amniotes
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
what are amniotes defined by?
embryos developed in extra-embryonic membrane
what are the two major lineages?
sauropsida and synapsida

what’s in the group synapsida?
therapsids and mammals
what’s in the group sauropsida?
birds, dinos, modern reptiles
what are major innovations for living on land?
keratinized skin, egg structure, rib ventilation of lungs, stronger jaws, expanded brain and sensory organs, high pressure cardiovascular system, water conserving nitrogen excretion
why does keratinized skin allow for life on land?
provides protection and limits water loss
why does egg structure allow for life on land?
semi-permeable membrane allows gas exchange and protects from desiccation
what’s in the yolk of an egg?
lipids, calcium, and protein
what’s in the albumen/white part of the egg?
some proteins, no lipids or carbs, used for water storage
which shell has higher conductance?
soft shelled eggs
what type of egg is more calcified?
hard shelled eggs
what are the three types of eggs?
Altricial Eggs, Precocial Eggs, Reptile Eggs
what are the parts of the egg?
amnion, allantois, chorion, shell, yolk sac
altrical eggs have ____ yolk, ___ water content, born with ___ feathers, ____ developed neuromuscular coordination, ____ on parents for food and warmth?
small, high, no, poorly, totally dependent
what animals have altrical eggs?
parrots, pigeons, ect
what are the characteristics of precocial eggs?
large yolk, low water content, well developed plumage, good installation, well developed neuromuscular coordination, feed them selves

what animals have a precocial egg?
Galliformes, ratites, waterfowl
what are the characteristics of a reptile egg?
high variable albumen content, yolk has lots of protein and lipids, embryo development stage at laying can vary, egg diapause: adaptation to seasonal environment
what gets diffused across the egg shell?
H2O, O2, CO2
____ of the egg varies with environment?
shape and thickness
what does the diffusion rate depend on?
length, pore diameter, number of pores
what happens as the embryo grows to increase gas flux?
egg shell gas conductance, gas partial pressure across eggshell
bird eggs always ___ water
loose
reptile eggs ___ water
gain or loose
why can turtle or croc eggs lose water and still successfully hatch?
large albumen
why do lizards need to take up water to hatch?
little albumen
water vapor is driven by ____.
diffusion gradients
liquid water moves from ___ water potential to ___ water potential
high, low
what is the egg tooth used for?
access air cell and to break shell
Squamata have a ___egg tooth and birds and reptiles have a ___.
real temporary tooth, temporary horn
what happens to sea turtle populations when incubation temps rise?
proportion of females increase
what does the secondary bony plate allow for mammals?
the ability to breath and chew
what does the secondary bony plate allow for crocs?
reinforce jaws for capturing and crushing prey
what is cranial kinesis?
top and bottom of jaw can move independently
how can animals swallow whole prey?
jaws can move side-to-side
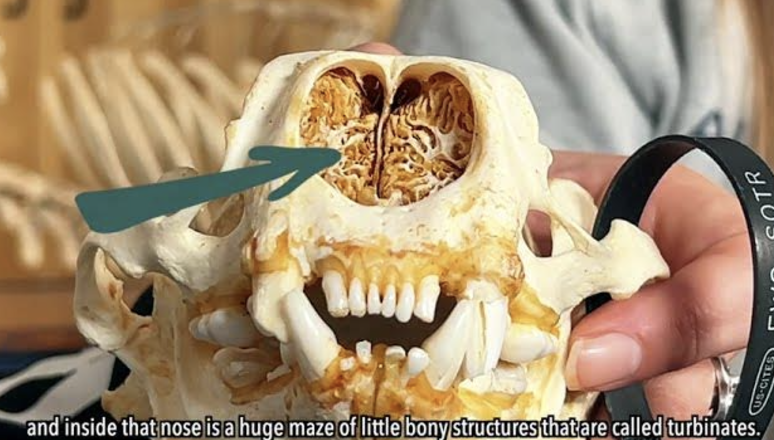
what do turbinate bones do?
prevent water and heat loss
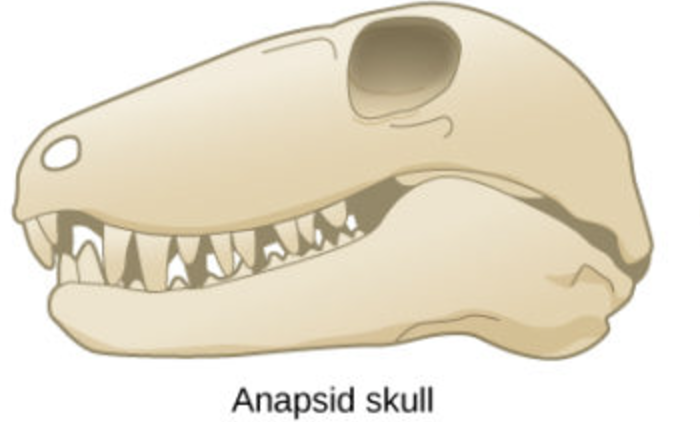
what are the characteristics of anapsid skulls?
No fenestra
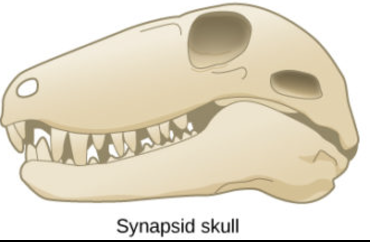
what are the characteristics of synapsid skulls?
increase brain size, 1 temporal fenestra, Temporal bar – jugal bone (j) & quadratojugal (qj)

what animals have a anapsid skull?
turtles
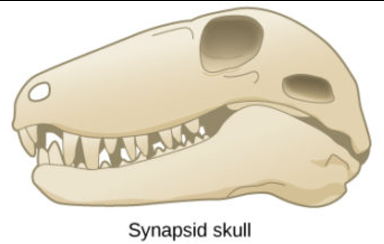
what animals have a synapsid skull?
early mammals
what are the characteristics of diapsid skulls?
2 temporal fenestra Upper & lower temporal bar
how are lizard skulls modified?
loss of lower bar
how are bird skulls modified?
loss of upper bar
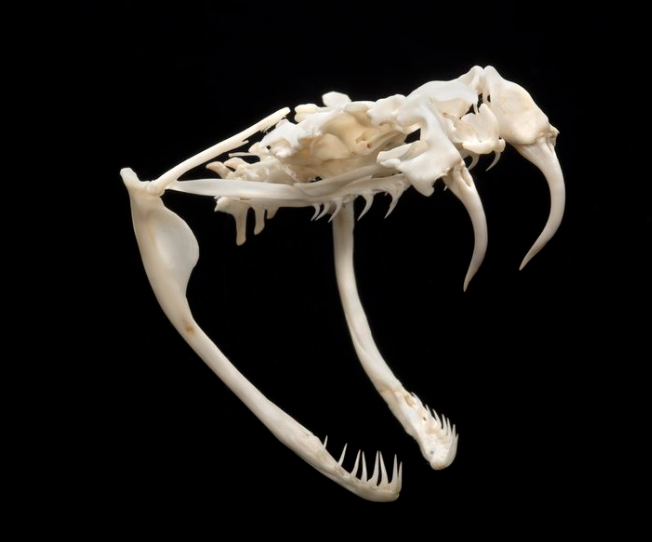
how are snake skulls modified?
loss of upper and lower bar
what does the sternum do?
protects the heart
what does the ankle bone allow?
running