AP Psych Memory Encoding and Intelligence
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
memory
archive of accumulated learning
3 steps of memory
encoding, storage and retrieval
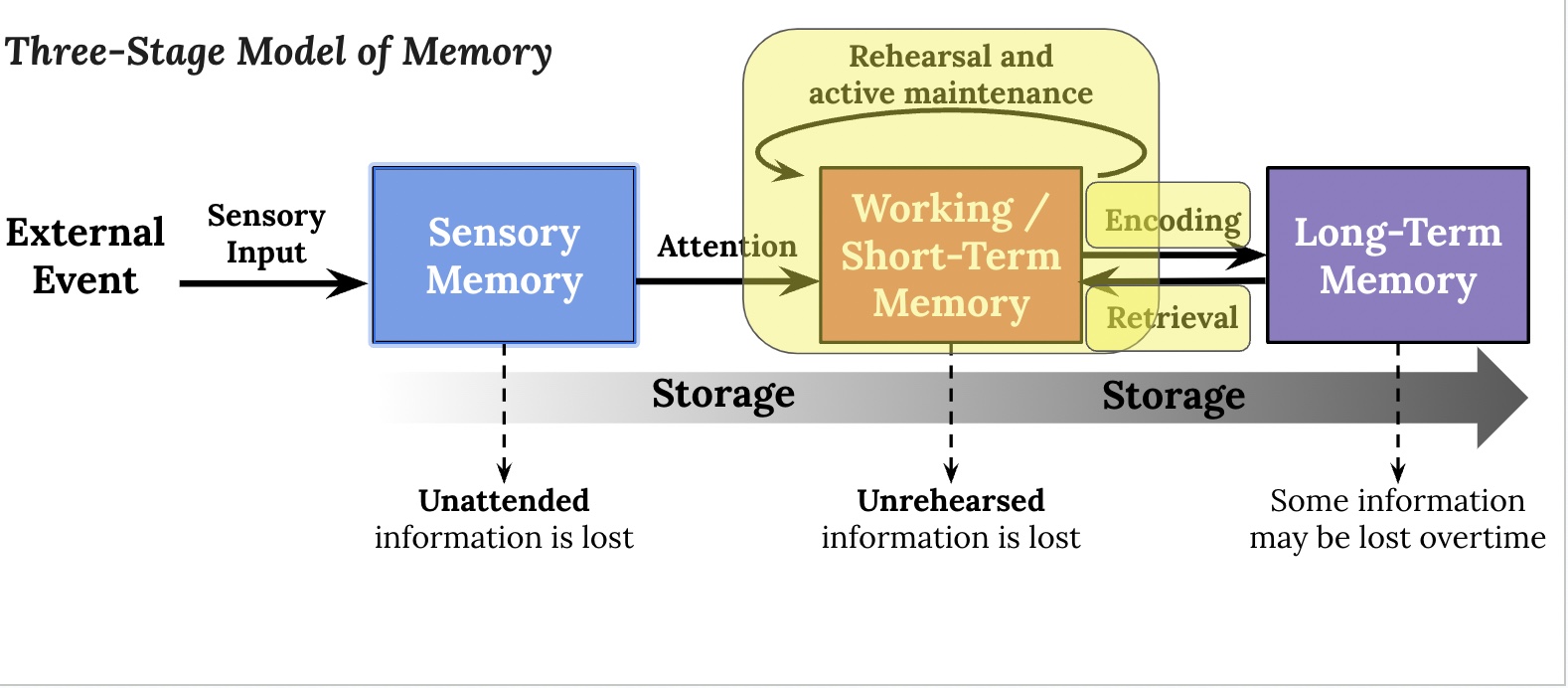
three stage model of memory
encoding long term memories pathways (2)
Automatic and Effortful Processing
Automatic Processing
Unconscious encoding that does not require our awareness
Effortful Processing
Encoding that requires attention and conscious effort
Implicit Memories (automatic pro.)
Learned skills or “classically conditioned associations”
Explicit Memories (effortful pro.)
Facts and experiences that we can consciously know and “declare”
4 branches off of implicit memories
space, time, frequency, procedural
Space
Memory of where things are
Where a certain diagram is in a slide deck
Driving a familiar route home
Time
Memory of when things happened
When you have psych class
What you did during your day
Frequency
Memory of how often things happen
Running into someone several times
The number of red lights you get on the way to school
Procedural
Memory of Skills you have learned
Riding a bike
Using scissors
Driving a car
4 branches off of explicit memories
Episodic, semantic, flashbulb, prospective
Episodic
Personally experienced events
A family vacation
What you had for dinner last night
Semantic
Facts and general knowledge
Psych definitions
How to solve a quadratic
Lines in a play
Flashbulb
A clear memory of an emotionally significant moment or event
Prom
Death of a relative
Prospective
Memory to perform a planned action at some future point in time.
I need to buy sriracha sauce on the way home
I need to submit my college application this weekend
Maintenance Rehearsal
Repeating of information to memorize it.
This type of rehearsal is also called rote rehearsal - thinking about and repeating the information in your mind
Strategies for Encoding Info —> Long Term Memory
Mnemonic devices, chunking, categories, hierarchies, spacing effect
Elaborative Rehearsal
A technique to help the short-term memory store thoughts or ideas and pass them into the long-term memory.
Mnemonic devices
Memory aids that use patterns of letters, ideas or associations.
Acronymns
Acronyms: A word made from the first letters of a series of words
Rhyming
Auditory stimuli and acoustic encoding to help with memory.
Imagery
Creating a mental picture of what you're trying to remember.
Story method
Involves organizing items into an original story.
Loci method
Also known as the “memory palace” method, this strategy involves placing objects or digits on a familiar route or place.
Peg method
Involves pre-memorizing a list of words that can be associated with numbers by making visual associations:
Kinesthetic
Uses movement or touch to help with memory.
Chunking
Organizing items into manageable pieces.
Categories
Organizing items into manageable pieces through their associations
Hierarchies
A type of organizing information into logical levels of association.
Spacing Effect
The impact of retention related to the frequency of studying or practicing.
Massed Practice
Studying information or practicing a skill in a short time period.
Distributed Practice
Repeatedly studying information or practicing a skill over a period of time.
Three Levels of Processing Theory
Shallow, Intermediate, and Deep
Shallow Level
Structural- When we focus on the surface level features of verbal information.
Font
Color
Spelling
Intermediate Level
Phonemic- When we pay attention to the sounds of the item we are processing.
Words that rhyme
Sound of the word
Song lyrics
Deep Level
Semantic- When we process information by giving in meaning to it by associating it with emotion, ideas or previous knowledge.
Relating a word to another word you already know
Relating a word to a specific memory
Memory Consolidation
The neural storage of long term memories / skills.
Explicit Memory Storage
We do not store information in single, precise locations. Instead the brain’s connectivity retains information through the interconnected structures and neurons (mostly in the cortex). Storage of explicit information is formed by a network.
Implicit Memory Storage
The encoding of implicit memories is conducted by the basal ganglia and the cerebellum, but the storage only occurs in the cerebellum.
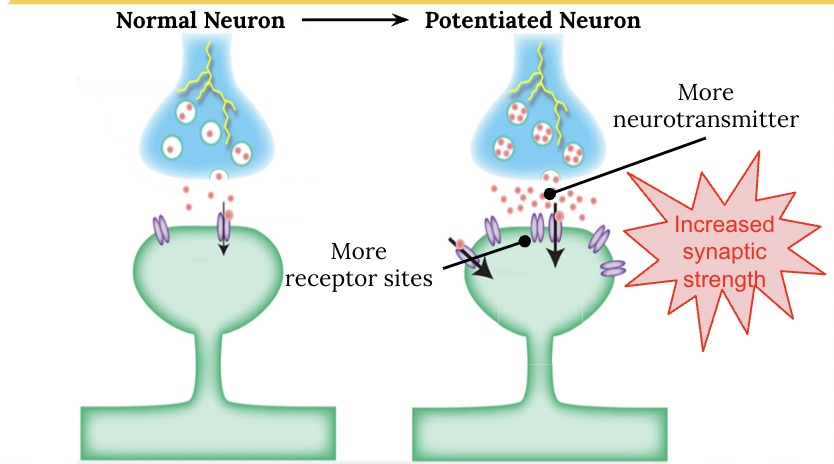
Long Term Potentiation
After repeated stimulation of a neuron, the neuron will increase…
the amount of neurotransmitter released
the number of postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor sites.
This allows for a long-term increase of a neuron’s firing potential.
This is the biological basis for memory
Highly Superior Autobiographical Memory (HSAM)
Their brains have slightly enlarged and highly active areas that have to do with memory. Literally remember everything of each day episodically.
Memory Retrieval
Getting memories from long-term memory into working memory.
Memory Retrieval 2 major branches
Recall (no cues needed) and Recognition (uses cues)
Context Dependent Memory Cue
The tendency to recall information or experiences when you are in the same physical space.
State Dependent Memory Cue
The tendency to recall information or experiences when you are in the same physical or mental state as when it was encoded.
Mood Congruent Memory Cue
The tendency to recall experiences that are consistent with one’s mood.
Serial Position
The tendency to remember information depending on the order it is given.
Primary effect
You tend to remember the information that is given first
Recency Effect
You tend to remember the information that is given last.
Priming
The activation of, often unconsciously,
of particular associations in memory.
Metacognition
The process of thinking about one's own thinking, or the awareness and control of one's thought processes. “Thinking about your own thinking”.
Testing Effect
Enhanced memory strategy after retrieving information, rather than simply rereading or reviewing information. Repeated self-testing increases retrieval ability
Interleaving
Retrieval practice strategy that involves the mixing the study of different topics. Regularly switching between topics means that you have to continually retrieve information from your memory and you don’t get overwhelmed with one topic.
Forgetting/Other Memory Challenges
Forgetting due to Encoding Failure
Proactive Interface
The forward acting disruptive effect of older learning on the recall of NEW information. Difficulty of encoding new information due to the interference of old information.
Retroactive Interface
The backward acting disruptive effect of newer learning on the recall of OLD information. Difficulty remembering information due to the disruption of new information.
Amnesia
Temporary or permanent memory loss.
Can be partial or total loss.
Anterograde Amnesia
Inability to learn new information (cannot store long-term memories)
Retrograde Amnesia
Inability to remember events from the past
Infantile Amnesia
The inability to remember anything from the first few months or years of life. Linked to the development and maturation of the hippocampus.
Constructive Memory
When we build inaccurate memories
Reconsolidation
Process in which previously stored memories are retrieved and altered and then re-encoded.
Imagination Inflation
Repeatedly imagining an event increases
a person's confidence that it actually
happened. Creating a false memory by
imagining an event can make someone
believe they actually experienced it.
Misinformation Effect
When a memory is corrupted by misleading
information.
When exposed to incorrect
information, our brains may encode that
information as part of our own (episodic) memory.
Source Amnesia
Faulty memory for how, when or where information is learned or imagined.
Intelligence
The ability to learn from experience, solve problems, and use knowledge to adapt to new situations.
6 intelligence theories
General IT (g), Fluid IT (Gf), Crystallized IT (Gc), CHC Theory, Multiple IT, Emotional IT (EQ)
General IT (g)
Humans have a general intelligence, made up of specific factors, that underlies all mental abilities.
Verbal ability
Vocabulary
Visual-spatial processing
Quantitative reasoning
Knowledge
Working memory
Comprehension
Fluid IT (Gf)
Our ability to reason speedily and abstractly.
Ex. Ability to solve logic problems.
Crystallized IT (Gc)
Our accumulated knowledge and verbal skills.
This increases throughout development.
CHC Theory
A combination of the previous theories: There is a general intelligence that is supported by fluid intelligence and crystallized intelligence.
Multiple IT
Sternberg’s 3 ITs and Gardner’s MT
Sternberg’s 3 Is (Triarchic Theory)
Analytic intelligence: Problem solving requiring convergent thinking
Creative intelligence: Ability to adapt to new situations / generate novel ideas (divergent thinking)
Practical intelligence: navigating everyday tasks / situations that are not easy or have multiple solutions.
Ex. A salesperson assessing a customer's needs and tailoring their pitch accordingly to close a deal .
Gardner’s Multiple Intelligences
Verbal-Linguistic
Interpersonal
Intrapersonal
Logical-Mathematical
Spatial
Bodily - Kinesthetic
Naturalistic
Musical
Emotional IT
Social and self awareness
Social Awareness
Understanding and responding to social situations and the emotions of others.
Self Awareness
Being able to understand and manage your own emotions
Key Abilities in Emotional Intelligence
Perceiving, understanding, and managing emotions
Perceiving emotions
Recognizing emotions on faces, in music, in art, stories, identifying your own emotions
Understanding emotions
Being able to predict emotions and how they may change or even blend.
Managing emotions
Knowing how to express emotions in varied situations and how to handle others’ emotions
Standardized
the test has required procedures and testing environment.
Test Validity
The test actually measures what it is
designed to measure
Content Validity
to what extent the test is comprehensive in asking questions about the behavior or skill.
Construct Validity
to what extent the test asks the right questions to determine a specific concept or trait
Predictive Validity
to what extent the test predicts the behavior or trait it is intended to measure.
Test Reliability
the test yields similar results each time it is
administered.
Test-retest reliability
taking the test or alternates of the
test result in similar scores.
Split-half reliability
Scores on one-half the of the test
produce similar results as the other half.
anti-bias
the test is developed to prevent socio-cultural bias
Stereotype threat
a self-confirming concept that one will be evaluated based on a negative stereotype.
IQ
(mental age/ chronological age) x 100
Flynn Effect
IQ scores have increased over time due to societal factors including better access to healthcare, nutrition, and socioeconomic status. Scores can be negatively influenced by poverty, discrimination and educational inequities.
Acheivement test
test that reflects what you have learned.
Aptitude test
test that demonstrates how you will perform in the future
attitude vs academic achievement
Academic achievement can be influenced by motivation and mindset.
Fixed mindset
The view that intelligence, abilities and talents and unchangeable, even with effort