Ap calc Vocab
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
New
Card Sorting
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
1
New cards
Twice differentiable
if you can differentiate its firs derivative
2
New cards
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
states that differentiation and integration are inverse operations.
3
New cards
Mean Value Theorem
if a function f is continuous on the closed interval \[a,b\], and differentiable on the open interval (a,b), then there exists a point c in the open interval (a,b) such that
4
New cards
Mean Value Theorm of Integrals
there exists a point c in the interval \[a,b\] where the function has the same average value as its definite integral over the interval.
5
New cards
Extreme Value Theorem
If f is continuous on a closed interval \[a,b\], the f attains an absolute maximum value f(c) and an absolute minimum value at some numbers c and d in \[a,b\].
6
New cards
intermediate value theorem
if you draw a continuous curve on a graph between two points, it must cross every y-value in between at least once.
7
New cards
absolute minimum
the lowest point of a function
8
New cards
absolute maximim
the highest point of a function
9
New cards
absolute value
the distance between a number and the origin
10
New cards
acceleration
the rate of change of velocity over time
11
New cards
Separation of variables
ex: dx/dy=yx ,, xdx=y/dy
12
New cards
even function
Symmetric with respect to the y axis
13
New cards
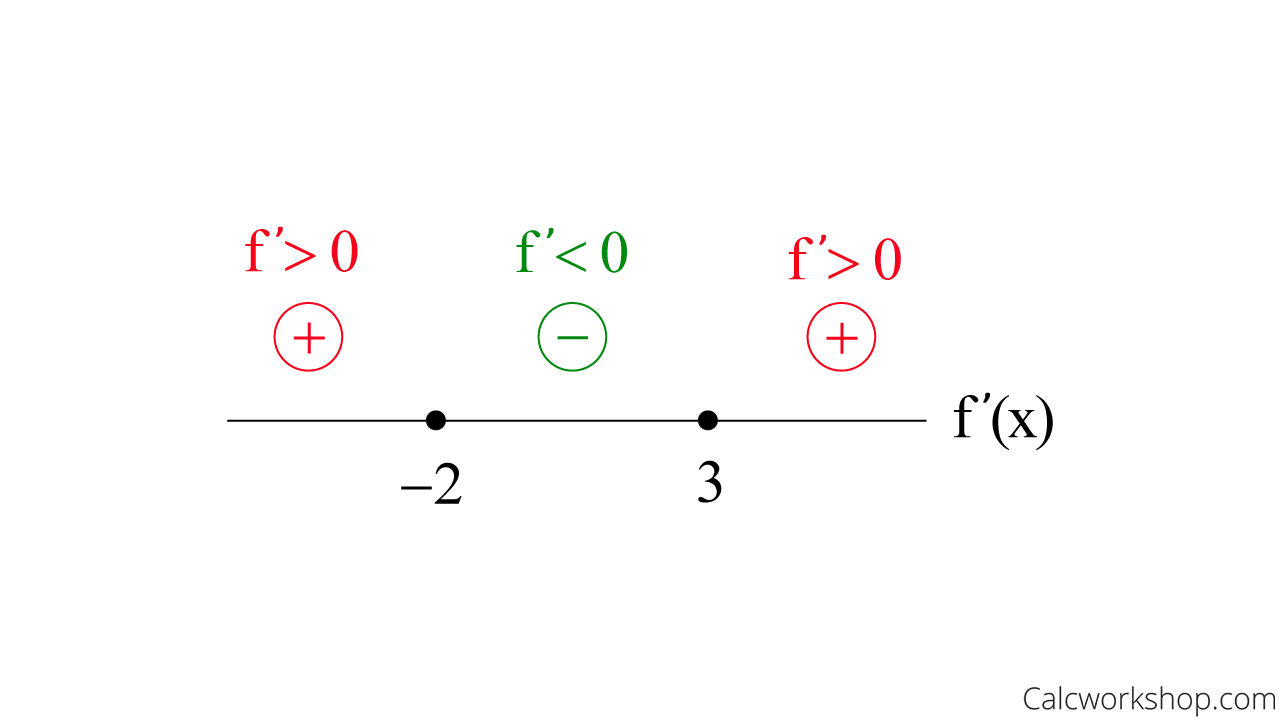
first derivatve test
Determines whether a point is minimum, maximum, or neither
14
New cards
inflection point
where the function changes from concave up to concave down or vice versa
15
New cards
instantaneous rate of change
the rate of change(value of the derivative) at a particular moment
16
New cards
inverse funcition
a function obatined by switching the x and y variables in a function
17
New cards
l'hopital's rule
Finding the derivative of the numerator and denominator to evaluate the limit of a function.
18
New cards
local extrema
a point where the graph has a peak or a valley
19
New cards
second derivative test
determines whether the function is concave down, up, of neither at a point.
Suppose f" is continuous near c. \n a) if f'(c)=0 and f"(c)>0 then f has a local minimum at c \n b) if f"=0 and f"(c)
Suppose f" is continuous near c. \n a) if f'(c)=0 and f"(c)>0 then f has a local minimum at c \n b) if f"=0 and f"(c)