Unit 4: Cells and Cellular Transport
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Archaea
Single celled organism that live in extreme conditions
Bacteria
Single celled organisms found in nearly every environment
Eukarya
Organisms whose cells have a nucleus enclosed within membranes
Eukaryotes
Have nucleus
Membrane-bound organelles
Large
Multiple and linear chromosomes
Reproduction sexually and asexually
EX: Plants, Fungi, Animals, Protists
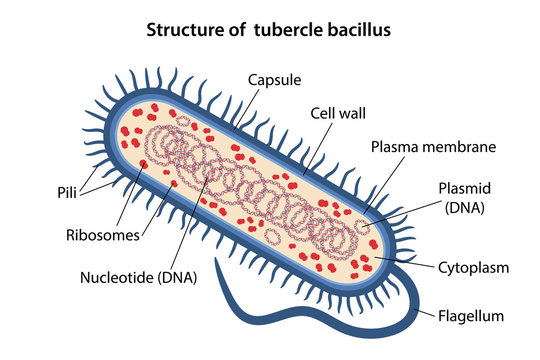
Prokaryotes
No nucleus
Smaller
Circular chromosomes
Asexual
Cell wall
EX: Bacteria, Archaea
Coccus
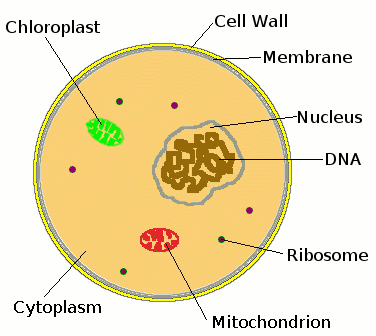
Baccillus
Animal Cells
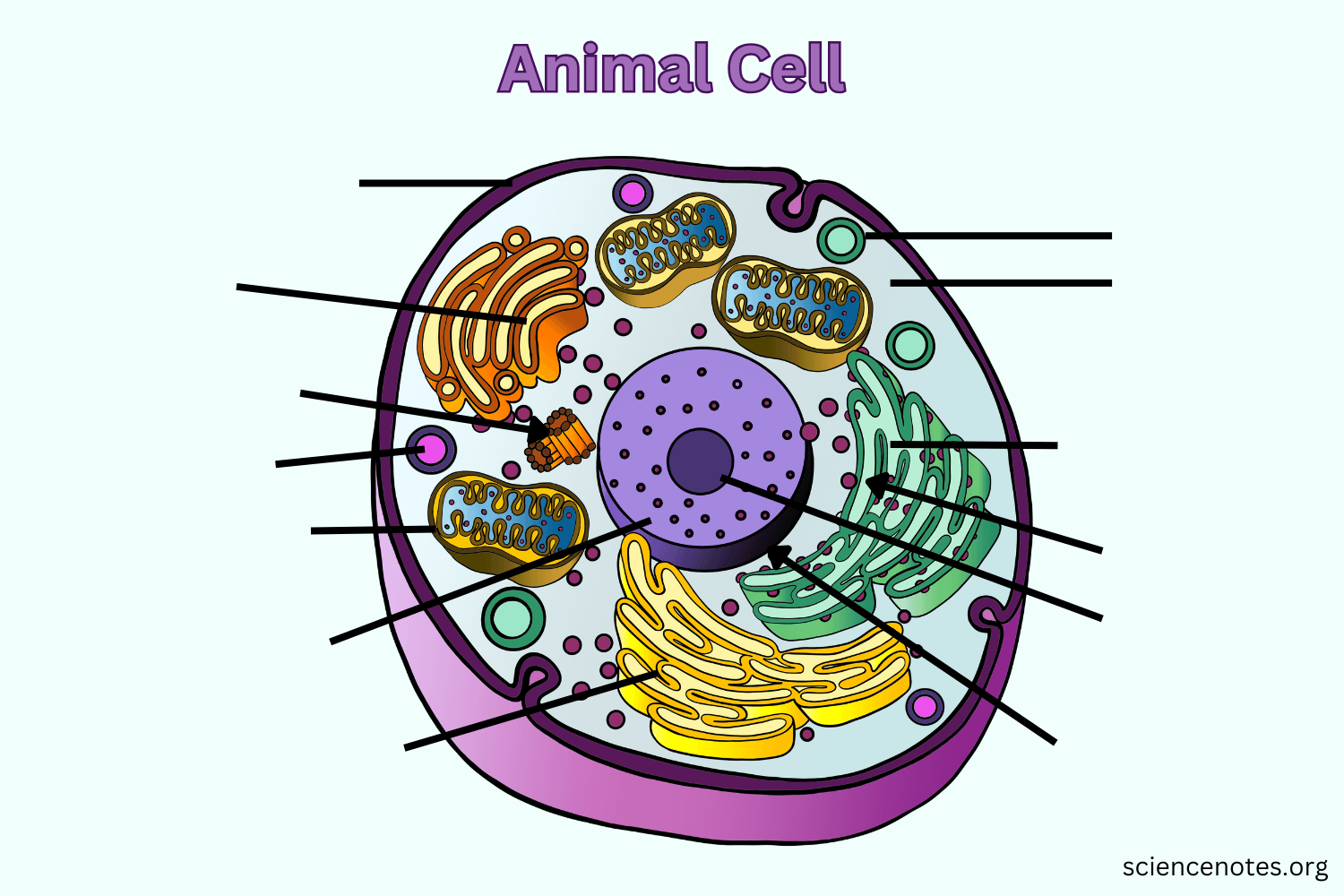
Cell membrane, Nucleus, DNA, Cytoplasm, ER, Ribosomes, Lysosomes, Mitochondria, Vesicle, Golgi
Plant Cell

Cell membrane, Cell Wall, DNA, Chloroplast, Cytoplasm, ER, Ribosomes, Mitochondria, Vesicle, Golgi, Vacuole, Cell Wall
Cell Membrane
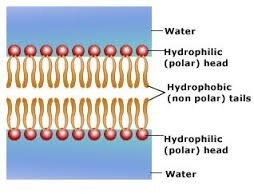
Regulates what enters and exits cells
A hydrophobic barrier → Gasses, hydrophobic molecules, and small polar molecules can go through cell membrane
Large polar molecules must use transport Proteins
Ribosomes
Site of protein synthesis
Cytoplasm
Gel-like fluid in the cell
DNA
Genetic information for cell
Mitochondria
Generates ATP for the cell
Golgi Body
Finalizes proteins, packaging final proteins and lipids into vesicles
Lysosome
A type of Vesicle that contains digestive enzymes
Rough ER
Makes changes to and folds proteins
Smooth ER
Makes lipids
Cytoskeleton
Supports structure of cell and helps transport vesicles
Chloroplast
Converts light energy into chemical energy
Central Vacuole
Supports shape of plant cells, storing water and nutrients
Flagella/Cillia
Hair link on cell surface for movement
Transport Proteins
Allows large molecules or large amounts of small molecules pass through cellular membrane
Glycoproteins
Recognizes self cells vs viruses and alerts the immune system
Receptor Protein
Bind to specific molecules, which signal molecules like hormones, neurotransmitters, or growth factors
Phagocytosis
Food enters the cell through a Vesicle
Pinocytosis
Liquid enters cell through Vesicle
Exocytosis
Molecules in a Vesicle leave the cell
Diffusion
When particles spread out evenly in an available spaces
Particles go from a high to low concentration until equilibrium
No energy is needed (passive transport)
Simple Diffusion
Particles go straight through membrane
Facilitated Diffusion
Particles go through a protein channel
Active Transport
Substances moving against concentration gradient, energy is required
Osmoregulation
How organisms maintain water balance
Tenocity
The ability of a solution to cause a cell gain/lose water '
Solutes cant pass cell membrane
Water diffuses
Flow is always from high to low
Isotonic
Same amount of solutes outside and inside of cell
Hypotonic
More water outside of cell
Water enters cell
Hypertonic
More water inside cell
Water leaves cell
Why are cells small
It helps them exchange materials faster with their environment. A higher surface area-to-volume ratio makes them more efficient.