase risk of heart & circulatory diseases
Increase risk of diabetes
Infections of lungs as breathing becomes difficult
Vitamin A deficiency (2)
Night blindness
Poor production of visual pigment
Xerophthalmia
Hardening & flaking of the cornea
Iron deficiency
Anaemia
Iron is needed for haemoglobin synthesis
Insufficient dietary iron limits oxygen transport by red blood cells
Energy release by aerobic respiration is reduced
Vitamin C deficiency
Scurvy
Production of some structural tissues is inhibited
Teeth becomes loose
Skin becomes flaky
Wounds bleed freely
Make immune system less efficient
Body becomes more prone to infection
Protein deficiency
Kwashiorkor
[swollen abdomen, slow down mental & physical development]Due to insufficient protein to be able to reabsorb water from tissues
Calcium / Vitamin D deficiency (3)
Poor development of bones
Children : Rickets [bow legs]
Adults : Osteoporosis [easy fracturing + poor healing of bones]
Energy requirements (activity level)
Active ppl need more energy
Energy requirements (age)
Children & teens need more energy than older ppl as they need energy to grow & are generally more active
Energy requirements (pregnancy)
Pregnant women need more energy as they need to provide energy for their babies to develop
Digestion of starch into glucose
Amylase digests starch into maltose.
Maltase digests maltose into glucose.
Digestion of protein
Protease digests proteins into amino acids
Digestion of lipids
Lipase digests lipids into fatty acids & glycerol
Where is bile produced
Liver
Where is bile stored
Gall bladder
Where is bile released
Small intestine
Role of bile 1 (acid)
Alkaline
Neutralise HCl in stomach that is too acidic for enzyme activity in small intestine.
Create alkaline pH for enzyme activity.
Role of bile 2 (fats)
Emulsifies fats [breaks the fat into tiny droplets]
Gives larger SA of fat for lipase to work on. Make digestion faster.
How does bolus move through the gut
Peristalsis [muscle contraction]
Full digestive system (7)
Mouth
Oesophagus
Stomach
Small intestine
Large intestine
Rectum
Anus
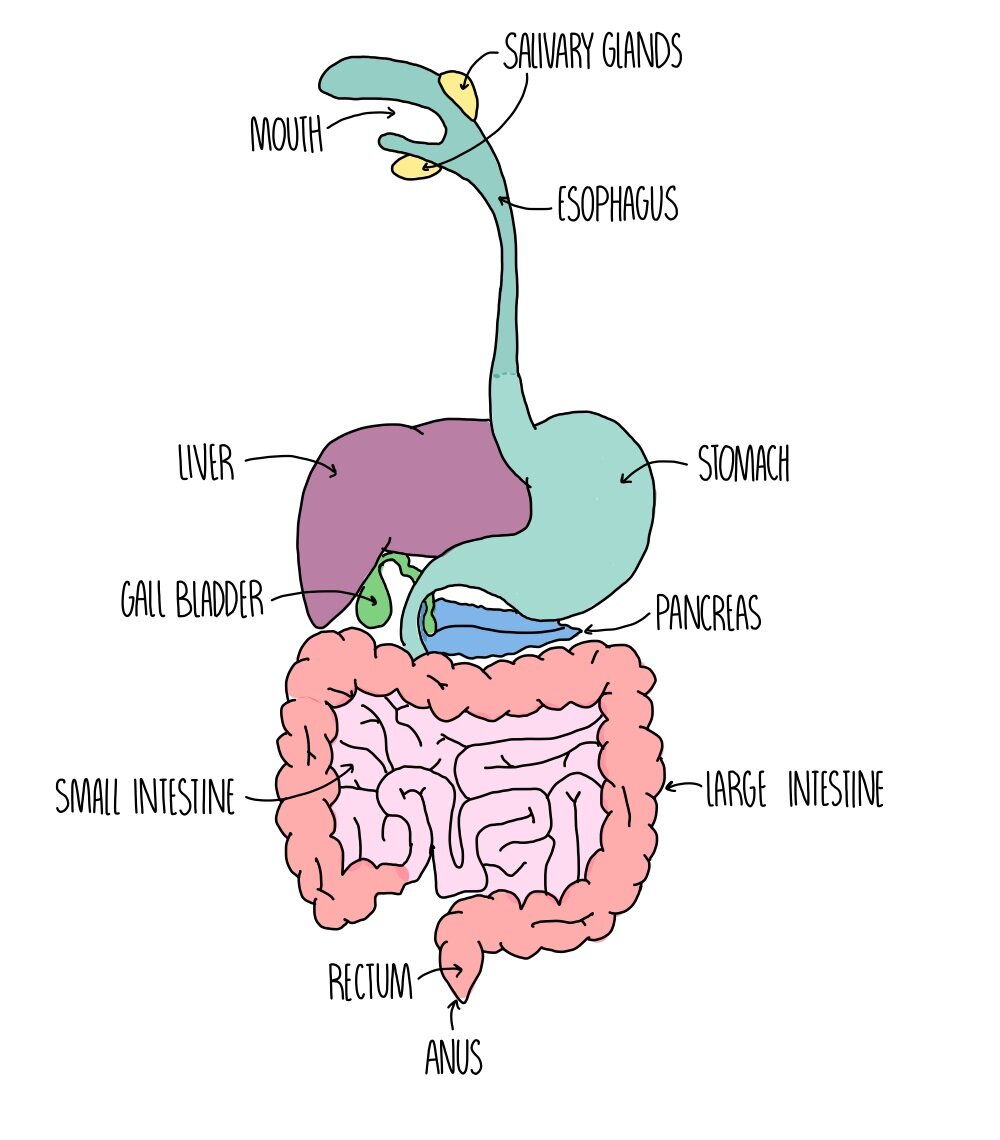
Mouth role
Chemical : Salivary glands in the mouth produce amylase enzyme in the saliva
Mechanical : Teeth break down food
Oesophagus role
Muscular tube connecting mouth to stomach
Stomach role (3)
Pummel food with muscular walls
Produces pepsin [protease enzyme]
Produce HCl for:
Kill bacteria
Give optimum pH for protease enzyme to work
Small intestine role (2)
Produce protease, amylase, lipase enzyme to complete digestion
Where nutrients are absorbed out of alimentary canal into the body
First part : duodenum
Last part : ileum
Large intestine role
Colon
Where excess water is absorbed from the food
Rectum role
Where faeces [undigested food] are stored
Anus role
Where faeces leave the body
Pancreas role
Produces protease, amylase, lipase enzymes then released into small intestine
Adaptation of small intestine (2)
Long - time to break down & absorb all the food before it reaches the end
Villi to increase SA for absorption
Adaptations of villi (4)
Many - increase SA for absorption
Each villi has microvilli to increase SA
Single cell thick wall - shorter distance for nutrients to diffuse into blood
Capillaries for good blood supply - maintain high conc. gradient for diffusion