ECHO 3 : Valvular Regurg
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
physiologic regurg is restricted to which area?
area immediately adjacent to valve closure
what are the semi quantitative measurements for valvular regurg
vena contracta width
CW doppler signal strength compared with antegrade flow
pressure half time (for AR)
Pulmonary venous flow (reversals)
CW doppler for mitral regurg is best in which view?
apical view
what are quantiative measures of valvular regurg?
regurgitant volume
regurgitant fraction
regurgitant orifice area
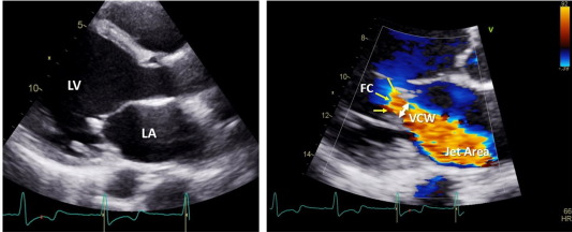
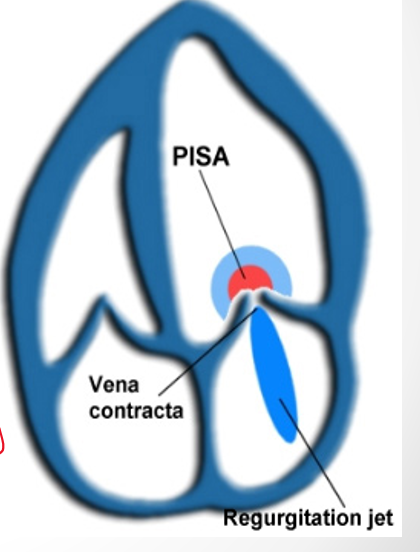
how does color doppler indicate mitral valve regurg?
vena contracta
jet area
flow convergence
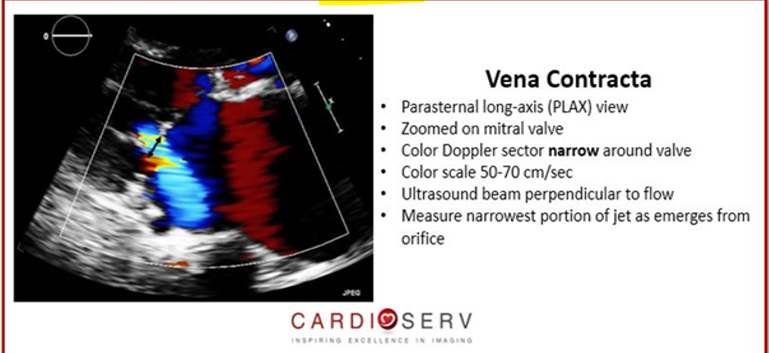
in what view is vena contracta measured?
PLAX (perpendicular to jet)
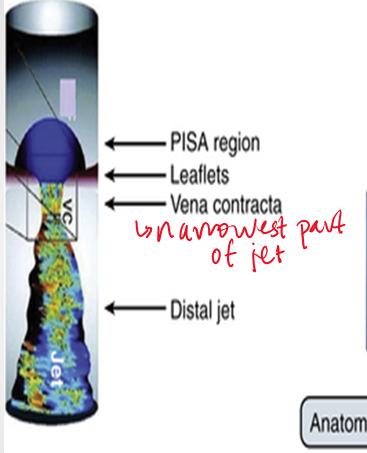
how do you measure vena contracta ?
narrowest portion of jet as it emerges from the orifice
what ranges for vena contracta indicate mild and severe mitral regurg?
mild : .3cm
severe : >/= .7cm
between .3 and .7 needs further evaluation (semi quant)
vena contracta is used for which valves?
mitral and aortic
what are the quantitative methods in mitral regurg?
PISA
stroke volume method
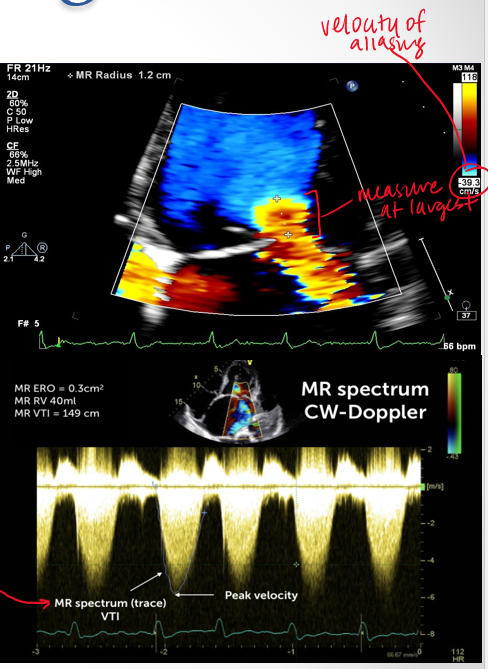
how do you obtain PISA measurement
4ch view
zoom in on MV
color doppler
lower color scale below 40
measure PISA radius
measure max velocity of regurg jet using CW doppler
what numbers does the PISA measurement give us?
velocity of aliasing
pisa radius
VTI trace
what is the stroke volume method?
stroke volume taken at two sites
what do these quantitative methods (PISA AND SV METHOD) give us?
lesion severity (EROA—> size of defect) and volume overload (Rvol → how much blood is regurgitant)
what is mild moderate and severe EROA (Cm²)
mild <.2
moderate .2-.39
severe : >/= .4
what is mild moderate and severe Rvol?
mild <30
moderae 30-59
severe >/= 60
what is proximal flow convergence and how is it measured?
as blood flows through constricted valve the blood converges and creates a hemispheric surface area
measured using PISA (proximal isovelocity hemispheric surface area)
PISA is more accurate for what type of jets/orifice?
jets : central
orifice : circular
(holosystolic MR)
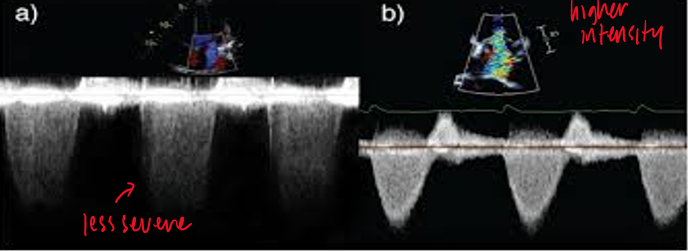
how is valvular regurg assessed with CW doppler?
signal intensity relative to antegrade flow
antegrade flow velocity
shape of velocity curve
how do you calcular regurgitant volume? **
regurgitant volume = Total SV - Forward SV
total sv → antegrade flow rate across regurg valve
forward sv → stroke volume across competent valve
what are the primary causes of mitral regurg?
myxomatous mitral valve disease (MVP)
degeneration of connective tissue
rheumatic disease
MAC
endocarditis
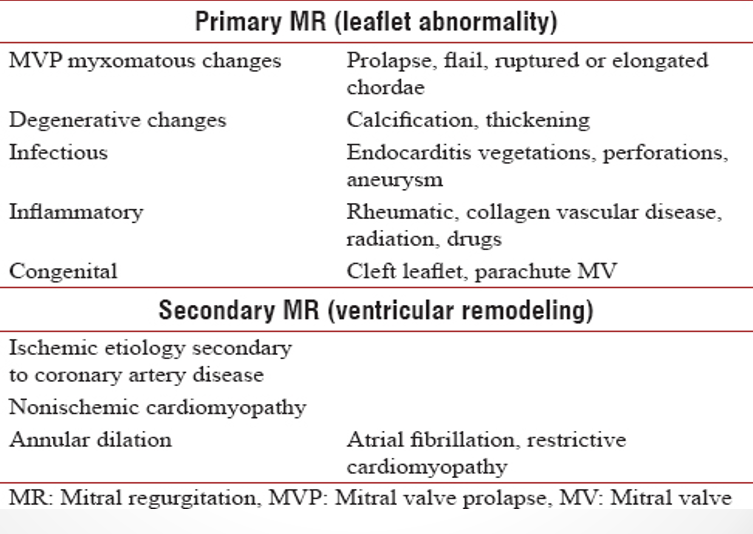
what are the secondary causes of mitral regurg?
LV dilation (cardiomyopathy)
ischemic MR (from pap muscle dysfunction)
LV dysfunction
what are the indicators of mitral valve regurg severity?
mitral valve pathology
color doppler (vena contracta, jet area, flow convergence)
mitral E ; pulm venous flow
CW
LA/LV size
what is an eccentric jet?
travels along atrial wall
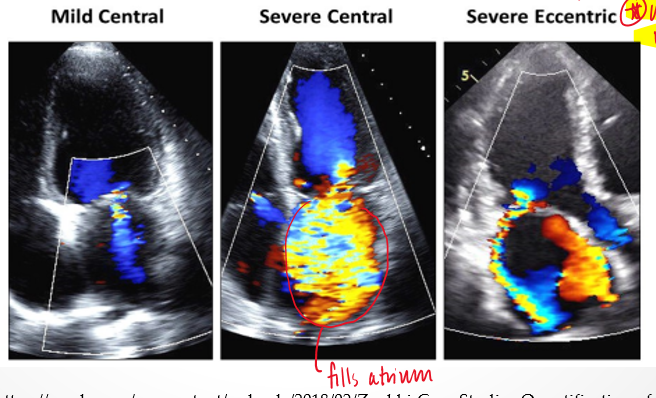
how does the severity of the mitral valve regurgitant jet change when it it eccentric?
severity is underestimated because energy dissipates when jet touches other structures
what is the coanda effect?
loss of momentum of eccentric reurgitant jet
what do you look for with pulmonary vein systolic flow reversal?
look for reversal of S wave
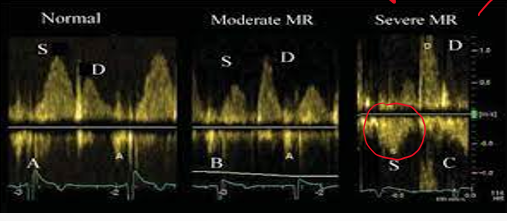
what is the most common cause of MR in developed countries? aka?
mitral valve prolapse
degenerative / myzomatous mitral valve disease
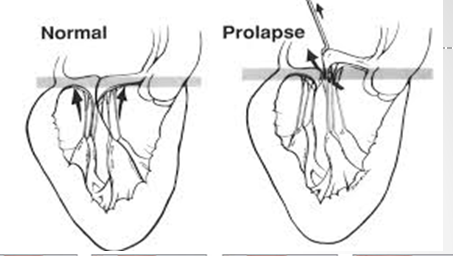
does prolapse cause regurg?
you can have prolapse without regurgitation
mitral valve prolapse involves which structure more often?
PMVL
how do the leaflets bulge in mitral valve prolapse?
upward and back into left atrium but tips still point into LV
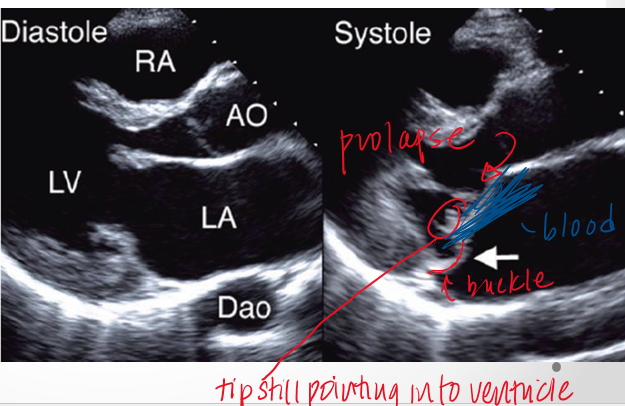
what is flail mitral leaflet?
when there is chordal rupture
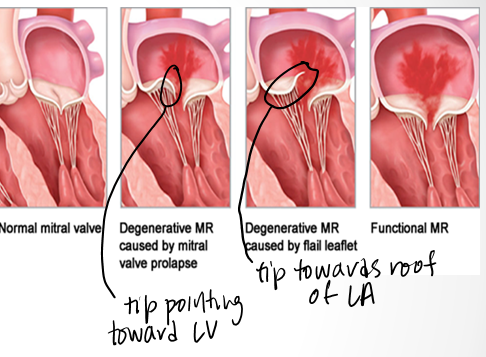
describe flail vs prolapse?
in prolapse chordal connections of leaflet to pap muscle are still intact so tip will still point to LV apex
in flail tip of leaflet will point towards the roof of the LA in systole
chronic MR leads to
left ventricular volume overload
how does chronic MR affect E/A velocity?
increased peak E velocity
due to additional regurg volume that must pass through MV during diastole
how does ao regurg affect the LV
volume overload initially (LV dilates)
then pressure and systolic dysfunction (hypertrophy)
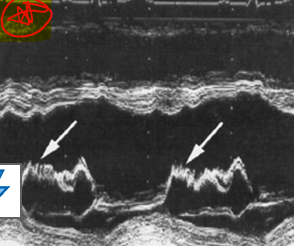
what is this?
diastolic fluttering of the AMVL caused by ao regurg
what murmur is associated with fluttering amvl due to ao regurg?
austin flint murmur
what are the signs and symptoms of ao regurg?
fatigue (not enough blood going out to body bc its going back into LV)
syncope (fainting)
SOB
palpitation
widened pulse pressure
how is color flow helpful in grading AI?
jet / LVOT width
measure percentage of the left ventricular outflow tract occupied by the ai jet
assess how far AI is going into the LV
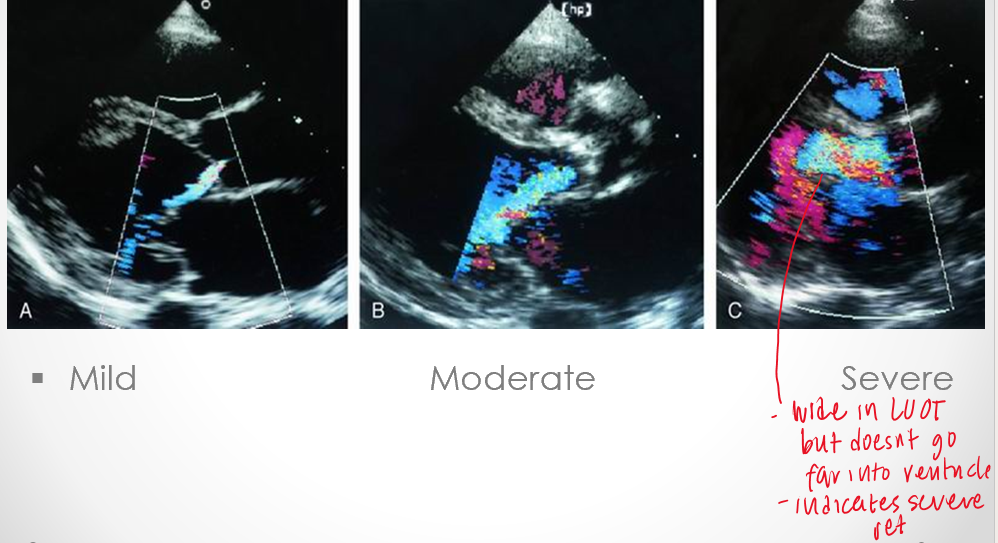
is color flow quantitative or qualitative?
semi quant
what are the etiologies of aortic regurg?
bicuspid valve (primary leaflet issue → congenital)
rheumatic disease (primary leaflet issue → acquired)
endocarditis (primary leaflet issue → acquired)
calcific disease (primary leaflet issue → acquired)
aortic root dilation (seocndary → abnormalities of ao root )
aortic root enlargement could be due to
marfan syndrome (tall people)
familial aortic aneurysm
hypertension
aortic dissection
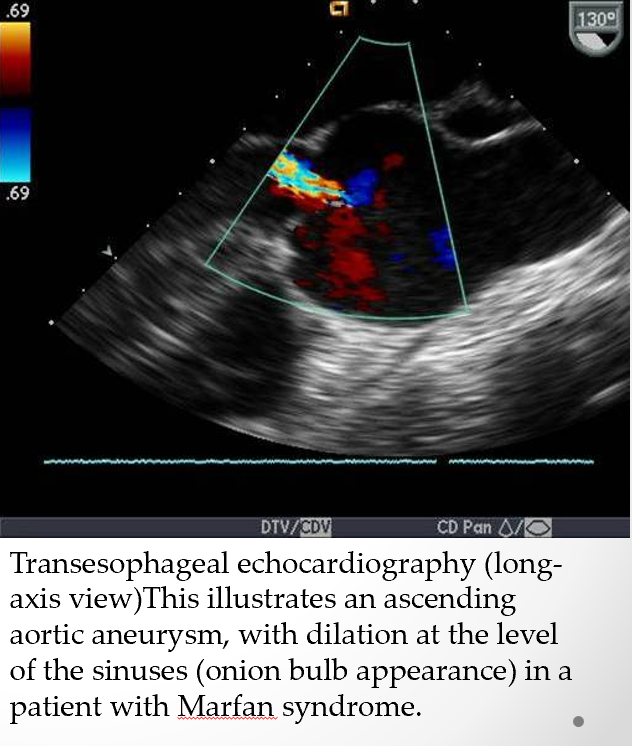
marfan syndrome is often cccompanied by
mitral valve prolapse
pulm art dilation
MAC
dilatation or dissection of descending thoracic ao/abd ao
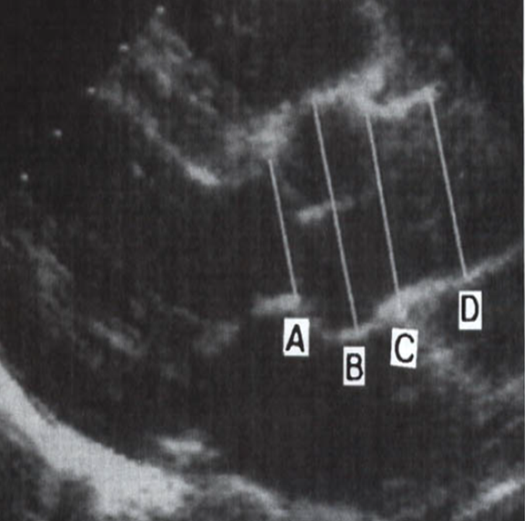
label
A : aortic annulus
B : sinuses of valsalva
C : sinotubular junction
D : ascending ao
how do quantify AI severity?
color flow doppler
vena contracta
CW doppler
descending ao diastolic flow reversal
pressure half time
density of velocity signal retrograde vs antegrade
what does the cross sectional area of vena contract represent?
measure of the effective regurgitant orifice area (narrowest area of actual flow)
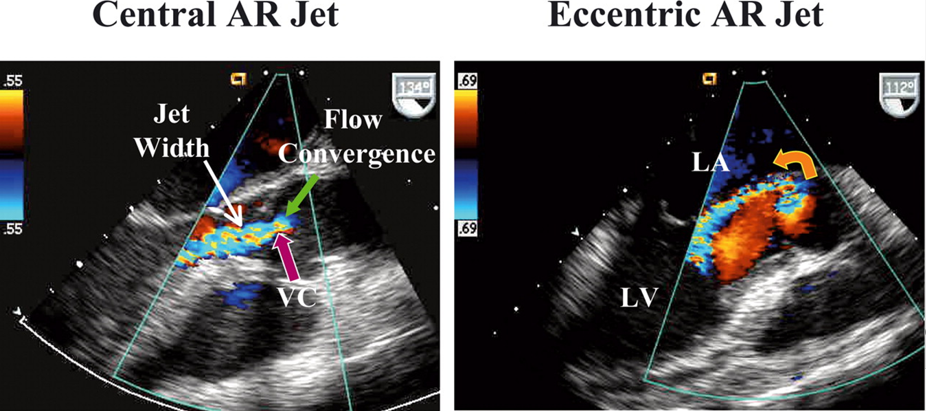
what measurements of vena contracta indicate mild, moderate and severe aortic regurg?
mild : <.3cm
moderate : .3 - .6cm
severe : > .6cm
what PHT values indicate severe mdeorate and mild ao regurg?
severe : steep slope <200ms
moderatie: 200-500 ms
mild : flat slope >500ms
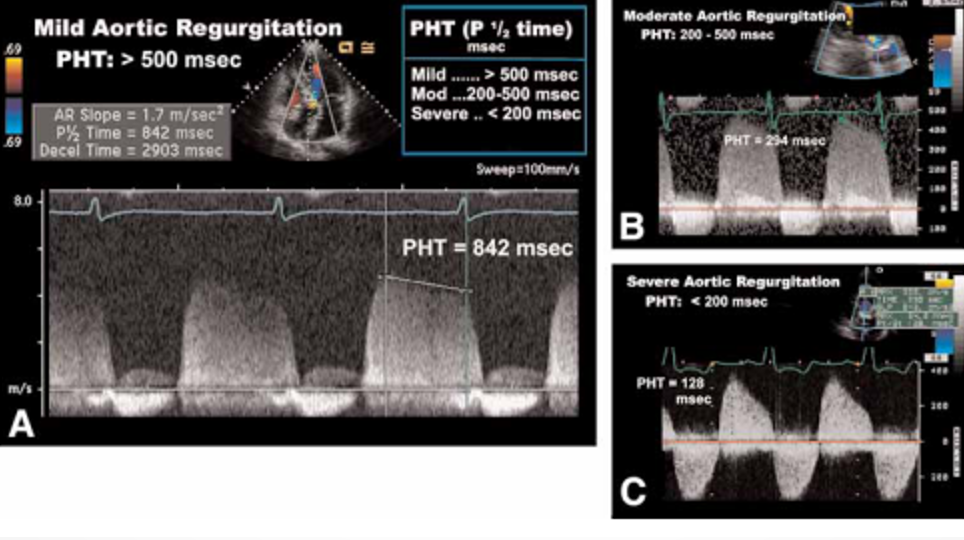
how does PHT compare in regurg vs stenosis
in stenosis a higher PHT = worse stenossi
in regurg a lower PHT = worse regurg
what is PHT?
when initial max velocity of blood across valve drops to 70% of its initial value OR
when pressure difference across valve is half initial pressure
(intiially AO has high pressure so there is high velocity but as LV fills from AI jet and normal LV filling, LV pressure increases)
why can PHT alone not be used to assess AO severity?
other factors such as chronicity of regurg, systolic BP, LV compliance can all influence how quickly the regurgitant jet can fill into the LV
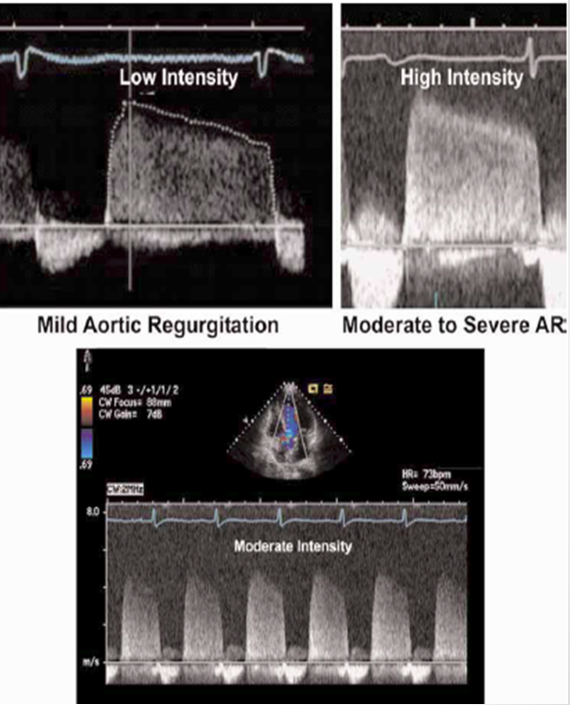
how does density of CW doppler give us information on AI
dense signals → greater quantity
faint signals → mild regurg
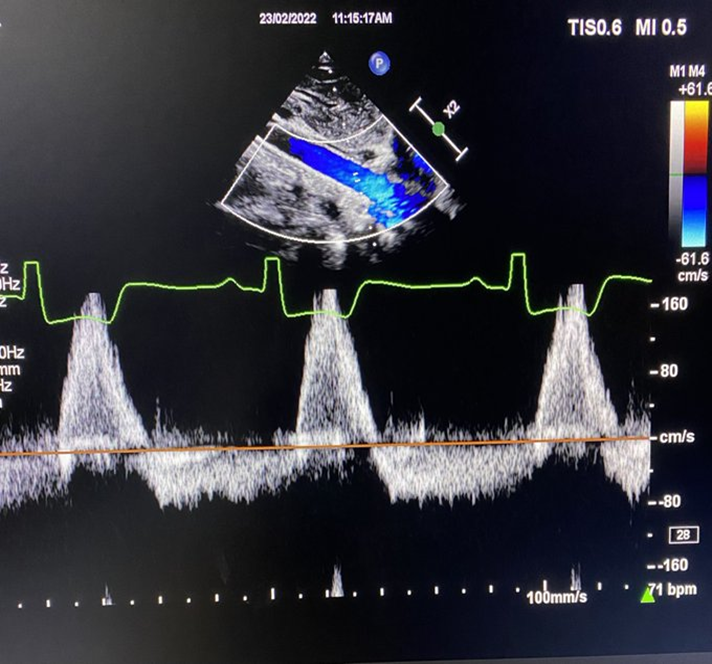
how is descending ao diastolic flow assesed?
taken at subcostal and SSN
look for evidence of holodiastolic flow reversal ( should not see SUSTAINED flow reversal thorugh diastole in aorta → severe regurg)
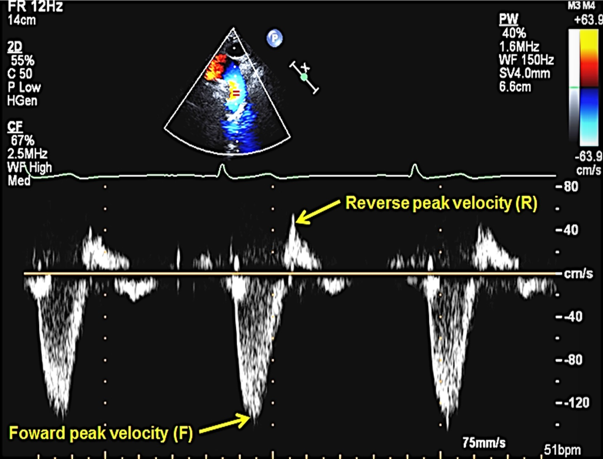
tricuspid regurg may be due to
primary valve disease
secondary to annular dilatation
what are the primary causes of TR?
endocarditis, ebstein anomaly, rheumatic disease, carcinoid, and myxomatous disease
what are the secondary causes of TR?
pulm hypertension
mitral valve disease
pulm parenchymal disease
primary pulm hypertension
**secondary based on presence of pulm hypertension and absence of structural abnormalities of leaflets
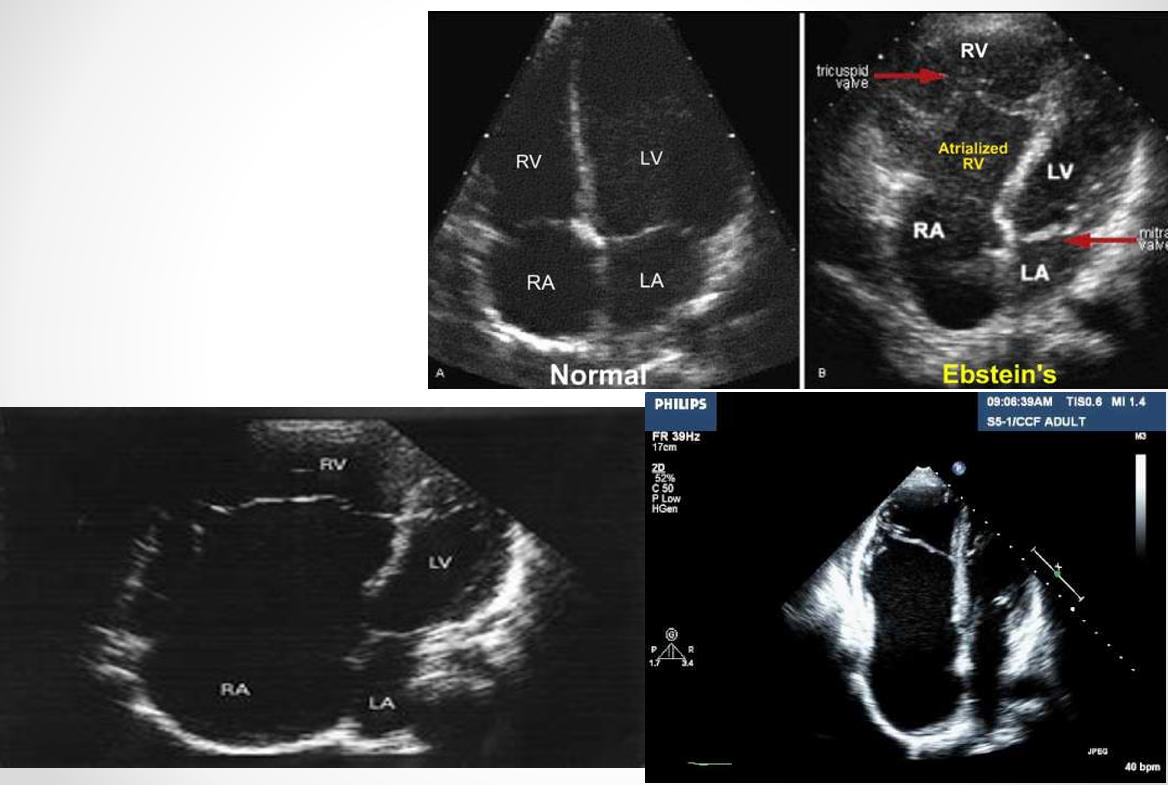
what is the ebstein anomaly? (DONT FOCUS ON)
apical displacement of one or more leaflets
insertion of tricuspid leaflet downward into RV (greater than 10mm from mitral valve leaflets)
vena contracta of - indicates severe TR
>7mm
in what percentage of cases does rheumatic disease involve TV?
20-30% of cases
TR is often secondary to
annular dilation due to primary RV dilatation and systolic dysfunction/pulm hypertension
pathologic pumonic regurg is most often due to
congenital heart diseases such as repaired TOF
review qs
what are the primary and secondary etiologies of MR?
primary
myxomatous mitral valve disease (MVP)
degeneration of connective tissue
rheumatic disease
MAC
endocarditis
secondary
LV dilation (cardiomyopathy)
ischemic MR (from pap muscle dysfunction)
LV dysfunction
review qs
what methods can assess mitral regurg?
PISA
stroke volume method
CW doppler
Color doppler (vena contracta, jet area, flow convergence)
Mitral E wave
Pulmonary venous systolic flow reversal
review qs
what methods can assess aortic regurg?
Color flow (jet/LVOT width, Vena contracta)
CW doppler (descending ao diastolic flow reversal, PHT, density of velocity signal retro vs ante)
review qs
fluttering of anterior mitral valve leaflet can be caused by what pathology?
ao regurg