Transport in Plants
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
What is a cotyledon?
Cotyledons are the first leaves of a seedling.
How many cotyledons are in the embryo of a dicotyledonous plant?
2
How are the pattern of veins in leaves of a dicotyledonous plant?
Usually network of veins
How are the flower parts of a dicotyledonous plant?
In multiples of 4 or 5
How is the arrangement of vascular bundles in the stem of a dicotyledonous plant?
ring-like
Mature xylem cells are …
dead
Pressure inside xylem vessels is … compared to atmospheric pressure.
lower
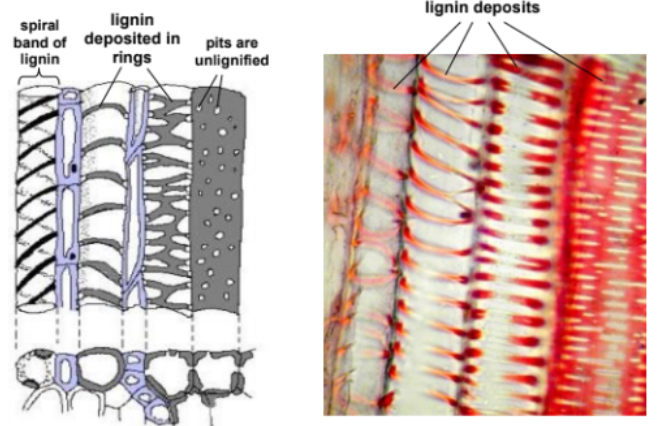
structure of xylem [2]
Long, hollow tube
> made up of many dead cells without cytoplasm and cross-walls
Inner walls are thickened with lignin
> (lignified walls)
what is the function o the long, hollow tube in xylem?
Reduces resistance
No obstruction of water and mineral salts flowing from roots to leaves
what is the function of xylem walls being thickened with lignin?
Strengthened to prevent collapsing due to low pressure
Components of Xylem Vessel Picture
What is translocation?
Transportation of sucrose and amino acids in the phloem from source to sink
What does phloem consist of?
mainly sieve tubes and companion cells
What does each sieve tube consist of?
Each sieve tube consists of a column of elongated, thin-walled living cells called sieve tube cells/elements
What are sieve plates?
Cross-walls separating the cells have many minute pores → gives appearance of a sieve → named sieve plates
Components of Phloem Vessel Picture
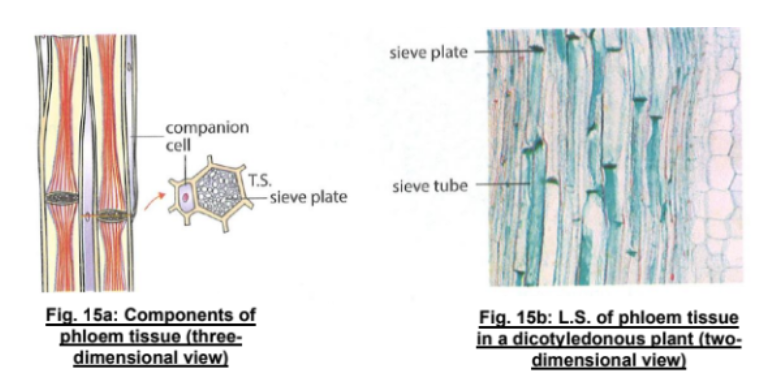
Structure of Phloem [5]
Found throughout the plant
Sieve tubes are made of sieve tube cells and separated by porous sieve plates
Sieve tube cells are alive but have no nuclei and reduced number of organelles
Each sieve tube cell has a companion cell beside it that has many mitochondria
Cytoplasm of companion cells is continuous with the cytoplasm of sieve tube cells
what is the function of phloem being found throughout the plant?
Facilitate translocation (define)
why are sieve tubes made of sieve tube cells and separated by porous sieve plates?
More efficient movement
Minimal obstruction of movement of sucrose and amino acids flowing in sieve tube
why are sieve tubes cells alive but have no nuclei and reduced number of organelles?
Maximise space for translocation of sucrose and amino acids
why does each sieve tube cell have a companion cell beside it that has many mitochondria
Facilitate active transport of sucrose in and out of sieve tube
Carry out metabolic processes needed to keep sieve tube cells alive
why is the cytoplasm of companion cells continuous with the cytoplasm of sieve tube cells
Facilitate rapid movement of metabolites between cytoplasm and sieve tube cells
The channels between companion cell and sieve tube cells are called
plasmodesmata
What are sources?
areas where sucrose and amino acids are loaded into the phloem (photosynthetic tissues)
What are sinks?
areas where sucrose and amino acids are unloaded and used (making fruits and seeds)
What are the 3 main layers of a dictotyledonous stem?
1) epidermis [outermost]
2) cortex
3) pith [innermost]
In stem:
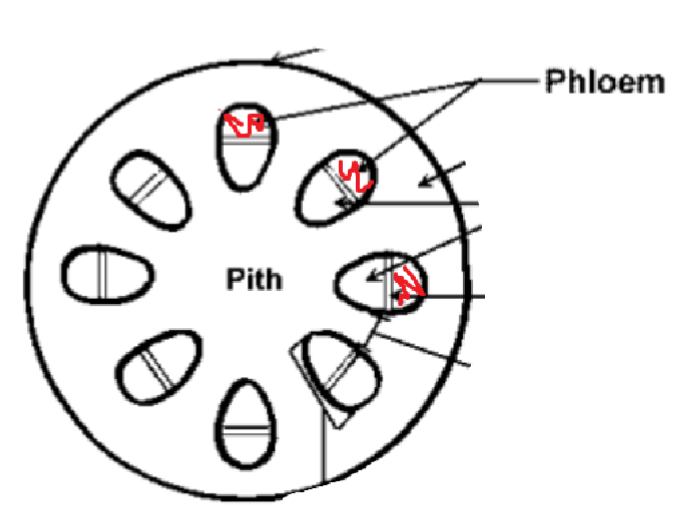
The phloem lies on the outer ring with a tissue called … between them.
cambium
The vascular bundles of a dicotyledonous stem are…[3]
> located next to the stem cortex
> arranged in a ring shape near epidermis of the stem
> arranged so that phloem are closer to epidermis and xylem are closer to pith
In stem:
In a vascular bundle, the xylem is …
closer inside
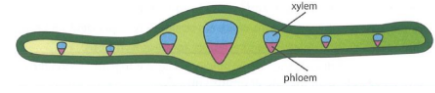
In a leaf,
Vascular bundles in a leaf are found…
along the spongy mesophyll
In a leaf,
The xylem is closer to the …
upper surface
In a leaf,
the phloem is closer to the ...
lower surface
What are the 4 main layers of a dicotyledonous leaf?
1) upper epidermis
2) palisade mesophyll
3) spongy mesophyll
4) lower epidermis
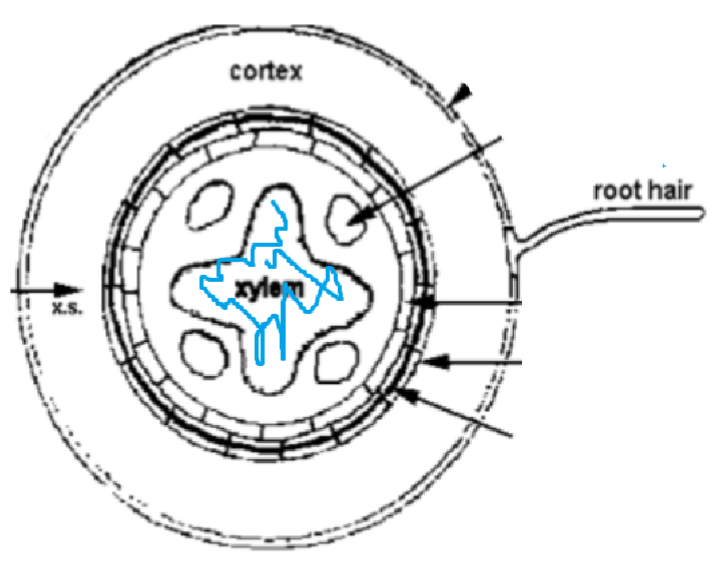
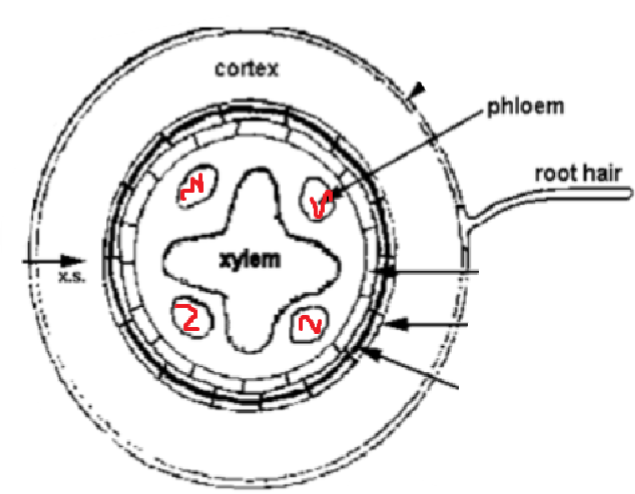
What are the three main layers for a dicotyledonous root?
1) epidermis [outermost]
2) cortex
3) endodermis
What does the epidermis of the root bear?
the root hair cells which are specialised epidermal cells.
Tell me about the root hair’s function.
Each root hair is a long and narrow extension growing out of the epidermal cell → increases SA to V ratio of root hair cell → increases rate of absorption of water by osmosis and mineral salts by diffusion/active transport
In a root,
The vascular bundles …
> located in the middle of the root, surrounded by the endodermis
> xylem vessels are cross shape
> phloem vessels are grouped into round areas surrounding xylem vessels
Experiment the Movement of Water in Plants
Aim: Investigate path of water through a plant
Procedure:
1) Take a celery plant and wash it with water to remove the soil
2) Allow plant to stand with its stem immersed in methylene blue solution
3) After a few hours, you can see that the blue dye has risen up the stem
4) Cut thin transverse sections of the stem
5) Place the sections on a glass slide and examine them with a light microscope
6) Sketch the transverse section to show the distribution of the blue colour in the main vein or vascular bundle
Observation:
Xylem has been stained blue.
As the xylem vessels have been stained blue, it can be concluded that water is transported from the source to the sink via the xylem vessels.
Experiment about the Movement of Food (Translocation)
1. Aphid Feeding Experiment
[6]
While feeding, the aphid stylet tip (mouth piece) is inserted into the phloem.
Aphid is anesthetized with CO2 while feeding.
The body of the aphid is cut off, leaving the stylet tip in the plant tissue.
Collection of fluid from the stylet tip will reveal that it contains sucrose and amino acids.
When the stem is sectioned and looked at under the microscope, it is observed that the stylet tip is inserted into the phloem sieve tube.
Experiment shows that the translocation of sugars and amino acids occur in the phloem.
Experiment about the Movement of Food (Translocation)
2. Ringing Experiment
[6]
Cut off the complete ring of the bark from the main stem, including phloem and cambium. The xylem will be exposed.
Prepare a control using an unringed stem.
Observe over a few days if there is swelling present.
Swelling will be seen above the removed ring.
Collection of these materials reveal that it contains sucrose and amino acids.
Experiment shows that the translocation of sugars and amino acids occur in the phloem.
Experiment about the Movement of Food (Translocation)
3. 14C Isotope Experiment
[4]
Plants are exposed to 14C isotope, a radioactive carbon isotope.
When photosynthesis takes place, the sugar formed will contain radioactive carbon.
The stem is then cut and its cross section is exposed onto an X-ray photographic film, where 14C will appear dark on the X-ray film.
The dark regions represent the positions of phloem in the stem.
What is a root hair?
Root hairs are narrow extensions of an epidermal cell in contact with the soil solution surrounding it, which is a dilute solution of mineral salts.
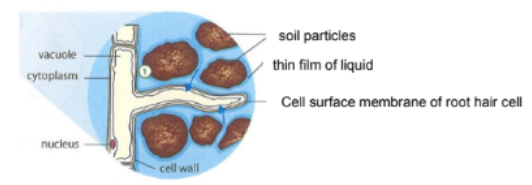
Pathway of Water from Roots to Leaves via Xylem [4]
Root hairs are narrow extensions of an epidermal cell in contact with the soil solution surrounding it, which is a dilute solution of mineral salts.
Cell sap of root hair cell has a lower water potential than the surrounding soil solution. There is a net movement of water molecules entering the root hair cell by osmosis across the partially permeable cell membrane.
The entry of water dilutes the root hair cell sap, which now has a higher water potential than the adjacent cortex cell. Water passed by osmosis from root hair cell A into cortex cell B.
The process continues until the water molecules enters the xylem vessels by osmosis and moves up the plant.
What is transpiration?
Transpiration is the loss of water vapour from the aerial parts of a plant by evaporation, especially through stomata of the leaves.
What is transpiration pull?
Transpiration pull is the suction force caused by transpiration and serves as the main factor that causes movement of water and mineral salts up the xylem.
How is water brought up xylem vessels despite gravity?
The evaporation of water from leaves removes water from xylem vessels by transpiration → results in a suction force (negative pressure) which pulls water up the xylem vessels
Suction force is due to transpiration pull
How does transpiration occur? [5]
Water moves out of the mesophyll cell to form a thin film of moisture. Water evaporates from the film to form water vapour in the intercellular air space.
Water vapour diffuses through the stomata to the drier air outside the leaf. This is transpiration.
As water evaporates from the thin film of moisture, more water moves out of the mesophyll cells to replenish it. This water loss causes the water potential of the mesophyll cells to decrease, becoming lower than that of its neighbouring mesophyll cell.
The mesophyll cells draw water from cells deeper inside the leaf with osmosis.
The mesophyll cells deeper in the leaf then draw water from the xylem by osmosis. This creates a suction force which pulls the whole column of water up xylem vessels, known as transpiration pull.
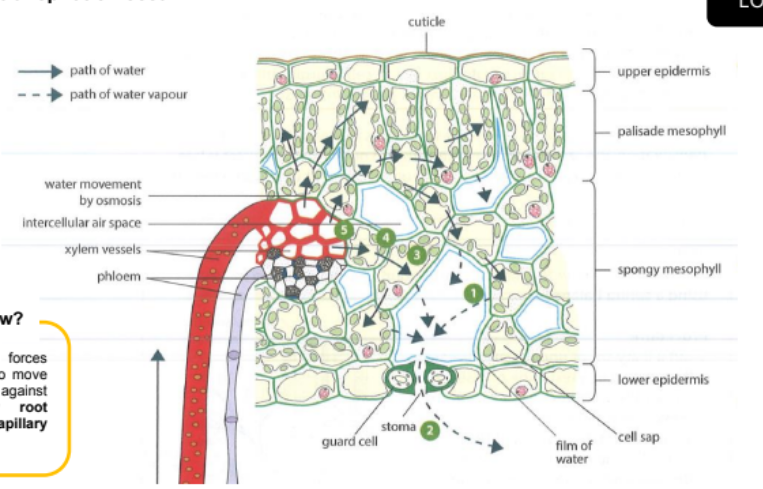
How is transpiration linked to gaseous exchange?
In daylight: stomata open → CO2 diffuse into leaf for photosynthesis
O2 and water vapour are more concentration in intercellular air spaces → diffuse out of leaf through stomata
Importance/Advantage of Transpiration
Transpiration pull is the main way water and mineral salts are drawn from roots to leaves.
Evaporation of water at the leaves cools the plants, preventing it from being scorched by the sun.
Water transported to leaves is used for photosynthesis and replacing water lost by cells.
Keeps cells turgid = keep leaves spread out widely to maximise absorption of sunlight
Measuring rate of transpiration [3]
A potometer directly measures the rate of water absorption by the plant.
The amount of water loss is less than the amount of water absorbed due to water being used in photosynthesis.
Assuming that the rate of water absorption is proportional to the rate of transpiration, the potometer is used to measure the rate of transpiration in the shoot.
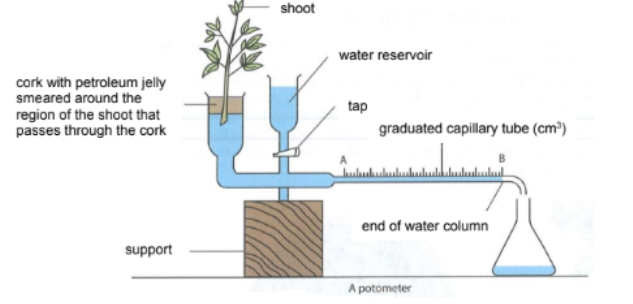
What factors affect transpiration?
Temperature
Humidity
Light intensity
Wind/Air Movement
How does temperature affect transpiration?
Temperature increase = Evaporation increase = Transpiration increase
How does humidity affect transpiration?
Intercellular air spaces in the leaf are normally saturated with water vapour.
Water vapour concentration gradient between the leaf and the atmosphere
Drier/Less humid
> steeper water vapour concentration gradient between leaf and atmosphere
> faster rate of diffusion of water vapour
> Transpiration increase
How does light intensity affect transpiration?
Light affects size of stomata → affects rate of transpiration
In sunlight, stomata open and become widen → transpiration increase
In darkness, stomata close → transpiration decrease
How does wind/air movement affect transpiration?
Wind blows away water vapour that accumulate outside the stomata → maintains water vapour concentration gradient between leaf and atmosphere
Stronger wind → Transpiration increase
Still air → water vapour diffuses out of the leaf → makes air around leaf more humid → Transpiration decrease
What is turgor pressure?
Turgor pressure (hydrostatic pressure) is the pressure exerted on a plant cell wall by water passing into the cell by osmosis. A turgid cell will have high turgor pressure.
What does turgor pressure in the leaf mesophyll cells help to do?
> support leaf, keep it firm
> spread leaf widely to absorb sunlight for photosynthesis
Why do plants wilt?
In strong sunlight → transpiration rate exceeds water absorption rate by roots → cells lose turgor and lose turgor pressure
Cells become flaccid → plants wilt
Advantages of Wilting [3]
When leaf folds up → surface area exposed to sun is reduced
Causes guard cells to become flaccid → stomata close
Transpiration rate reduced
Disadvantages of Wilting [4]
Rate of photosynthesis reduced because water becomes limiting factor
Stomata closed → CO2 entering leaf reduced
CO2 becomes limiting → photosynthesis decrease
Folding of leaf reduces SA exposed to sunlight → reduces photosynthesis
Summary of Factors Affecting Transpiration
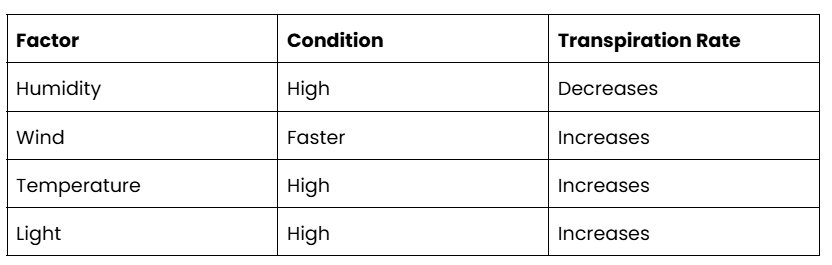
Location of Xylem!
Stem:
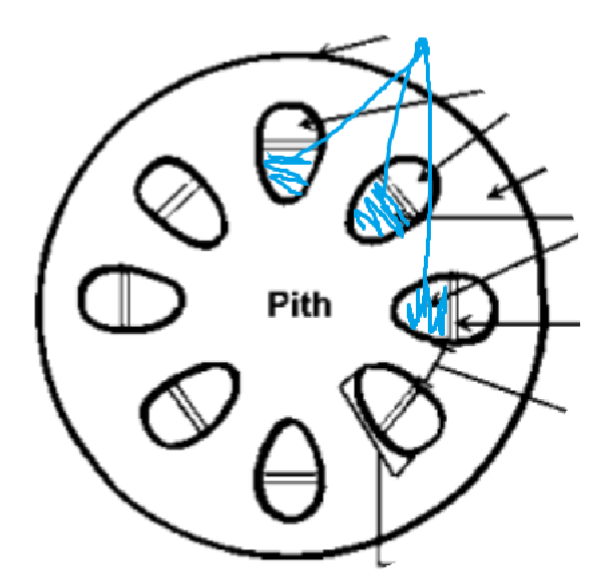
Leaf:
Root:
Location of Phloem!
Stem:
Leaf:
Root:
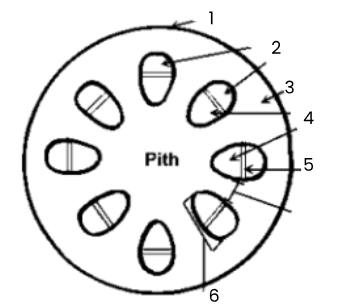
1
epidermis

2
phloem

3
cortex

4
xylem

5
cambium

6
vascular bundle
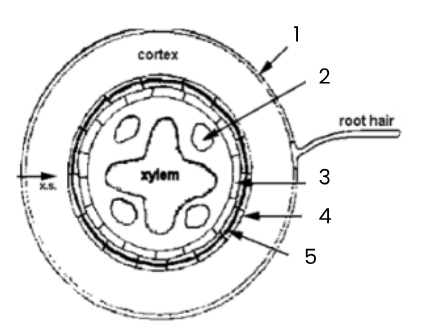
1
epidermis

2
phloem

3
pericycle (meristematic tissue)

4
endodermis

5
casparian strip (band around endodermis)
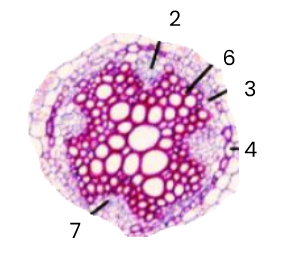
2
phloem

3
pericycle (meristematic tissue)

4
endodermis

6
xylem

7
cambium (meristematic tissue)