2B- Proteins and genetics
1/14
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
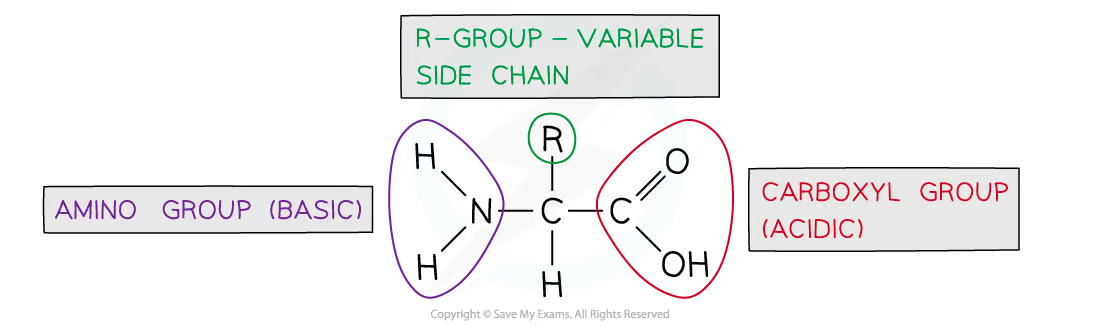
What is the basic structure of an amino acid?
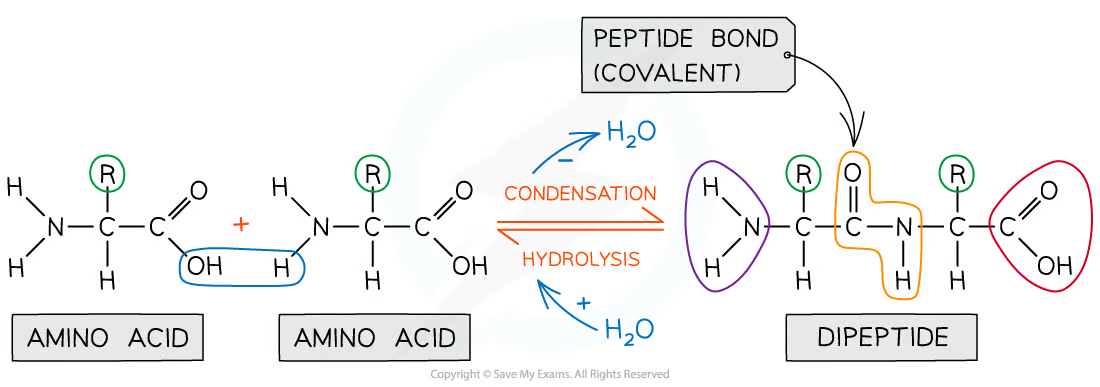
How are polypeptides made?
Amino acids join together in condensation reactions forming peptide bonds between the amine and carboxyl group→also forms water
What is meant by the primary structure of a protein?
Basic amino acid sequence joined by peptide bonds
Describe the secondary structure of a protein
Where the amino acid is folded either into a alpha helix or a pleated beta sheet bonded by simple hydrogen bonds
Describe the tertiary structure of a protein
Precise 3d coiled shape
can include helixes + sheets
Shape depends on sequence of amino acids
Polar R groups attract other polar molecules so are hydrophilic
What bonds are formed in the tertiary structure? How strong are they?
Disulfide bonds- Strong
Ionic bonds- Strong
Hydrogen bonds- Weak
Hydrophobic/philic interactions- Weak
Describe the quaternary structure of a protein
Many proteins made of 2 or more polypeptide chains
Describe a globular protein
Round and compact
soluble in water (hydrophilic on outside)
hydrophilic R groups
specific shape important to their function E.g enzymes, hormones, glycoproteins, haemoglobin.
Describe a fibrous protein
Long strands
Insoluble in water (hydrophobic on outside)
Structured roles
E.g Keratin in hair + skin, cartilage, bones, blood vessels
Collagen forms polypeptide chains form a triple helix creating fibres
Describe the structure of collagen
Described as a repeating amino acid structure with the chains coiled around each other. Bonds are then formed between these chains such as hydrogen, disulfide and ionic bonds.
What is a function of collagen
Provides strength and flexibility
What are the parts of a nucleotide
Nitrogenous base (A,T,G,C,U)
Phosphate
Pentose sugar (ribose/deoxyribose)
Describe transcription
Hydrogen bonds between the bases are broken
RNA polymerase lines up free RNA nucleotides to the template strand and complementary base pairs + phosphodiester + hydrogen bonds
once it finishes assembling at the stop codon the mRNA moves out of the nucleus through nuclear pores → attaches to a ribosome.
Describe translation
attaches to a ribosome
tRNA with complementary anticodons attach to the mRNA
tRNA also transports amino acids to ribosome
the amino acids on the tRNA are joined by peptide bonds
the tRNA moves away leaving the amino acid behind.
repeats forming a polypeptide chain
What is a gene
a sequence of bases in DNA that codes for an amino acid sequence/protein