Knowt 6 - Living Primates
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Characteristics and Survey
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Paleozoic Era
First amphibians and reptiles
541 - 251 Ma
Mesozoic Era
"Age of Reptiles"
First mammals (ca. 150 Ma)
252 - 66 Ma
Cenozoic Era
65 – 0 Ma
Adaptive radiation of mammals
Mammals
Enlarged neocortex, placental development, heterodontia, endothermic
ca. 150 Ma
Plesiadapiforms
An order of primate-like mammals (proprimates)
Ancestor to all primates (?)
ca. 66 – 55 Ma

Euprimates
Omomyids (ca. 56 – 34 Ma)
Adapids (ca. 55 – 34 Ma)
Omomyids (ca. 56 – 34 Ma)

Adapids (ca. 55 – 34 Ma)

Primate Characteristics
Limbs and Locomotion
Diet and Teeth
Senses and the Brain
Maturation, Learning, Behavior
Limbs and Locomotion
1. Erect posture (d)
2. Flexible and generalized limbs (a)
3. Prehensile hands and feet (d)
4. Nails instead of claws (d)
Diet and Teeth
5. Generalized dentition (a)
6. Generalized diet (a)
Senses and the Brain
7. Color vision (d)
8. Binocular and stereoscopic vision (d)
9. Decreased reliance on olfaction (d)
10. More complex brain (d)
Maturation, Learning, Behavior
11. Longer gestation; prolonged maturation; longer lives (d)
12. Dependent on learned behavior (d)
13. Social living arrangements (d)
14. Diurnal (d)
Dental Formula
A ratio expressing the number of each tooth type in one quadrant of the mouth
Primates have molars with low, rounded cusps
Dental Formula Examples
Placental Mammals: 3.1.4.3
OW Primates: 2.1.2.3
NW Monkeys: 2.1.3.3
Arboreal Hypothesis
Traits evolved as adaptations for living in trees
Visual Predation Hypothesis
Traits evolved as adaptations for hunting prey
Angiosperm Radiation Hypothesis
Traits evolved as adaptations for collecting fruits
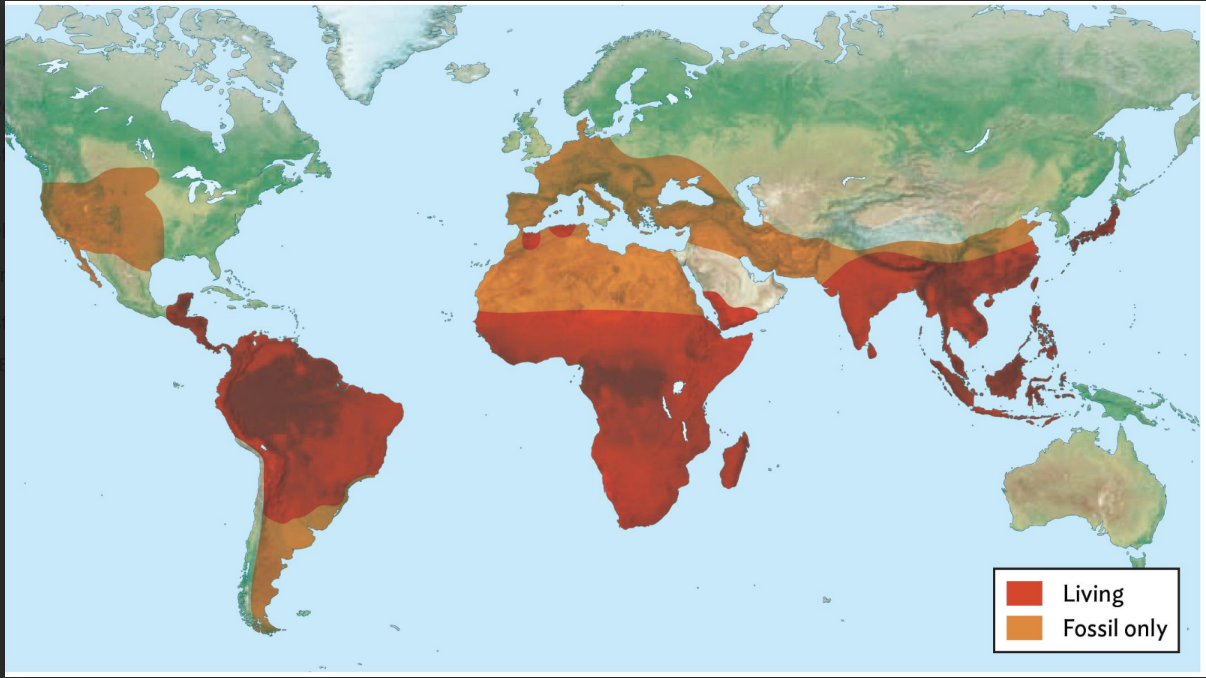
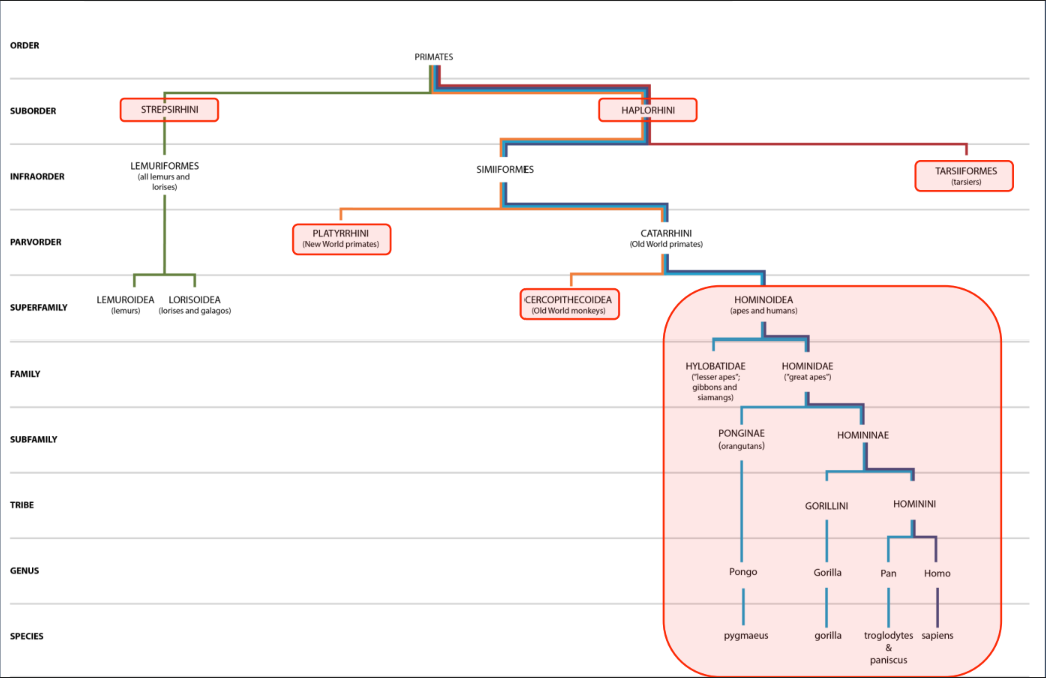
Primate Classification Map
Primates Map