Mass Transfer Exam 1
4.8(9)
Card Sorting
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:07 PM on 11/1/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
1
New cards
T or F: Because the enriching section of a distillation column has higher concentrations of the less volatile product in it, it tends to be the cooler portion of a distillation system.
False
2
New cards
T or F: For a distillation column, the lower the reflux ratio, the lower the utility costs for proper operation.
True
3
New cards
T or F: In a typically used industrial distillation column, the liquid surface is boiling violently and is well mixed which is not true for the vapor phase.
True
4
New cards
Distillation is possible only of the solution components are ___
a. volatile
b. non-volatile
c. cryogenic
d. none of the mentioned
a. volatile
b. non-volatile
c. cryogenic
d. none of the mentioned
volatile
5
New cards
If the vapor pressure of the two components in a binary mixture is same, then it is a _____
a. isotope
b. azeotrope
c. differential boiling point
d. none of the mentioned
a. isotope
b. azeotrope
c. differential boiling point
d. none of the mentioned
azeotrope
6
New cards
The use of vapor produced from the reboiler is ____
a. to strip out more volatile component from liquid
b. to strip out less volatile component from the liquid
c. to increase the temperature of the fractionator bottom
d. none of the mentioned
a. to strip out more volatile component from liquid
b. to strip out less volatile component from the liquid
c. to increase the temperature of the fractionator bottom
d. none of the mentioned
to strip out more volatile component from liquid
7
New cards
The reflux of liquid produced from the condenser is ___
a. to strip out more volatile component from vapor
b. to strip out less volatile component from the vapor
c. to decrease the temperature of the fractionator top
d. none of the mentioned
a. to strip out more volatile component from vapor
b. to strip out less volatile component from the vapor
c. to decrease the temperature of the fractionator top
d. none of the mentioned
to strip out less volatile component from the vapor
8
New cards
The light key components are ____
a. more volatile
b. less volatile
c. non volatile
d. none of the mentioned
a. more volatile
b. less volatile
c. non volatile
d. none of the mentioned
more volatile
9
New cards
The heavy key components are ____
a. more volatile
b. less volatile
c. non volatile
d. none of the mentioned
a. more volatile
b. less volatile
c. non volatile
d. none of the mentioned
less volatile
10
New cards
If the feed enters the distillation column at its dew point, then the slope of the feed line is _____
a. infinity
b. 0
c. 1
d. between 0 and 1
a. infinity
b. 0
c. 1
d. between 0 and 1
0
11
New cards
If the feed enters the distillation column at its boiling point, then the slope of the feed line is ____
a. infinity
b. 0
c. 1
d. between 0 and 1
a. infinity
b. 0
c. 1
d. between 0 and 1
infinity
12
New cards
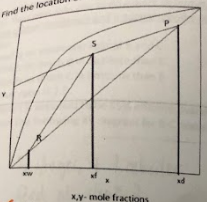
What is the location of the condenser in the figure?
a. P
b. R
c. S
d. no condenser
a. P
b. R
c. S
d. no condenser
P
13
New cards
At total reflux,
a. residue is 0
b. distillate is 0
c. reflux is 0
d. all of the mentioned
a. residue is 0
b. distillate is 0
c. reflux is 0
d. all of the mentioned
distillate is 0
14
New cards
The point where the operating line and the equilibrium line meet in distillation methods is known as ___
a. plait point
b. Q point
c. pinch point
d. none of the mentioned
a. plait point
b. Q point
c. pinch point
d. none of the mentioned
pinch point
15
New cards
Gilliland Correlation is arranged to estimate the ___
a. numbers of stages
b. numbers of reboiler
c. numbers of feed
d. numbers of column
a. numbers of stages
b. numbers of reboiler
c. numbers of feed
d. numbers of column
numbers of stages
16
New cards
Once the components are identified, in a multicomponent distillation they are called ___
a. key components
b. mixed components
c. flow components
d. gain components
a. key components
b. mixed components
c. flow components
d. gain components
key components
17
New cards
Raising the column pressure results in ____
a. lower relative volatility
b. higher relative volatility
c. no effect
d. decreased throughput
a. lower relative volatility
b. higher relative volatility
c. no effect
d. decreased throughput
lower relative volatility
18
New cards
At minimum reflux, number of stages is
a. unity
b. infinite
c. minimized
d. negative
a. unity
b. infinite
c. minimized
d. negative
infinite
19
New cards
Which of the following is true for Fick's law?
a. used to determine the steady-state flux of a component
b. relies on time-dependence of concentration
c. predicts molecular flow from low to high concentration
d. only reliable at low temperatures and high pressures
a. used to determine the steady-state flux of a component
b. relies on time-dependence of concentration
c. predicts molecular flow from low to high concentration
d. only reliable at low temperatures and high pressures
used to determine the steady-state flux of a component
20
New cards
Which of the following is always true for equimolar diffusion with any two components (A&B)?
a. dCA/dt = dCB/dt
b. JA = -JB
c. MWA = MWB
d. TA = -TB
a. dCA/dt = dCB/dt
b. JA = -JB
c. MWA = MWB
d. TA = -TB
JA = -JB
21
New cards
In a binary system, the higher the concentration of the less volatile species in the feed to a flash drum:
a. the higher the liquid flow rate leaving the drum
b. the higher the vapor flow rate leaving the drum
c. the larger the flash drum
d. cannot determine
a. the higher the liquid flow rate leaving the drum
b. the higher the vapor flow rate leaving the drum
c. the larger the flash drum
d. cannot determine
The higher the liquid flow rate leaving the drum
22
New cards
The value of Ki can be expressed as:
a. yj/xi
b. yi/xj
c. xi/yi
d. yi/xi
a. yj/xi
b. yi/xj
c. xi/yi
d. yi/xi
yi/xi
23
New cards
The relative volatility of components i and k can be defined as:
a. Ki/Kj
b. K/Kj
c. yi/y
d. xi/x
a. Ki/Kj
b. K/Kj
c. yi/y
d. xi/x
Ki/Kj
24
New cards
The energy balance around a distillation column is given by:
a. F*hF + Qc + Qr = D*hD + B*hB
b. F*hF - Qc + Qr = D*hD + B*hB
c. V1*H1 + Qc = L0*h0 + D*hD
d. V1*H1 - Qc = L0*h0 + D*hD
a. F*hF + Qc + Qr = D*hD + B*hB
b. F*hF - Qc + Qr = D*hD + B*hB
c. V1*H1 + Qc = L0*h0 + D*hD
d. V1*H1 - Qc = L0*h0 + D*hD
F*hF + Qc + Qr = D*hD + B*hB
25
New cards
The material balance around the condenser is given by:
a. F = D - B
b. F = D + B
c. V = L + D
d. V = L - D
a. F = D - B
b. F = D + B
c. V = L + D
d. V = L - D
V = L + D
26
New cards
The reflux ratio can be defined as:
a. V/L
b. D/L
c. V/B
d. L/D
a. V/L
b. D/L
c. V/B
d. L/D
L/D or L0/d
27
New cards
The slope of the top operating line in distillation is:
a. V/L
b. L/V
c. Vbar/Lbar
d. Lbar/Vbar
a. V/L
b. L/V
c. Vbar/Lbar
d. Lbar/Vbar
L/V
28
New cards
The intercept of the bottom operating line in distillation is:
a. Lbar/Vbar
b. Vbar/Lbar
c. 1 - Lbar/Vbar
d. 1 + Lbar/Vbar
a. Lbar/Vbar
b. Vbar/Lbar
c. 1 - Lbar/Vbar
d. 1 + Lbar/Vbar
1 - Lbar/Vbar
29
New cards
HETP stands for:
a. height of efficient total packing
b. height equivalent to theoretical plate
c. height expected to product
d. high energy thermal plasma
a. height of efficient total packing
b. height equivalent to theoretical plate
c. height expected to product
d. high energy thermal plasma
height equivalent to theoretical plate
30
New cards
Column diameter is most dependent on:
a. tray type used
b. reboiler duty
c. liquid velocity
d. vapor velocity
a. tray type used
b. reboiler duty
c. liquid velocity
d. vapor velocity
vapor velocity
31
New cards
Which of the following is used when determining tray spacing?
a. propensity of liquid to foam/entrain
b. need for person to access top of trays
c. a&b
d. none of the above
a. propensity of liquid to foam/entrain
b. need for person to access top of trays
c. a&b
d. none of the above
propensity of liquid to foam/entrain
need for person to access top of trays
need for person to access top of trays
32
New cards
The phenomena of the flowing liquid toward the wall of tower and dispersed in lateral direction is called ___
a. channeling
b. flow casting
c. entraining
d. regimens
a. channeling
b. flow casting
c. entraining
d. regimens
channeling
33
New cards
As a rule of thumb, the overall efficiency is:
a. 0.1 to 0.3
b. 0.3 to 0.5
c. 0.5 to 0.7
d. 0.7 to 0.9
a. 0.1 to 0.3
b. 0.3 to 0.5
c. 0.5 to 0.7
d. 0.7 to 0.9
0.5 to 0.7
34
New cards
When sizing a column, switching for trays to packing usually results in:
a. increased height
b. decreased height
c. no change in height
d. no change in trend
a. increased height
b. decreased height
c. no change in height
d. no change in trend
decreased height
35
New cards
In steady state diffusion, which of the following remains constant?
a. concentration gradient
b. kinetic energy of particles
c. potential energy of particles
d. change of concentration with respect to temperature
a. concentration gradient
b. kinetic energy of particles
c. potential energy of particles
d. change of concentration with respect to temperature
concentration gradient
36
New cards
Which of the following law is used for steady state diffusion?
a. Fick's Law
b. Newton's Law of Diffusion
c. Bragg's Law
d. Charles's Law
a. Fick's Law
b. Newton's Law of Diffusion
c. Bragg's Law
d. Charles's Law
Fick's Law
37
New cards
Which of the following is not a part of Fick's first law at steady-state?
a. diffusion flux
b. diffusion coefficient
c. change in concentration with respect to position in space
d. change in concentration with respect to time
a. diffusion flux
b. diffusion coefficient
c. change in concentration with respect to position in space
d. change in concentration with respect to time
change in concentration with respect to time
38
New cards
T or F: Flux is in the opposite direction to the direction of the increasing concentration gradiant
True
39
New cards
T or F: For a system containing A and B only, steady state equimolar counter diffusion requires that the flux of a is the negative of the flux of B
true
40
New cards
The higher the concentration of volatile species in the feed to a flash drum:
a. the higher the liquid flow rate
b. the higher the vapor flow rate
c. the larger the flash drum
d. cannot determine
a. the higher the liquid flow rate
b. the higher the vapor flow rate
c. the larger the flash drum
d. cannot determine
the higher the vapor flow rate
41
New cards
The overall material balance for a flash drum is:
a. F = V - L
b. F = V/L
c. F = V + L
d. F = F * L
a. F = V - L
b. F = V/L
c. F = V + L
d. F = F * L
F = V + L
42
New cards
For multi-component flash distillation, the equation used for iterative solving is the
a. Michaelis-Menten
b. Monod
c. Van der Waals
d. Rachford-Rice
a. Michaelis-Menten
b. Monod
c. Van der Waals
d. Rachford-Rice
Rachford-Rice
43
New cards
The overall material balance for a distillation column is:
a. F = D - B
b. F = D + B
c. V = L + D
d. V = L - D
a. F = D - B
b. F = D + B
c. V = L + D
d. V = L - D
F = D + B
44
New cards
When heat is supplied to bottom of liquid stage to vaporize a portion, it is called:
a. condensing
b. boil-up
c. cooling
d. desalting
a. condensing
b. boil-up
c. cooling
d. desalting
boil-up
45
New cards
When a portion of the overhead product is returned to the column, it is called:
a. reflux
b. dew point
c. boil-up
d. relative BP
a. reflux
b. dew point
c. boil-up
d. relative BP
reflux
46
New cards
The energy balance around the condenser is given by:
a. F*hF + Qc + Qr = D*hD + B*hB
b. F*hF - Qc + Qr = D*hD + B*hB
c. V1*H1 + Qc = L0*h0 + D*hD
d. V1*H1 - Qc = L0*h0 + D*hD
a. F*hF + Qc + Qr = D*hD + B*hB
b. F*hF - Qc + Qr = D*hD + B*hB
c. V1*H1 + Qc = L0*h0 + D*hD
d. V1*H1 - Qc = L0*h0 + D*hD
V1*H1 + Qc = L0*h0 + D*hD
47
New cards
The quality of feed represents:
a. The fraction of liquid in the feed
b. The fraction of vapor in the feed
c. The apparent fraction of liquid in the feed
d. The apparent fraction of vapor in the feed
a. The fraction of liquid in the feed
b. The fraction of vapor in the feed
c. The apparent fraction of liquid in the feed
d. The apparent fraction of vapor in the feed
The apparent fraction of liquid in the feed
48
New cards
The fraction of the feed represents:
a. The fraction of liquid in the feed
b. The fraction of vapor in the feed
c. The apparent fraction of liquid in the feed
d. The apparent fraction of vapor in the feed
a. The fraction of liquid in the feed
b. The fraction of vapor in the feed
c. The apparent fraction of liquid in the feed
d. The apparent fraction of vapor in the feed
The apparent fraction of vapor in the feed
49
New cards
Which of the following is NOT necessarily true for Constant Molar Overflow?
a. the volume flows are constant
b. the molar flows are constant
c. the heat of vaporization is constant between stages
d. the heat capacity is constant between stages
a. the volume flows are constant
b. the molar flows are constant
c. the heat of vaporization is constant between stages
d. the heat capacity is constant between stages
the volume flows are constant
50
New cards
Total reflux condition at steady-state means that:
a. D = 0
b. B = 0
c. F = 0
d. all of the above
a. D = 0
b. B = 0
c. F = 0
d. all of the above
D = 0, B = 0, F = 0
51
New cards
Minimum reflux is the point where:
a. reflux is zero
b. bottoms flow is maximized
c. the separation can be completed with an infinite number of stages
d. reflux = distillate
a. reflux is zero
b. bottoms flow is maximized
c. the separation can be completed with an infinite number of stages
d. reflux = distillate
the separation can be completed with an infinite number of stages
52
New cards
process of separating components based on differences in volatility
distillation
53
New cards
product of a distillation separation containing the majority of the more volatile components coming from the top of the unit
distillate
54
New cards
the product of a distillation separation containing the majority of the less volatile components coming from the bottom of the unit
bottoms
55
New cards
the ratio of the condensed overhead vapor flow that is returned to the column vs the amount that is taken off as product (L/D)
reflux ratio
56
New cards
Order the following from most volatile to least volatile:
propane
i-pentane
n-pentane
methane
propane
i-pentane
n-pentane
methane
methane
propane
i-pentane
n-pentane
propane
i-pentane
n-pentane
57
New cards
What are the two state variables you can adjust in flash distillation to change the composition of the product streams?
drum pressure and feed temperature
58
New cards
What are the four flow regimes possible in distillation?
bubble, foam, froth, and spray
59
New cards
For the light key component, equilibrium relation is
a .yK=x
b. Kx=y
c. depend upon trays
d. cannot be specified
a .yK=x
b. Kx=y
c. depend upon trays
d. cannot be specified
Kx=y
60
New cards
If the fractional recovery of light key in the distillate id FR, then the light key in the feed is
a. DxD=(FRD)+FxLK
b. DxD=(FRD)-FxLK
c. DxD=(FRD)FxLK
d. DxD=(FRD)
a. DxD=(FRD)+FxLK
b. DxD=(FRD)-FxLK
c. DxD=(FRD)FxLK
d. DxD=(FRD)
DxD=(FRD)FxLK
61
New cards
For multi-component systems, Fenske Method gives
a. minimum reflux
b. minimum strip
c. maximum reflux
d. minimum trays
a. minimum reflux
b. minimum strip
c. maximum reflux
d. minimum trays
minimum trays
62
New cards
For multi-component systems, Underwood Equations gives
a. minimum reflux
b. minimum strip
c. maximum reflux
d. minimum trays
a. minimum reflux
b. minimum strip
c. maximum reflux
d. minimum trays
minimum reflux
63
New cards
The component balance of the more volatile component is given as
a. FzF=DxD+BxB
b. FzF=DxD-BxB
c. FzF=DxD/BxB
d. FzF=DxD*BxB
a. FzF=DxD+BxB
b. FzF=DxD-BxB
c. FzF=DxD/BxB
d. FzF=DxD*BxB
FzF=DxD+BxB
64
New cards
A pinch point may occur at intersection of feed line and
a. stream line
b. stripping line
c. rectifying line
d. equilibrium line
a. stream line
b. stripping line
c. rectifying line
d. equilibrium line
equilibrium line
65
New cards
The real number of trays are obtained as a ratio of
a. number of ideal trays and flow rate
b. number of ideal trays and efficiency
c. number of ideal trays and reflux ratio
d. number of ideal trays and stripping ratio
a. number of ideal trays and flow rate
b. number of ideal trays and efficiency
c. number of ideal trays and reflux ratio
d. number of ideal trays and stripping ratio
number of ideal trays and efficiency
66
New cards
Which of the following is an important assumption of McCabe Thiele method?
a. heat loss is maximum
b. heat loss is negligible
c. heat loss is infinite
d. cannot be specified
a. heat loss is maximum
b. heat loss is negligible
c. heat loss is infinite
d. cannot be specified
heat loss is negligible
67
New cards
Which is a proper form of Henry's Law?
a. Ptot=Hb*xb
b. yb=Hb*xb
c. yb=Hb/xb
d. Pb=Hb*xb
a. Ptot=Hb*xb
b. yb=Hb*xb
c. yb=Hb/xb
d. Pb=Hb*xb
Pb=Hb*xb
68
New cards
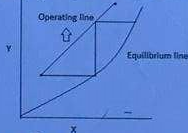
Which is represented by the figure?
a. stripper
b. scrubber
c. heat exchanger
d. three-phase extractor
a. stripper
b. scrubber
c. heat exchanger
d. three-phase extractor
scrubber
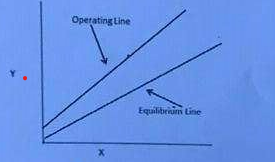
69
New cards
Which is represented by the figure?
a. stripper
b. scrubber
c. heat exchanger
d. three-phase extractor
a. stripper
b. scrubber
c. heat exchanger
d. three-phase extractor
stripper
70
New cards
A scrubber is designed to
a. remove contaminant from liquid phase
b. remove contaminant from gas phase
c. separate two liquids
d. dissolve solid in gas phase
a. remove contaminant from liquid phase
b. remove contaminant from gas phase
c. separate two liquids
d. dissolve solid in gas phase
remove contaminant from gas phase
71
New cards
A stripper is designed to
a. remove contaminant from liquid phase
b. remove contaminant from gas phase
c. separate two liquids
d. dissolve solid in gas phase
a. remove contaminant from liquid phase
b. remove contaminant from gas phase
c. separate two liquids
d. dissolve solid in gas phase
remove contaminant from liquid phase
72
New cards
How many trays are represented in the drawing?
a. 0
b. 1
c. 2
d. 3
a. 0
b. 1
c. 2
d. 3
2