DD: Lesson 13: Introduction to bioinformatics - the human genome project - target selection
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Define genome
A whole set of genes plus all the DNA between your genes
How many base pairs does each cell contain?
3 billion base pairs
Define genomics
The study of the whole genome and how it works
What is the percentage range for genes that code for DNA?
1% - 2%
How many base pairs can a single gene have?
Hundreds or millions of base pairs
What does genes make?
Proteins

How many genes do humans have?
23,000 genes

How many genes do rice have?
41,000 genes

How many genes does bread mould have?
10,000 genes
How many genes does chicken pox virus have?
70 genes
What is bioinformatics?
A multi-disciplinary area that integrates biology with informatics, computer science and mathematics
When did bioinformatics occur?
In the 60s and 70s
What is the role of bioinformatics?
De-code DNA
When did the human genome project start?
1990
When did the human genome project end?
2003
How much did the first genome cost?
£2.7 billion
What did the human genome project do for the first time?
Make the human genetic blueprint completely readable
What did the human genome project discover?
See which genes cause diseases
What did the human genome project allow?
For genetic diagnostics to progress
How many nanometres is each nucleotide?
0.33
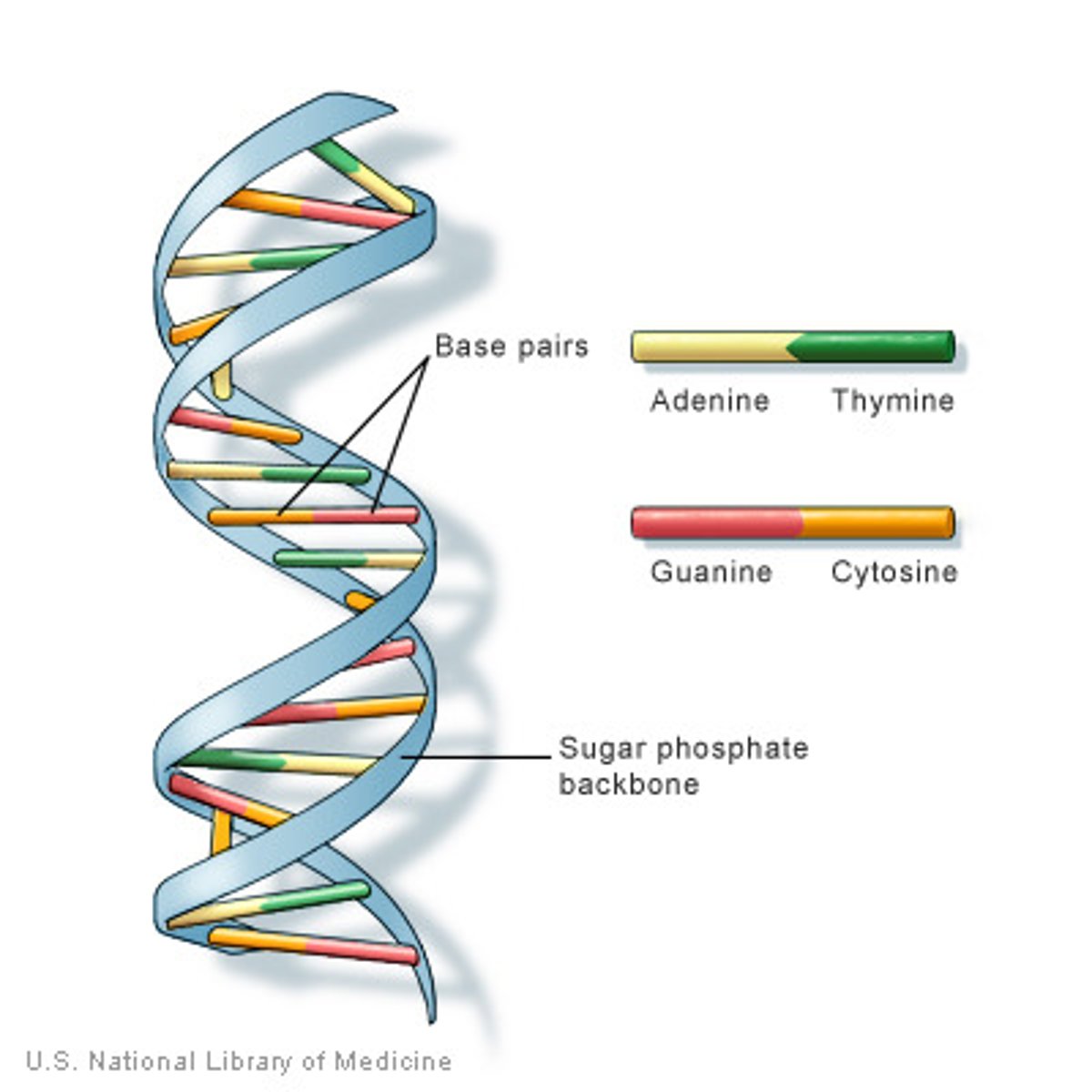
How many nanometres is the space between a double helix?
2.2 - 2.6
How many nanometres is a banana's diameter?
40,000,000

What is sequencing?
Reading the human genome letter by letter
How long does it take to read DNA today?
Less than a day
How much does it cost to read DNA today?
£1000
What happens to cells?
They are sampled/genome
What happens to these samples?
They are fragmented
What happens after the fragmentation?
End repair/adaptor ligation
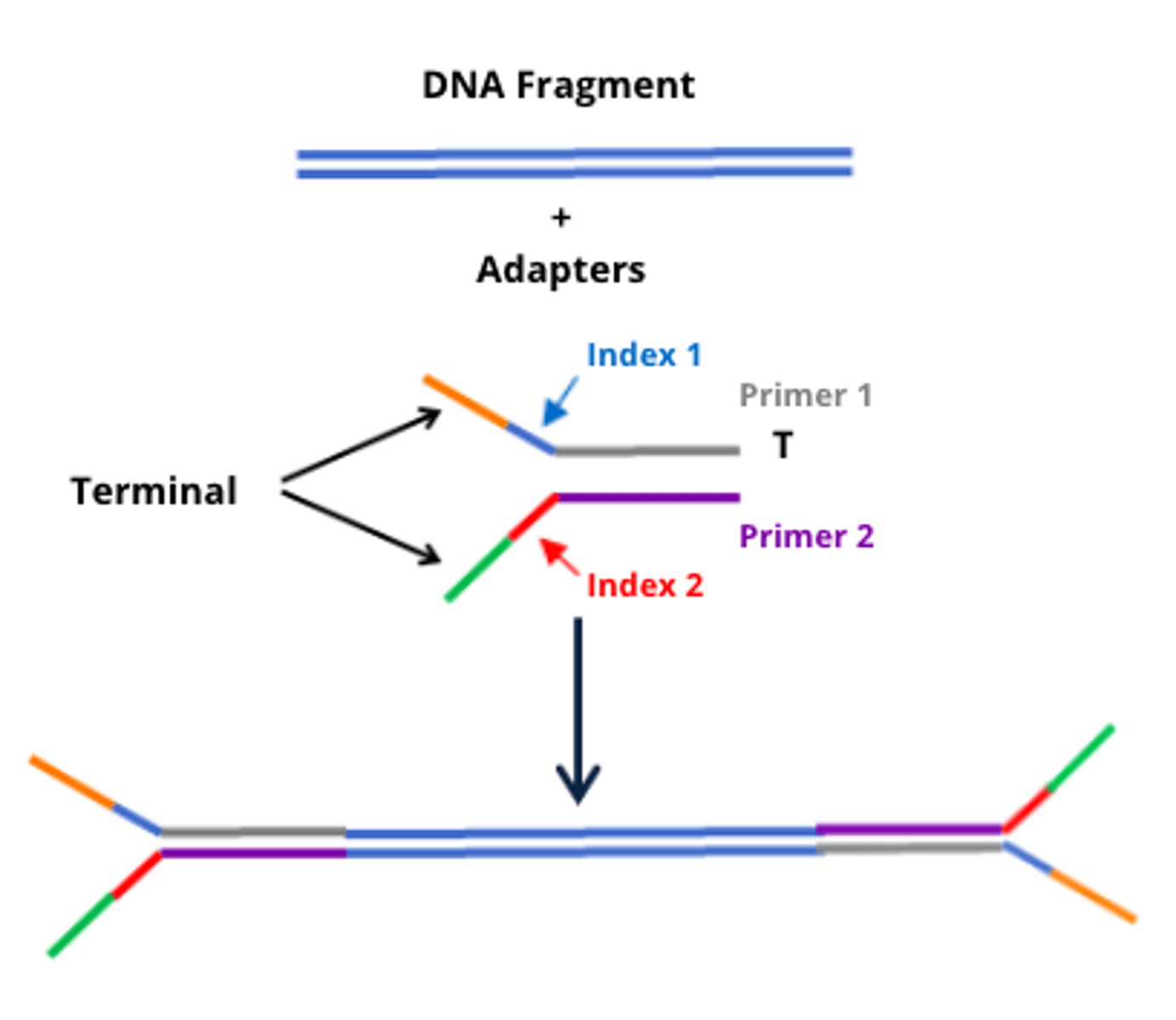
How many copies are made off the adaptor ligation?
Thousands of copies
What happens to the thousands of copies?
Genomic samples into sequence machine
What happens to the data after the sequencing machine?
A bioinformatic analysis is done on the data
What does whole genome sequencing provide?
A high resolution, base by base
What types of variants are captured using genome sequencing?
1) Large variants
2) Small variants
What does whole genome sequencing identify?
Potential causative variants
What can be done is there might be other variants?
Further follow up studies of gene expression and regulation mechanisms
What does whole genome sequencing deliver?
Large volumes of data in short amount of time
What does whole genome sequencing support?
The assembly of novel genomes
How were volunteers recruited?
In a blinded process
What is the percentage range of human DNA sequences being near identical to other people?
99.6% - 99.9%
What is the percentage range of genomic differences between humans?
0.1% - 0.4%
What is the ancestry of most of the genomes sequenced?
European
How many genomic variants re there in each individual?
10 million
What are the 3 impacts of the genomic variants in terms of disease risk?
1) Increases the risk of disease
2) Has no effects on disease risk
3) Decreases the risk of disease
What is the most aggressive form of breast cancer?
Triple negative breast cancer
What is triple negative breast cancer also known as?
TNBC
Who are more likely to be diagnosed with TNBC?
Black women
What link is there to genetic variation and TNBC?
Genetic variation contributes to predisposing some women to aggressive cancers
What is differential gene expression?
Differences in abundance of gene from one cell to another or one person to another
What are the 5 ways the human genome project has helped?
1) Precision medicine in cancer and other diseases
2) Undiagnosed diseases
3) Rare diseases
4) Molecular biology research
5) Variations between closely related species
What are the 5 reasons genomes are sequenced?
1) To create a reference genome
2) To do comparative studies
3) To understand how a species responds to changes under drug pressure
4) To understand how species diversify
5) To understand how species are related
What are the 2 reasons the human reference genome is always being modified?
1) Many repeated and long regions weren't sequenced
2) It wasn't diverse enough
What needs to be done every time a genome is sequenced?
Align it to the reference to see if it matches
By 2035 how many babies will get whole genome sequencing at birth?
650,000
By 2035 what will genomics underpin?
Early diagnosis and interventions
By 2035 what will happen to cancer?
1) Early cancer detection
2) Cancer treatment stratification and monitoring
What is pharmacogenomics?
Give people the right drugs at the right time
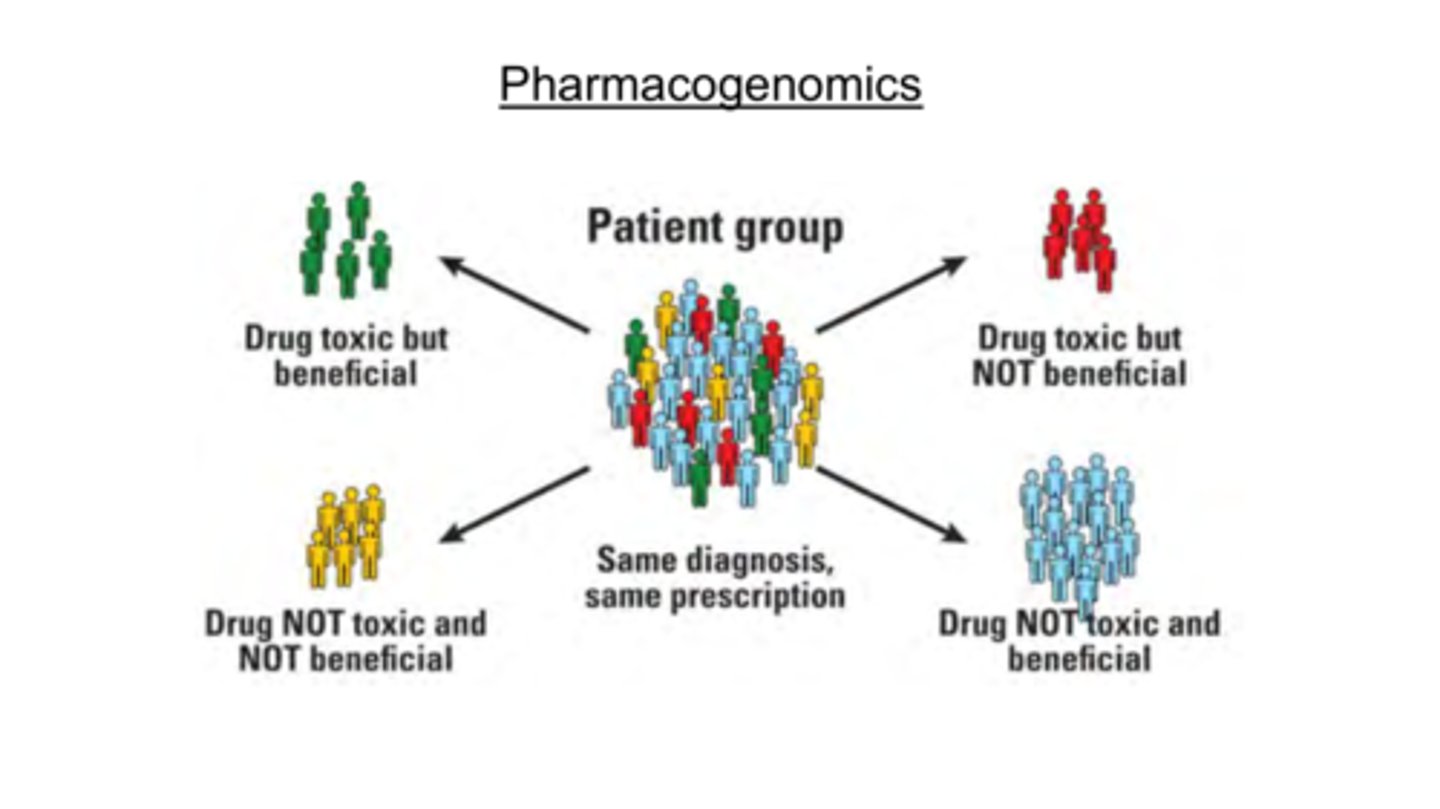
What are the 3 reasons bioinformatics is used in healthcare?
1) Uncover the differences in people's genetic makeups
2) Personalised medicine
3) New classifications
How does bioinformatics make new classifications?
They move from traditional phenotype to genotypic characteristics
What are the 5 stages of the drug development pipeline?
1) Basic research
2) Lead discovery
3) Preclinical development
4) Clinical development
5) FDA filing
How many years does lead discovery take?
3 years
How many years does preclinical development take?
1 year
How many years does clinical development take?
6 years
How many years does FDA filing take?
1.5 years
What occurs in basic research?
Target ID and selection
What occurs in lead discovery?
Candidate selection
What occurs in preclinical development?
IND filing
What occurs in clinical development?
NDA filing
What research is used in target selection?
Academic research
What companies also do target selection?
Pharmaceutical companies
What is a drug target?
A molecule in the body that is associated with a particular disease process
What are drug targets usually?
Proteins
What are the 5 reasons drug targets occur?
1) Mutations
2) Insertions
3) Deletions
4) Chromosomal translocation
5) Epigenetic changes
What are the 2 reasons why drugs fail?
1) Due to efficacy
2) Ineffective target selection and validation
Where is DNA/RNA or proteins extracted from?
Different cell types
What is performed on DNA and RNA?
DNA/RNA sequencing
What is performed on protein?
Proteomics
What does bioinformatics do to DNA, RNA sequencing and proteomics?
Identify differential gene/protein expression
Give 6 examples of a gene/protein list
1) P53
2) HER2
3) MUC1
4) EPCAM
5) CD24
6) ALDH1
What does the gene and protein list identify?
Novel compounds against target