NEUROGENESIS
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What is neurogenesis?
The process by which new neurons are formed in the brain
When does it occur?
Neurogenesis not only occurs during brain development and early post-natal period, but also in adulthood in specific brain regions such as the hippocampus.
Where does neurogenesis occur in adults?
the subventricular zone (border of the lateral ventricles)
the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus
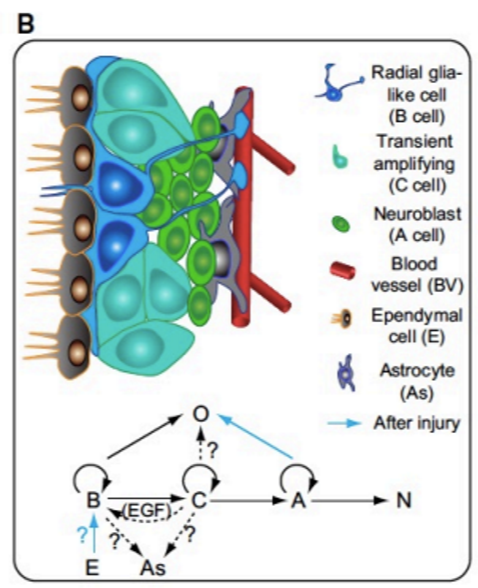
Describe neurogenesis in the subventricular zone
radial glial cells (RGL cells) can change their morphology and become oligodendrocytes (O cells) OR transient amplifying cells (C cells) (B → C, RGL→ O)
C cells can become neuroblasts (NB cells) which undergo neural fate forming immature neurons (N) (C → NB → N)
radial glial cells (B cells) and transient amplifying cells (C cells) can also become Astrocytes (As) (RGL → As, C → As)
In the presence of injury:
Neuroblasts (A cells) can become oligodendrocytes (O cells) (NB → O)
RGL, C & A cells can also regenerate
in the presence of EGF, transient amplifying cells (C cells) can also revert back to radial glial cells (RGL cells)
So:
RGL cells = radial glia-like cells
C cells = transient amplifying cells
NB cells = neuroblasts
N = immature neuron
O = oligodendrocytes
As = astrocytes
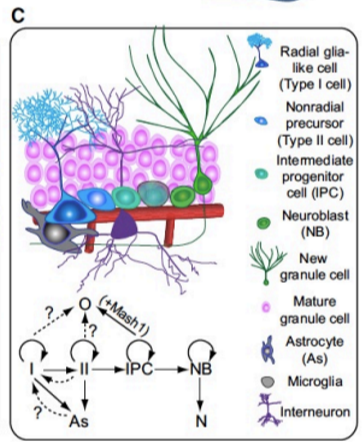
Describe neurogenesis in the hippocampus
Same pathway but instead:
C cells = non-radial precursor cells
Extra step: IPC - where C cells become IPCs, which then become A cells
So: RGL→ C → IPC → NB → N
RGL and C calls can become Astrocytes
In the presence of Mash1:
NB can become O
RGL cells, C cells, IPCs, NBs can also regenerate
How do we know all of these cells exist?
They express different proteins, so can be marked
Markers for subventricular zone neurogenesis:
RGL cells = nestin (and a less but also C cells)
NB, N = DCX
Mature neurons = NeuN, Calbindin
As = GFAP
Markers for hippocampus neurogenesis:
RGL cells = nestin
IPC, NB = MCM2
NB, N = DCX
Mature neurons = NeuN, Calbindin
As = GFAP
What are two important processes that occur during neurogenesis?
Immature cells are usually under tonic GABA activation (depolarised by GABA)
There are also critical periods for survival and synaptic input is really critical for neuronal survival
Describe how Klf9 impacts neuronal integration and memory post neurogenesis
Klf9 functions as a negative regulator of dendritic spines
Klf9 and thus spine elimination in dentate gyrus cells robustly enhances their integration and survival
Enhanced integration reorganises local afferent connectivity and promotes global remapping in the dentate gyrus.
In a mouse with enhanced integration and survival of DGCs (increased Klf9), their contextual and long-term memory precision is enhanced due to the promotion of new neurons in the dentate gyrus
Describe another neurogenic site and provide evidence that neurogenesis occurs here
The cerebral cortex is also a site of neurogenesis
Study that injected monkeys with BrdU marker and used immunohistochemistry:
Found cells lining the lateral ventricle 2h after injection
After one week, these cells started to migrate towards the cortex
By two weeks they were all cortical neurons
List some other potential sites of neurogenesis
NTS, ARC of the hypothalamus, striatum and possibly the amygdala
What is the function of the NTS and how is it important in controlling the baroreceptor reflex?
The Nucleus Tractus Solitarius (NTS) is crucial for processing sensory information from baroreceptors, facilitating reflex control of blood pressure.
The NTS is plastic e.g. Can change blood pressure set points in response to long term environmental changes
Evidence that neurogenesis occurs in the NTS
Nestin staining of the central canal in the NTS found that they do express nestin so are radial glia-like cells
EdU positive cells found in the central canal
Used neuronal markers to confirm they are neurons being produced
The findings indicate that the NTS is a neurogenic niche
Why do we use EdU not BrdU?
DNA is so tightly packed that it's hard to get an antibody to bind without denaturation
We use EdU because you can use a chemical reaction rather than an antibody to label it
What happens to NTS neurogenesis during hypertension
Lots of EdU expression in hypertensive rats
thus there seems to be increased neurogenesis in hypertensive animals
Hypertensive rats seem to have greater numbers of newborn NTS neurons, but we don’t know why.
What physiological consequences do the integration of new-born neurons in the NTS have?
New-born NTS neurons are quite important for a set point in blood pressure
increase the set point of blood pressure