Chapter 3 End of Chapter questions (copy)
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Knowledge and Comprehension
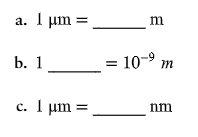
Fill in the following blanks.
A
a. 10^-6 m
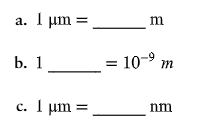
Fill in the following blanks.
B
b. 1 nm
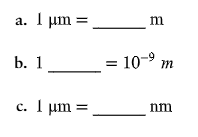
Fill in the following blanks.
C
c. 10³ nm
Which type of microscope would be best to use to observe each of the following?
a stained bacterial smear
Compound light microscope
Which type of microscope would be best to use to observe each of the following?
unstained bacterial cells: the cells are small, and no detail is needed
Darkfield microscope
Which type of microscope would be best to use to observe each of the following?
unstained live tissue when it is desirable to see some intracellular detail
Phase-contrast microscope
Which type of microscope would be best to use to observe each of the following?
a sample that emits light when illuminated with ultraviolet light
flourescence microscope
Which type of microscope would be best to use to observe each of the following?
intracellular detail of a cell that is 1 micrometers long
electron microscope
Which type of microscope would be best to use to observe each of the following?
unstained live cells in which intracellular structures are shown in color
Differential interference contrast microscope
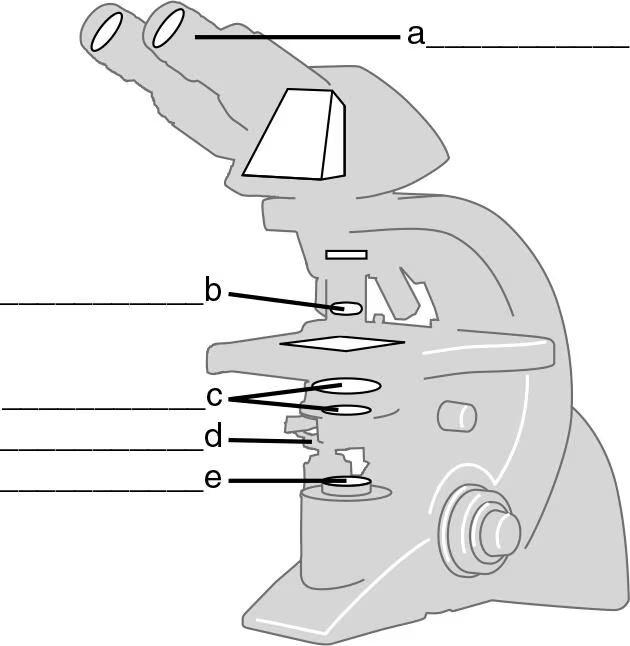
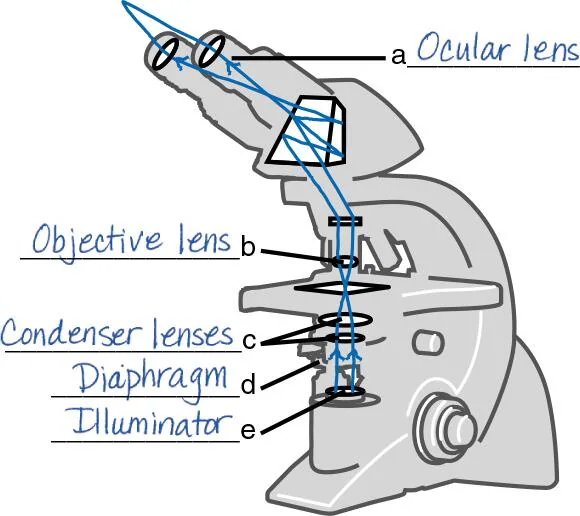
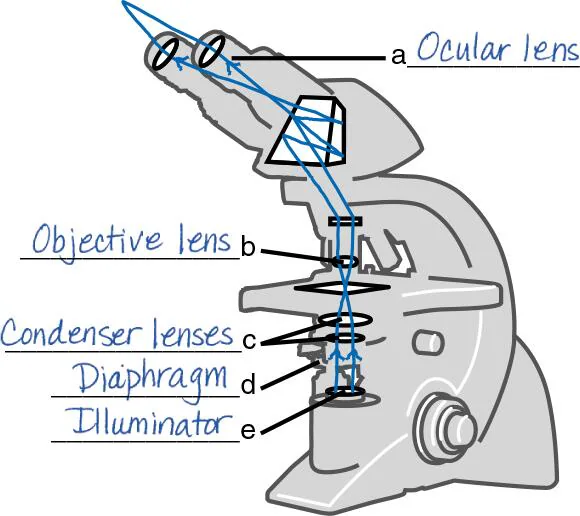
DRAW IT Label the parts of the compound light microscope in the following figure, and then draw the path of light from the illuminator to your eye.
A
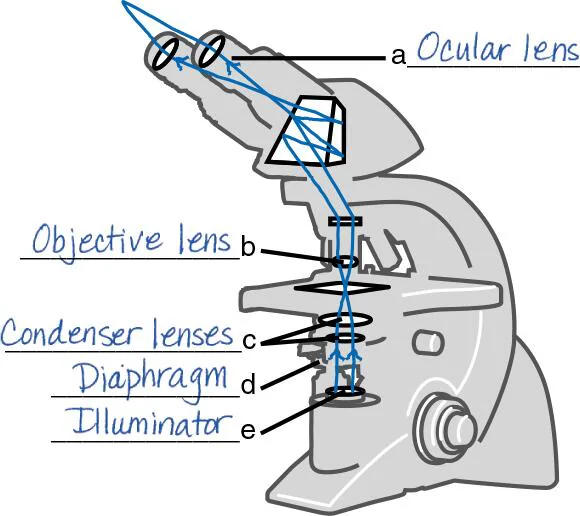
DRAW IT Label the parts of the compound light microscope in the following figure, and then draw the path of light from the illuminator to your eye.
B
DRAW IT Label the parts of the compound light microscope in the following figure, and then draw the path of light from the illuminator to your eye.
C
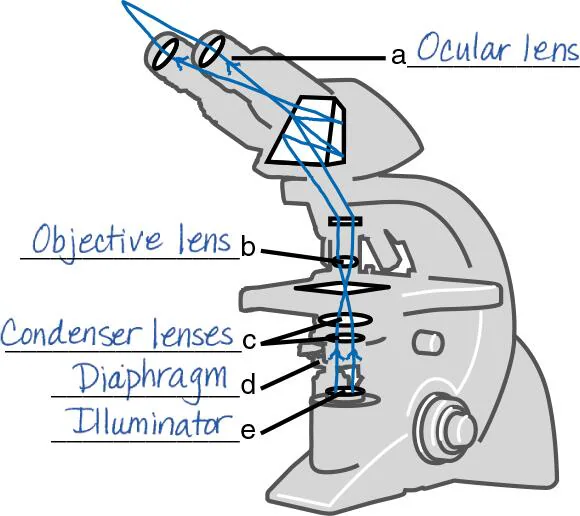
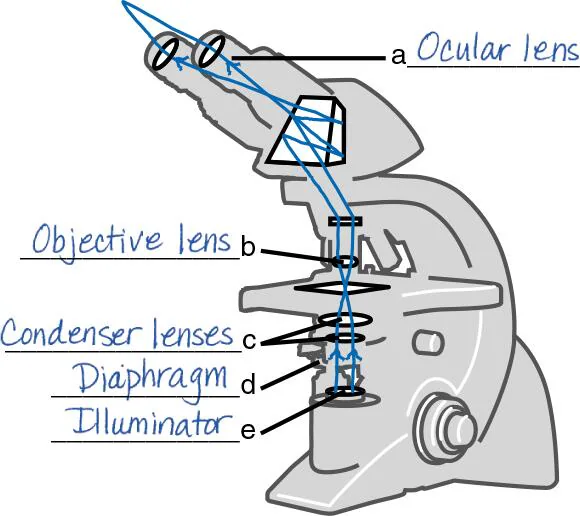
DRAW IT Label the parts of the compound light microscope in the following figure, and then draw the path of light from the illuminator to your eye.
D
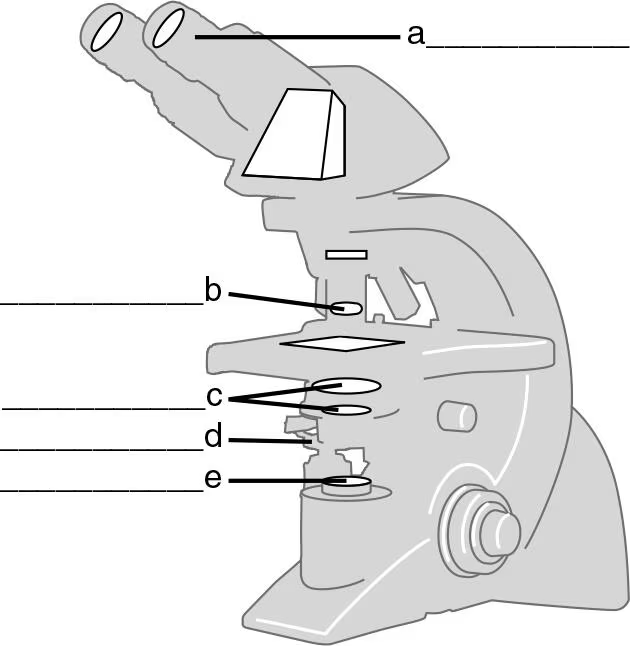
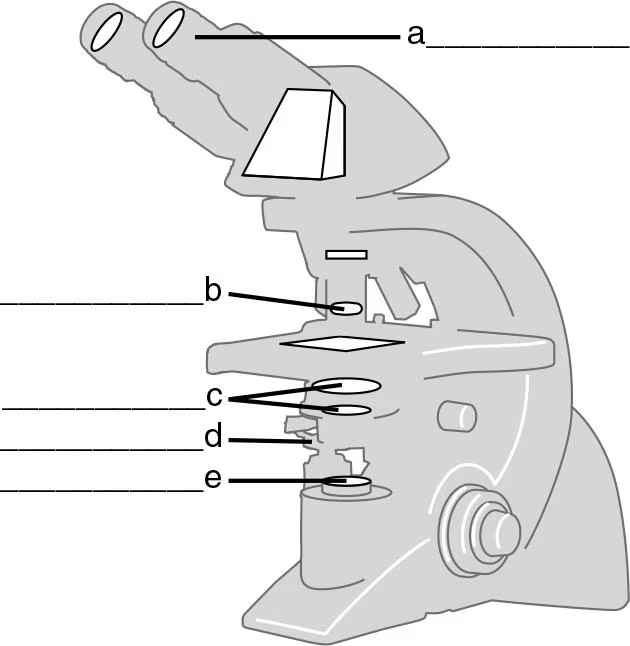
DRAW IT Label the parts of the compound light microscope in the following figure, and then draw the path of light from the illuminator to your eye.
E
Calculate the total magnification of the nucleus of a cell being observed through a compound light microscope with a 10x ocular lens and an oil immersion lens.

The maximum magnification of a compound microscope is (a) ________; that of an electron microscope, (b) ________. The maximum resolution of a compound microscope is (c) ________; that of an electron microscope, (d) ________. One advantage of a scanning electron microscope over a transmission electron microscope is (e) ________.
A
1,500x
The maximum magnification of a compound microscope is (a) ________; that of an electron microscope, (b) ________. The maximum resolution of a compound microscope is (c) ________; that of an electron microscope, (d) ________. One advantage of a scanning electron microscope over a transmission electron microscope is (e) ________.
B
10,000,000x
The maximum magnification of a compound microscope is (a) ________; that of an electron microscope, (b) ________. The maximum resolution of a compound microscope is (c) ________; that of an electron microscope, (d) ________. One advantage of a scanning electron microscope over a transmission electron microscope is (e) ________.
C
0.2 micrometers
The maximum magnification of a compound microscope is (a) ________; that of an electron microscope, (b) ________. The maximum resolution of a compound microscope is (c) ________; that of an electron microscope, (d) ________. One advantage of a scanning electron microscope over a transmission electron microscope is (e) ________.
D
10 picometers
The maximum magnification of a compound microscope is (a) ________; that of an electron microscope, (b) ________. The maximum resolution of a compound microscope is (c) ________; that of an electron microscope, (d) ________. One advantage of a scanning electron microscope over a transmission electron microscope is (e) ________.
E
Seeing 3D detail
Why is a mordant used in the Gram stain?
Mordant combines with the basic dye to form a complex that will not wash out of gram-positive cells.
Why is a mordant used in the flagella stain?
Mordant accumulates on the flagella so that they can be seen with a light microscope.
What is the purpose of a counterstain in the acid-fast stain?
A counterstain stains the colorless non–acid-fast cells so that they are easily seen through a microscope.
What is the purpose of a decolorizer in the Gram stain?
Decolorizer removes the color from gram-negative cells.
What is the purpose of a decolorizer in the acid-fast stain?
Decolorizer removes the color from non–acid-fast cells.

Fill in the following table regarding the Gram stain:
A + E
purple, purple

Fill in the following table regarding the Gram stain:
B + F
purple, purple

Fill in the following table regarding the Gram stain:
C + G
purple, colorless

Fill in the following table regarding the Gram stain:
D + H
purple, red
DRAW IT A sputum sample from Calle, a 30 year old Asian elephant, was smeared onto a slide and air dried. The smear was fixed, covered with carbolfuchsin, and heated for . After washing with water, acid-alcohol was placed on the smear for 30 seconds. Finally, the smear was stained with methylene blue for 30 seconds, washed with water, and dried. On examination at 1000x, the zoo veterinarian saw red rods on the slide. What microbe do these results suggest?
An acid-fast bacterium (Mycobacterium)
Multiple Choice
Assume you stain Bacillus by applying malachite green with heat and then counterstain with safranin. Through the microscope, the green structures are
cell walls
capsules.
endospores.
flagella.
impossible to identify.
3
Three-dimensional images of live cells can be produced with
darkfield microscopy.
fluorescence microscopy.
transmission electron microscopy.
confocal microscopy.
phase-contrast microscopy.
4
Carbolfuchsin can be used as a simple stain and a negative stain. As a simple stain, the pH is
2
higher than the negative stain.
lower than the negative stain.
the same as the negative stain.
2
Looking at the cell of a photosynthetic microorganism, you observe the chloroplasts are green in brightfield microscopy and red in fluorescence microscopy. You conclude:
chlorophyll is fluorescent.
the magnification has distorted the image.
you’re not looking at the same structure in both microscopes.
the stain masked the green color.
none of the above
1
Which of the following is not a functionally analogous pair of stains?
nigrosin and malachite green
crystal violet and carbolfuchsin
safranin and methylene blue
ethanol-acetone and acid-alcohol
All of the above pairs are functionally analogous.
1
Which of the following pairs is mismatched?
capsule—negative stain
cell arrangement—simple stain
cell size—negative stain
Gram stain—bacterial identification
none of the above
5
Assume you stain Clostridium by applying a basic stain, carbolfuchsin, with heat, decolorizing with acid-alcohol, and counterstaining with an acidic stain, nigrosin. Through the microscope, the endospores are 1, and the cells are stained 2.
1—red; 2—black
1—black; 2—colorless
1—colorless; 2—black
1—red; 2—colorless
1—black; 2—red
4
Assume that you are viewing a Gram-stained field of red cocci and blue rods through the microscope. You can safely conclude that you have
made a mistake in staining.
two different species.
old bacterial cells.
young bacterial cells.
none of the above
2
In 1996, scientists described a new tapeworm parasite that had killed at least one person. The initial examination of the patient’s abdominal mass was most likely made using
brightfield microscopy.
darkfield microscopy.
electron microscopy.
phase-contrast microscopy.
fluorescence microscopy.
1
Which of the following is not a modification of a compound light microscope?
brightfield microscopy
darkfield microscopy
electron microscopy
phase-contrast microscopy
fluorescence microscopy
3
Analysis
In a Gram stain, a step could be omitted and still allow differentiation between gram-positive and gram-negative cells. What is it?
counter staining with safranin
Using a compound light microscope with a resolving power of 0.3 micrometers, a 10x ocular lens, and a 100x oil immersion lens, would you be able to discern two objects separated by
3 micrometers?
0.3 micrometers?
300 nm?
yes
yes
yes
the resolving power of the microscope with the use of its strongest lens is 0.3 µm, which means the microscope is able to see differences in objects that are 0.3 µm (equal) and greater. 300 nm is equal to 0.3 µm so, the microscope can see all the 3 distances
Why isn’t the Gram stain used on acid-fast bacteria?
If you did Gram stain acid-fast bacteria, what would their Gram reaction be?
What is the Gram reaction of non–acid-fast bacteria?
these bacteria have mycolic acid in their cell walls which prevents the stain from entering the cells
the bacteria appear colorless because the cell walls are resistant to Gram stain
there would be a typical reaction, either gram-positive or gram-negative
Endospores can be seen as refractile structures in unstained cells and as colorless areas in Gram-stained cells. Why is it necessary to do an endospore stain to verify the presence of endospores?
because they can't be differentiated from inclusion of stored material without a special stain
endospores can't be stained by ordinary methods (such as gram staining) because the dyes don't penetrate the wall of the endospore
Clinical Applications and Evaluations
In 1882, German bacteriologist Paul Erhlich described a method for staining Mycobacterium and noted, “It may be that all disinfecting agents which are acidic will be without effect on this [tubercle] bacillus, and one will have to be limited to alkaline agents.” How did he reach this conclusion without testing disinfectants?
Mycobacterium bacteria have mycolic acid in their cell walls, this makes them acidic and resistant to binding with acidic agents
as acidic structures repel acidic agents, alkaline agents would have to be used to disinfect areas with Mycobacterium
Laboratory diagnosis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae infection is based on microscopic examination of Gram-stained pus. Locate the bacteria in this light micrograph. What is the disease?
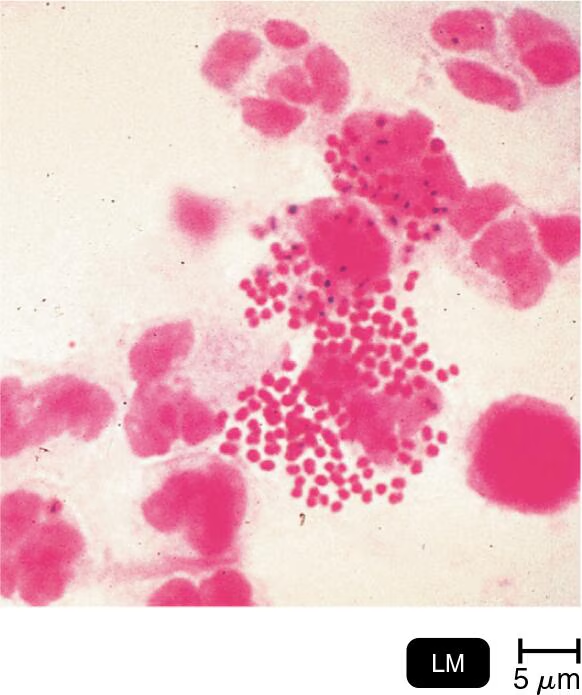
the disease is Gonorrhoea which is caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae
when seen on a Gram stain, Neisseria gonorrhoeae are gram-negative diplococci
Assume that you are viewing a Gram-stained sample of vaginal discharge. Large (10 micrometer) nucleated red cells are coated with small ( 0.5 micrometer wide by 1.5 micrometer long) blue cells on their surfaces. What is the most likely explanation for the red and blue cells?
the small blue cells are called "clue cells", which are epithelial cells of the vagina that are caused by Gardnerella vaginalis (a group of gram-positive bacteria)
the large red cells are epithelial cells, that make up the epithelium that cover the body (inside and out) including the urinary tract
could be Bacterial Vaginosis (BV) due to Gardnerella vaginalis, as evidenced by the presence of clue cells