Week 8 PEDs Questions
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
A nurse is providing teaching about the management of epistaxis to an adolescent. Which of the following positions should the nurse instruct the adolescent to take when experiencing a nosebleed?
a
Sit up and lean forward.
b
Sit up and tilt the head up.
c
Lie in a supine position.
d
Lie in a prone position.
a Sit up and lean forward.
Instruct the adolescent to sit up and lean to lean forward to prevent aspiration when experiencing a nosebleed.
A nurse is providing teaching about epistaxis to the parent of a school-age child. Which of the following should the nurse include as an action to take when managing an episode of epistaxis?
Select all that apply.
a
Press the nares together for at least 10 min.
b
Breathe through the nose until bleeding stops.
c
Pack cotton or tissue into the naris that is bleeding.
d
Apply ice across the bridge of the nose.
e
Insert petroleum into the naris after the bleeding stops.
a Press the nares together for at least 10 min.
d Apply ice across the bridge of the nose.
The child should breathe through the mouth, not the nose, until the bleeding stops.
A nurse is providing teaching to the parent of a child who has a new prescription for liquid oral iron supplements. Which of the following statements by the parent indicates an understanding of the teaching?
a
“I should take my child to the emergency department if his stools become dark.”
b
“My child should avoid eating citrus fruits while taking the supplements.”
c
“I should give the iron with milk to help prevent an upset stomach.”
d
“My child should take the supplement through a straw.”
d “My child should take the supplement through a straw.”
Milk prevents absorption of the iron. The supplement should be given 1 hr before or 2 hr after consuming milk
A child’s stools will become a tarry-green color if the iron supplement dose is adequate.
Vitamin C increases absorption of the iron and should be encouraged while taking the supplement.
A nurse is preparing to administer iron dextran IM to a school-age child who has iron deficiency anemia. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
a Administer the dose in the deltoid muscle.
b Use the Z-track method when administering the dose.
c Avoid injecting more than 2 mL with each dose.
d Massage the injection site for 1 min after administering the dose.
b Use the Z-track method when administering the dose.
The nurse should administer the injection into a large muscle mass such as the ventrogluteal.
The nurse should avoid injecting more than 1 mL with each dose.
To reduce irritation and skin staining, the nurse should not massage the injection site after administering the dose.
A nurse is caring for an infant whose screening test reveals a potential diagnosis of sickle cell disease. Which of the following tests should the nurse expect the provider to prescribe to distinguish whether the infant has sickle cell disease or sickle cell trait?
a Sickle solubility test
b Hemoglobin electrophoresis
c Complete blood count
d Transcranial Doppler
b Hemoglobin electrophoresis
The transcranial Doppler is performed to assess intracranial vascular flow and detect the risk for cerebrovascular accident. It will not distinguish between sickle cell disease and sickle cell trait.
A complete blood count tests for anemia. It indicates the average size of the red blood cells, and the amount of hemoglobin in the red blood cells. It will not distinguish between sickle cell disease and sickle cell trait.
The sickle solubility test is a screening tool that detects the presence of abnormal hemoglobin but does not distinguish between the trait and the disease.
Factor VIII (Hemo A) vs Factor IX (Hemo B)
Cofactor (helper) in clot formation
Works with Factor IX to activate Factor X (which leads to clot formation)
Made in the endothelial cells of blood vessels
Treatment: Factor VIII infusion or Desmopressin (DDAVP) (can stimulate Factor VIII production)
Immediate bleeding post-injury (severe)
Enzyme (activator) in clot formation
Directly activates Factor VIII to start the clotting cascade
Made in the liver
Treatment: Factor IX infusion – DDAVP is NOT effective
Delayed bleeding post-injury (severe or mild)
Wounds may stop bleeding at first, then restart later
Why does Hemo A/B have normal platelets/PT but abnormal aPTT?
Disorders of the Intrinsic Pathway (aPTT Test) (VIII/IX)
Only aPTT is prolonged
Not a platelet disorder (initial plug formed but no stable fibrin clot)
Normal
Not a disorder of the Extrinsic Pathway (PT test): Involves Factor VII
Normal due to no link to VIII/IX
Common Pathway: Both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways converge to form a stable clot.
Compare and contrast the following blood disorders
Hemophilia A (VIII) & B (IX)
Von Willebrand Disease (vWD)
Vitamin K Deficiency or Liver Disease
DIC (Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation)
Hemophilia A (VIII) & B (IX)
Prolonged aPTT but normal PT and platelets
Von Willebrand Disease (vWD): Prolonged aPTT but also has platelet dysfunction.
Vitamin K Deficiency or Liver Disease: Both PT and aPTT are prolonged.
DIC (Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation): Prolonged PT and aPTT, with low platelets.
Desmopressin (DDAVP)
Synthetic form of vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone, ADH).
Primary Function: Water retention
Secondary Function: Clotting (Tx: Hemophilia A & VWF)
Stimulates stored factor VIII and von Willebrand facor (vWF) release from endothelial cells of blood vessels
Factor IX originates from the liver, so this medication has no effect on Hemophilia B
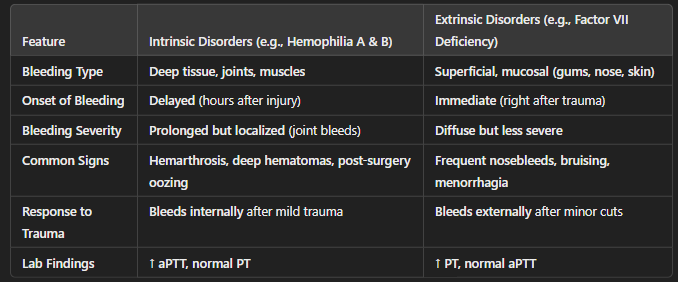
Intrinsic vs Extrinsic Bleeds
"Deep and Delayed" Bleeding (Inside Bleeding - Deep Tissues)
Deep tissue bleeding: Hemarthrosis (joint bleeds), muscle hematomas, deep bruises.
Delayed bleeding: Initial clot formation occurs normally, but bleeding restarts hours later because the fibrin clot is weak.
Prolonged oozing after trauma (e.g., dental procedures, circumcision).
Clinical Example: A child with hemophilia gets a small bump on the knee, appears fine at first, but hours later the joint swells with painful hemarthrosis.
"Fast and Superficial" Bleeding (External Bleeding - Skin/Mucosa)
Immediate bleeding after injury: The extrinsic pathway is the first responder for clotting, so patients bleed quickly and don't stop as easily.
Superficial mucosal bleeding: Frequent nosebleeds (epistaxis), gingival bleeding, heavy menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia), easy bruising.
Petechiae and ecchymoses due to fragile clot formation.
Clinical Example: A patient with Factor VII deficiency gets a minor cut while shaving but bleeds excessively and continuously, requiring pressure to stop.
A nurse is planning caring for a toddler who is hospitalized and has been diagnosed with a Wilms’ tumor. Which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take?
a
Palpate the child’s abdomen to identify the size of the tumor.
b
Monitor the child for hypertension
c
Teach the parents about dialysis.
d
Obtain a 24-hr urine specimen from the child.
b Monitor the child for hypertension
The child who has a Wilm’s tumor is at risk for hypertension due to increased renin production. Pressure applied to the abdomen could rupture the encapsulated tumor; therefore, the nurse should not include palpating the toddler’s abdomen in the plan of care.
Wilms’ tumor is usually unilateral leaving the child with one unaffected kidney; therefore, the nurse would not need to include teaching the parents about dialysis in the plan of care.
A urinalysis, not a 24-hour urine is obtained for diagnostic evaluation of Wilms’ tumor; therefore, the nurse should not include teaching about a 24 hour urine specimen in the plan of care.
A nurse is teaching the parent of a child who has a Wilms’ tumor. Which of the following statements should the nurse include in the teaching?
Select all that apply.
a
“Your child will need to have chemotherapy for 12 months.”
b
“Most children who have Wilms’ tumors also have congenital anomalies.”
c
“Surgery is done usually within 48 hours of diagnosis.”
d
“Palpating the tumor could cause spread of the cancer.”
e
“Further treatments will start immediately after surgery.”
c “Surgery is done usually within 48 hours of diagnosis.”
d “Palpating the tumor could cause spread of the cancer.”
e “Further treatments will start immediately after surgery.”
When taking action and teaching the parent of a child who has a Wilm’s tumor, the nurse should include in the teaching that prompt removal of the tumor is best practice for treatment of Wilms’ tumor; therefore, surgery to remove the tumor is usually performed within 48 hours of diagnosis. The nurse should also teach the parent that palpating the abdomen can cause rupture of the encapsulated tumor which can cause the cancer to spread. Additionally, the nurse should teach the parent that chemotherapy, and possibly radiation therapy, will begin immediately after surgery.
The length of time the child will receive chemotherapy treatment depends on the stage of the tumor
About 10% of children who have Wilms’ tumors have congenital anomalies
A nurse is providing teaching to the parent of a child who has a neuroblastoma. Which of the following statements should the nurse include in the teaching?
Select all that apply.
a
“Chemotherapy and radiotherapy may be necessary for treatment.”
b
“Your child will need a bone marrow biopsy.”
c
“Your child will be paralyzed because of this tumor.”
d
“Most children are diagnosed around age 12.”
e
“Your child will need surgery for resection of the tumor.”
a “Chemotherapy and radiotherapy may be necessary for treatment.”
b “Your child will need a bone marrow biopsy.”
e “Your child will need surgery for resection of the tumor.”
Physical effects depend on the size and location of the tumor.
Most cases occur before the age of 10 years, with a median age of 19 months.
A nurse is caring for a child who is receiving radiation following the surgical removal of a Wilm’s tumor. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
a
Wash the radiation marks from the skin after each treatment.
b
Cover the radiation site with snug, synthetic clothing.
c
Instruct the caregiver to avoid using lotion on the site of radiation.
d
Expose the radiation site to sunlight for 10 minutes a day.
c Instruct the caregiver to avoid using lotion on the site of radiation.
The nurse should wash the site with lukewarm water being careful not to remove the skin markings.
The child who is receiving radiation therapy should wear loose, cotton clothing, not snug, synthetic clothing
The child who is receiving radiation therapy should have the site of radiation exposed to air; however, heat and sunlight should be avoided.
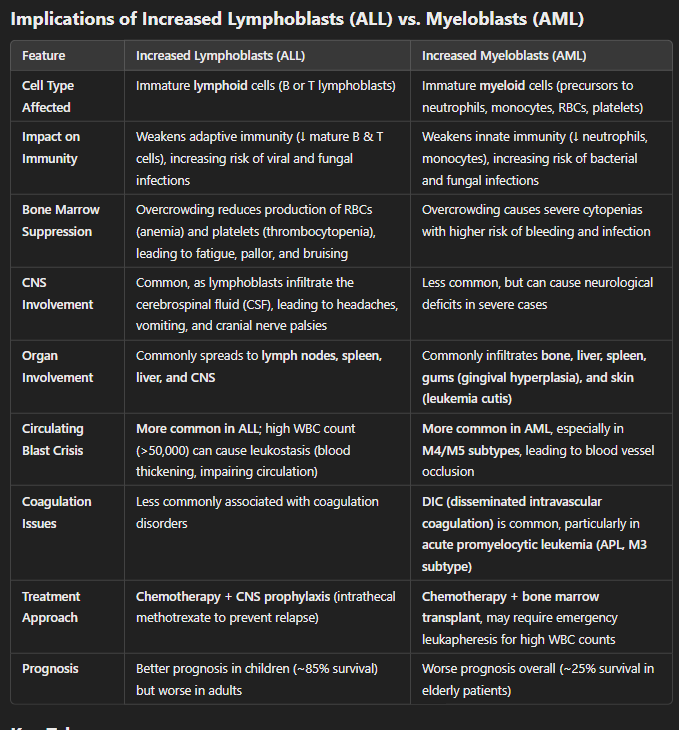
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) vs Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
Both cause pancytopenia (low RBCs, WBCs, and platelets) due to bone marrow overcrowding.
Both require aggressive chemotherapy, and in high-risk cases, bone marrow transplantation.
More common in children
~85% survival in children, worse in adults
Involves the progenitors (immature lymphocytes)
Less mature B/T cells = Weakened adaptive immunity
CNS involvement more common
Immune dysfunction (more viral infections), CNS infiltration, lymph node involvement.
More common in adults
~25% survival in older adults
Involves the progenitors (granulocytes, monocytes, RBCs, platelets)
Less neutrophils/monocytes = Weakened innate immunity
May present with gum hypertrophy and leukemia cutis (skin lesions).
Severe infection risk (more bacterial/fungal), gum hypertrophy, DIC risk.
A nurse is assessing a child who has leukemia. Which of the following should the nurse expect to find?
Select all that apply.
a
Hypothermia
b
Anorexia
c
Petechiae
d
Erythema
e
Unsteady gait
b Anorexia
c Petechiae
e Unsteady gait
The child who has leukemia will exhibit pallor, not erythema.
The child who has leukemia will have a low-grade fever, not hypothermia.
A nurse is planning care for an infant who is scheduled to have a lumbar puncture. Which of the following actions should the nurse include in the plan of care?
a
Cleanse the thoracic area of the infant’s back with an antiseptic solution.
b
Apply a eutectic mixture of local anesthetic cream just before the procedure begins.
c
Restrain the infant during the procedure to prevent movement.
d
Position the infant with his head extended and chin raised.
c Restrain the infant during the procedure to prevent movement.
A local anesthetic cream should be applied 45 to 60 min prior to the procedure.
The lumbar area of the infant’s back should be cleansed prior to the procedure.
The infant should be positioned with his neck flexed and chin to the chest.
A nurse is providing teaching to the parents of a child who has a new prescription for chemotherapy. Which of the following statements by the parents indicates understanding of the teaching?
a
“My child should not be given any steroids while on chemotherapy.”
b
“My child will receive donor stem cells during chemotherapy.”
c
“I will need to monitor my child for infection and fever.”
d
“I should use clean technique when accessing my child’s port.”
c “I will need to monitor my child for infection and fever.”
Children who are receiving chemotherapy my receive corticosteroids as an adjunct to treatment or to minimize adverse effects of treatment.
Children receive donor stem cells during Hematopoietic stem cells transplants, not during treatment with chemotherapy.
When accessing an implanted ventral venous access device, the parent should use aseptic technique, not clean technique.
A nurse is caring for a child who has thrombocytopenia. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Select all that apply.
a
Monitor for manifestations of bleeding.
b
Administer routine immunizations.
c
Obtain rectal temperatures.
d
Avoid peripheral venipunctures.
e
Limit visitors.
a Monitor for manifestations of bleed
d Avoid peripheral venipunctures.
A nurse is caring for a child who is being evaluated for osteosarcoma. Which of the following manifestations should the nurse expect the child to report?
a
Pain
b
Discoloration of the skin
c
Abdominal mass
d
Easy bruising
a Pain
When caring for a child who is being evaluated for osteosarcoma, the nurse should expect the child to report bone pain. The child may also report weakness, swelling, decreased movement, limping, weight loss, and the inability to lift a heavy object. The child and family may also report an unexplained weight loss.
A nurse is caring for a child following an above-the-knee amputation. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
a
Avoid discussing the amputation.
b
Inform the child and caregivers that chemotherapy will not be need after surgery.
c
Prepare the child for a prosthesis fitting.
d
Maintain the affected limb in the dependent position.
c Prepare the child for a prosthesis fitting.
the nurse should prepare the child for a prosthesis fitting to help the child cope with the transition.
The loss of a limb entails a grieving process; therefore, the nurse should encourage discussion to facilitate grieving, not avoid discussing the amputation.
A nurse is providing home care information to the parents of a child who is receiving chemotherapy. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching?
Select all that apply.
a
Manifestations of infection
b
Bleeding precautions
c
Hand hygiene
d
Homeschooling
e
Airborne precautions
a Manifestations of infection
b Bleeding precautions
c Hand hygiene
Children who are receiving chemotherapy can continue to attend school following recommendations of the provider. Homeschooling should not be included in the teaching.
A nurse is assessing a child who has rhabdomyosarcoma of the nasopharynx. Which of the following manifestations should the nurse expect to find?
Select all that apply.
a
Enlarged neck lymph nodes
b
Pain
c
Sinusitis
d
Epistaxis
e
Strabismus
a Enlarged neck lymph nodes
b Pain
d Epistaxis
Sinusitis is a manifestation of rhabdomyosarcoma of the paranasal sinuses.
A nurse is teaching the caregiver of a preschool child about factors that affect the child’s perception of death. Which of the following factors should the nurse include in the teaching?
a
Preschool children have no concept of death.
b
Preschool children perceive death as temporary.
c
Preschool children often regress to an earlier stage of behavior.
d
Preschool children experience fear related to the disease process.
b Preschool children perceive death as temporary.
School-age children, not preschoolers, experience fear related to the disease process
Toddlers, not preschoolers, often regress to an earlier stage of behavior
A nurse is caring for a child who is dying. Which of the following should the nurse identify as manifestations of impending death?
Select all that apply.
a
Heightened sense of hearing
b
Tachycardia
c
Difficulty swallowing
d
Sensation of being cold
e
Cheyne-Stokes respirations
c Difficulty swallowing
e Cheyne-Stokes respirations
Client’s experience a sensation of heat even though the body feels cool to touch as a physical manifestation of approaching death.
Bradycardia, not tachycardia, is a physical manifestation of approaching death.
A decrease in the senses of smell, sight, and hearing are physical manifestations of approaching death, not a heightened sense of hearing.
A nurse is reviewing palliative care with an assistive personnel (AP) who is assisting with the care of a child who has a terminal illness. Which of the following statements by the AP indicates an understanding of palliative care?
a
“I’m sure the family is hopeful that the new medication will stop the illness.”
b
“I’ll miss working with this client now that only nurses will be caring for the child.”
c
“I will get all the client’s personal objects out of the room.”
d
“I will listen and respond as the family talks about their child’s life.”
d “I will listen and respond as the family talks about their child’s life.”
Palliative care focuses on the process of dying and grieving, which includes using therapeutic communication; therefore, this statement by the AP indicates an understanding of palliative care.
Breakthrough pain
Sudden, intense flare-up of pain that occurs even though a patient is already receiving regular pain medication.
It "breaks through" the baseline pain control provided by long-acting pain medications.
A charge nurse in a hospice care office is planning an in-service to provide coping strategies to nurses who care for dying children. Which of the following are strategies should the nurse include in the in-service?
Select all that apply.
a
Remain in contact with the family after their loss.
b
Develop a professional support system.
c
Take time off from work.
d
Suggest that a hospital representative attend the funeral.
e
Demonstrate feelings of sympathy toward the family.
a Remain in contact with the family after their loss.
b Develop a professional support system.
c Take time off from work.
A side effect of chemotherapy is bone marrow suppression which can result in all of the following
EXCEPT
A. Thrombocytopenia
B. Neutropenia
C. Anemia
D. Alopecia
D. Alopecia
Bone marrow suppression (myelosuppression) is a common side effect of chemotherapy, affecting the production of blood cells. This leads to:
Thrombocytopenia (A): Low platelet count → increased risk of bleeding and bruising.
Neutropenia (B): Low white blood cell count → increased risk of infection.
Anemia (C): Low red blood cell count → fatigue, pallor, and weakness.
Alopecia (D) is a side effect of chemotherapy but is not caused by bone marrow suppression. Instead, it results from chemotherapy damaging rapidly dividing hair follicle cells.
Neuroblastoma is a brain tumor.
A. True
B. False
B. False
Neuroblastoma is not a brain tumor. It is a cancer that originates in the sympathetic nervous system, typically in the adrenal glands located above the kidneys or in nerve tissue along the spine, chest, abdomen, or pelvis.
While it affects nerve cells, it does not originate in the brain. However, in advanced cases, it can metastasize (spread) to the brain.
Antiemetic Medications OTC & 24 hours Pre-Chemo
Ondansetron (Zofran)
Diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
Dexamethasone (Steroid)
Vesicants
(Irritating Chemotherapy drugs)
Risk of extravasation (tissue damage).
Must be certified to handle
Considered a MEDICAL EMERGENCY for cancer patients
Fever (>100F)
A nurse is caring for a 3-year-old client who has been recently diagnosed with Wilms' tumor. Which of the following assessment parameters must be modified to properly care for this client before surgery?
Omit abdomen palpation.
Assess skin integrity every hour.
Assess neurologic status every 2 hr.
Omit bowel sound auscultation.
Omit abdomen palpation.
Wilms' tumor (nephroblastoma) is a kidney tumor that is highly vascular and fragile. Palpating the abdomen can rupture the tumor capsule, leading to tumor seeding and metastasis.
A nurse is caring for a 3-year-old toddler who has rhabdomyosarcoma and is currently receiving chemotherapy. Which of the following should the nurse identify as a possible complication while the toddler receives treatment?
Otorrhea
Weight gain
Developmental delays in thinking.
Bilateral effusion
Developmental delays in thinking.
Rhabdomyosarcoma is a soft tissue malignancy that affects muscles, connective tissue, or hollow organs (e.g., bladder). Chemotherapy is a primary treatment and can lead to neurocognitive delays, especially in young children whose brains are still developing.
Rhabdomyosarcoma itself does not directly cause bilateral effusions. Effusions can be seen in certain cancers (e.g., lung cancer, lymphoma), but they are not a primary concern in rhabdomyosarcoma.
Rhabdomyosarcoma is a cancer of what kind of tissue?
A. bone marrow
B. brain
C. skeletal muscle
D. renal tissue
C. skeletal muscle
This age group has a view of death as being temporary.
A. Toddler
B. Preschool
C. School age
D. Adolescent
B. Preschool
A nurse is providing teaching about iron deficiency anemia to the parents of a toddler. Which of the following should the nurse recommend as a method of preventing iron deficiency anemia?
Avoid a diet that consists primarily of milk.
Administer fat-soluble vitamins daily.
Include fluoridated water in the toddler's diet.
Limit intake of high-protein foods.
Avoid a diet that consists primarily of milk.
A nurse is assessing a school-age child. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an indication that the child may have a bleeding disorder?
Frequent falls
Dental caries
Mood changes
Swollen and stiff knees
Swollen and stiff knees
A nurse is caring for a child who has retinoblastoma that has potentially metastasized to the brain. Which of the following diagnostic tests should the nurse anticipate for determining if metastasis of the brain has occurred?
Complete blood cell (CBC) count
Genetic testing
Bone biopsy
Lumbar puncture
Lumbar puncture
A nurse is assessing a child who is in sickle cell crisis. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect?
High fever
Bradycardia
Pain
Constipation
Pain
A nurse is caring for a child on the oncology unit. The child's parents are asking the nurse about the cancer diagnosis. Which of the following information should the nurse provide the parents about the most common malignant renal and intra-abdominal tumor of childhood?
Ewing sarcoma
Osteosarcoma
Neuroblastoma
Wilms' tumor
Wilms' tumor
Wilms' tumor (nephroblastoma) is the most common malignant renal (kidney) and intra-abdominal tumor in children. It usually affects children under age 5 and is often detected by parents as a painless, firm abdominal mass.
❌ Ewing sarcoma – A bone tumor, not a renal or intra-abdominal tumor. Commonly affects the pelvis, femur, or ribs in adolescents.
❌ Osteosarcoma – Also a bone tumor, mostly found in long bones like the femur. Not related to the kidneys or abdomen.
❌ Neuroblastoma – A tumor of the adrenal glands or sympathetic nervous system, often occurring in the abdomen, chest, or spine, but not specifically a renal tumor.
A nurse is caring for a toddler who has von Willebrand disease. The toddler's parents are concerned about the bleeding risk with vaccinations. Which of the following is accurate information the nurse should share with the parents?
Toddlers with von Willebrand disease should only receive vaccines available as nasal sprays to avoid bleeding from intramuscular injections.
Toddlers with bleeding disorders are encouraged to stay up-to-date on vaccinations. The benefit of vaccinations outweighs the risk of bleeding.
Toddlers with bleeding disorders should only receive one vaccine at a time due to the risk of bleeding at injection site.
Toddlers with bleeding disorders should not receive any vaccinations, because the risk of bleeding outweighs the benefit of the vaccinations.
Toddlers with bleeding disorders are encouraged to stay up-to-date on vaccinations. The benefit of vaccinations outweighs the risk of bleeding.
A nurse is providing education to a 10-year-old child newly diagnosed with hemophilia and their parents. The parents state that they are withdrawing their child from participating in any sports or physical activities because they are worried the child will get injured. Which of the following statements made by the nurse is most appropriate?
"You should not allow your child to play any sport due to the risk of injury."
"You should allow your child to participate in age-appropriate activities, such as riding a bike using proper protective gear."
"You should not allow your child to ride a bike or go skateboarding with their classmates."
"You should allow your child to play any sport they want to play."
"You should allow your child to participate in age-appropriate activities, such as riding a bike using proper protective gear."
A nurse is assessing a pediatric client whose diagnostic results indicate that they may have osteosarcoma. Which of the following manifestations should the nurse expect to find?
(Select All that Apply.)
The client has a fractured femur.
The client has an eye that is bulging.
The client reports pain while trying to play sports.
The client has a lump on their body.
The client reports frequent vomiting.
The client has a fractured femur.
The client reports pain while trying to play sports.
The client has a lump on their body.
A nurse is caring for a child who has retinoblastoma and is receiving chemotherapy. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an indication that the child is developing leukopenia from the treatment?
The presence of an acute otitis media infection.
The child's gums bleed whenever they brush their teeth.
The child gets lightheaded when going from a sitting to a standing position.
Large, darkened discoloration to client's skin occurs whenever their blood is drawn.
The presence of an acute otitis media infection.
A nurse is discharging a child who has sickle cell anemia after an acute crisis episode. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching?
"Monitor your child's temperature daily."
"Restrict outdoor play activity to 1 hour per day."
"Offer fluids to your child multiple times every day."
"Apply cold compresses when your child expresses pain."
"Offer fluids to your child multiple times every day."
A nurse in a pediatric clinic is caring for a child who has iron deficiency anemia and a new prescription for ferrous sulfate tablets. Which of the following instructions should the nurse provide the parents regarding administration of this medication
Give with a 240 mL (8 oz) glass of milk.
Administer at mealtimes.
Give with orange juice.
Administer at bedtime.
Give with orange juice.
A nurse is teaching the caregiver of a two-year-old toddler who has cancer about the care the toddler will receive in a specialty pediatric hospital. Which of the following responses by the caregiver demonstrates an understanding of the teaching?
"Children who need hospital admission will receive specialized care related to their illness and developmental level."
"My toddler will receive medical and childcare while my partner and I are at work."
"My toddler will receive first aid and health education while they are here."
"Children here will receive complete developmental screenings at routine intervals."
"Children who need hospital admission will receive specialized care related to their illness and developmental level."
Pediatric hospitals focus on medical treatment and specialized care, not routine childcare for working parents.
First aid and health education are more commonly provided in urgent care settings or community health programs.
A specialty pediatric hospital focuses on specialized treatments, surgeries, and long-term medical care rather than general first aid.
Developmental screenings are usually done by pediatricians during well-child visits, not as a primary service in a specialty hospital.
While developmental assessments may be included in treatment, they are not the hospital’s primary focus.
Iron deficiency anemia is the most preventable mineral disturbance.
A. True B. False
A. True
An aplastic crisis in sickle cell anemia is
A. collection of sickled cells in the venous system resulting in severe pain
B. a temporary decrease in RBC production resulting in extreme anemia
C. excessive pooling of blood in the spleen resulting in splenomegaly
D. increased rate of RBC destruction resulting in anemia, reticulocytosis, and/or jaundice
B. a temporary decrease in RBC production resulting in extreme anemia
An aplastic crisis in sickle cell anemia occurs when bone marrow temporarily stops producing red blood cells (RBCs). This leads to a sudden, severe drop in hemoglobin and can result in life-threatening anemia.
Often triggered by viral infections, especially parvovirus B19.
Can also be caused by severe nutritional deficiencies.
Increased rate of RBC destruction resulting in anemia, reticulocytosis, and/or jaundice
This describes a hyperhemolytic crisis, where excessive RBC breakdown causes severe anemia, jaundice, and high reticulocyte counts.
Hemophilia A is a deficiency in
A. Factor V
B. Factor VIII
C. Factor IX
D. Factor XX
B. Factor VIII
A nurse is educating the family of a client regarding the steps of coagulation cascade. In which order should the nurse provide the steps of coagulation? (Move the steps into the box on the right, placing them in the order of performance. Use all the steps.)
Blood vessel constriction
Platelet adhesion
Platelet activation and aggregation
Clotting factors triggered
Conversion on prothrombin to thrombin
Conversion of fibrin to fibrinogen
1⃣ Blood vessel constriction – Vasoconstriction occurs immediately after injury to minimize blood loss and reduce blood flow to the damaged site.
2⃣ Platelet adhesion – Platelets stick to the damaged vessel wall via von Willebrand factor (vWF), forming the initial plug.
3⃣ Platelet activation and aggregation – Platelets release chemical signals (ADP, thromboxane A2) to attract and activate more platelets, leading to the formation of a platelet plug (primary hemostasis).
4⃣ Clotting factors triggered – The coagulation cascade (intrinsic and extrinsic pathways) is activated, ultimately forming the common pathway.
5⃣ Conversion of prothrombin to thrombin – Prothrombin (Factor II) is converted to thrombin (Factor IIa), a key enzyme that promotes clot stabilization.
6⃣ Conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin – Thrombin converts fibrinogen (Factor I) to fibrin, forming an insoluble fibrin mesh that reinforces the clot (secondary hemostasis).
A nurse is caring for a client who has sickle cell disease, and the parents want clarification on the cause of pain and it's management. Which of the following statements should the nurse include in their education? Select all that apply.
Vaso-occlusion is a major cause of pain in clients with sickle cell disease.
Clients with sickle cell disease who experience pain crisis are always able to treat their pain with oral medications at home.
Clients with sickle cell disease can have acute pain which lasts less than 6 months or chronic pain which lasts longer than 12 months.
The average pain score in clients with sickle cell disease is 7 on a scale of 0 to 10.
Sickle cell crisis is defined by the presence of pain in 6 or more body areas.
Vaso-occlusion is a major cause of pain in clients with sickle cell disease is correct. Vaso-occlusion is a major cause of pain in clients with sickle cell disease and is one of the most common types of acute pain events, also called "sickle cell crisis". Episodes of pain with vaso-occlusion can vary in severity and can be intermittent in presentation.
The average pain score in clients with sickle cell disease is 7 on a scale of 0 to 10 is correct. The median pain scale scores for clients with sickle cell disease is 7 on a scale of 0 to 10, 0 being no pain, and 10 being severe pain.
Sickle cell crisis is defined by the presence of pain in 6 or more body areas is correct. Clients can experience pain in various parts of their body at varying levels. More than half of clients with sickle cell disease who experience "sickle cell crisis", or "pain crisis", report pain in 6 or more areas of the body and described severe pain.
Clients with sickle cell disease can have acute pain which lasts less than 6 months or chronic pain which lasts longer than 12 months is incorrect. Clients can experience acute pain (lasting less than 6 months) or chronic pain (lasting longer than 12 months) in various parts of their body at varying levels. More than half of clients with sickle cell disease who experience "sickle cell crisis", or "pain crisis", report pain in 6 or more areas of the body and described severe pain.
Clients with sickle cell disease who experience pain crisis are always able to treat their pain with oral medications at home is incorrect. Pain is a very common manifestation related to vaso-occlusion. Clients with sickle cell disease may require hospitalization for pain management due to the severity.
A nurse is providing teaching to the parents of a pediatric client who will be undergoing a bone marrow biopsy. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching?
Fasting is not required prior to the procedure.
After the procedure, the sample is viewed under a microscope.
The provider will use a suction catheter to obtain the bone marrow specimen.
The test is used to diagnose iron deficiency anemia.
After the procedure, the sample is viewed under a microscope.
Fasting is recommended prior to a bone marrow biopsy to prevent aspiration.
During a bone marrow biopsy, the provider uses a specialized needle to obtain the bone marrow specimen.
Bone marrow biopsies are used to diagnose aplastic anemia.
The nurse is caring of a 3-year-old client with iron deficiency anemia. The parents are concerned about the child's picky eating habits. Which of the following statements should the nurse provide to help guide the parents during mealtimes? Select all that apply.
"Try to ensure that mealtimes are safe and enjoyable."
"You should continue to offer a wide variety of food options to your child, including fruits and vegetables."
"When introducing new foods, offer small portions."
"You should set the expectation that your child should finish everything on their plate at each meal."
"Maintain a routine for your child during mealtimes."
"You should continue to offer a wide variety of food options to your child, including fruits and vegetables" is correct. It can take 10 to 20 attempts to get a child to try a new food.
"Try to ensure that mealtimes are safe and enjoyable" is correct. Creating a mealtime that is safe and enjoyable is important.
"Maintain a routine for your child during mealtimes" is correct. Maintaining a routine during mealtimes can help to alleviate anxiety associated with meals. Picky eating habits are not likely to resolve on their own and require consistency and patience from the child and the caregiver.
"When introducing new foods, offer small portions" is correct. It can take 10 to 20 attempts to get a child to try a new food, so introducing small portions allows the child to become familiar with the new food item.
"You should set the expectation that your child should finish everything on their plate at each meal" is incorrect. Meals should not be forced if a child is not hungry, as this can lead to anxiety associated with meals.
The nurse is providing care to a school-aged child who has a prescription for desmopressin for treatment of Von Willebrand disease. The nurse provides education to the parents for this new medication. Which of the following statement by the parents indicates an understanding of the precautions while taking desmopressin?
"If my child has a fever, I should give them NSAIDs."
"I should ensure my child restricts fluids for 18 to 24 hours after a dose of desmopressin."
"I should not give my child acetaminophen for pain or fever reduction while receiving desmopressin."
"I should ensure that my child has nothing to eat for 4 hours after a dose of desmopressin."
"I should ensure my child restricts fluids for 18 to 24 hours after a dose of desmopressin."
Desmopressin (DDAVP) is a synthetic form of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) used to increase von Willebrand factor (vWF) and factor VIII levels in patients with von Willebrand disease (Type 1) and mild hemophilia A.
Desmopressin causes water retention, which can lead to hyponatremia (low sodium levels) and fluid overload if fluid intake is not controlled.
The nurse is assessing an adolescent client with sickle cell disease. The parents report that the client has had 3 hospitalizations this year for pain crisis. The nurse identifies that the client is at a greater risk for which of the following psychosocial deficit?
Anxiety and Depression
Functional Impairment
Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD)
Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD)
Functional Impairment
Studies have demonstrated that pediatric clients who experience 3 or more pain crises are more likely to experience functional impairment, such as decreased ability to complete activities of daily living and attend school.
Clients with sickle cell disease can have anxiety and depression, although functional impairment goes beyond just anxiety and depression, and seen in clients who have more than 3 hospitalizations in a year for pain crises.
The nurse is providing discharge instructions to an adolescent client who has immune thrombocytopenia. The nurse educates the client about potential psychosocial and developmental support needs. Which of the following statements made by the client indicates the education provided was understood?
"My schoolwork should not be impacted by my diagnosis."
"I may need additional time to get caught up on schoolwork for missing school."
"I should be able to keep up with my peers during physical activities."
"I should be able to regulate emotions and behavior, as my counterparts in school."
"I may need additional time to get caught up on schoolwork for missing school."
Clients with thrombocytopenia may require additional support in school with accommodation to ensure success The accommodations may be related to missed school for medical visits or hospitalization, including providing additional time to complete assignments.
Clients with immune thrombocytopenia have trouble with emotional and behavioral regulation as well as challenges with executive functioning when compared to healthy children, based on the Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Functioning and Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaires.
A nurse in the emergency department is caring for a toddler who presents with manifestations of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Which of the following laboratory tests should the nurse anticipate being prescribed to verify this diagnosis? Select all that apply.
Electrolytes
Complete blood count
Activated partial thromboplastin time
Liver function tests
Prothrombin time
Fibrinogen test
Complete blood count is correct. A CBC can evaluate blood cell counts including platelets, which would be low in a client with DIC.
Activated partial thromboplastin time is correct. APTT assesses how long the blood takes to clot, which would be prolonged in a client with DIC.
Prothrombin time is correct. PT assesses how long the blood takes to clot, which would be prolonged in a client with DIC.
Fibrinogen test is correct. This test assesses the amount of fibrinogen in the blood, this would be decreased in a client with DIC.
Electrolytes is incorrect. This test is not necessary to rule out DIC and is not typically performed to evaluate bleeding.
Liver function tests is incorrect. This test is not typically performed in cases where DIC is suspected.
A nurse is evaluating an infant for manifestations of iron deficiency anemia (IDA). Which of the following indicators should the nurse use to evaluate the risk for IDA? Select all that apply.
History and physical examination
Complete blood count
Family history
Electrolytes
Focused dietary history
History and physical examination is correct. The history and physical examinations assess for the presence of risk factors for IDA and presence of physical manifestations of IDA.
Focused dietary history is correct. Dietary screening is a tool that can be used to identify the risk of IDA.
Complete blood count is correct. CBC is a simple, cost-effective tool to measure hemoglobin.
Family history is incorrect. Family history is not an indicator for risk of IDA.
Electrolytes is incorrect. Electrolytes are not a part of an evaluation for IDA.
A nurse is caring for an infant client who has sickle cell anemia. The guardian of the infant is seeking advice on steps to reduce the risk of infection for the child. After the nurse provides education, which of the following responses by the guardian indicates an understanding of infection prevention? Select all that apply.
"My child should take prophylactic antibiotics until at least five years of age."
"My child does not need to be on daily prophylactic medication until five years old."
"My child should only receive inactivated vaccines."
"My child should receive the influenza and pneumococcal vaccines annually."
"My child should not receive the influenza vaccine annually."
"My child should receive the influenza and pneumococcal vaccines annually" is correct. Infection prevention should be a focus of health promotion in clients with sickle cell disease. Pediatric clients with sickle cell disease should adhere to the childhood vaccine schedule and receive the influenza vaccine annually, as well as the pneumococcal vaccine.
"My child should take prophylactic antibiotics until at least five years of age" is correct. Clients with sickle cell disease are started on prophylactic penicillin until 5 years of age. Adhering to the prescribed dosage and schedule is an important factor for infection prevention
"My child should only receive inactivated vaccines" is incorrect. Pediatric clients should adhere to the childhood vaccine schedule.
"My child does not need to be on daily prophylactic medication until five years old" is incorrect. Clients with sickle cell disease are started on prophylactic penicillin at least until 5 years of age. Adhering to the prescribed dosage and schedule is an important factor for infection prevention.
"My child should not receive the influenza vaccine annually" is incorrect. Pediatric clients with sickle cell disease should adhere to the childhood vaccine schedule and receive the influenza vaccine annually, as well as the pneumococcal vaccine.
A nurse is reviewing the medical record of a school-aged client who has immune thrombocytopenia. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as a potential cause for this disorder? Select all that apply.
H. Pylori infection
Recent viral infections
Exposure to environmental allergens
Any new foods on the last day
Comorbid autoimmune disorders
Recent contact dermatitis
Recent viral infections is correct. Specific viruses that have been identified as triggers for immune thrombocytopenia include influenza, varicella zoster (chicken pox), HIV, Epstein Barr virus, and COVID-19.
Comorbid autoimmune disorders is correct. Autoimmune disorders such as thyroid disease, lupus erythematosus, and thyroid disease can also cause immune thrombocytopenia.
H. Pylori infection is correct. A bacterial infection that has been linked to immune thrombocytopenia is an H. pylori infection.
Recent contact dermatitis is incorrect. Contact dermatitis might present as urticaria all over the body, not a petechial rash.
Any new foods on the last day is incorrect. Immune thrombocytopenia is not associated with an allergic reaction. An allergic reaction would present as urticaria all over the body, not a petechial rash.
Exposure to environmental allergens is incorrect. Exposure to environmental allergens may cause reactions, such as rhinorrhea, watery eyes, and sneezing. Environmental allergens are not a known trigger for immune thrombocytopenia.
The nurse is caring for a client with hemophilia. The parents ask the nurse to clarify the difference between the inheritance patterns of hemophilia and Von Willebrand disease. Which of the following statements should the nurse make?
Hemophilia is an autosomal recessive disease, and Von Willebrand disease is an x-linked dominant disease.
Hemophilia is an autosomal dominant disease, and Von Willebrand disease is an x-linked recessive disease.
Hemophilia is an x-linked recessive disease and Von Willebrand disease is an autosomal dominant disease.
Hemophilia is an x-linked dominant disease, and Von Willebrand disease is an autosomal recessive disease.
Hemophilia is an x-linked recessive disease and Von Willebrand disease is an autosomal dominant disease.
Hemophilia – X-linked Recessive Inheritance
Only males are usually affected, while females are carriers (since males have only one X chromosome).
Caused by mutations in the F8 (Factor VIII) or F9 (Factor IX) genes, located on the X chromosome.
Von Willebrand Disease (VWD) – Autosomal Dominant Inheritance
Most common inherited bleeding disorder.
Unlike hemophilia, VWD affects both males and females equally because it is autosomal, meaning it is carried on a non-sex chromosome.
Caused by a deficiency or dysfunction of von Willebrand factor (vWF), which helps platelets stick together and stabilize Factor VIII.
A nurse is preparing to discharge a school aged client who was admitted for sickle cell pain crisis. At discharge, the client reports pain in their back as a 3 on a pain scale of 0 to 10. Which of the following interventions should the nurse include when educating the client’s parents about appropriate pain management? Select all that apply.
Over the counter analgesics
Hydration
Ice pack
Deep breathing exercises
Warm compress
Over the counter analgesics
Hydration
Deep breathing exercises
Warm compress
Ice or cold packs should never be used on clients with sickle cell disease as this can induce vasoconstriction, which can subsequently lead to further pain and vaso-occlusion.
A nurse is providing care to a client with immune thrombocytopenia that is experiencing a nosebleed. Identify the sequence the nurse should follow to address the client's nosebleed. (Move the steps into the box on the right, placing them in the order of performance. Use all the steps.)
Apply ice to the bridge of the nose
Tilt the client's head slightly forward
Place client in a seated position
Apply pressure to the nose for up to 20 min
1⃣ Place client in a seated position – This prevents aspiration and promotes comfort.
2⃣ Tilt the client’s head slightly forward – Tilting forward prevents blood from flowing down the throat, reducing the risk of choking or nausea.
3⃣ Apply pressure to the nose for up to 20 minutes – Firmly pinch the soft part of the nose (just below the nasal bridge) to help stop bleeding.
4⃣ Apply ice to the bridge of the nose – Cold therapy causes vasoconstriction, which can help reduce blood flow and control bleeding.
Chemotherapy Side Effects
1. Bone Marrow Suppression
Anemia → Monitor Hgb & Hct, may require blood transfusion.
Neutropenia (↓ WBC count) → Risk of infection:
Fever >100°F = Medical Emergency!
Monitor ANC (Absolute Neutrophil Count):
<1000/mm³ = Risk for sepsis.
Treat with blood cultures & prophylactic antibiotics.
Thrombocytopenia (↓ Platelets) → Risk of bleeding.
2. Risk for Anaphylaxis
Monitor for:
Flushing, rash, urticaria (hives).
Angioedema, difficulty breathing.
Hypotension, nausea/vomiting.
Management:
STOP drug immediately.
Maintain IV line with saline.
Monitor patient closely.
3. Infection Control
Avoid crowded places.
Wear a mask if ANC is low.
Strict hand hygiene.
Visitor restrictions to prevent exposure to illness.
Monitor for fever & signs of infection.
Nausea/Vomiting
Pre-treat with Ondansetron (Zofran), Benadryl, and Dexamethasone.
Hair loss (Alopecia) → Educate that hair will regrow but may look different.
Mucosal ulceration → Painful mouth sores, requires bland, soft diet & mouth rinse.
Neuropathy → Medications like Vincristine can cause:
Constipation (↓ bowel innervation).
Jaw pain.
Foot drop, weakness, numbness.
Hemorrhagic cystitis → Prevent blood in urine with hydration & frequent voiding.
Chemotherapy
Long-term central venous access devices or peripherally inserted central catheters may be used.
Interferes with DNA & RNA production, preventing cell replication.
Targets rapidly dividing cells, both cancerous and normal.
Administer antiemetics before
Allow small, favorite food choices.
Assess the mouth for mucosal ulcers.
Offer cool fluids to prevent dehydration and soothe mucous membranes.
Monitor for side effects.
Ensure routine vaccinations and follow-up care.
Maintain strict infection control practices.
Wilms’ Tumor
Malignant kidney or abdominal tumor.
Typically unilateral (10% are bilateral).
Diagnosed before age 5 (most common in ages 2-3).
Rarely metastasizes.
Wilms’ Tumor S/S
Painless, firm, nontender abdominal mass.
Fatigue, weight loss, fever.
Hematuria (blood in urine).
Hypertension
If metastasized → Dyspnea, cough, chest pain
Wilms’ Tumor Interventions
Diagnostic Tests:
Labs: BUN, creatinine, CBC, urinalysis.
Imaging: Abdominal ultrasound, CT scan, bone marrow aspiration.
Treatment:
Surgical removal of the tumor & kidney.
Chemotherapy & radiation (if bilateral tumors).
Post-op chemo/radiation for large or metastatic tumors.
Nursing Care:
DO NOT PALPATE THE ABDOMEN (prevents trauma to tumor site).
Assess coping/support for child & family.
Monitor growth, development, & infection risk.
Provide emotional support (avoid false reassurance).
Neuroblastoma
Malignant tumor of the adrenal gland, sympathetic chain, head, neck, pelvis, or chest.
95% diagnosed before age 10 (median age: 19 months).
More common in males.
50% of cases have metastasized before diagnosis
Difficult to detect beforehand
Neuroblastoma S/S
Palpable abdominal mass.
Weight loss, constipation, anorexia.
Diaphoresis, hypertension.
If metastasized → Jaundice, dark skin nodules, dyspnea, facial/neck edema.
Neuroblastoma Interventions
Diagnostic Tests:
Labs: CBC, coagulation studies, urine catecholamines.
Imaging: Skeletal survey, CT scans (skull, chest, abdomen), bone marrow biopsy.
Treatment:
Surgical tumor removal.
Chemotherapy & radiation for metastasis.
Nursing Care:
DO NOT PALPATE the abdomen.
Monitor for infection (neutropenic precautions)
Support child & family (discuss grief & prognosis).
Provide diversional activities (age-appropriate).
Radiation Therapy
Delivered in divided doses over weeks.
Targets fast-growing cells, including cancer and healthy cells.
Common side effects: Skin irritation, nausea, fatigue, long-term organ damage
Nursing Actions
Wear lead aprons
Educate and support the child and family
Client Education
Do not wash off site markings.
Wash marked areas with lukewarm water, using hands (not washcloths), and pat dry.
Avoid hot/cold water, soaps, creams, lotions, and powders unless prescribed.
Wear loose cotton clothing.
Protect the area from sun exposure with hats and long sleeves.
Seek medical care for blisters, weeping, or red/tender skin.
Who Can Administer Chemotherapy?
Only certified nurses can give chemotherapy.
If you’re not certified, you must call the oncology team.
Risks of Chemotherapy
Vesicants: Cause severe tissue damage if leaked from IV.
Anaphylaxis: Severe allergic reaction requiring immediate intervention.
Hypersensitivity Reactions: Itching, hives, difficulty breathing, hypotension.
Managing Chemotherapy Hypersensitivity
Pre-medications: Tylenol, Benadryl, Steroids.
STOP infusion immediately if reaction occurs.
Monitor for fever & other symptoms.
Leukemia
Most common childhood malignancy.
Cancer of the blood that develops in the bone marrow.
Causes increased immature WBCs, which crowd out normal cells.
↓ RBCs → Anemia.
↓ WBCs (Neutropenia) → Infection Risk.
↓ Platelets (Thrombocytopenia) → Bleeding & Bruising.
Infiltration of organs leads to:
Liver, spleen, lymph node fibrosis.
CNS involvement → ↑ Intracranial pressure.
Other affected organs:Testes, prostate, ovaries, GI tract, kidneys, lungs.
Peak onset: 2-5 years.
Higher risk in:
Boys (more than girls).
Family history of leukemia.
Down Syndrome.
Leukemia S/S
Early vague symptoms: Fatigue, anorexia, headache.
Physical Signs:
Low-grade fever.
Pallor, increased bruising/petechiae.
Listlessness, enlarged liver/lymph nodes/joints.
Bone & joint pain.
Vomiting, unsteady gait.
Enlarged kidneys/testicles (late-stage).
Signs of ↑ ICP (intracranial pressure).
Leukemia Interventions
Chemotherapy:
Vesicants (irritating drugs) → Risk of extravasation (tissue damage).
Use of implanted port (Port-a-Cath) to reduce vein damage.
Anaphylaxis risk → Pre-medicate with Tylenol, Benadryl, steroids.
Cranial Radiation (for CNS involvement):
Side Effects: Fatigue, skin burns.
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT):
Possible cure (60-70%).
Risks:
Graft-vs-Host Disease (GVHD).
Infection risk.
Severe organ damage.
Implement protective isolation:
Private, positive-pressure room.
HEPA-filtered air, minimum 12 air exchanges/hr.
No fresh flowers, dried plants, or potted plants.
Wear a mask, gloves, and gowns.
Client Education
Increased risk for infection and bleeding until transplanted stem cells grow.
Bone Marrow Aspiration/Biopsy
(Definitive Test Leukemia Test)
Findings: Excess leukemic blast cells.
Common Site: Posterior iliac crest (tibia in infants <18 months).
Nursing Actions:
Apply topical anesthetic (45 min-1 hr before).
Assist with conscious sedation (propofol).
Apply pressure dressing post-procedure.
Monitor for bleeding & infection (24 hrs).
Other tests include
CSF Analysis
Liver and Kidney Function studies
Leukemia Chemotherapy Treatment Phases (3)
Induction/Remission Therapy: Achieve complete remission (<5% leukemic cells in bone marrow).
Intensification Therapy (Consolidation): Eliminate remaining leukemic cells and prevent resistance.
Maintenance Therapy: Sustain remission; requires frequent CBC monitoring.
Osteosarcoma
Commonly affects metaphysis (end) of long bones (Femur).
Adolescents at peak risk.
Treatment:
Amputation or limb salvage.
Chemotherapy.
Osteosarcoma Interventions
Single or combination therapy before and/or after surgery.
High-dose methotrexate with citrovorum factor rescue, doxorubicin, cisplatin, ifosfamide, etoposide.
Nursing Actions
Administer antiemetics before treatment to control nausea/vomiting.
Monitor and manage adverse effects of chemotherapy.
Client Education
Watch for infection, skin breakdown, and nutritional deficiency.
Maintain good hygiene.
Understand proper use of vascular access devices.
Follow bleeding precautions and manage active bleeding properly.
Ewings Sarcoma
Affects the shaft of long bones/trunk bones.
Common in Caucasian children under 20 years.
Treatment:
Radiation (main treatment).
Chemotherapy (no amputation)
Biopsy
Ewings Sarcoma Interventions
Vincristine, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide
Alternating with ifosfamide and etoposide.
Nursing Actions
Administer antiemetics before treatment to control nausea/vomiting.
Monitor and manage adverse effects of chemotherapy.
Client Education
Watch for infection, skin breakdown, and nutritional deficiency.
Maintain good hygiene.
Understand proper use of vascular access devices.
Follow bleeding precautions and manage active bleeding properly.
Surgical Interventions for Bone Tumors
Surgical Biopsy
Tumor biopsy under anesthesia to determine cancer type.
Nursing Actions:
Provide preoperative and postoperative care.
Ensure adequate pain relief.
Monitor for infection signs.
Conduct vital signs and wound care assessments.
Educate on post-procedure care
Limb Salvage Procedure (Bone & Joint Replacement)
Preoperative chemotherapy shrinks the tumor before surgery.
Nursing Actions:
Administer preoperative chemotherapy.
Manage adverse effects.
Provide postoperative care and pain relief.
Understand postoperative care.
Be aware of chemotherapy side effects (hair loss).
Limb Amputation
Chemotherapy may be given before and after amputation.
Nursing Actions:
Provide preoperative and postoperative care.
Offer emotional support.
Assess and medicate for phantom limb pain.
Help plan clothing adjustments for prosthesis use.
Prepare for temporary prosthesis fitting post-surgery.
Cooperate with physical therapy.
Role-play scenarios (e.g., explaining the prosthesis to others).
Recognize that anger and grief are normal responses.
Rhabdomyosarcoma
Malignant tumor in skeletal muscle.
Most common soft tissue sarcoma in children.
Frequently affects:
Head, neck, orbit of the eye.
Diagnostics:
MRI, CT, Biopsy (assess metastasis).
Treatment:
Surgery + Chemotherapy + Radiation.
Rhabdomyosarcoma S/S
CNS: Impaired cranial nerve function, stiff neck.
Orbit: Proptosis (bulging eye), bruising.
Nasopharynx: Stuffy nose, pain, nasal obstruction, epistaxis.
Middle Ear: Chronic otitis media, pain, facial paralysis.
Perineum: Bowel/bladder obstruction.
Extremities: Pain, palpable fixed mass.
Rhabdomyosarcoma Interventions
Medications
Chemotherapy: Vincristine, actinomycin D, cyclophosphamide, ifosfamide, topotecan, irinotecan, doxorubicin (given for ~1 year).
Therapeutic Procedures: Localized Radiation Therapy
Used with chemotherapy and surgery.
Surgical Interventions: Surgical Biopsy
Tumor is biopsied under anesthesia to confirm cancer and determine tissue type.
Complications of Radiation in Bone/Tissue Tumors
Pelvic irradiation can cause sterility and secondary cancers.
Palliative Care
Focuses on symptom management & quality of life.
Used when cure is not possible.
Support for child & family.
Hospice Care
Specialized care for end-of-life
Pain control & comfort.
Support family’s grieving process.
Nursing Interventions for End-of-Life Care
Supporting the Child and Family
Allow anticipatory grieving to help the family cope.
Ensure consistency in nursing staff to provide stability.
Encourage guardians to stay with the child.
Maintain a normal, comfortable environment.
Communicate honestly and respectfully.
Promote the child's independence when possible.
Encourage the child to complete unfinished tasks.
Assist with religious or cultural rituals.
Offer emotional support and privacy.
Pain and Comfort Management
Administer analgesics to control pain.
Use soft lighting, quiet music, and calming measures.
Provide comfort items like favorite blankets or toys.
No concept of death, mirror parental emotions.
Egocentric thinking
May regress in behavior
Infants/Toddlers (0-3)
View death as temporary (magical thinking)
May feel guilt (believe they caused death)
Interpret separation as punishment
Preschool (3-6)
Understands death is permanent, curious about afterlife, may fear being alone.
Fear disease, death, and loss of control
May act out or resist cooperation
School (6-12)
Adult-like concept, struggle with acceptance, body image concerns.
Experience guilt and shame
May avoid expressing emotions
Adolescents (12-20)
Nursing Self-Care Strategies
Express personal grief.
Take breaks & maintain general health.
Develop empathy.
Join support groups.
Attend funeral services if desired.
Maintain contact with the family.
Use mindfulness techniques.