BIOL 434 Lab Practical - Flashcards on Marine and Terrestrial Invertebrates
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Phylum Porifera
Phylum of sponges
Classes:
- Calcarea
- Hexactinellida
- Demospongiae
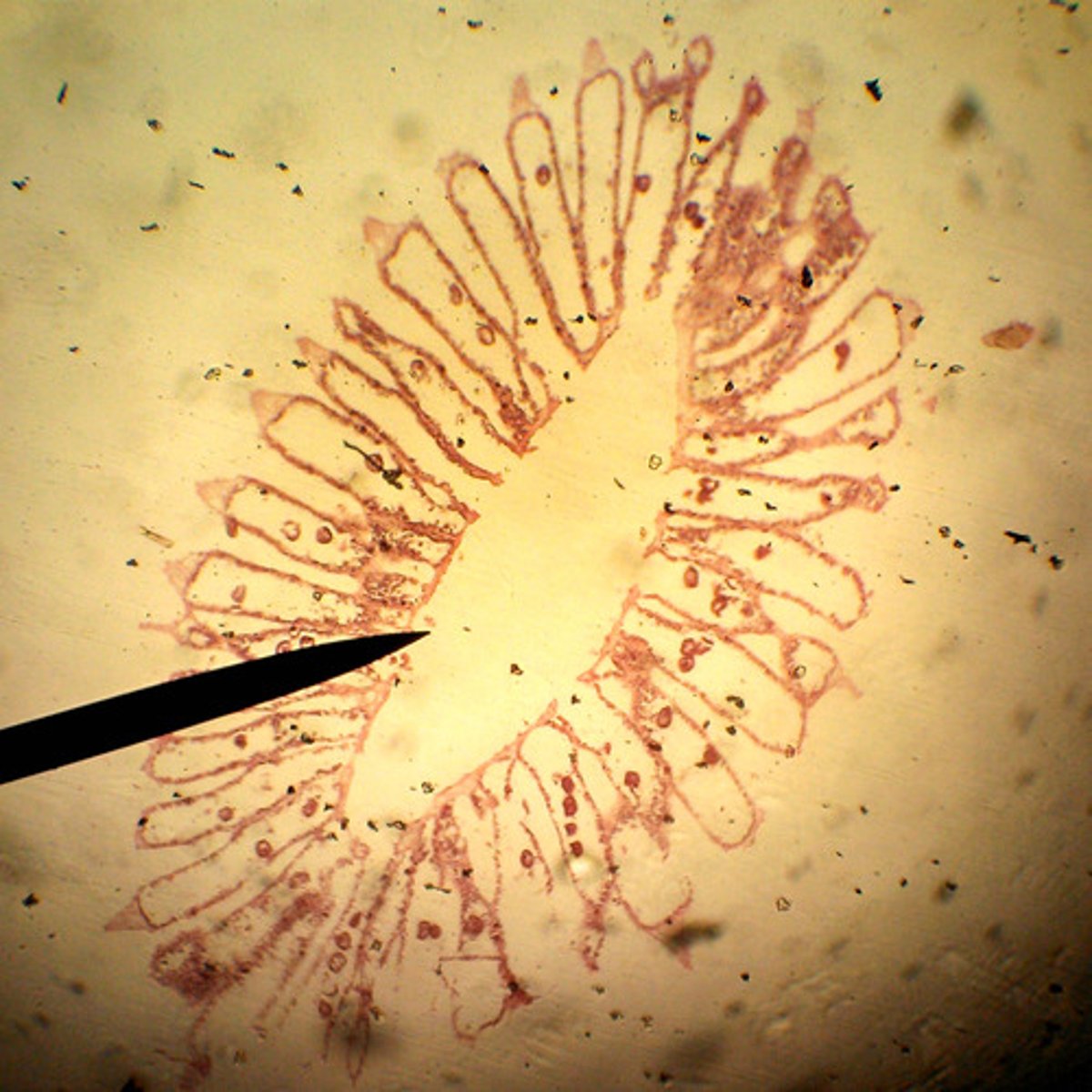
Class Calcarea
Class of sponges
- spicules made from calcium carbonate
- spicules can be straight lines or have 3 or 4 rays
- hard to the touch
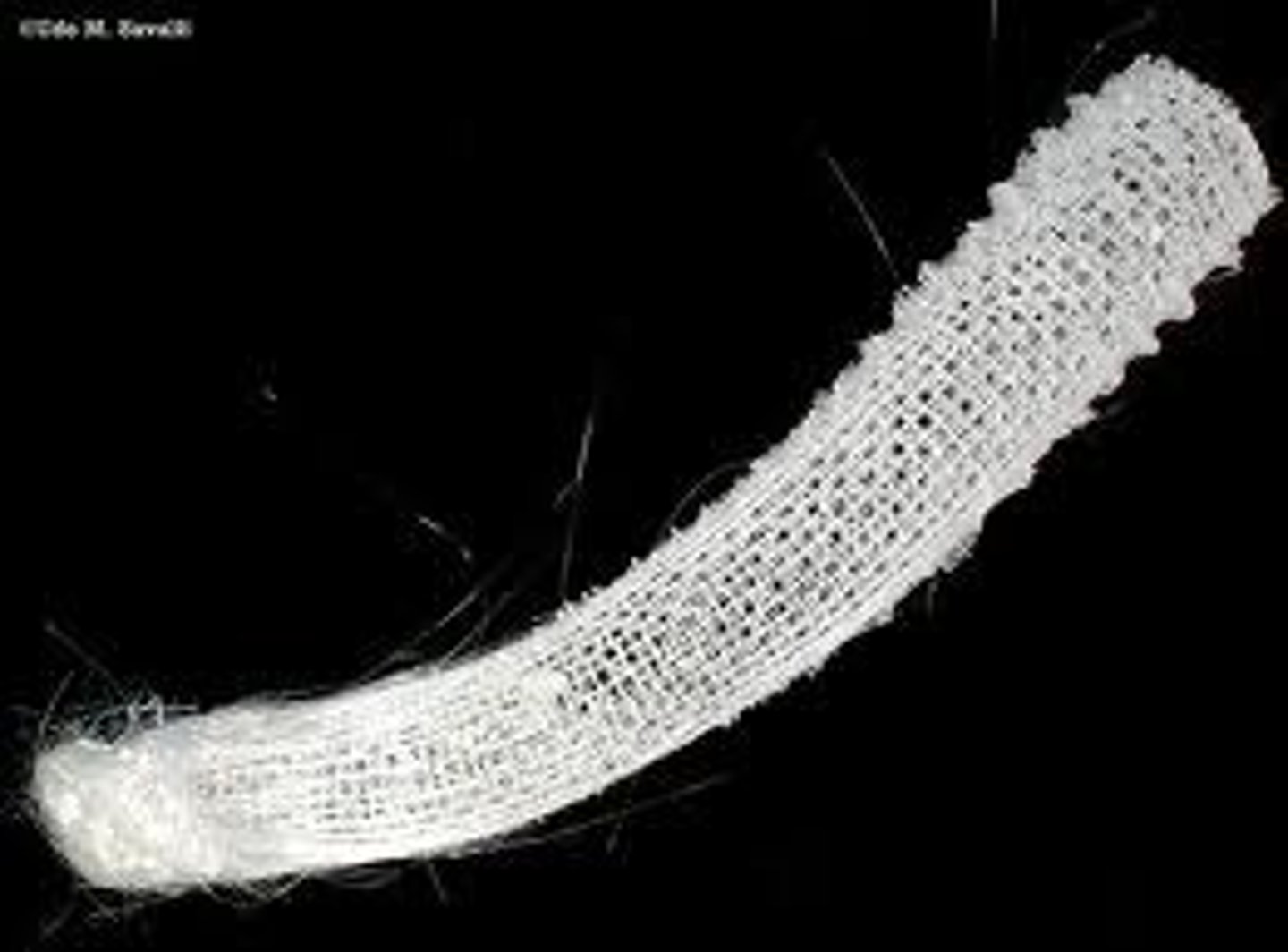
Class Hexactinellida
Class of sponges
- spicules are 6-pointed and are made of silica
- "glass sponges"
- they have fiberglass at the bottom
Class Demospongiae
Class of sponges
- spicules vary widely in shape and size
- spicules are made of silica (many also have a spongin network)
Phylum Cnidaria
Phylum of jellyfish, corals, hydras, and cube jellies
Classes:
- Anthozoa
- Scyphozoa
- Hydrozoa
- Cubozoa
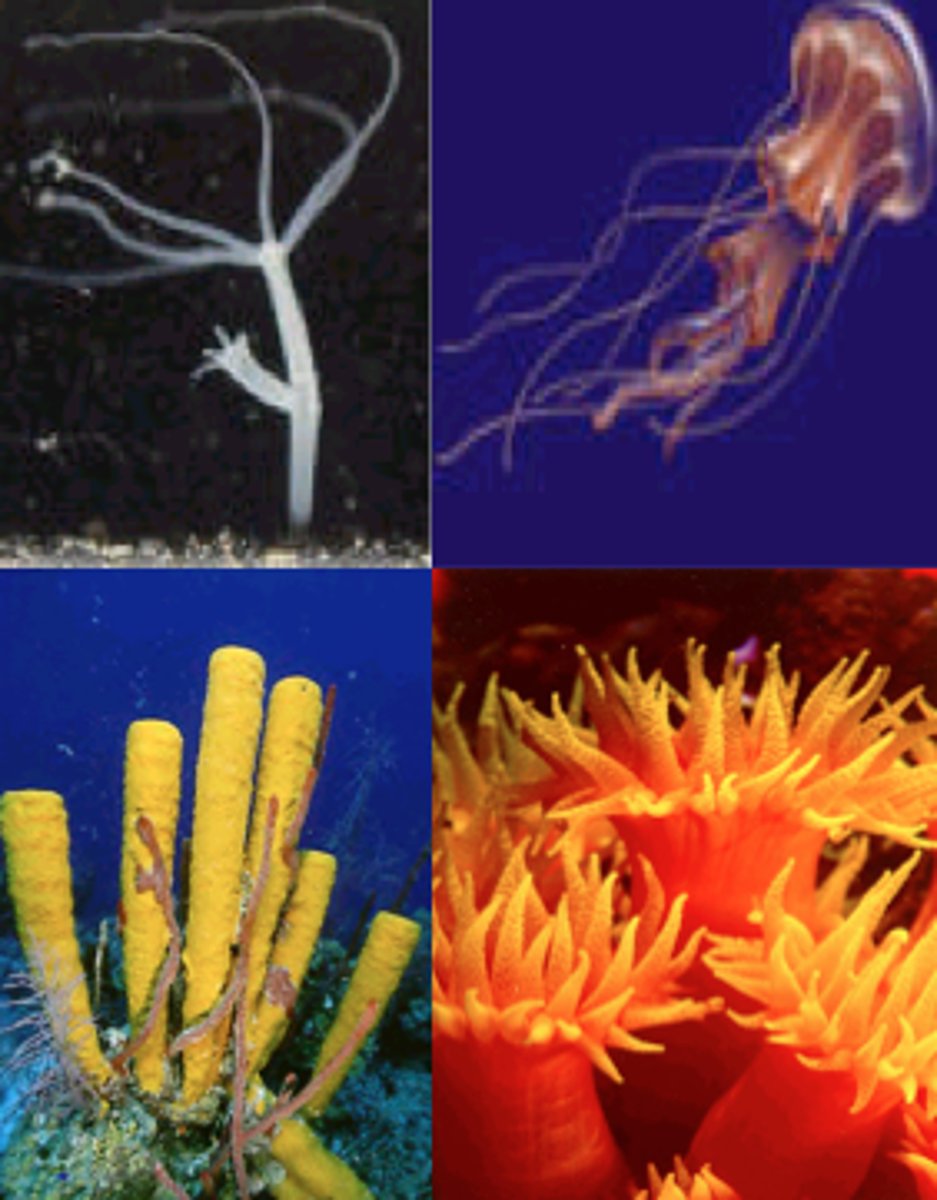

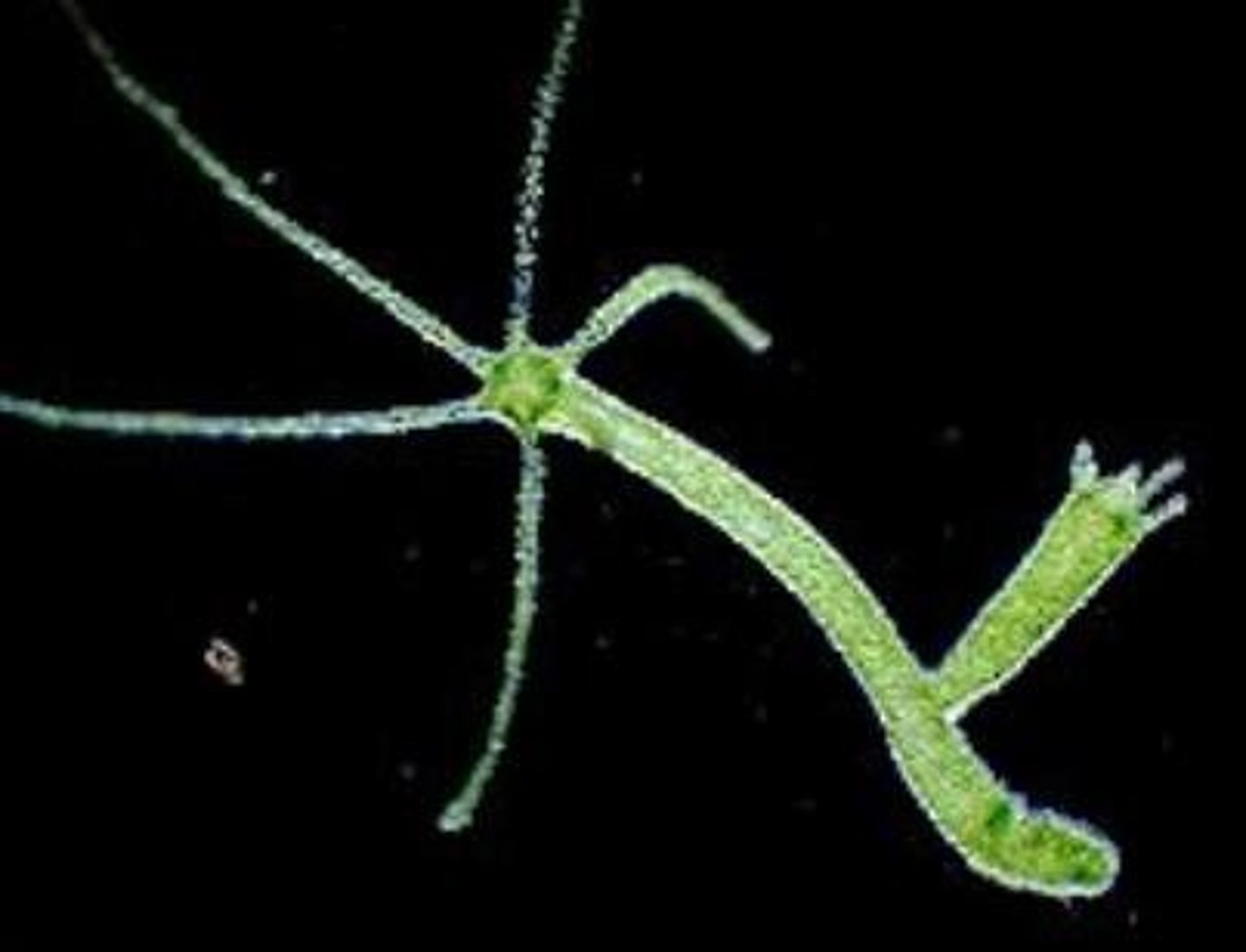
Class Hydrozoa
Class of cnidarians
- ex. freshwater Hydra, Portugese man o' war
- can be colonial, solitary, or as siphonophores in polyp colonies
- can reproduce sexually or asexually, with complex life cycles

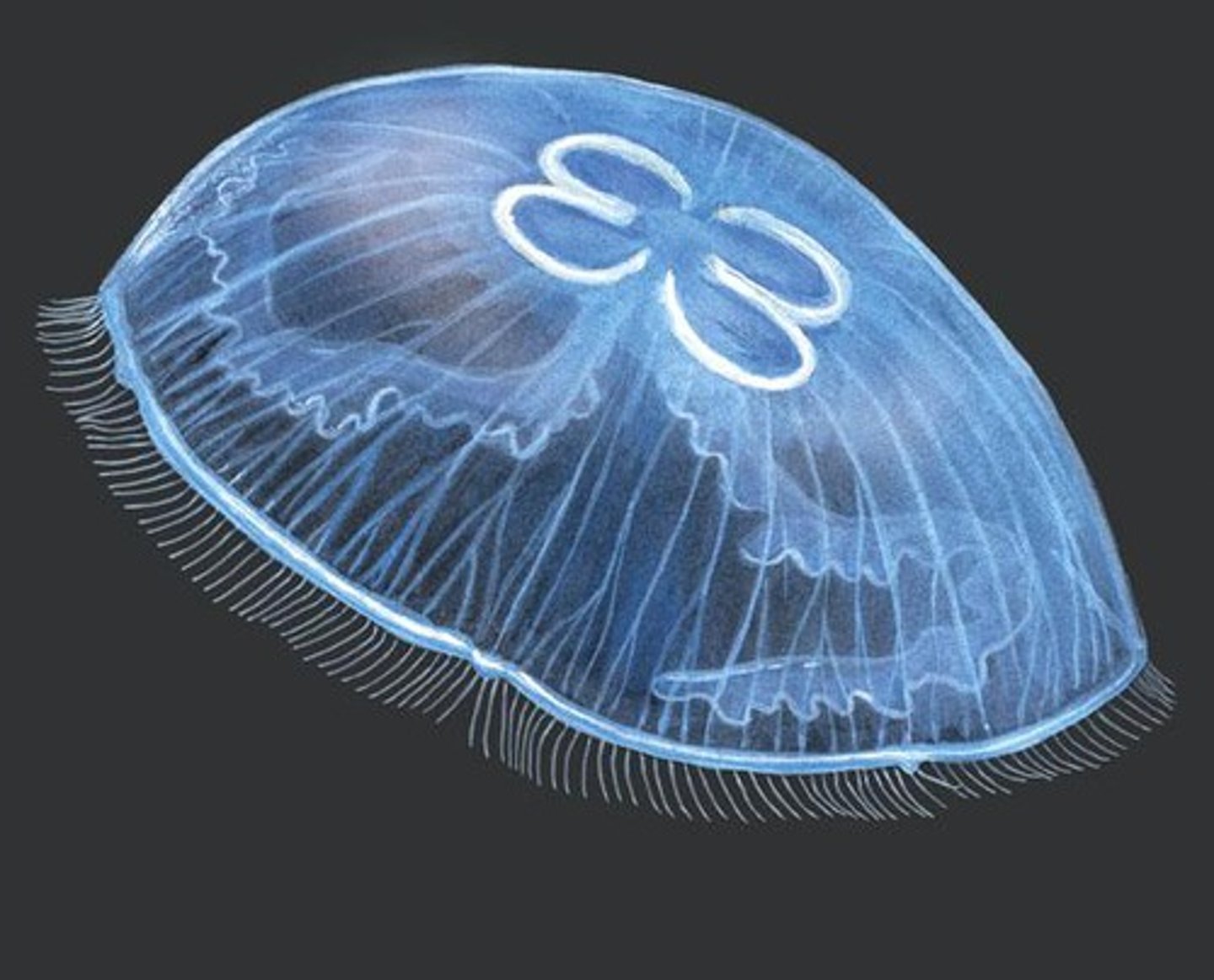
Class Scyphozoa
Class of cnidarians (jellyfish)
- ex. Aurelia
- life cycle = planulae, scyphistoma, strobila (early), strobila (late), ephyra
- alternation of generations with asexual polyps and sexual medusae
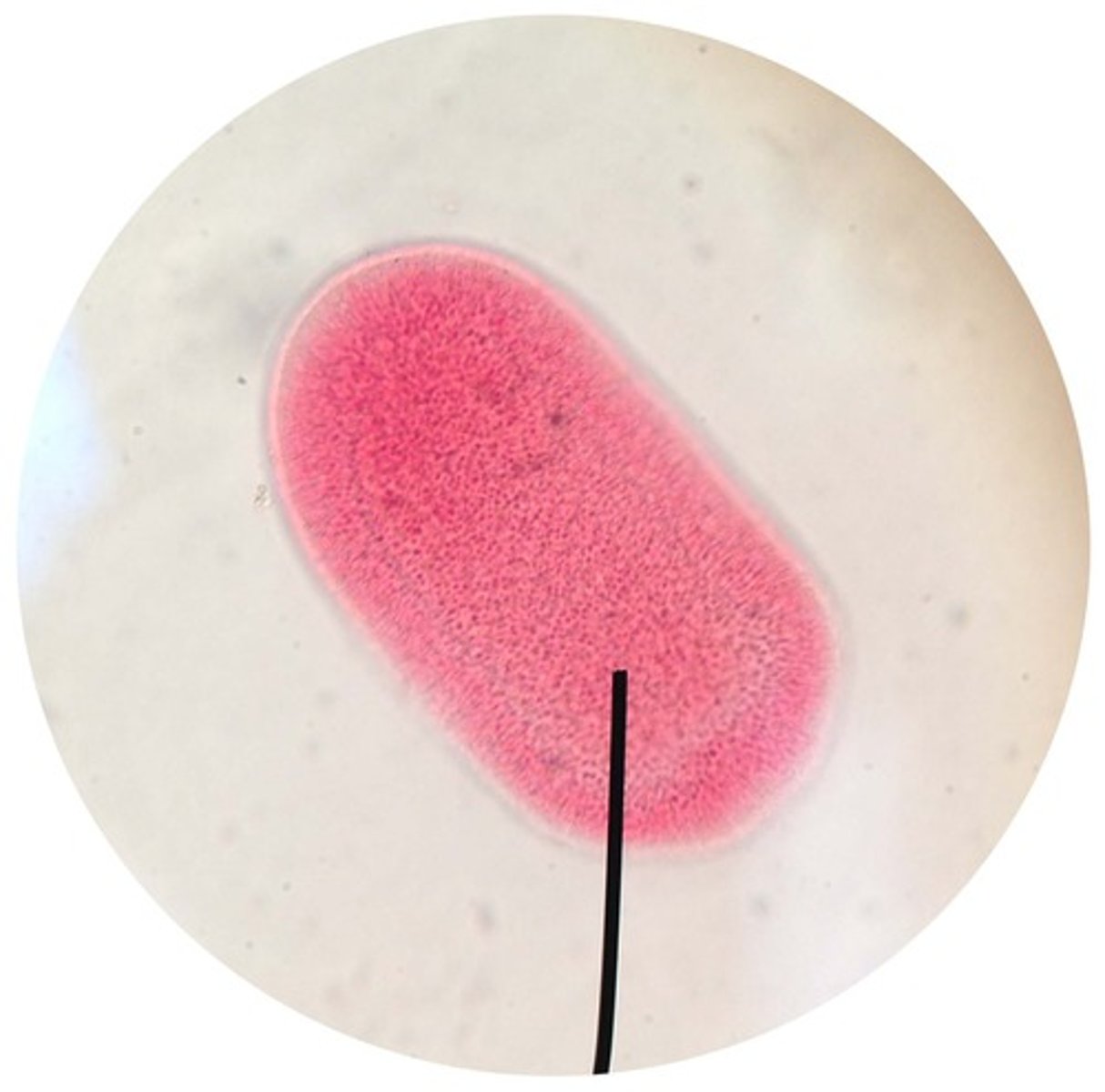
Jellyfish planulae
- the free-swimming larval stage that develops after fertilization
- planula eventually settles on a substrate and develops into the next stage
Jellyfish scyphistoma
- the polyp stage that arises from the settled planula
- it is fixed in one place and can reproduce asexually by budding
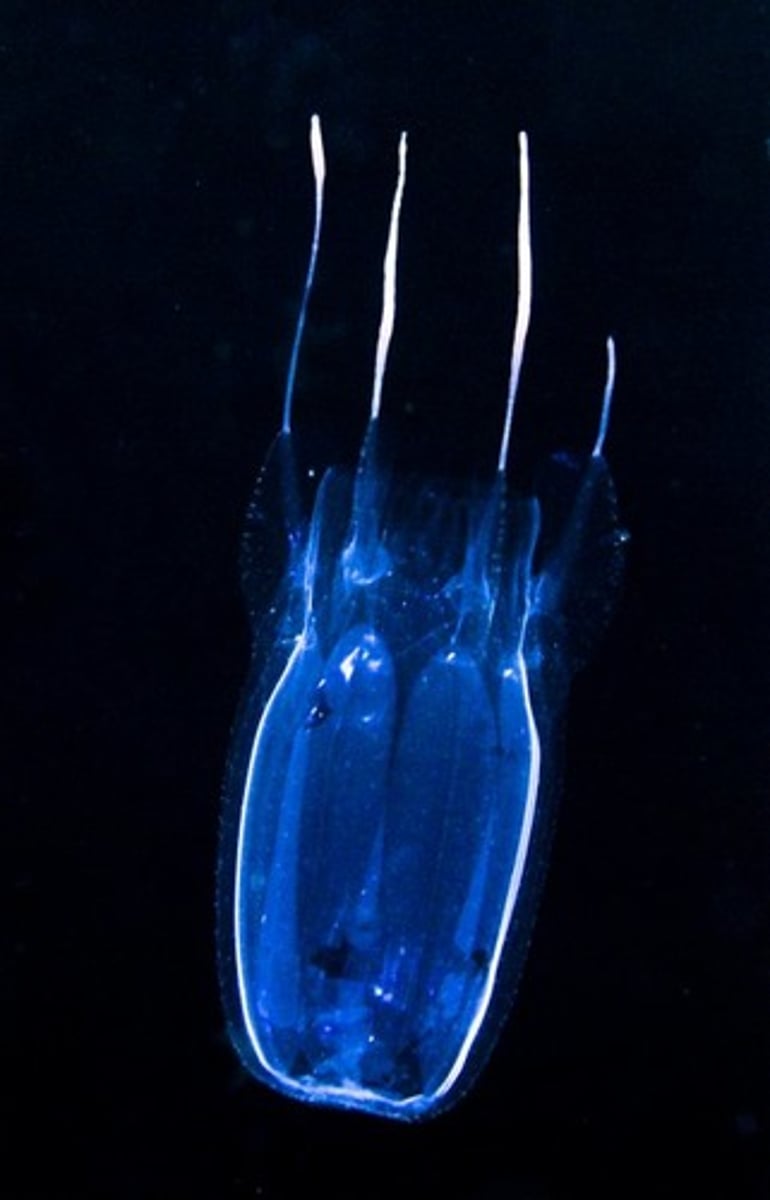
Jellyfish strobila (early)
- scyphistoma undergoes a process called strobilation, where it segments transversely
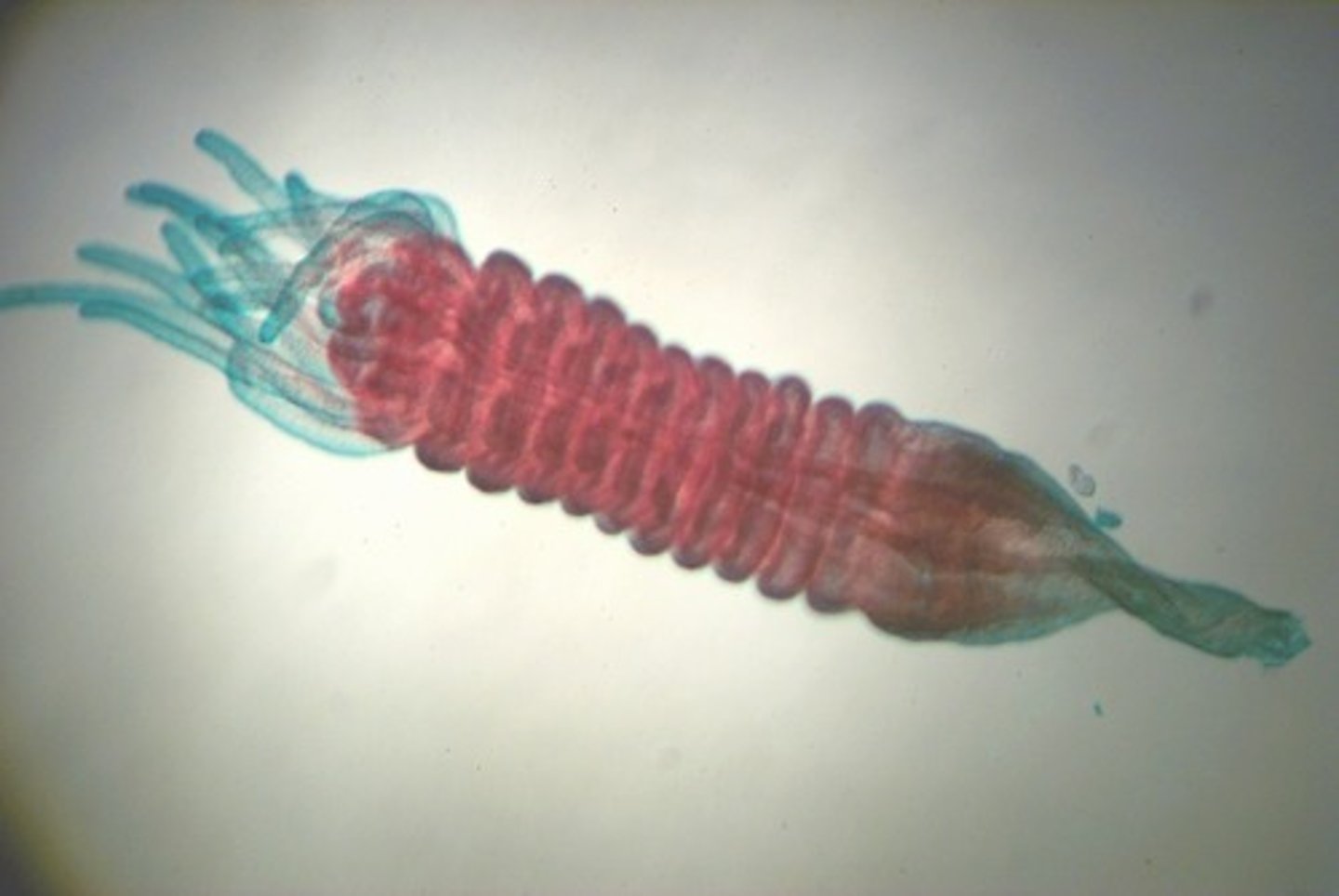

Jellyfish strobila (late)
- in this stage, the segments are more developed and resemble a stack of discs, each of which will become an individual ephyra
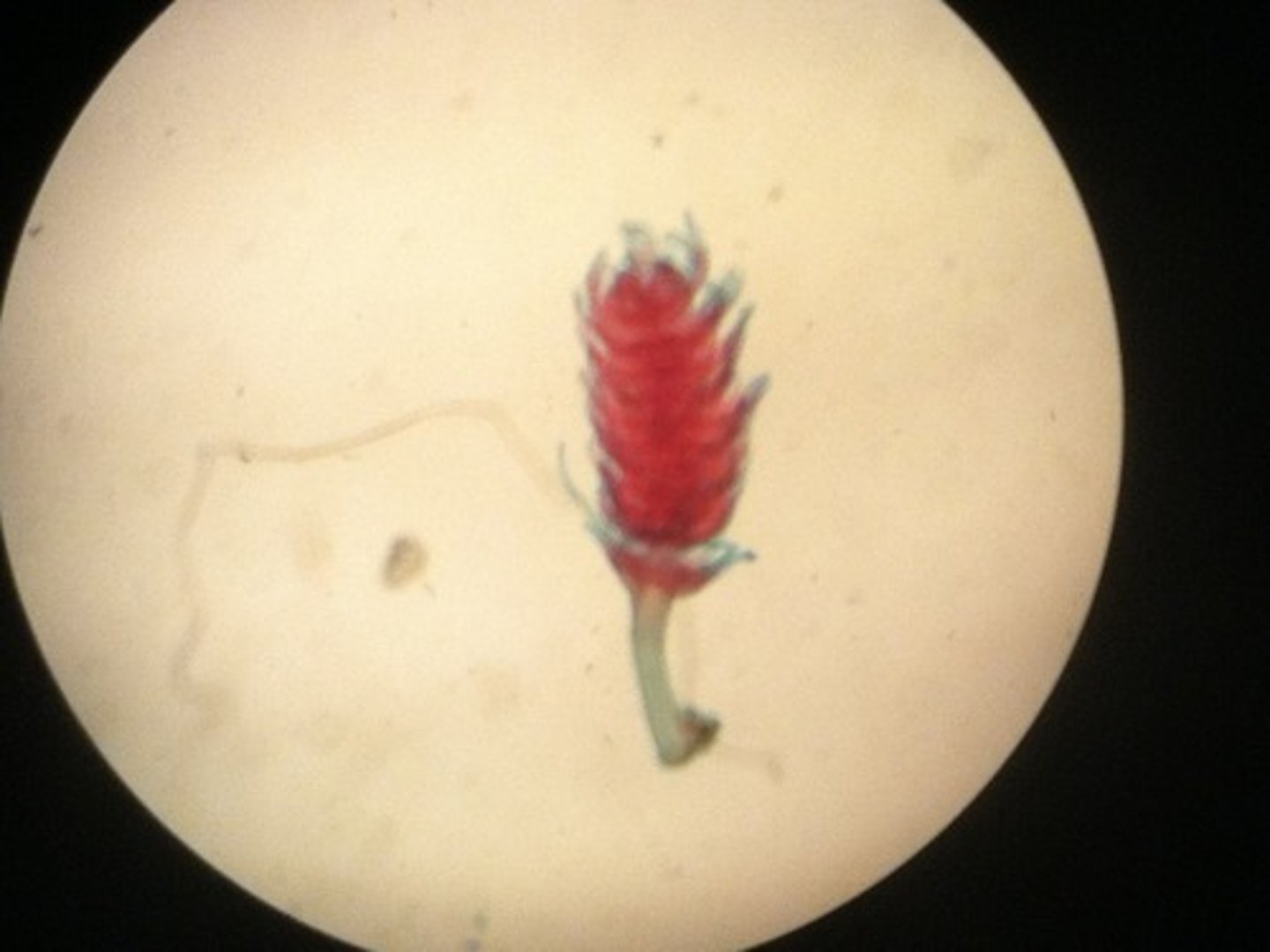
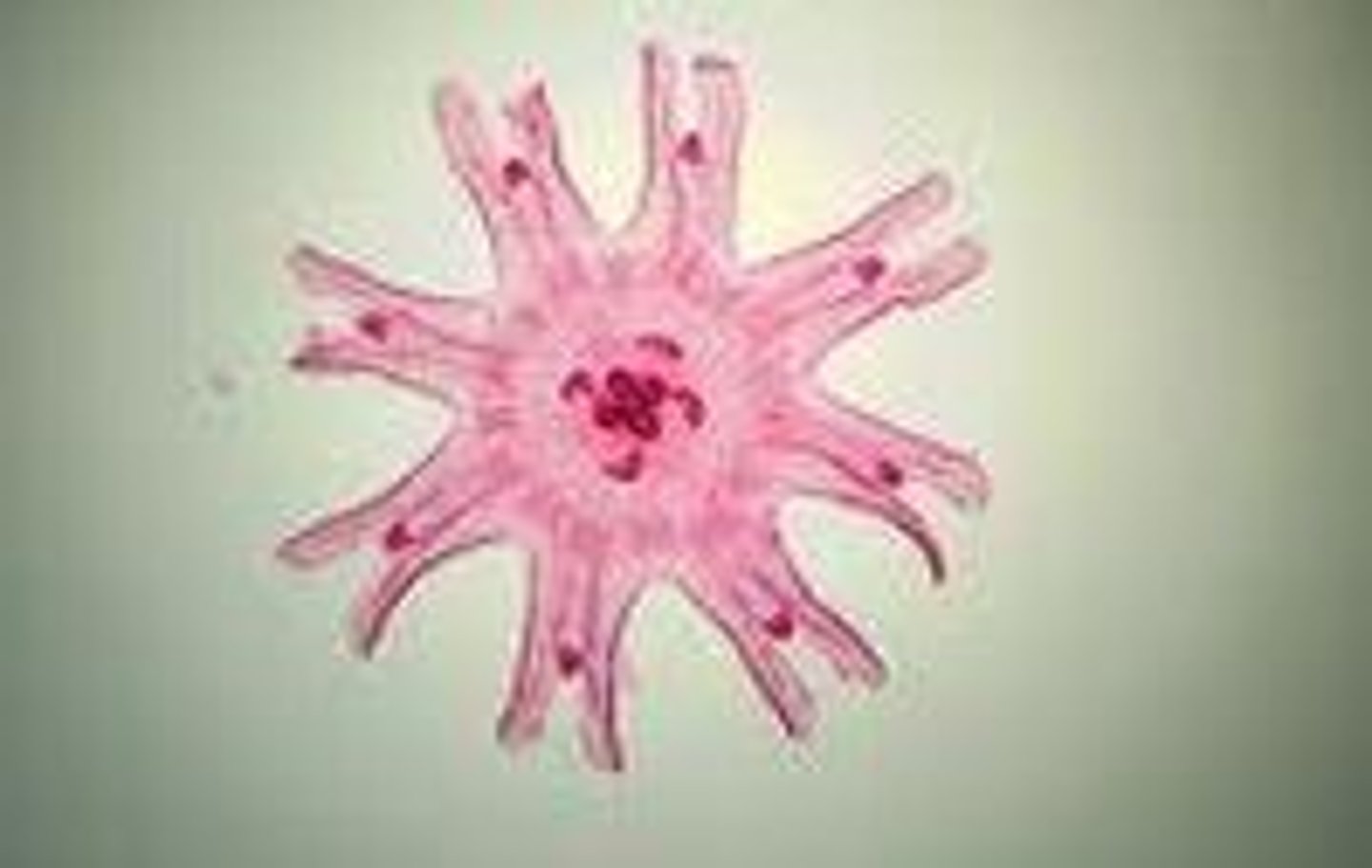
Jellyfish ephyra
- these are the juvenile medusae that bud off from the strobila
- they will eventually grow into adult medusae, completing the life cycle

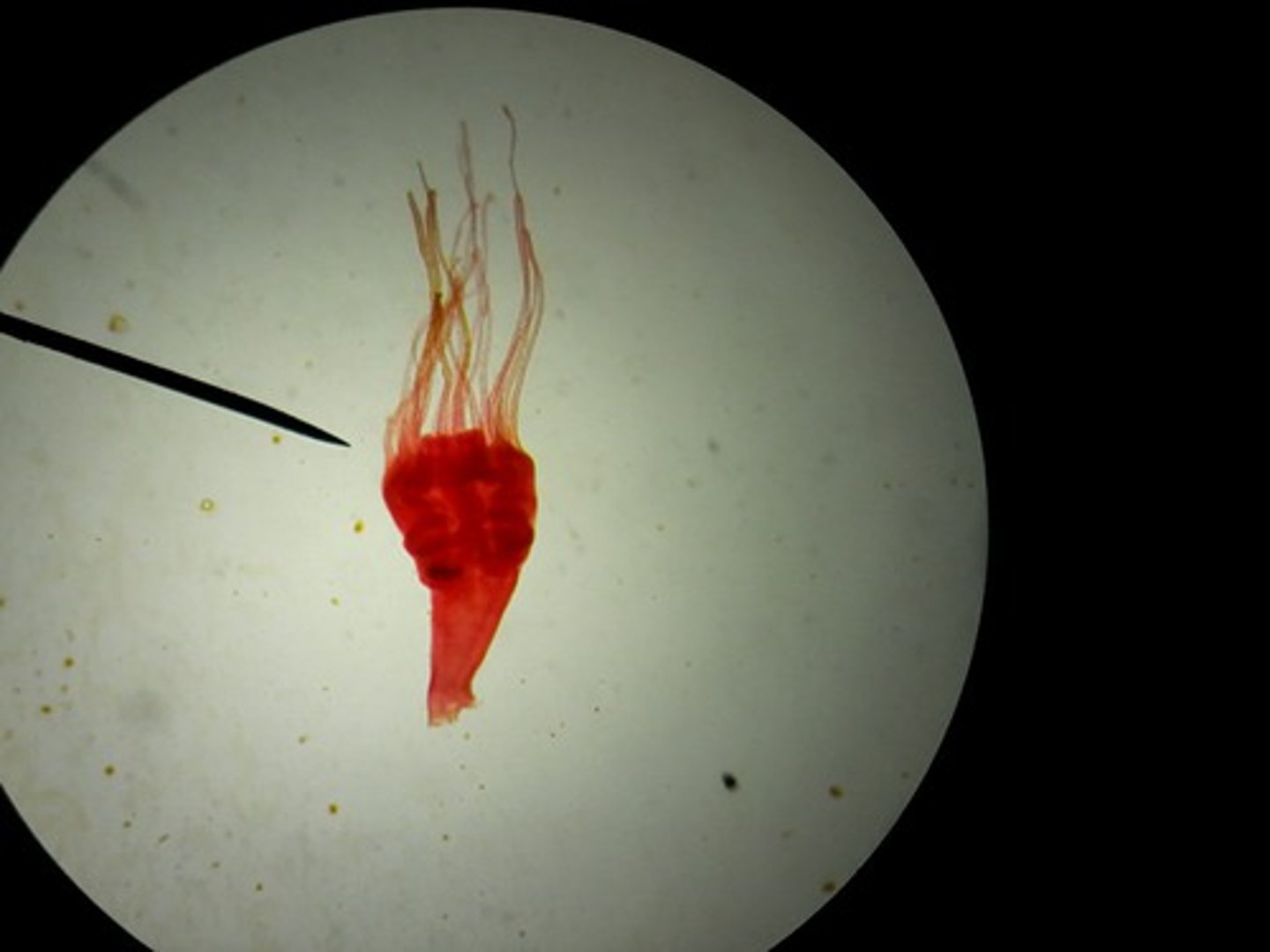
Class Cubozoa
Class of cnidarians (cube jellies)
- boxy-looking
- often highly venomous
- medusa stage is dominant; polyp stage is short-lived and simple
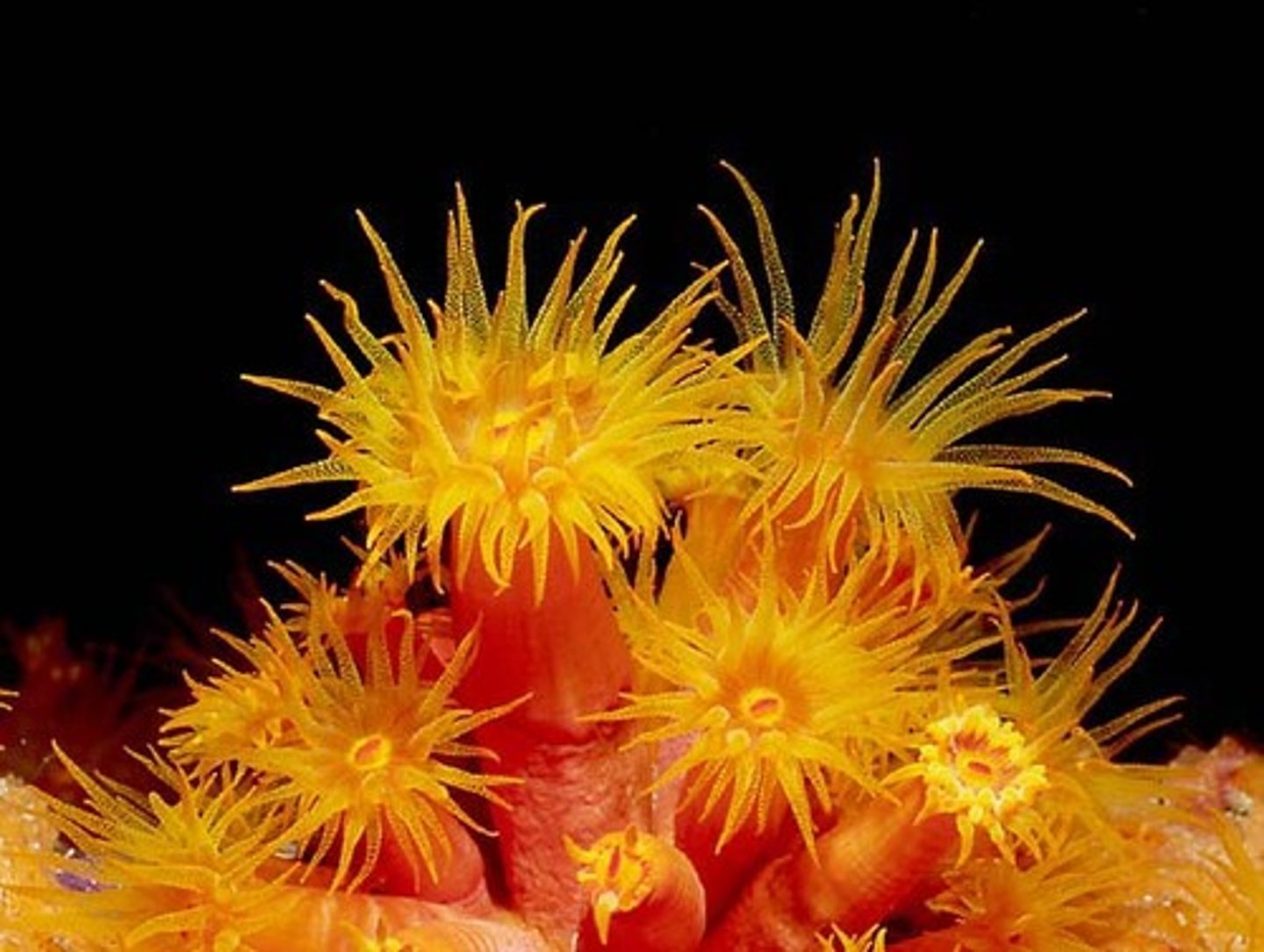
Class Anthozoa
Class of cnidarians (corals, anenomes, sea pens)
- ex. Metridium
- exclusively polyp form; no medusa stage
- both sexual and asexual reproduction

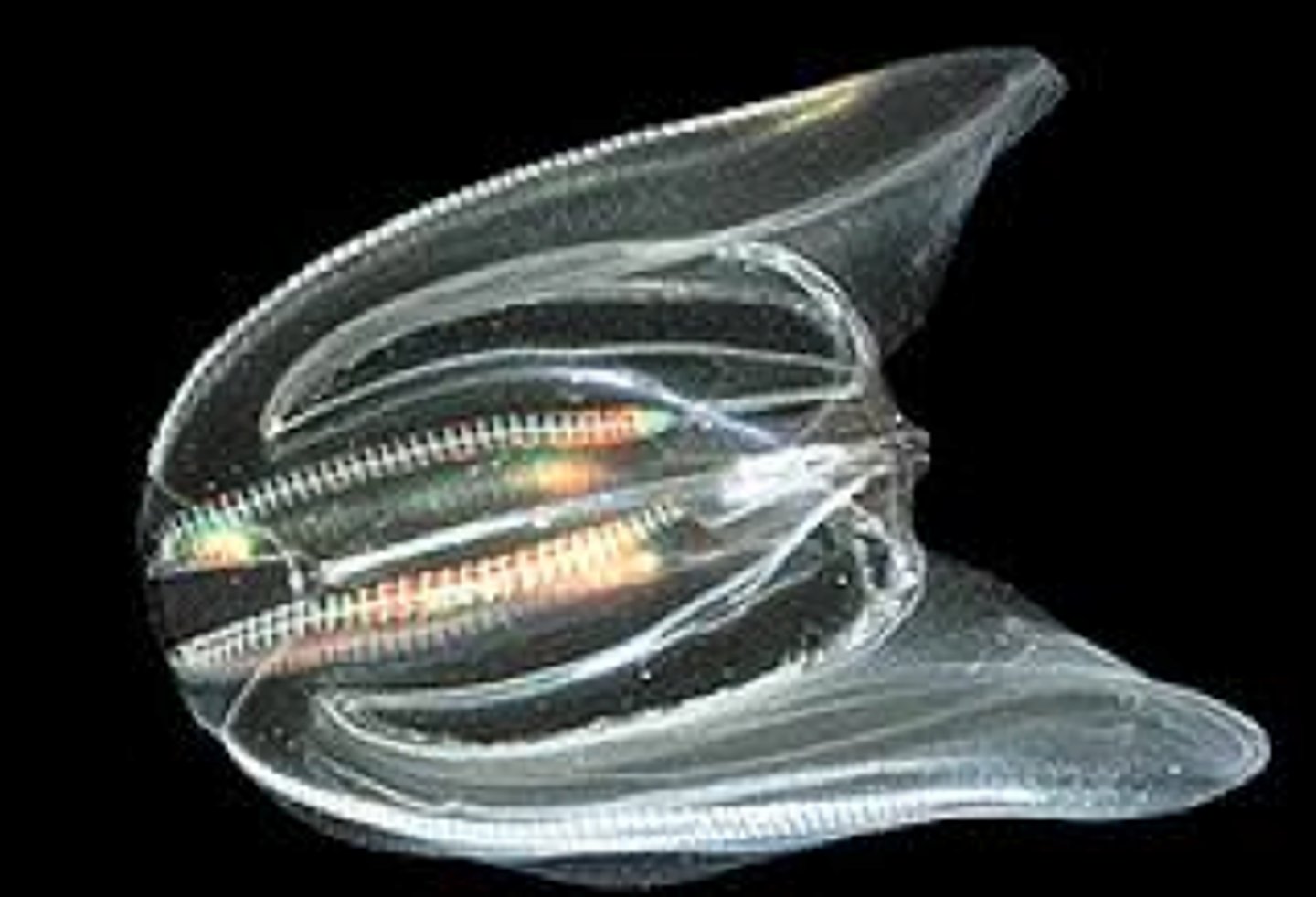
Phylum Ctenophora
Phylum of comb jellies
- ex. Beroë, Pleurobrachia, Bolinopsis, and Mnemiopsis
- have comb rows on edges of bell
- apical sense organ allows ctenophores to balance and orient themselves in water

Phylum Echinodermata
Phylum of starfish, sea urchins, and sea cucumbers
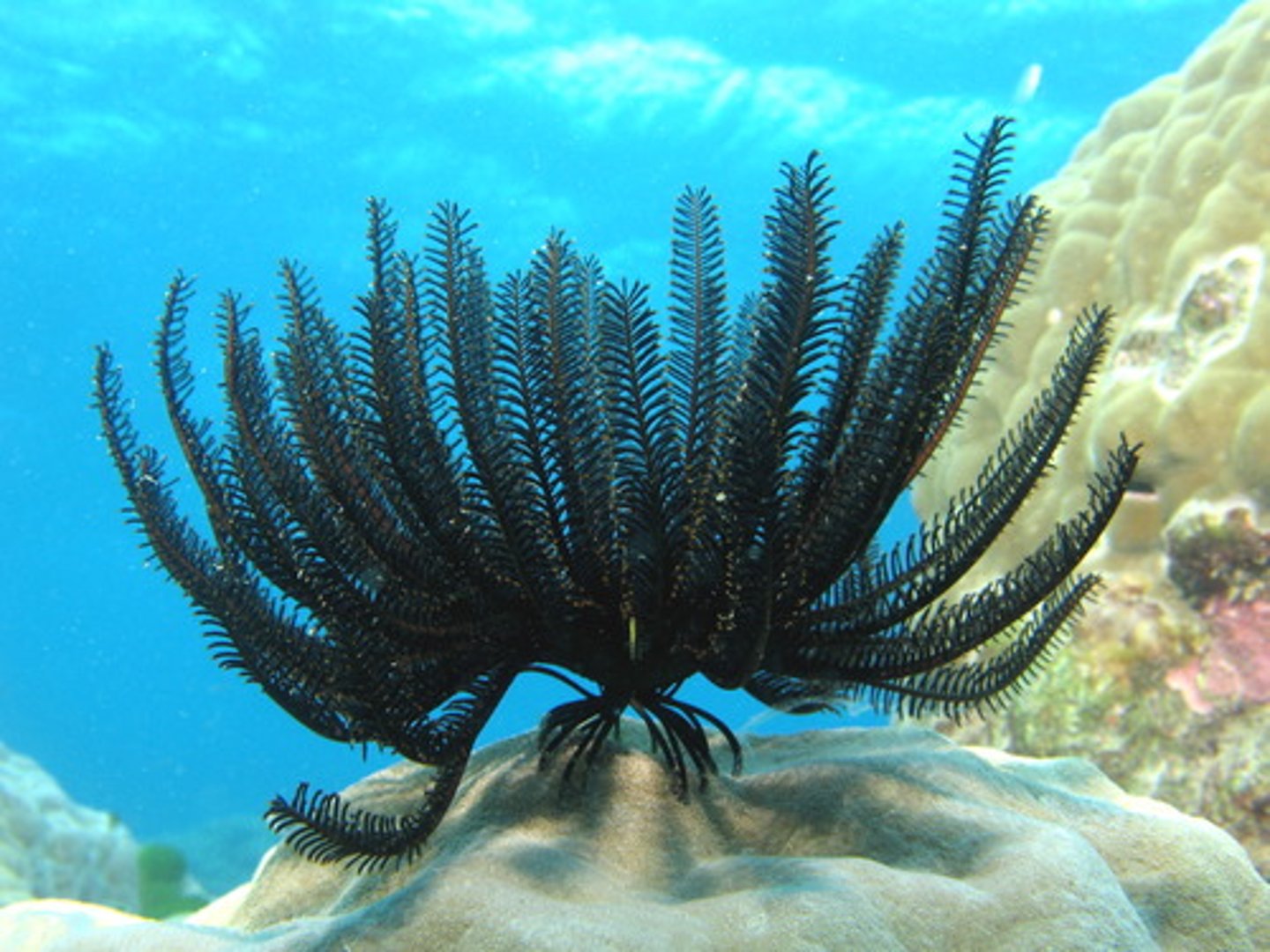
Class Crinoidea
Class of echinoderms (feather stars)
-rep type: Antedon

Class Ophiuroidea
Class of echinoderms (brittle stars)
- central disc with long, flexible arms distinct from the disc; no suction cups on tube feet
- scavengers, detritivores, or filter feeders
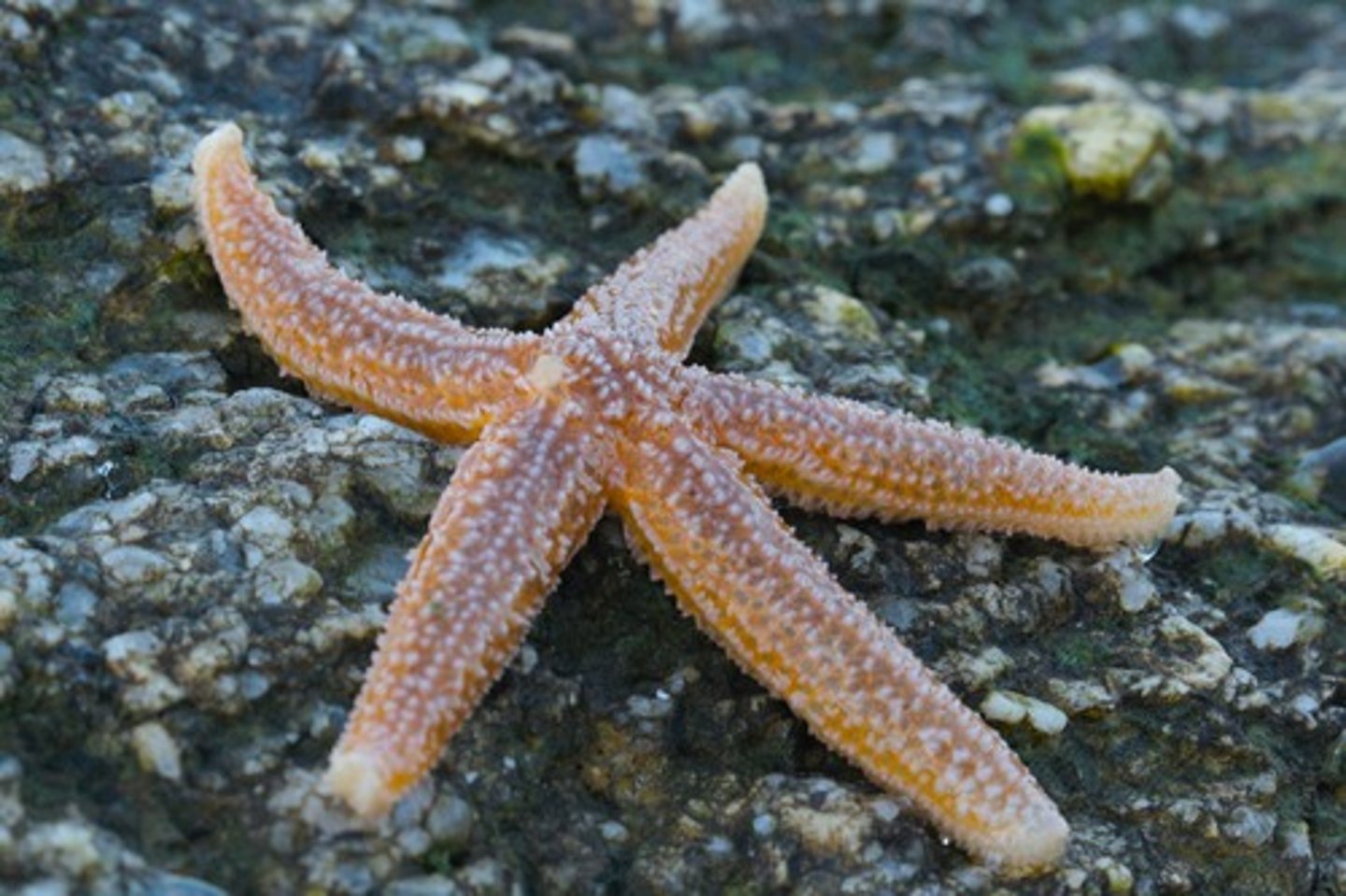
Class Asteroidea
Class of echinoderms (sea stars)
- ex. Asterias
- 5 arms radiating from a central disc; possess tube feet with suction for movement and feeding
- water vascular system: madreporite --> stone canal --> ring canal --> radial canal --> tube feet
- life cycle: early cleavage, blastula and gastrula, bipinnaria larva, brachiolaria larva, whole mount

Starfish early cleavage
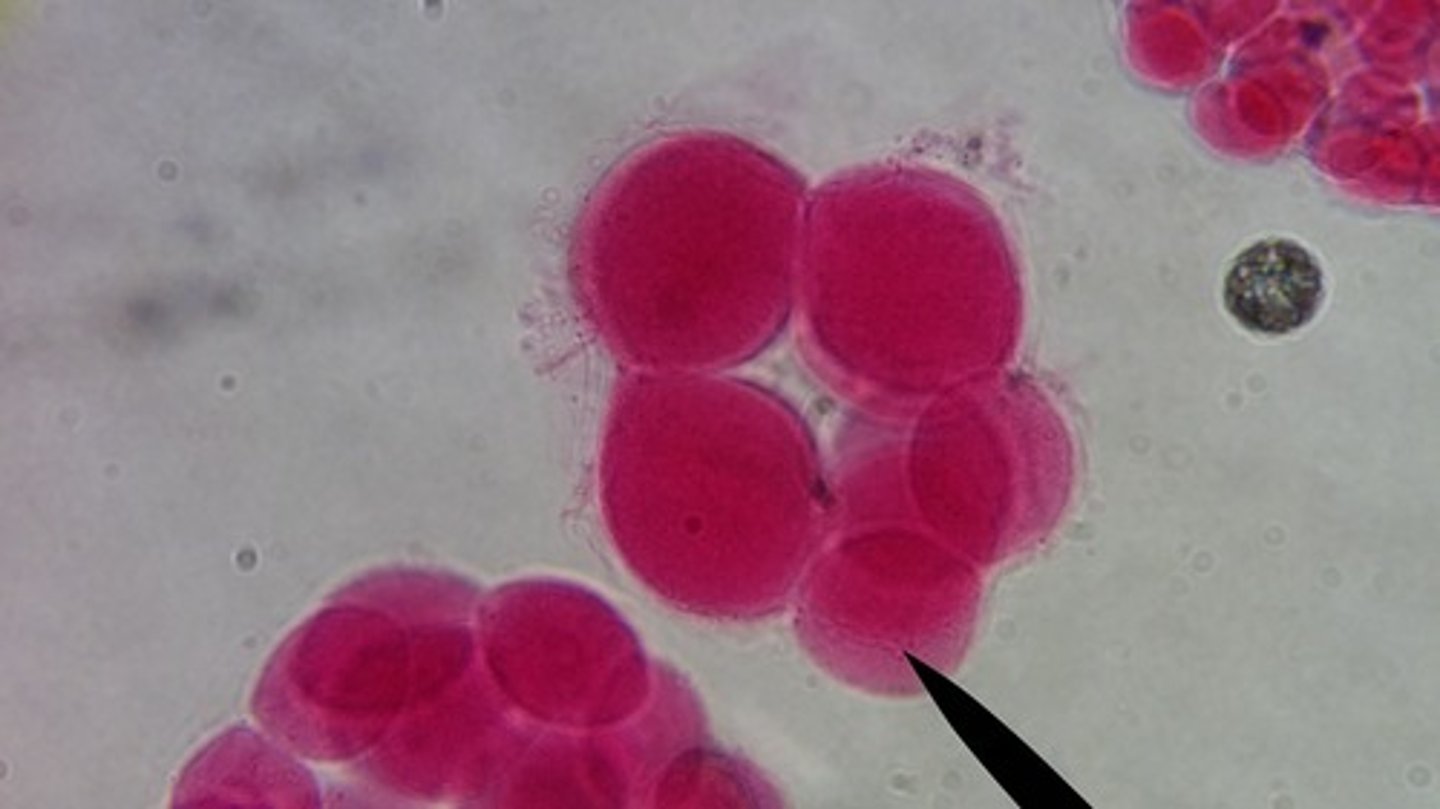
Starfish blastula and gastrula
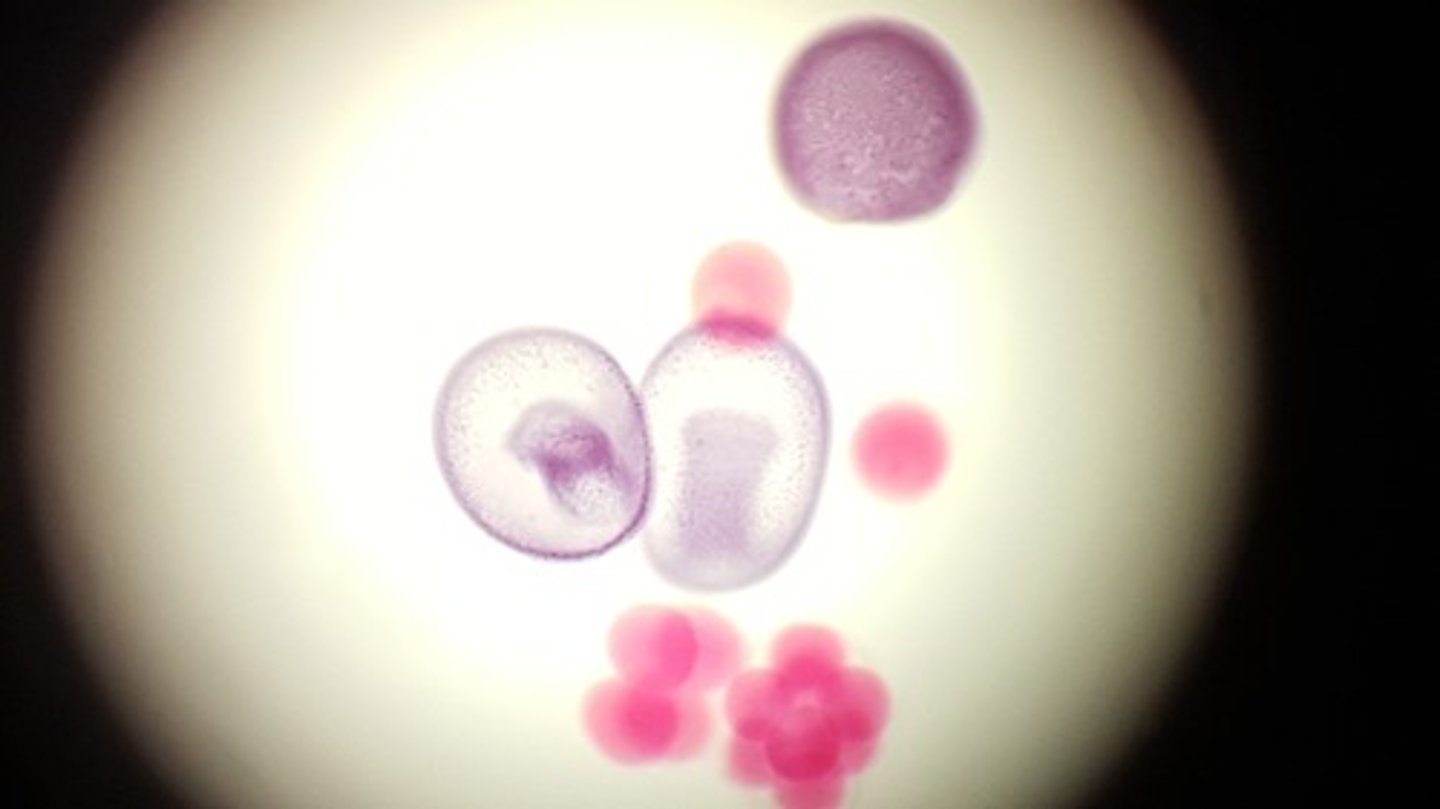
Starfish bipinnaria
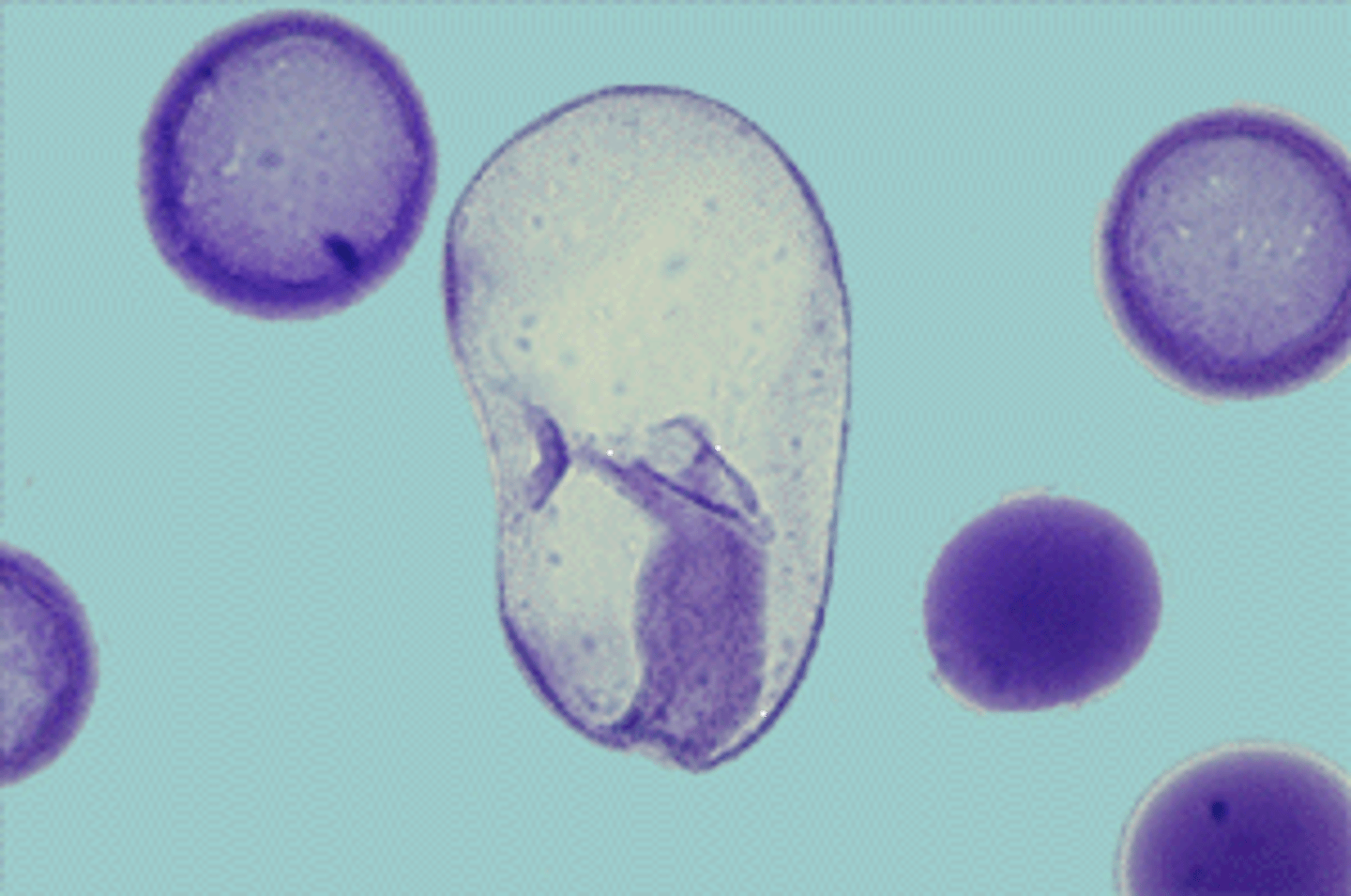
Starfish brachiolaria
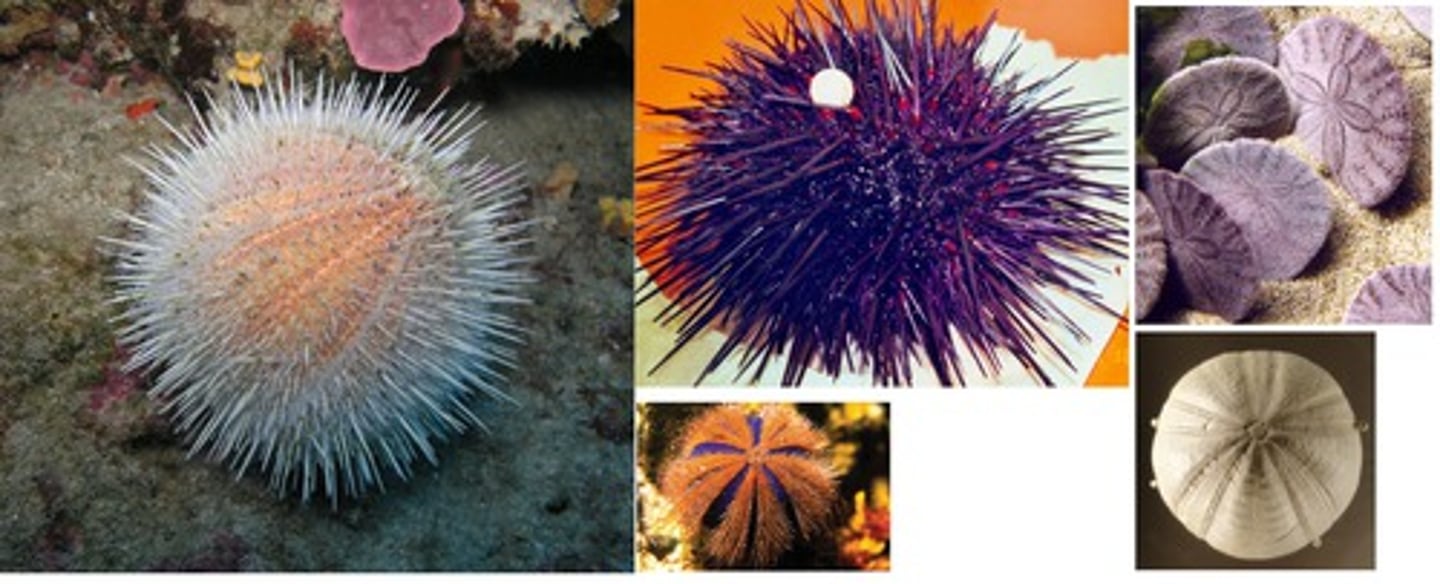
Class Echinoidea
Class of echinoderms (sea urchins, sand dollars)
- globular or flattened body covered with spines; no arms, but have a central mouth on the underside
- mostly herbivorous, grazing on algae; some are detritivores

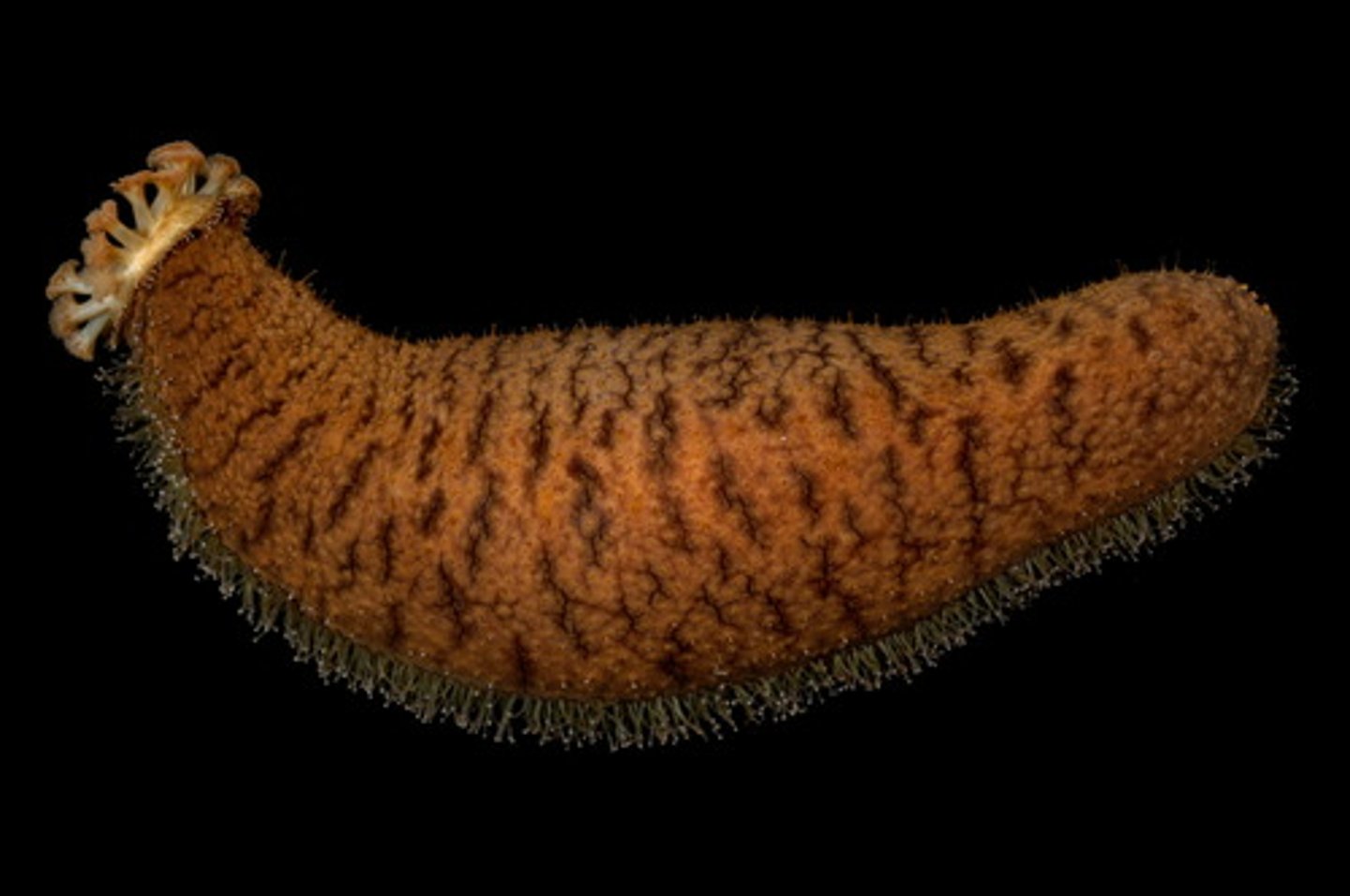
Class Holothuroidea
Class of echinoderms (sea cucumbers)
- elongated, soft-bodied; leathery skin; tube feet often modified into tentacles around the mouth
- detritivores, feeding on organic matter in the sediment

Phylum Platyhelminthes
Phylum of flukes and tapeworms
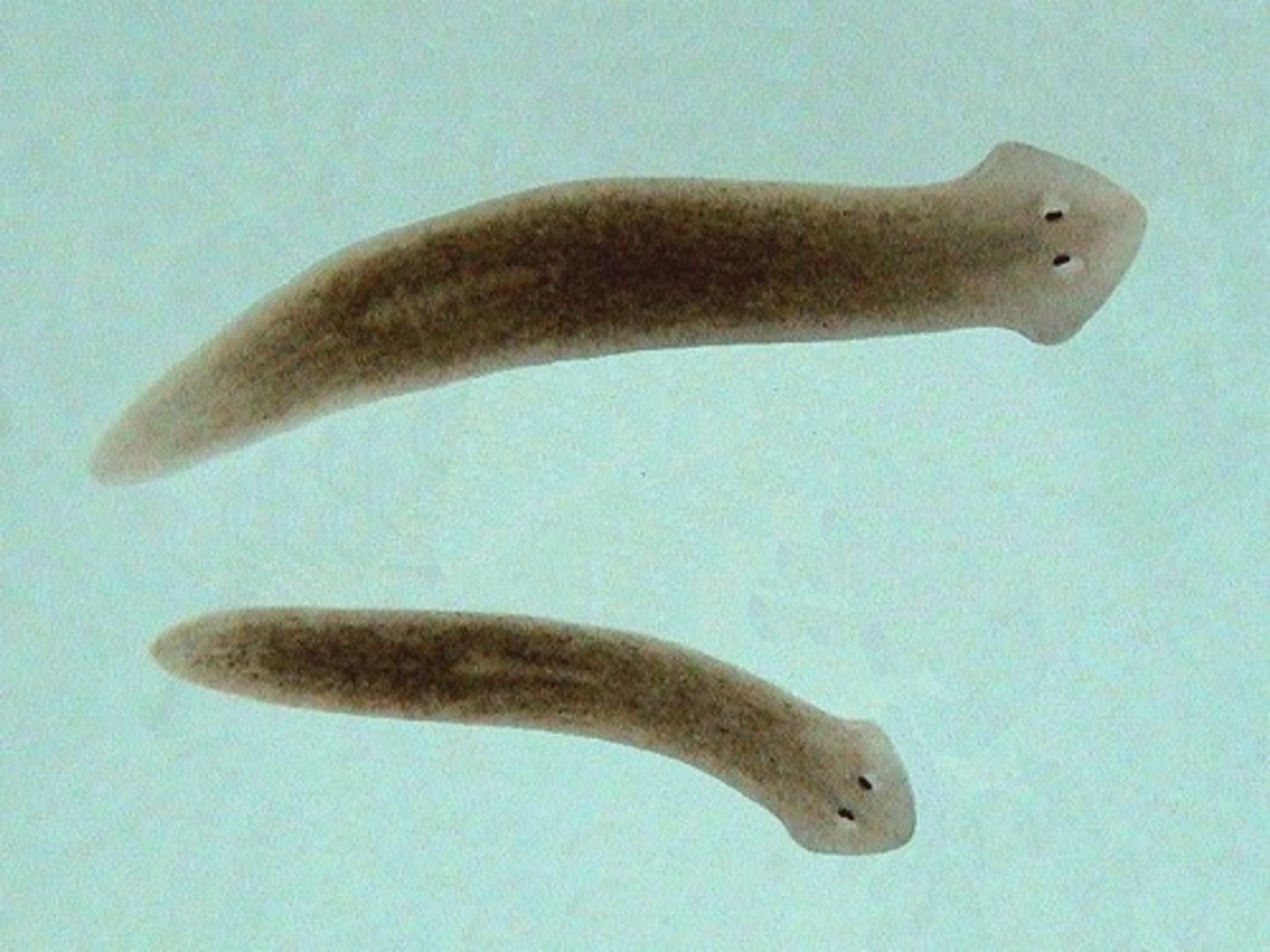
Class Turbellaria
Class of platyhelminths (flatworms)
- ex. Planaria
-eye spots
-acoelomate

Class Trematoda
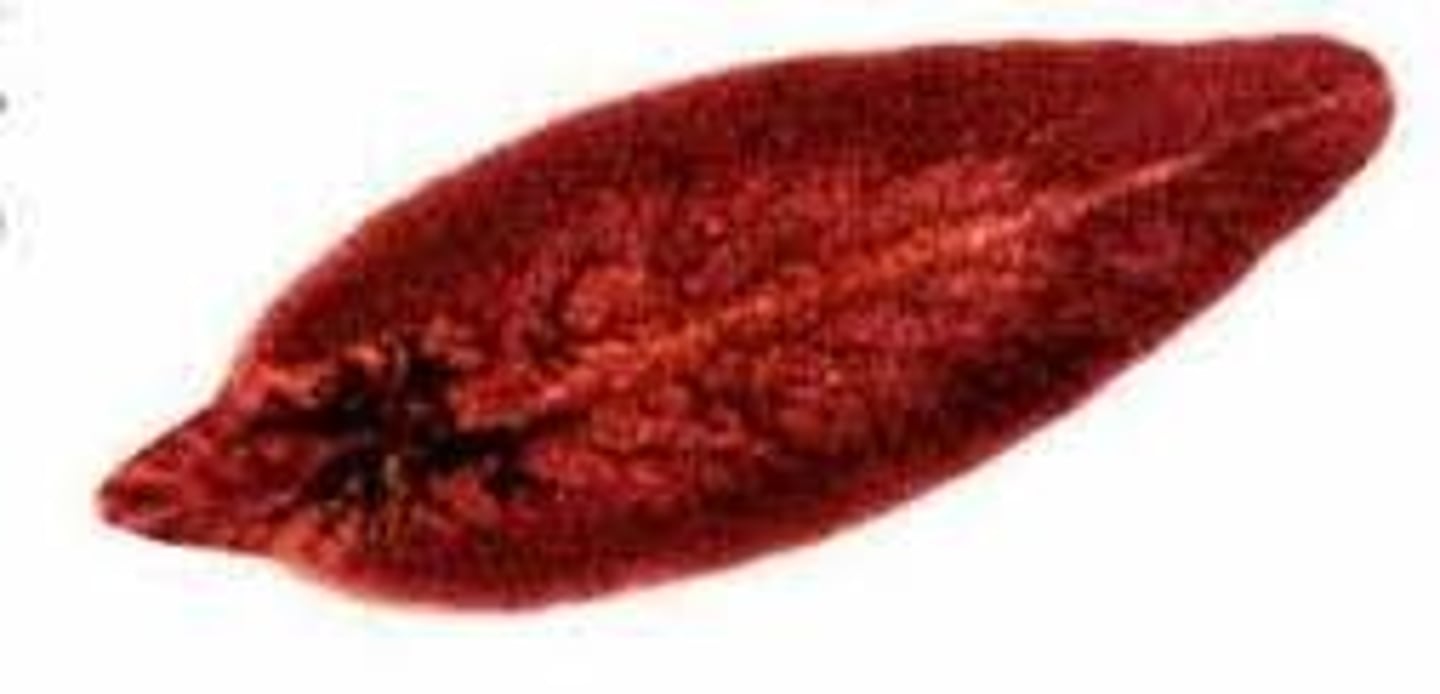
Class of platyhelminths (flukes)
- ex. Chinese liver fluke
- life cycle: eggs, sporocysts, redia larva, cercaria larva (sexually mature in humans, out with feces, hatches after snail eats it, becomes sporocysts --> redia --> cercaria --> into water and attaches to fish host through muscle --> humans eat)

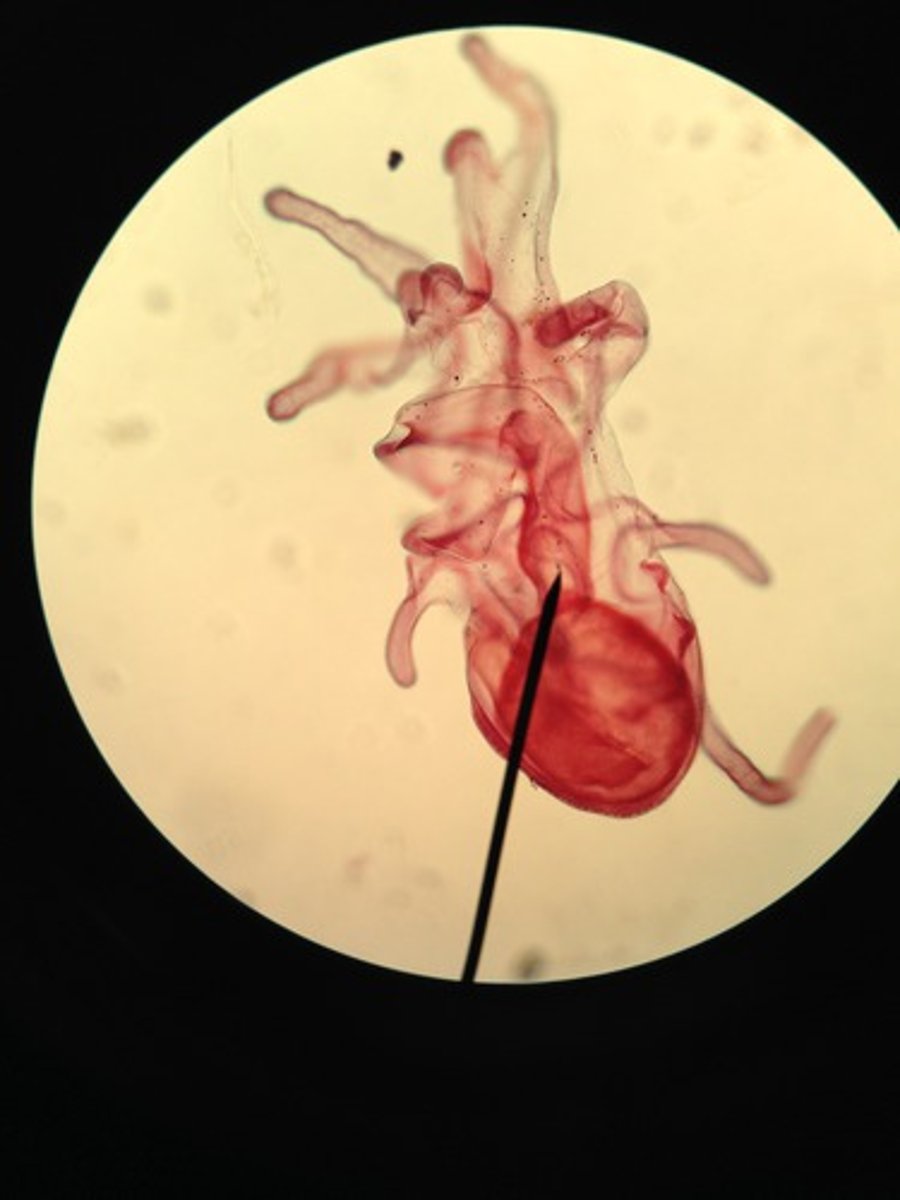
Class Cestoda
Class of platyhelminths (tapeworms)
- ex. pork tapeworm
- head adapted for latching and sucking
- life cycle: human intestine, gravid proglottids out with feces, eaten by pigs, goes from blood vessel to muscle, eaten by humans
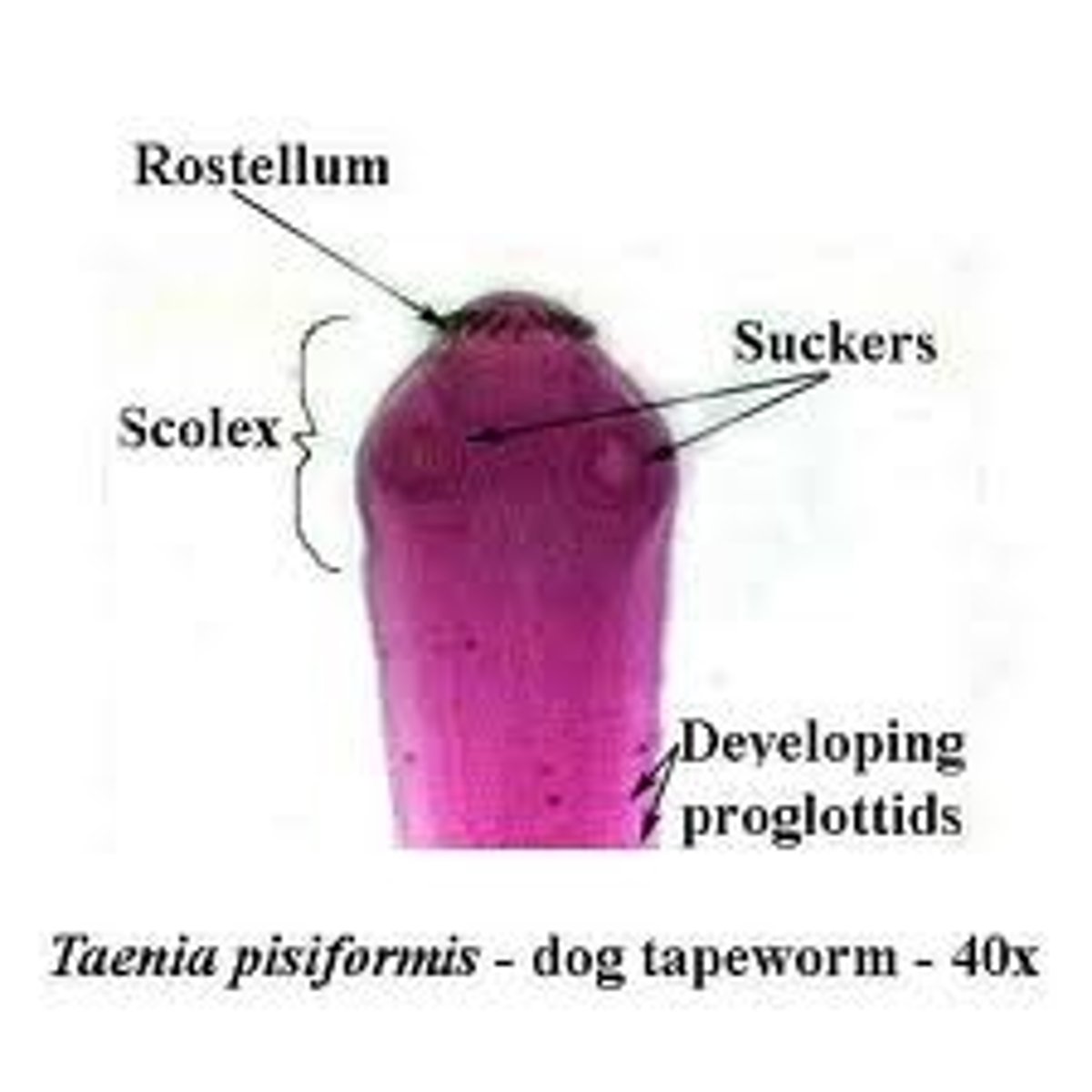
Phylum Nemertea
Phylum of nemerteans
- ex. Cerebratulus
- acoelomate, have space for nose thing (rhynchocoel)
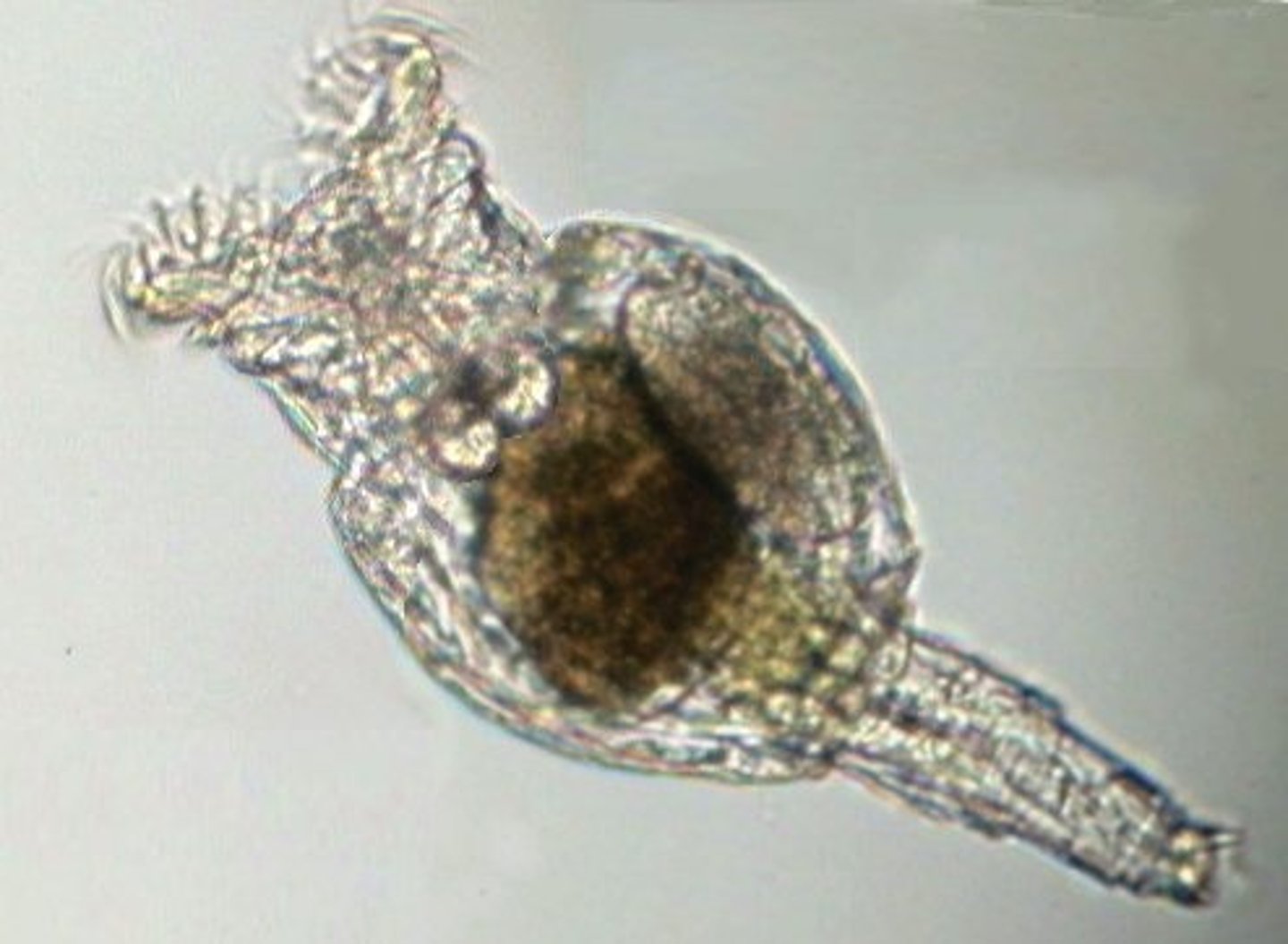
Phylum Rotifera
Phylum of rotifers
- corona = ciliated ring near head
- mastax = mouth area below corona
- tiny and white
Phylum Nematoda
Phylum of nematodes
- ex. Ascaris
- pseudocoelomate
- hooked and smaller = male
- a pale brown and kind of wrinkly looking

Phylum Brachiopoda
Phylum of lampshells
- ex. Terebratella
- top shell is different than bottom
- may have long fleshy bit sticking out
Phylum Bryozoa
Phylum
- looks like moss
- features heterozooids
Phylum Annelida
Phylum of segmented worms
- ex. earthworm
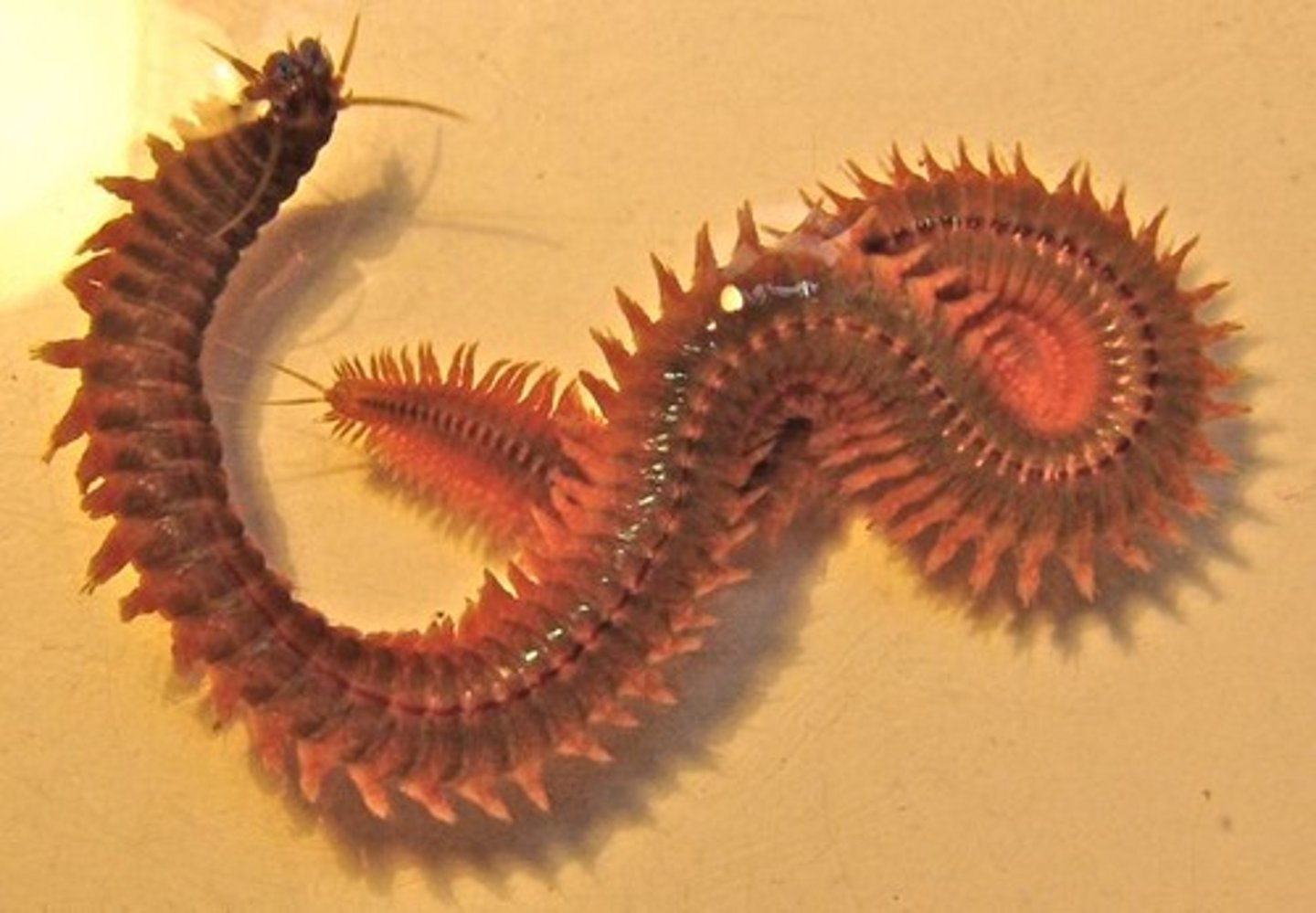
Class Polychaeta
Class of annelids
- ex. Nereis
- long, highly segmented, have legs
- Errantia vs Sedentaria: legged vs quill worms

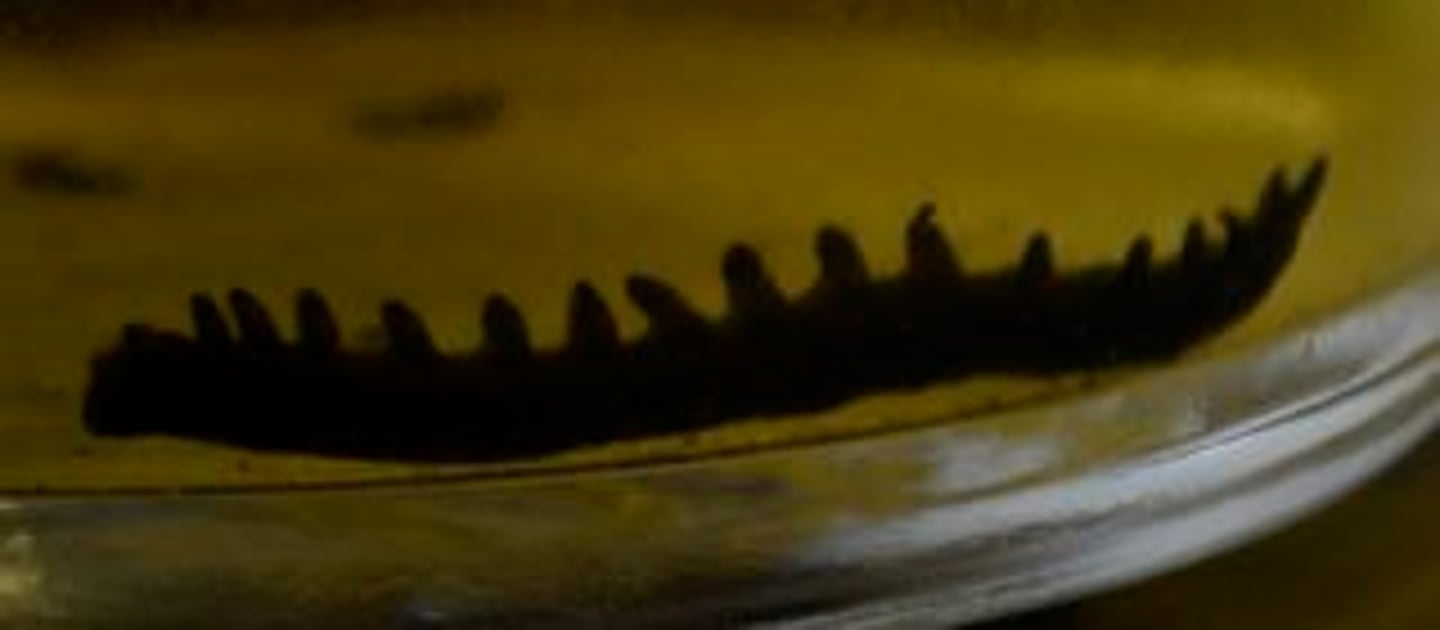
Phylum Onychophora
Phylum of velvet worms
- ex. Peripatus
- have pretty prominent legs, shorter than Nereis

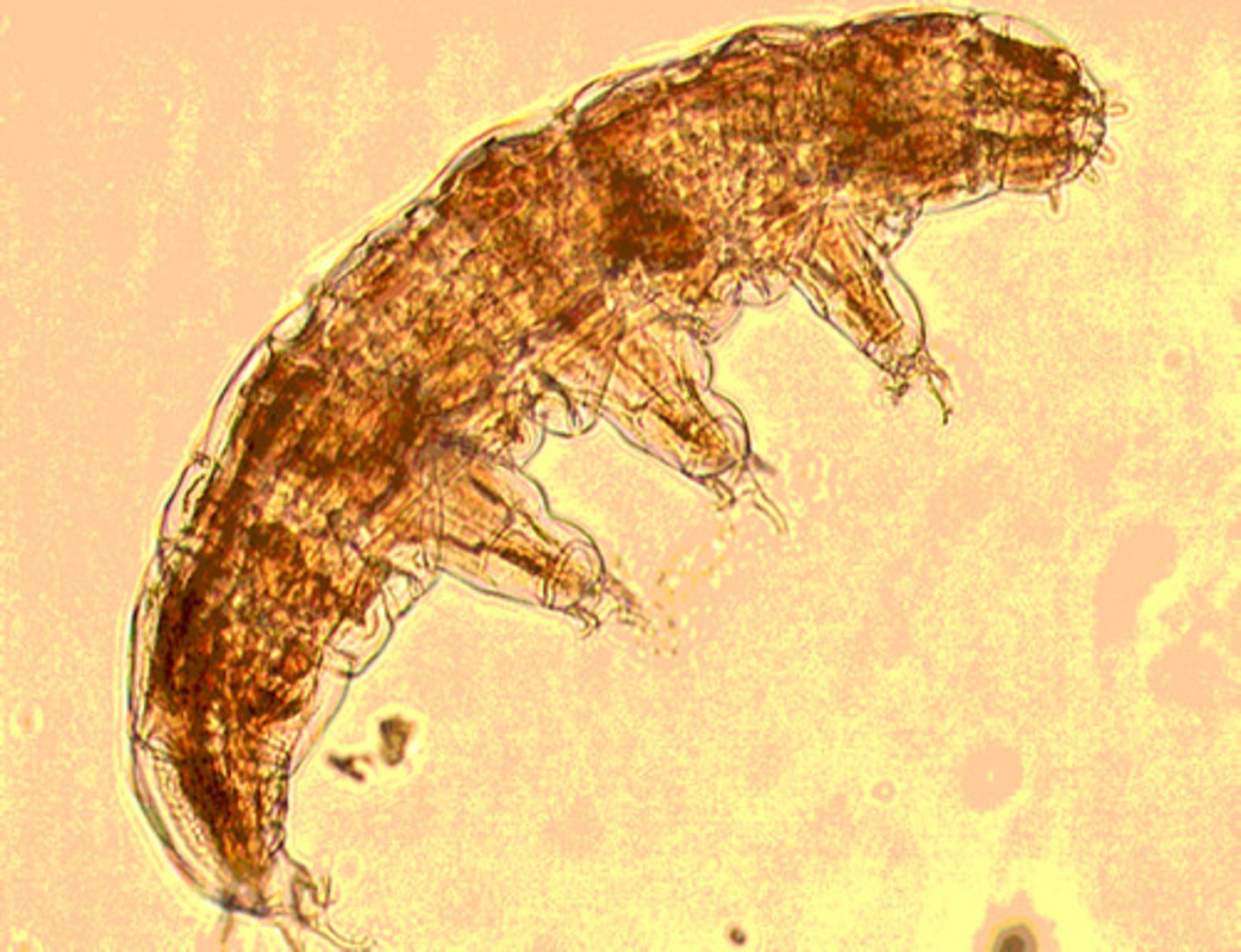
Phylum Tardigrada
Phylum of water bears
- found in moss
Phylum Mollusca
Phylum of snails, clams, nudibranchs, and cuttlefish
Classes:
- Polyplacophora
- Bivalvia
- Gastropoda
- Cephalopoda
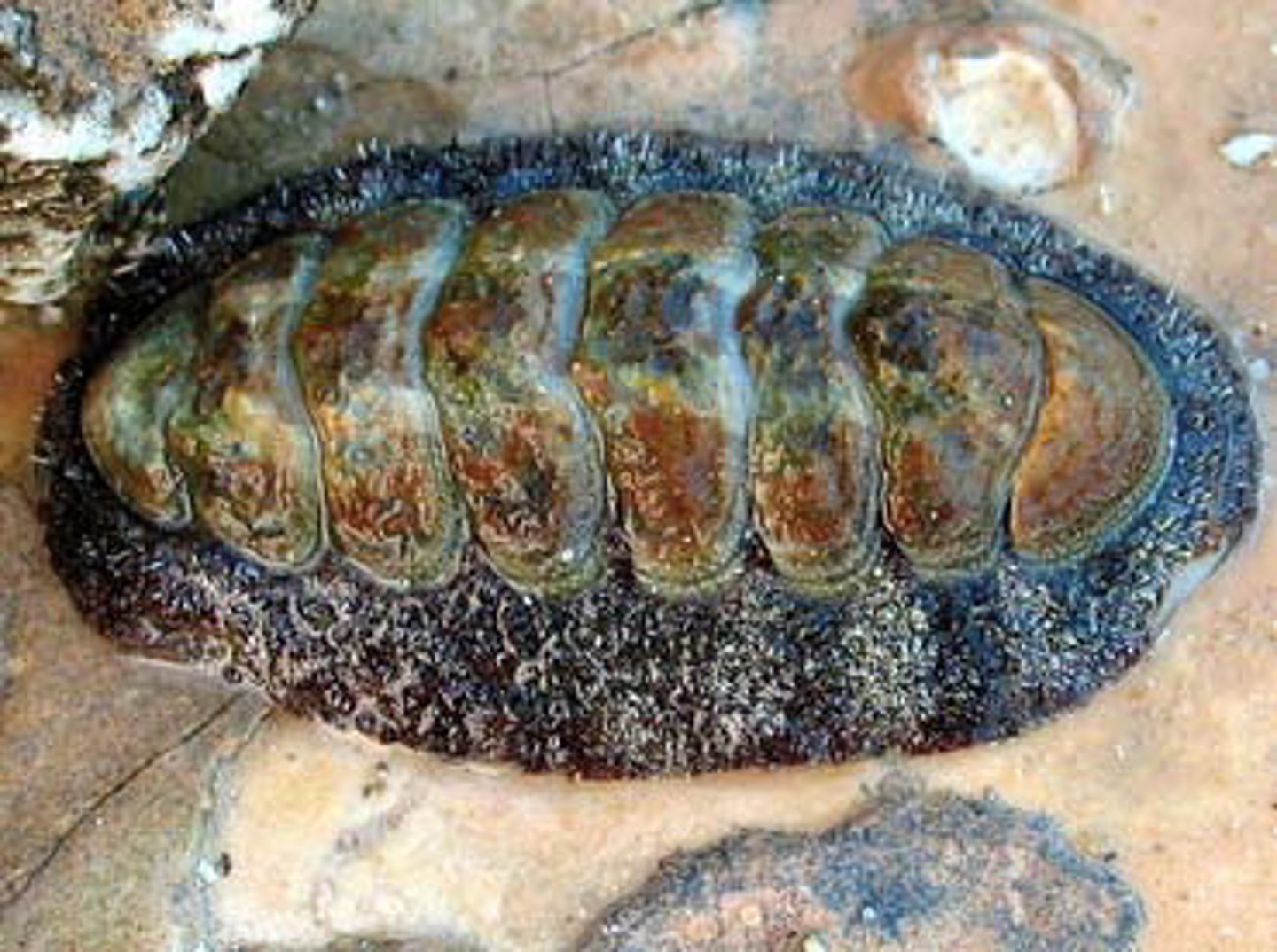
Class Polyplacophora
Class of molluscs (chitons)
- ex. Katharina
- shell segmented into 8 parts

Class Gastropoda
Class of molluscs (snails, slugs, abalones, periwinkles)
- ex. Helix (land snail)
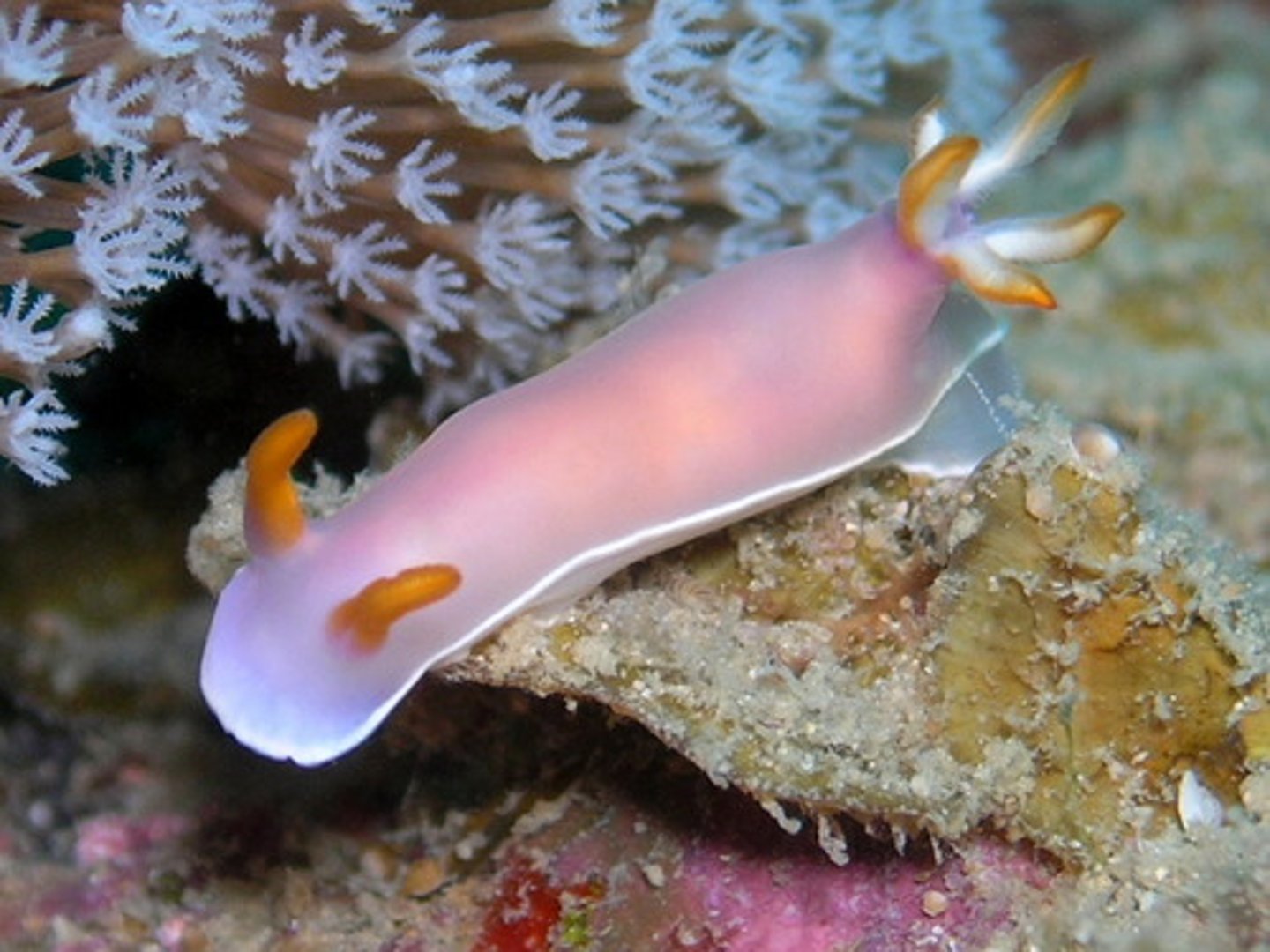
Group Opisthobranchia
Group within the class Gastropoda (group of nudibranchs)

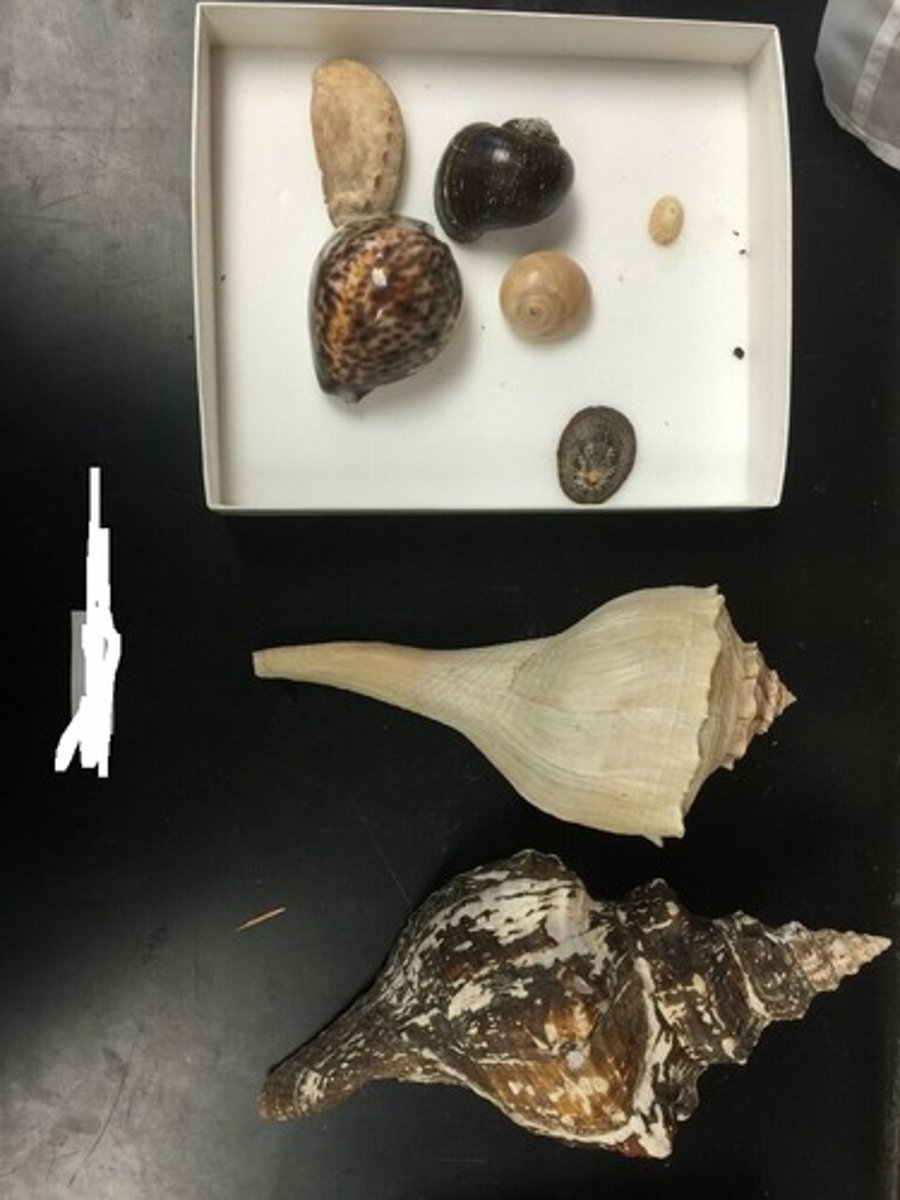
Group Prosobranchs
Group within the class Gastropoda (limpets, whelks, conchs, cowries; everything that's not a snail, slug, or nudibranch)

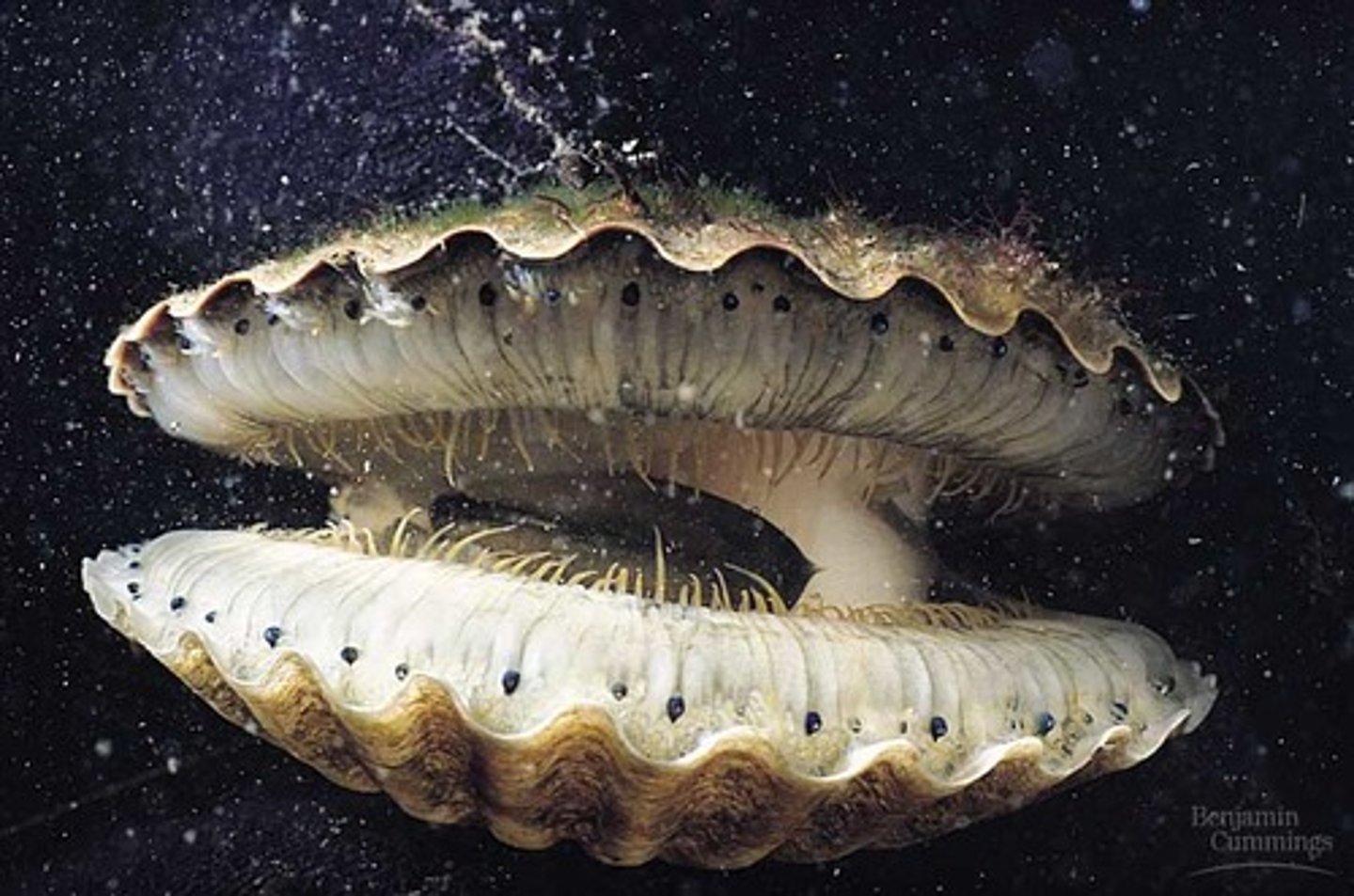
Bivalvia
Class of molluscs (clams, oysters, scallops)
-rep type: Venus
-muscles, gills, foot, mantle

Cephalopoda
Class of mollusks (squid, octopi, cuttlefish)
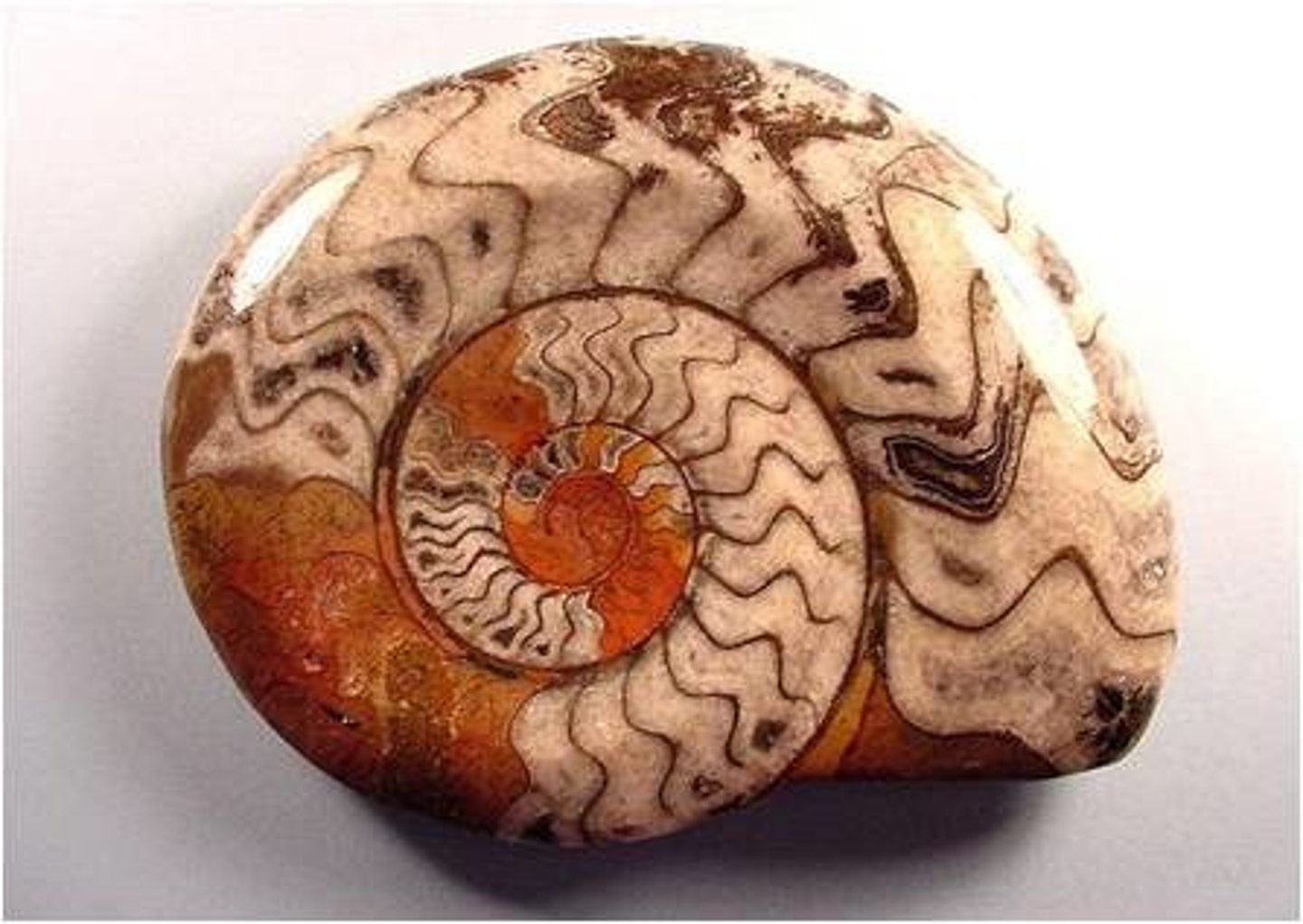
Ammonoidea
Subclass of cephalopods and mollusks
-wavy shell connections

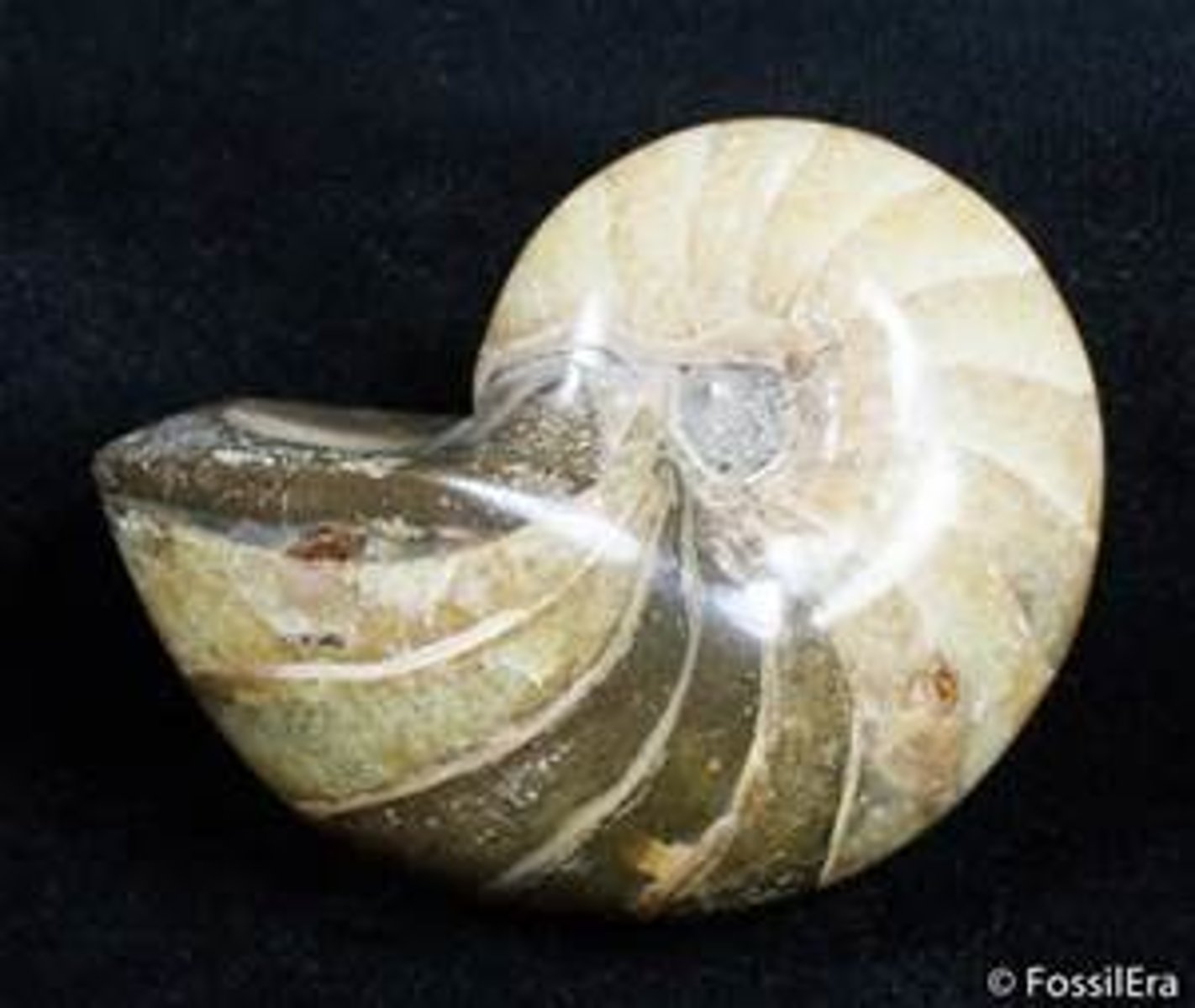
Nautiloidea
Subclass of cephalopods and mollusks
-straight shell connections

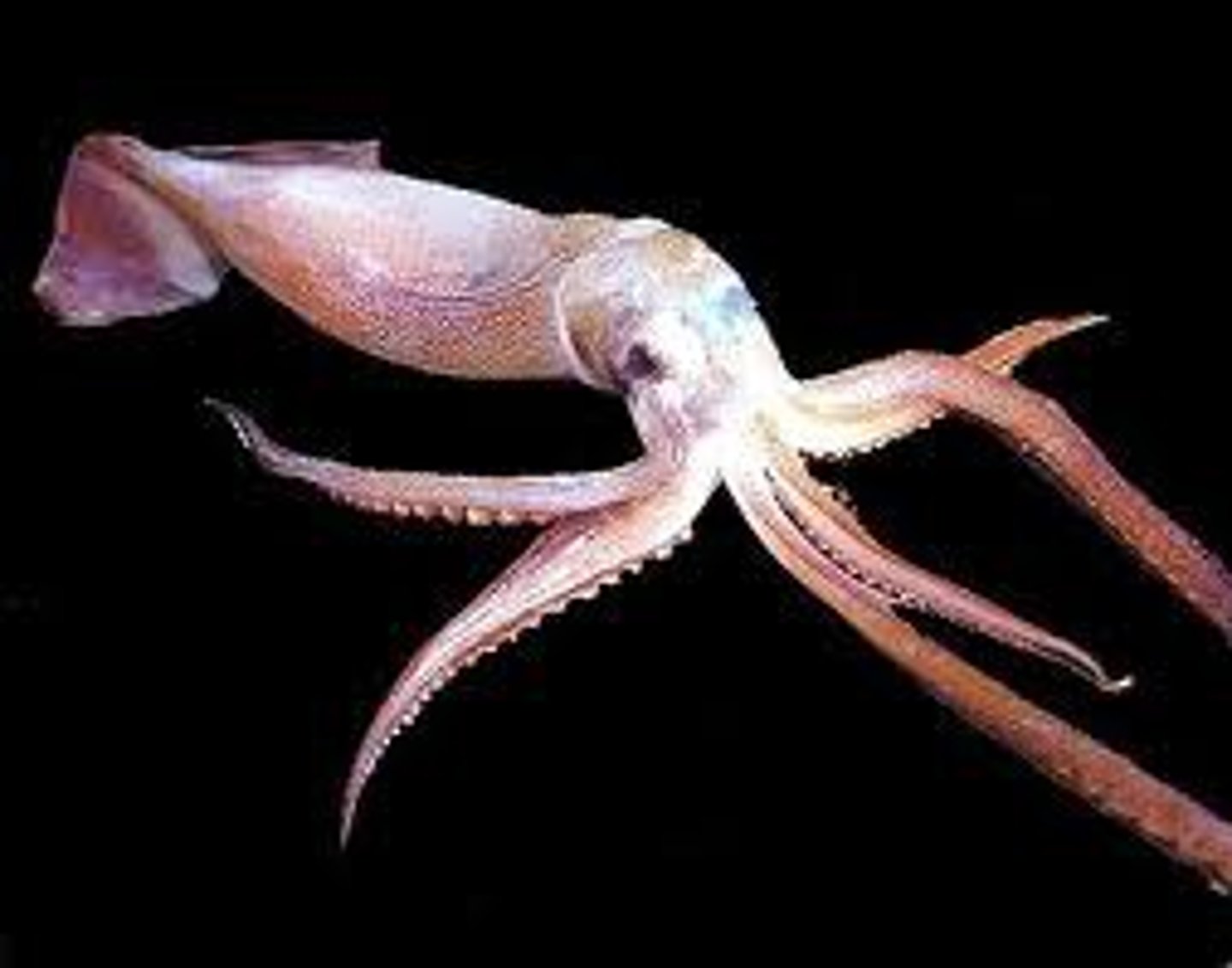
Coleoidea
Subclass of cephalopods and mollusks
-Cuttlefish - cuttlebone (chalkly, white, light)
-Squid - pen (plasticy, dark red)
-Octopodes

Arthropoda
Phylum of crabs, scorpions, ticks, barnacles, and insects
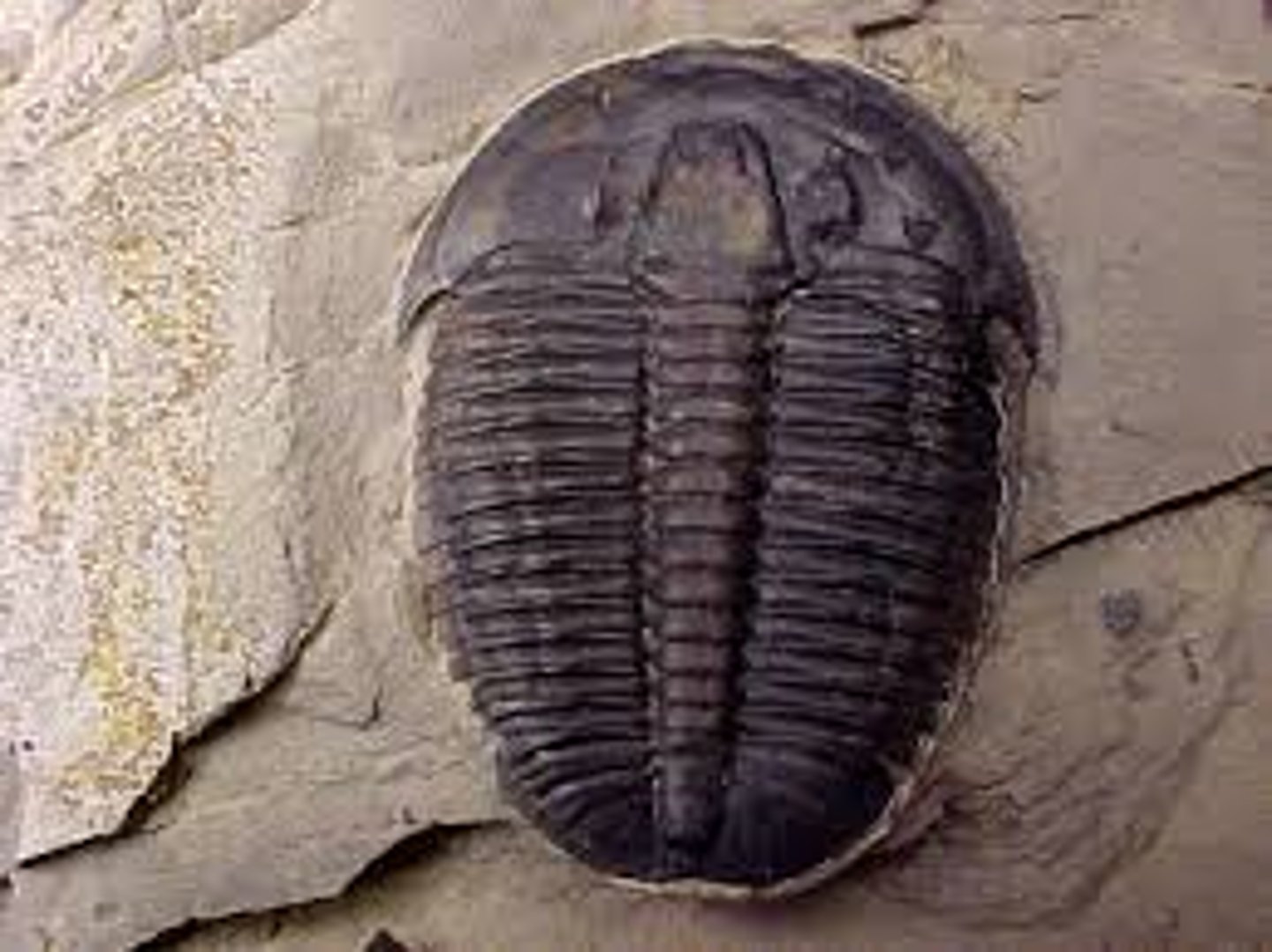
Trilobitamorpha
Subphylum of arthropods
-fossils that are highly segmented and kind look like horseshoe crabs

Chelicerata
Subphylum of arthropods
-named for claw-like mouthparts
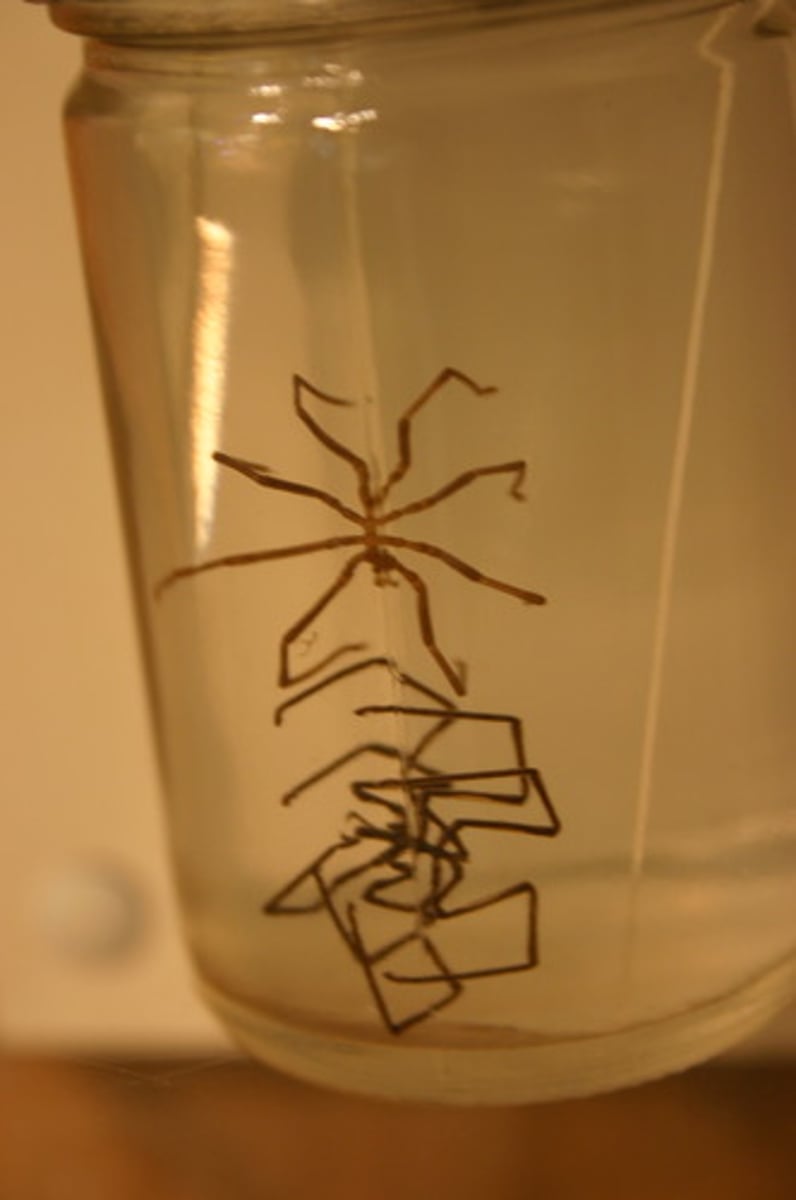
Pycnogonida
Class of chelicerates and arthropods (sea spiders)
-pale yellow thing that looks like a mechanical tumbleweed)

Crustacea
Superclass of mandibulates and arthropods
-named for hard outer covering
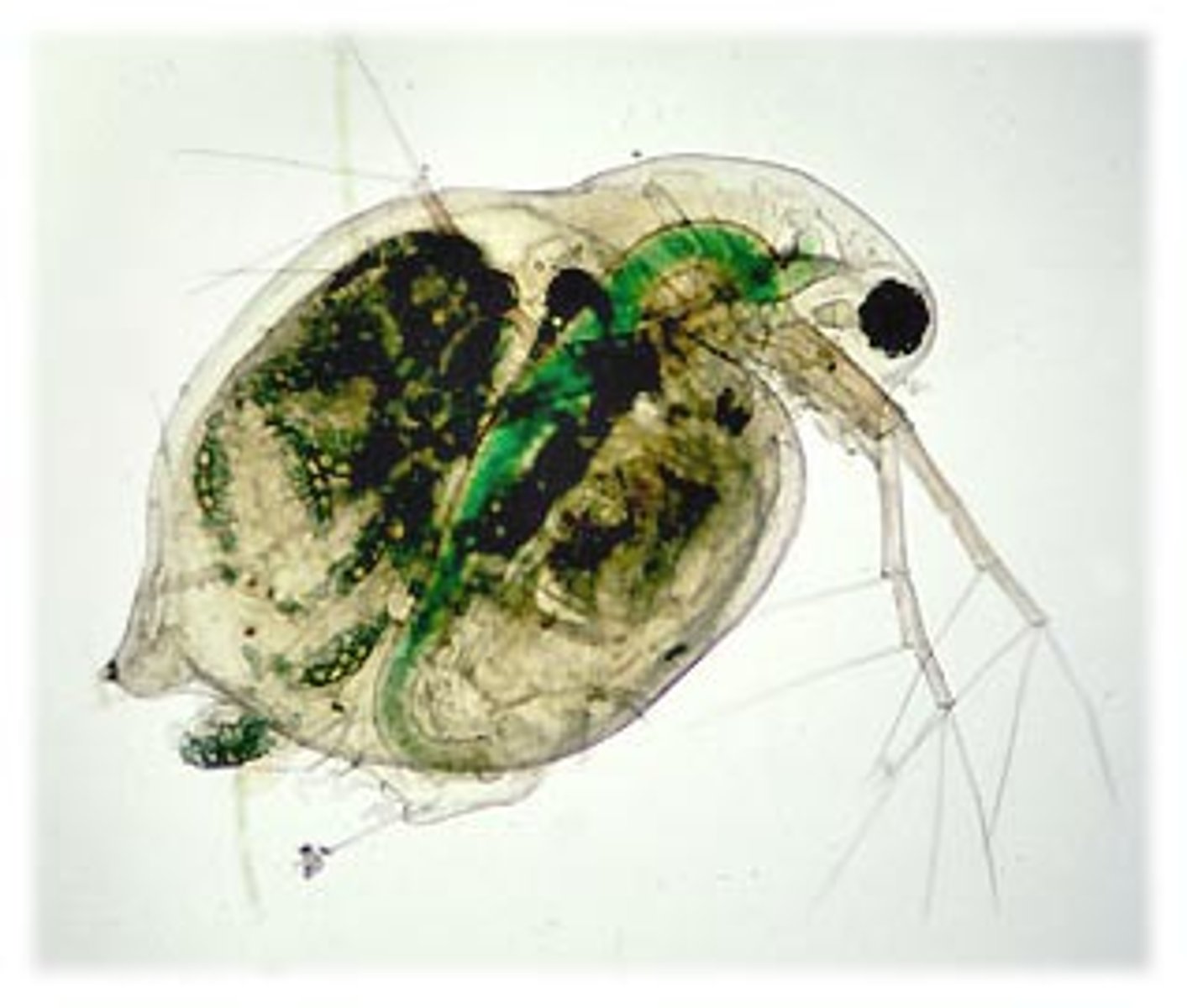
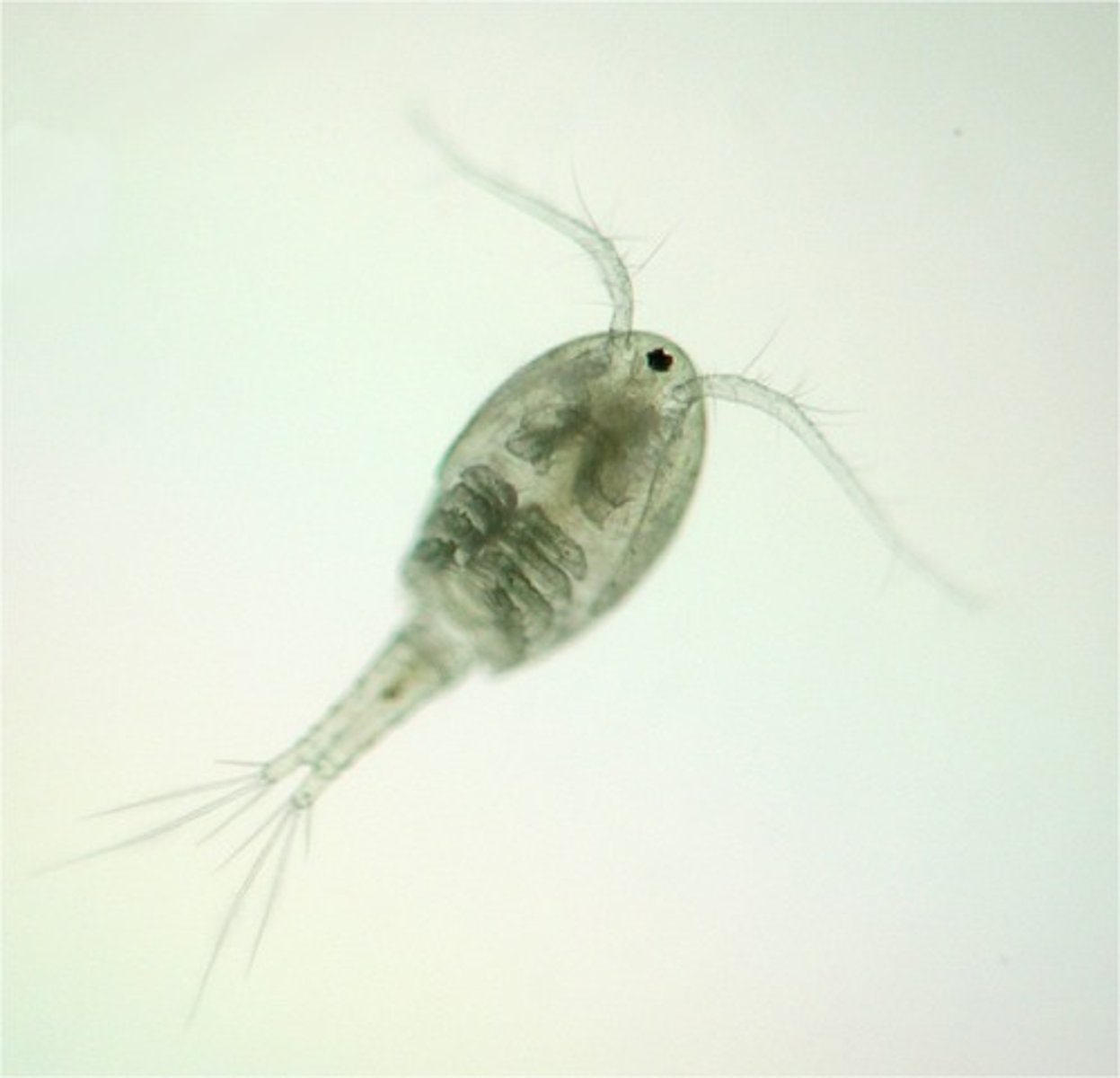
Branchipoda
Class of crustaceans, mandibulates, and arthropods (fairy shrimp and water fleas)
-shrimp are fuzzy and not that small

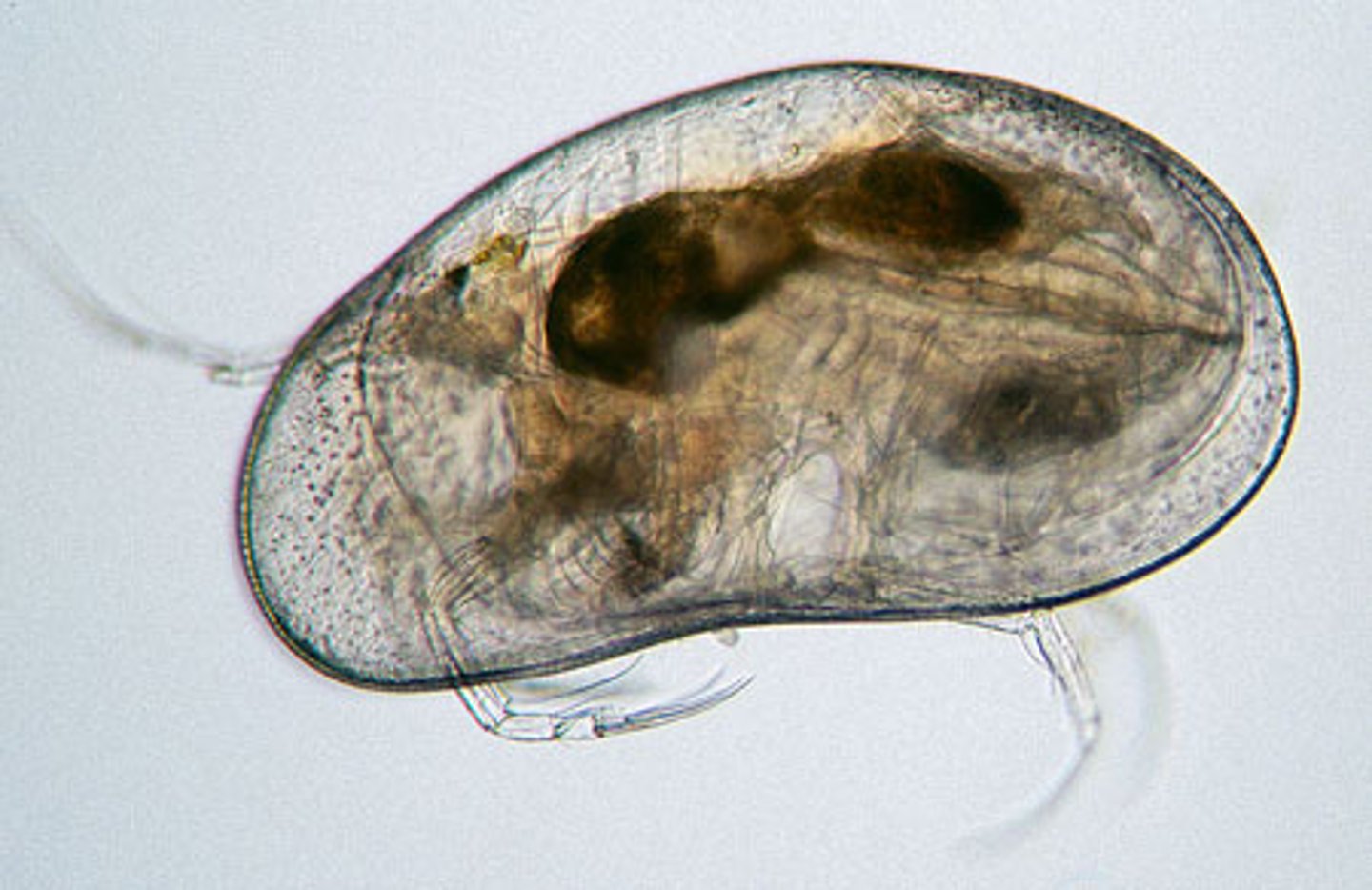
Ostracoda
Class of crustaceans, mandibulates, and arthropods (seed shrimp)
-have a little shell around them
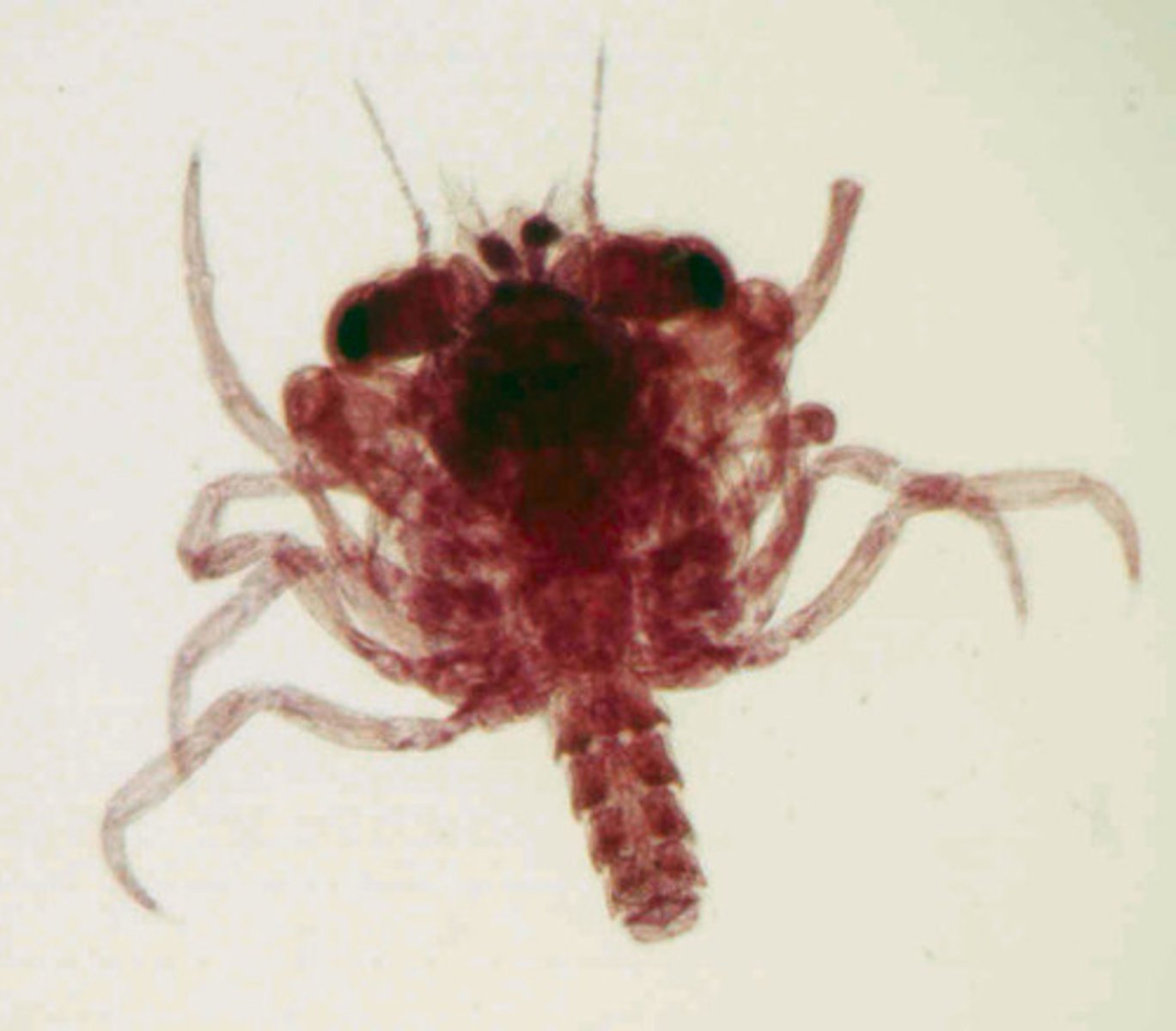
Copepoda
Class of crustaceans, mandibulates, and arthropods
-long antennae and fleshy tail

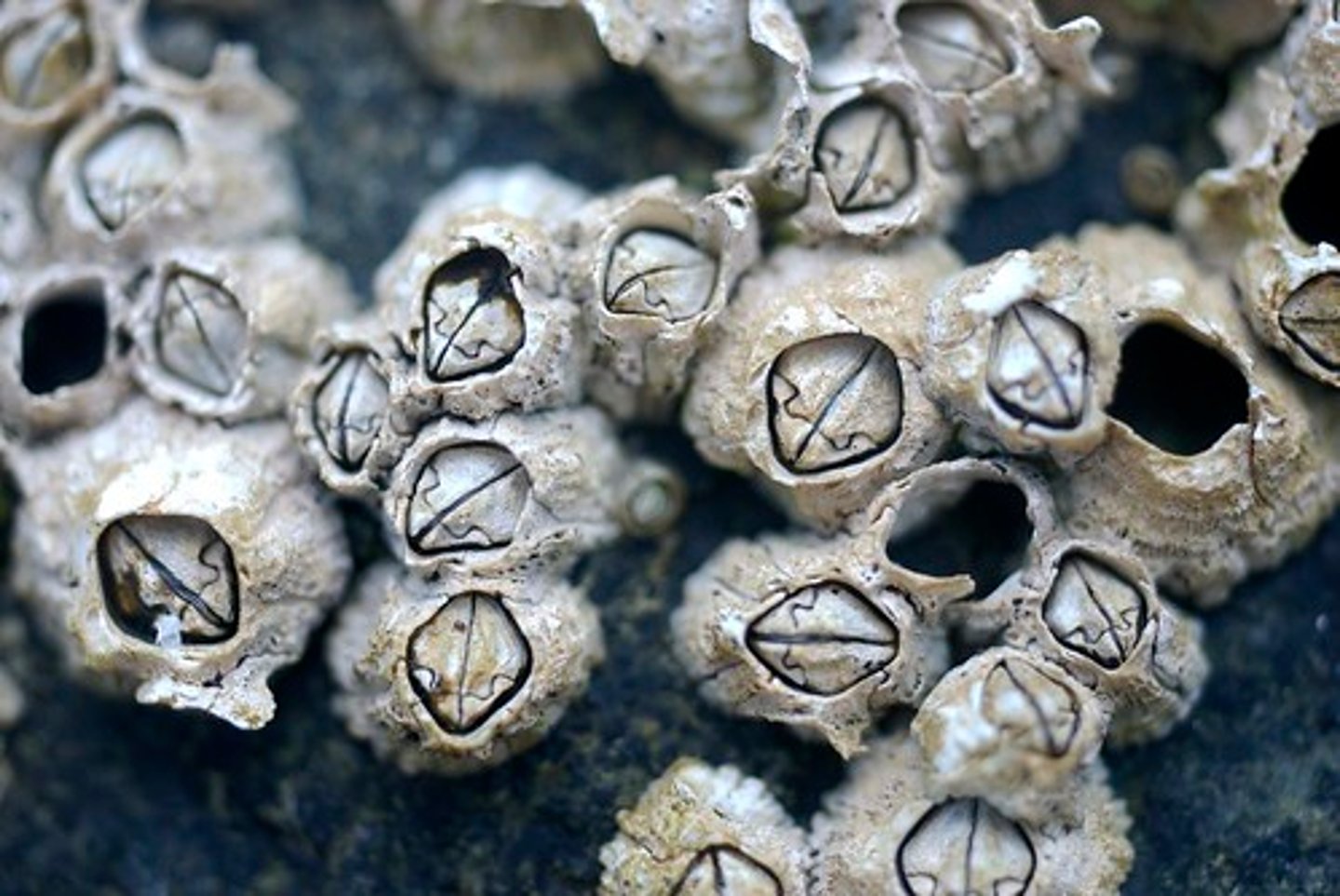
Cirripedia
Class of crustaceans, mandibulates, and arthropods (barnacles)

Malacostraca
Class of crustaceans, mandibulates, and arthropods (shrimp, pillbugs)
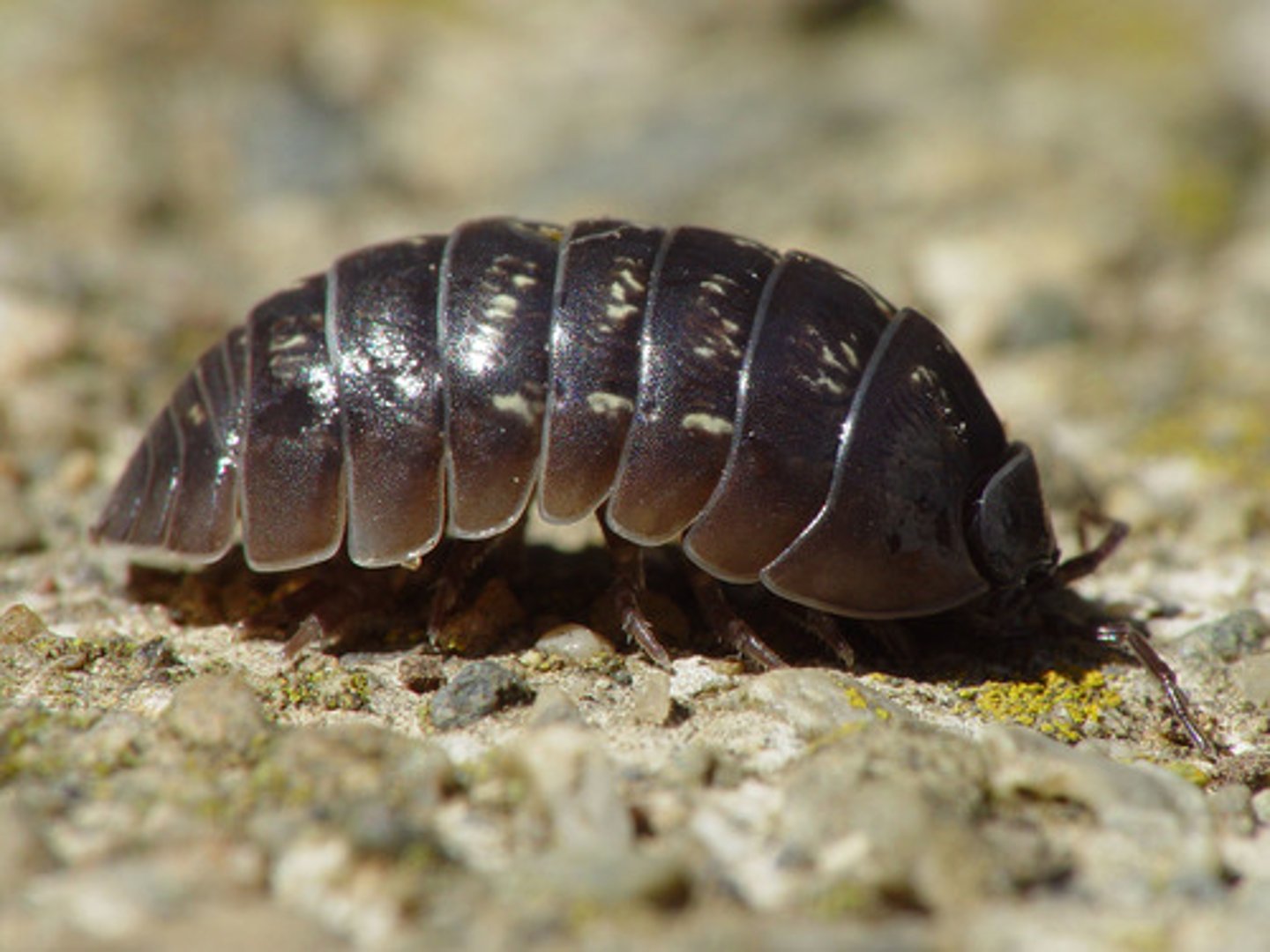
Isopoda
Order of malacostracans, crustaceans, mandibulates, and arthropods (pillbugs)

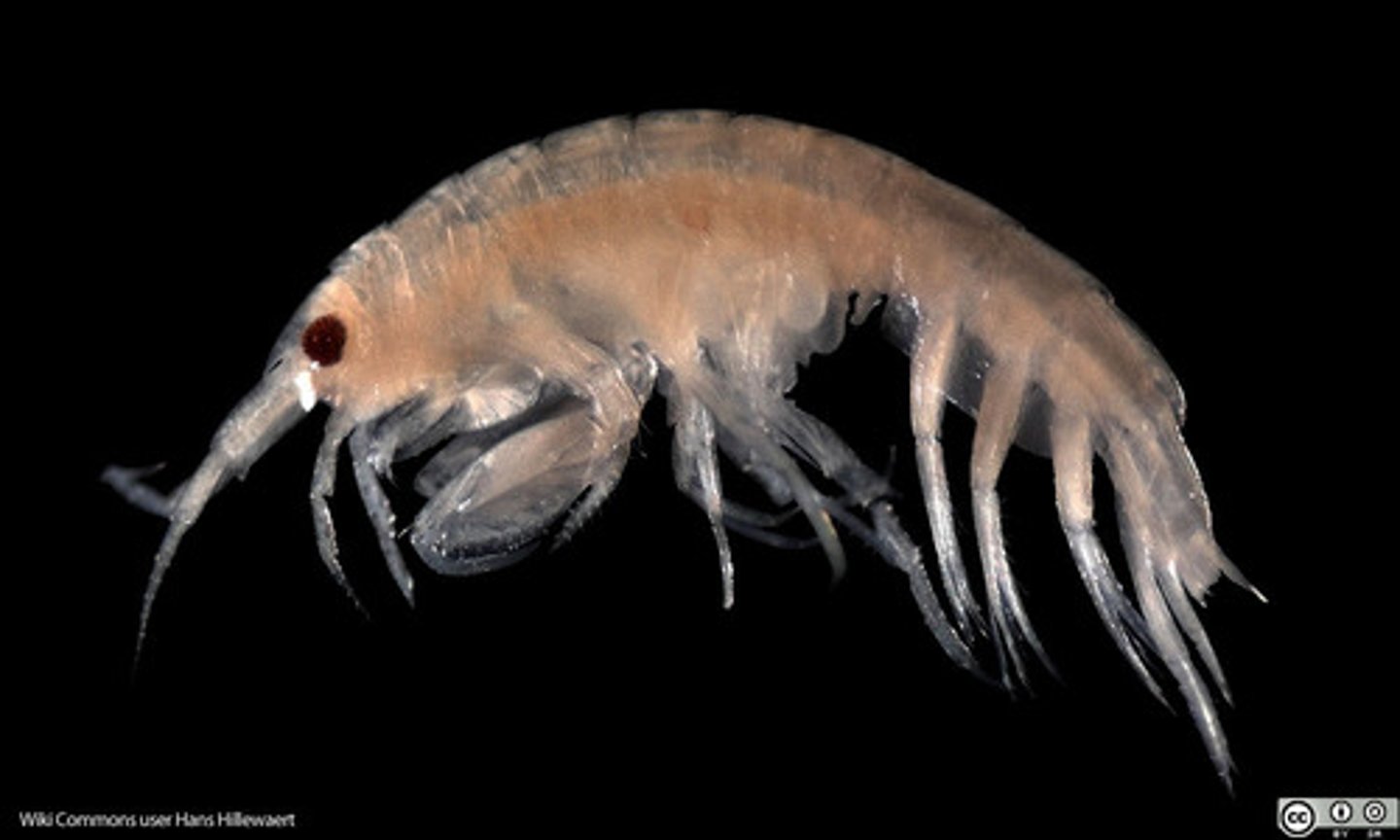
Amphipoda
Order of malacostracans, crustaceans, mandibulates, and arthropods (beachhoppers)

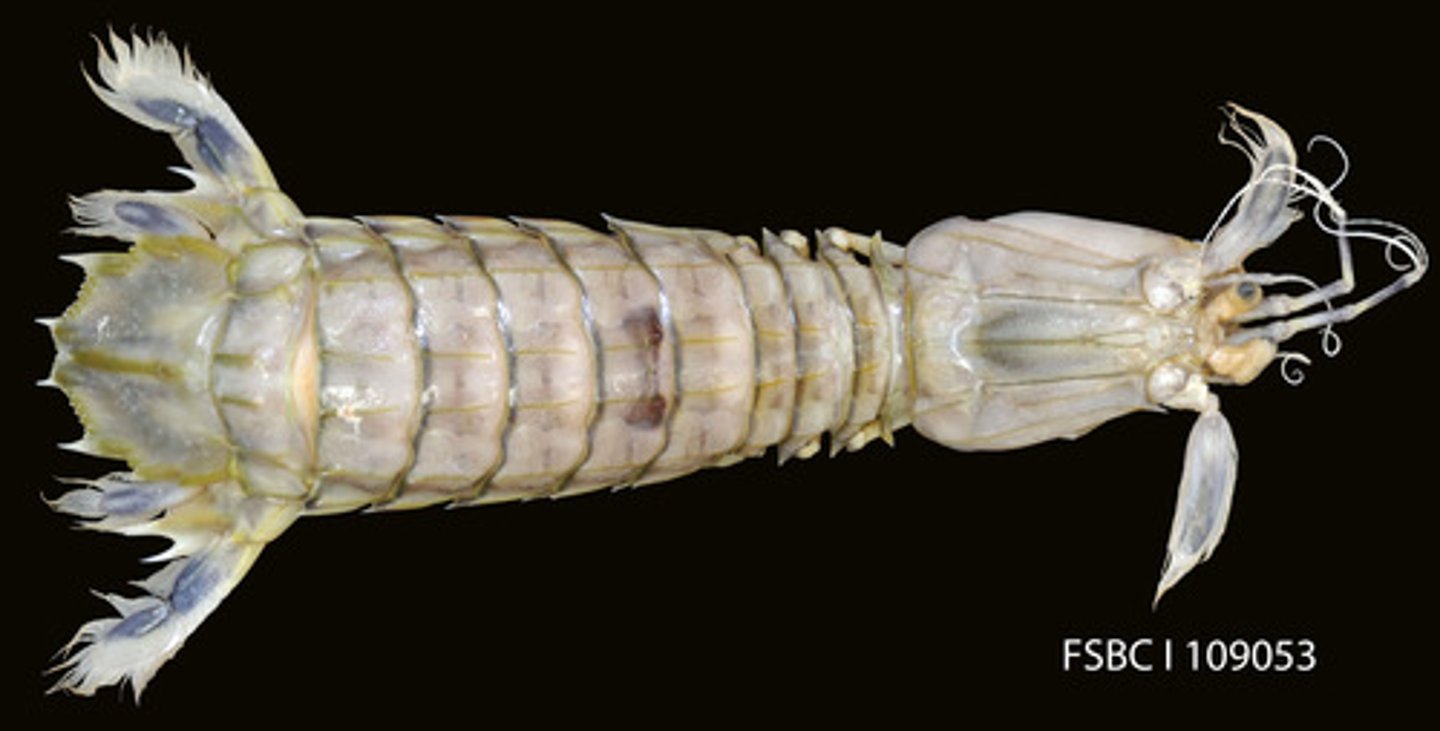
Stomatopoda
Order of malacostracans, crustaceans, mandibulates, and arthropods (mantis shrimp)

Decapoda
Order of malacostracans, crustaceans, mandibulates, and arthropods (shrimp, crayfish, lobster, crabs)
-life cycle: nauplius larvae, zoea, megalops
-have cephalothorax and abdomen
-chela = big claws
-crayfish anatomy: swimmerettes, uropod (tail platess), mandible + maxillipeds
Crab nauplius larva
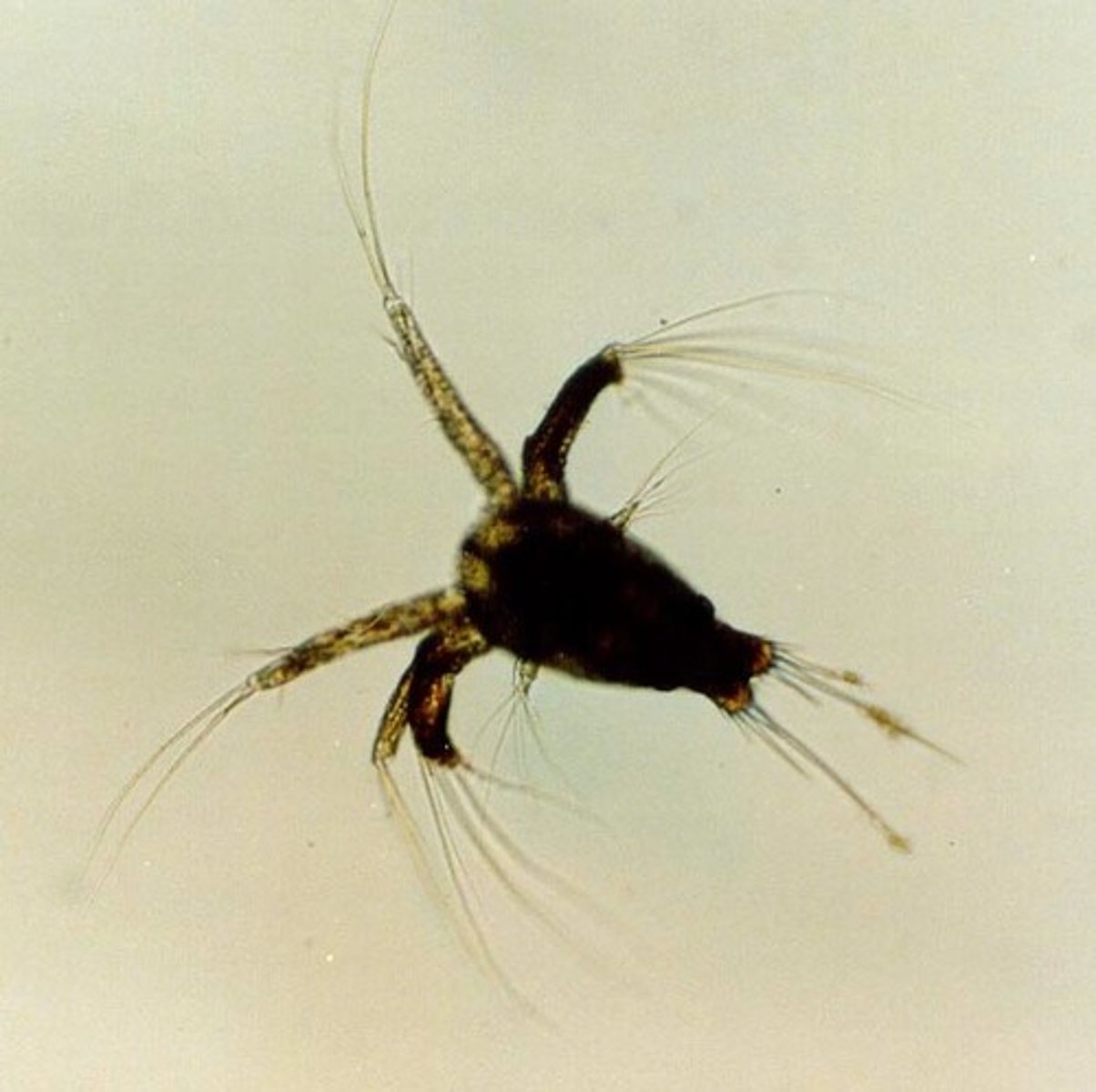

Crab zoea larva
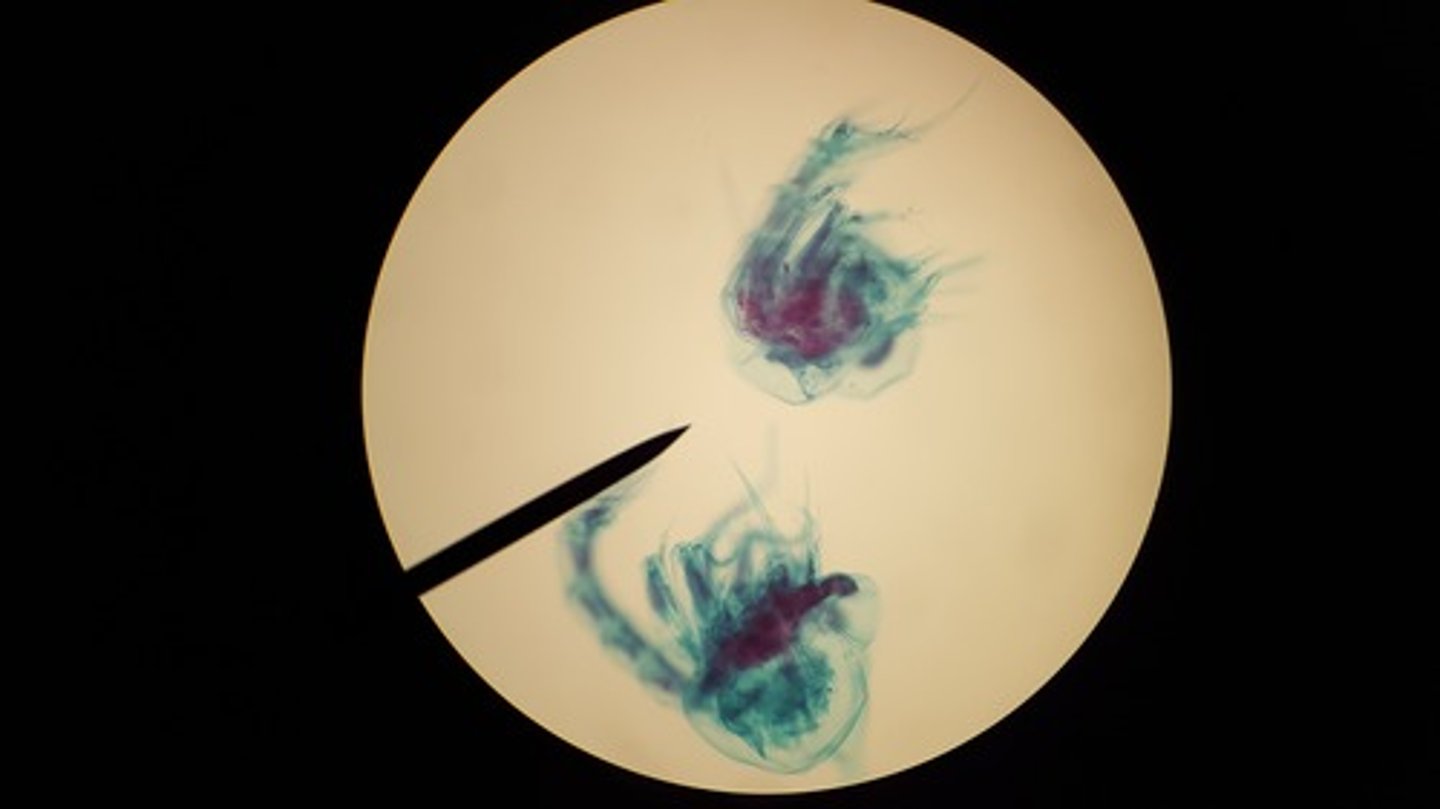
Crab megalops larva

Myriapoda
Superclass of mandibulates and arthropods
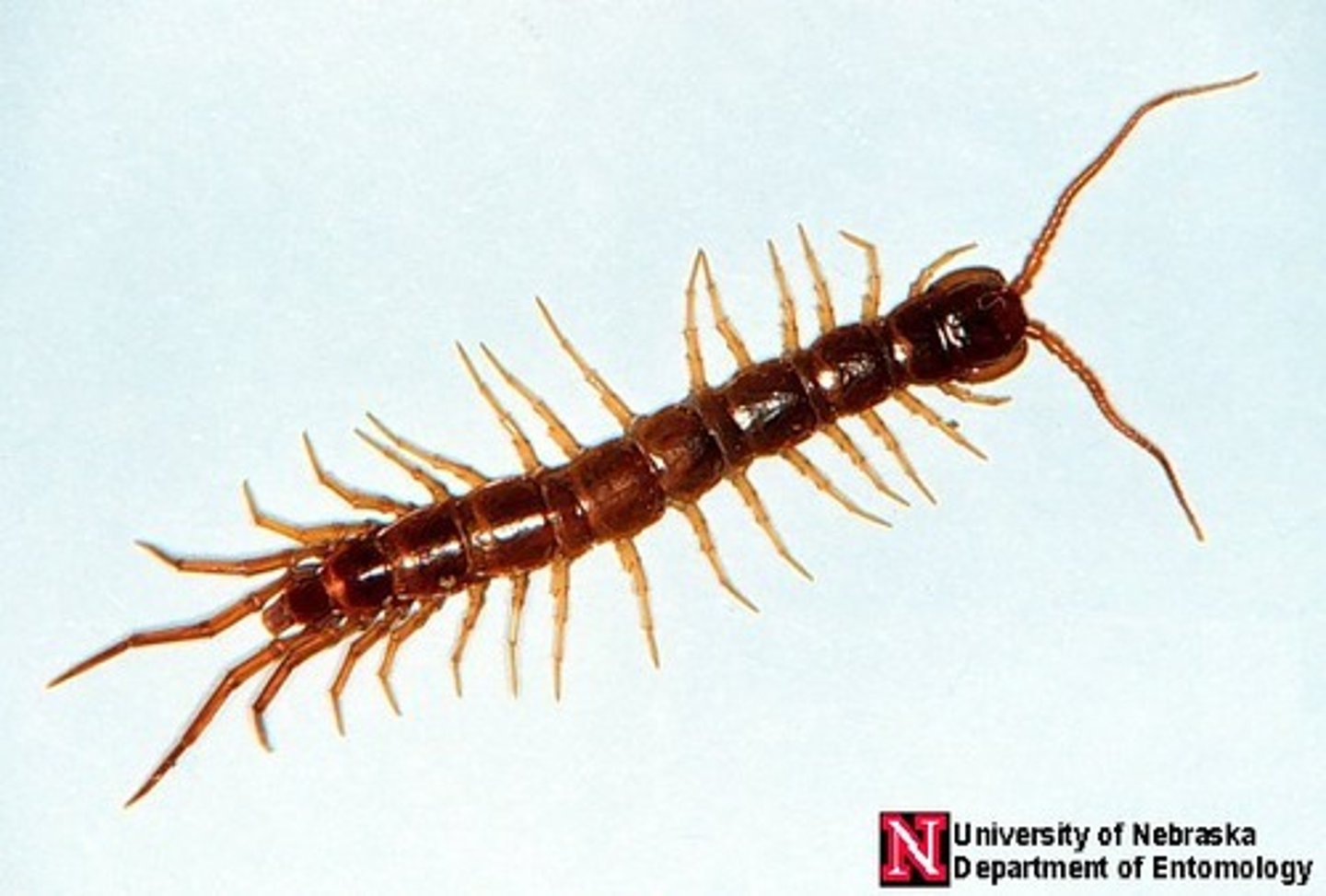
Chilopoda
Class of myriapods, mandibulates, and arthropods (centipedes)

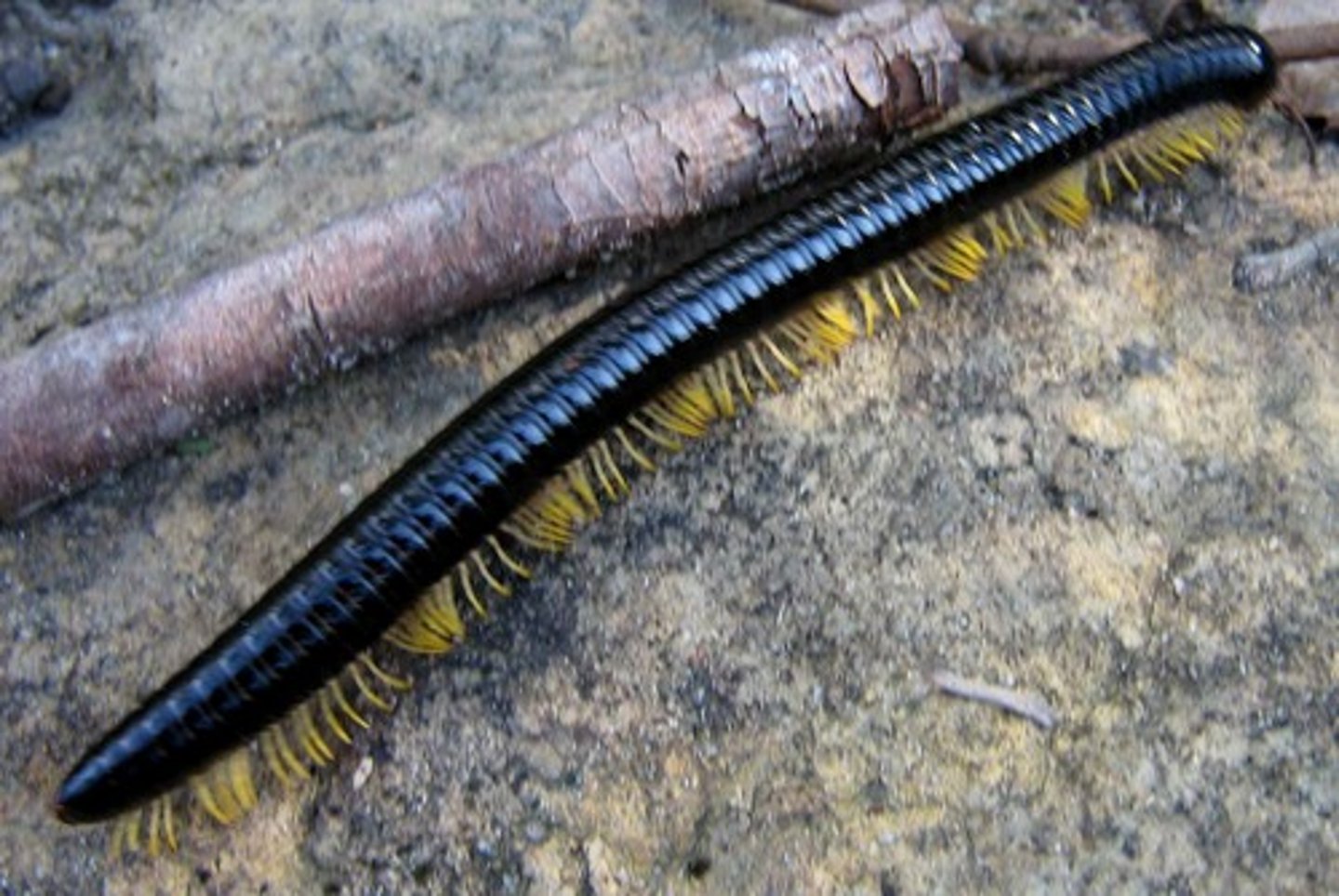
Diplopoda
Class of myriapods, mandibulates, and arthropods (millipedes)

Hexapoda
Superclass of mandibulates and arthropods