Neur200 UMD Exam 1
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
autonomic nervous system
the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart). Its sympathetic division arouses; its parasympathetic division calms.
somatic nervous system
the division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body's skeletal muscles
enteric nervous system
The nervous system of the gastrointestinal tract. It controls secretion and motility within the Gi tract, and is linked to the central nervous system.
central nervous system
consists of the brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body
nervous system cell types
neurons and glial cells
CNS processing
Information processing occurs at every relay synapse. Sensory information may be distributed to multiple nuclei and centers in the spinal cord and brain
Microbiome
all of the microorganisms that live in a particular environment, such as a human body
vagus nerve
the tenth cranial nerve that innervates digestive organs, heart and other areas
brain
The mass of nerve tissue that is the main control center of the nervous system
sympathetic nervous system
a set of nerves that prepares the body for action in challenging or threatening situations
parasympathetic nervous system
a set of nerves that helps the body return to a normal resting state
skull
cranium
dura mater
thick, outermost layer of the meninges surrounding and protecting the brain and spinal cord
arachnoid mater
middle layer of the meninges
subarachnoid space
a space in the meninges beneath the arachnoid membrane and above the pia mater that contains the cerebrospinal fluid
pia mater
thin, delicate inner membrane of the meninges
meninges
three protective membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
plasma-like clear fluid circulating in and around the brain and spinal cord
CSF functions
buoyancy, protection, chemical stability
stem cells
unspecialized cells that are able to renew themselves for long periods of time by cell division
neurogenesis
the development of new neurons
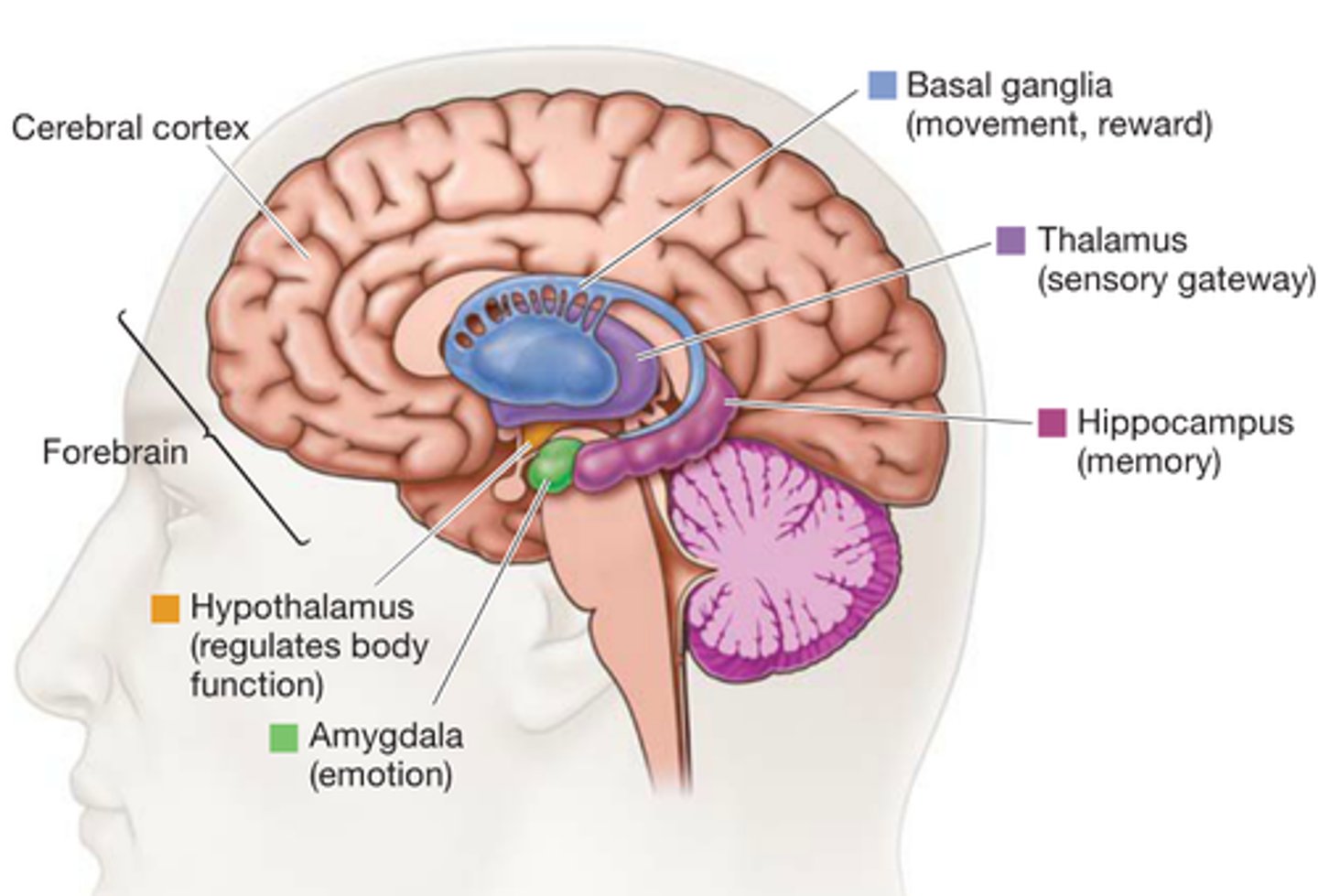
Hippocampus
A neural center located in the limbic system that helps process explicit memories for storage.
syncytium
A large multinucleate cell, typically formed by the fusion of many smaller cells during development (e.g. a skeletal muscle cell), or formed by nuclear division in the absence of cellular division.
Neuron Doctrine
The hypothesis that the brain is composed of separate cells that are distinct structurally, metabolically, and functionally.
Neuron vs. Nerve
- neuron - a single cell
- nerve - a large bundle of many different axons from different neurons
Glia
cells found throughout the nervous system that provide various types of support for neurons
Glia functions
provide support, structure, and nourishment for neurons; participate in communication
intracellular homeostasis
Gradients of ions/metabolites along cellular membrane
extracellular homeostasis
A constant glomerular filtration rate allows the kidneys to make filtrate and maintain _____________ _____________.
blood-brain barrier
Blood vessels (capillaries) that selectively let certain substances enter the brain tissue and keep other substances out
Dopamine
influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion
L-dopa
A drug for Parkinson's disease that contains the precursors to dopamine so that once it is in the brain, it will be converted to dopamine.
immune system
A system (including the thymus and bone marrow and lymphoid tissues) that protects the body from foreign substances and pathogenic organisms by producing the immune response
footplates
astrocytes
Brain metabolism
[bioenergetics and regulation of metabolism] uses glucose except in prolonged starvation where it uses ketolysis
Glucose
the form of sugar that circulates in the blood and provides the major source of energy for body tissues. When its level is low, we feel hunger.
myelin sheath
A layer of fatty tissue segmentally encasing the fibers of many neurons; enables vastly greater transmission speed of neural impulses as the impulse hops from one node to the next.
Ventricles
Lower chambers of the heart
cerebral aqueduct
connects the third and fourth ventricles
choroid plexus
A highly vascular portion of the lining of the ventricles that secretes cerebrospinal fluid.
neuron
a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system
unipolar, bipolar, multipolar
structural classification of neurons
synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
presynaptic terminal
(end bulb or bouton) point where an axon releases chemicals
postsynaptic
referring to the region of a synapse that receives and responds to neurotransmitter
Dendrite
the bushy, branching extensions of a neuron that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body
dendritic spines
short outgrowths that increase the surface area available for synapses
Soma
cell body of a neuron
Axon
the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands
Information flow in a neuron
dendrite, cell body, axon, terminal
spinal cord
Nerves that run up and down the length of the back and transmit most messages between the body and brain
spinal nerves
31 pairs of nerves arising from the spinal cord
dorsal and ventral roots
fuse laterally to form spinal nerves
dorsal root ganglia
contain cell bodies of sensory neurons
afferent, efferent
Some ___ neurons are specialized to detect stimuli, whereas ____ neurons send signals to the effectors of the nervous system.
Interneurons
neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs
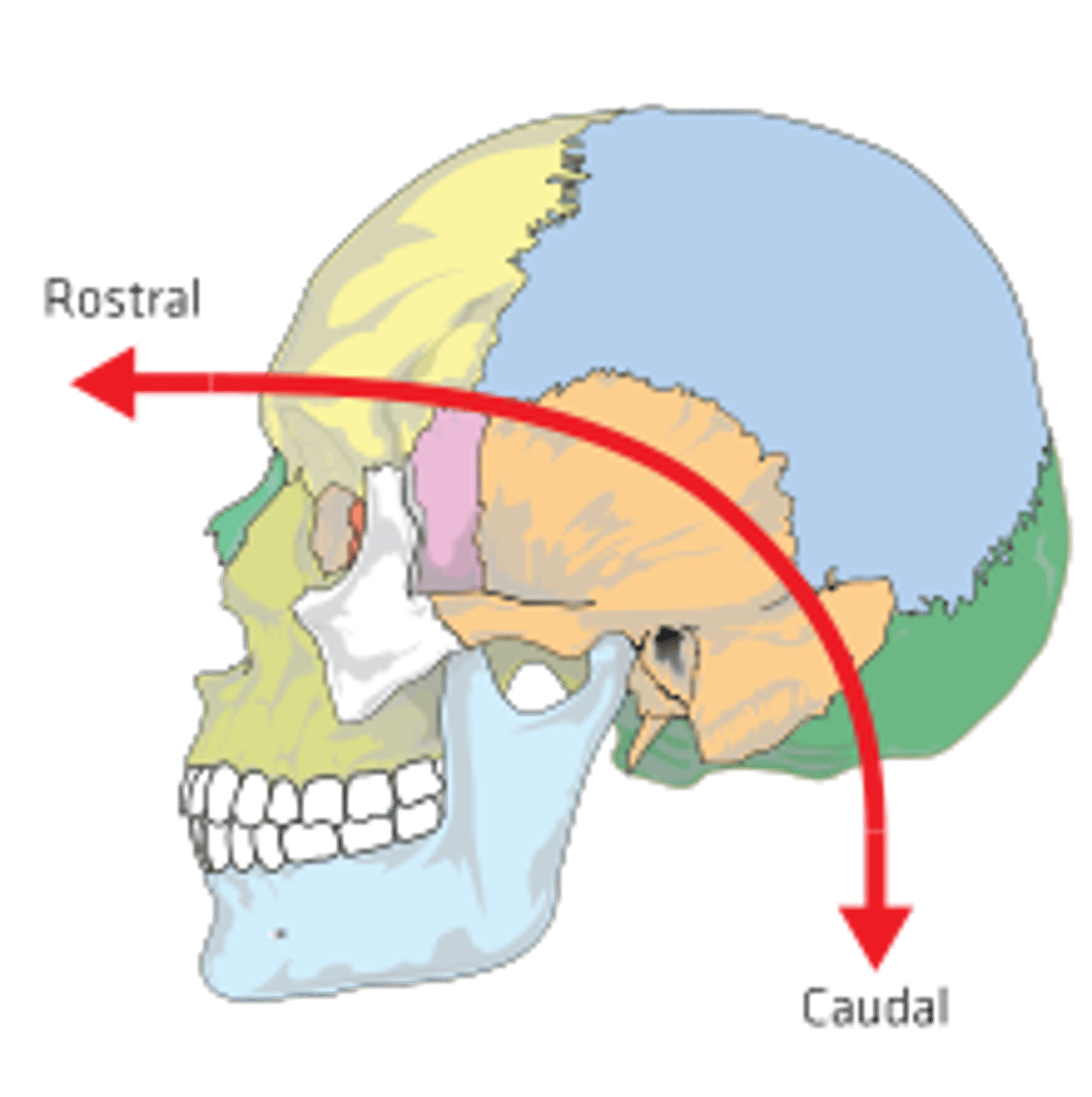
Caudal/Rostral
toward the tail, away from the head
medial/lateral
toward the midline/away from the midline
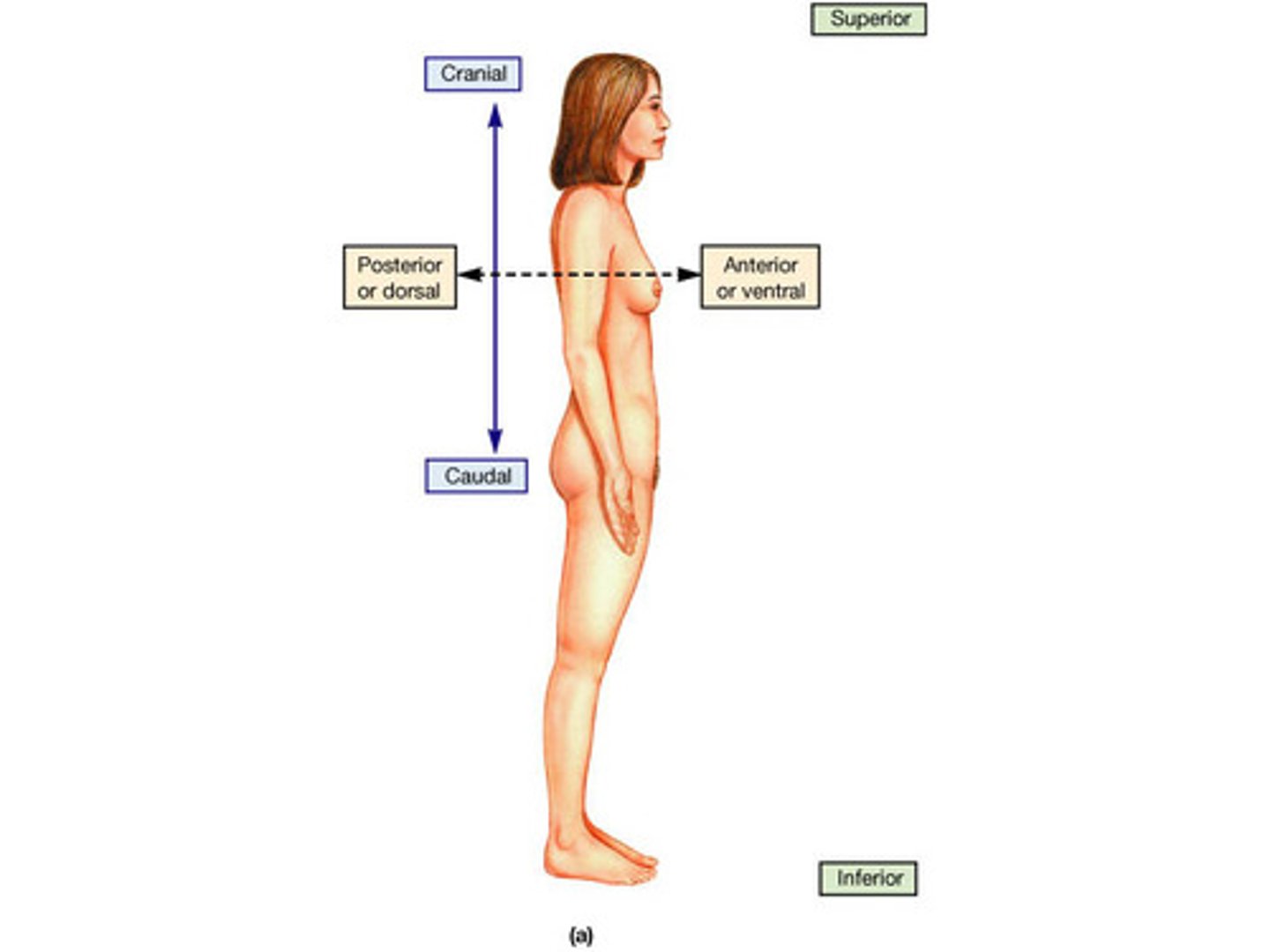
dorsal/ventral
backside/belly side
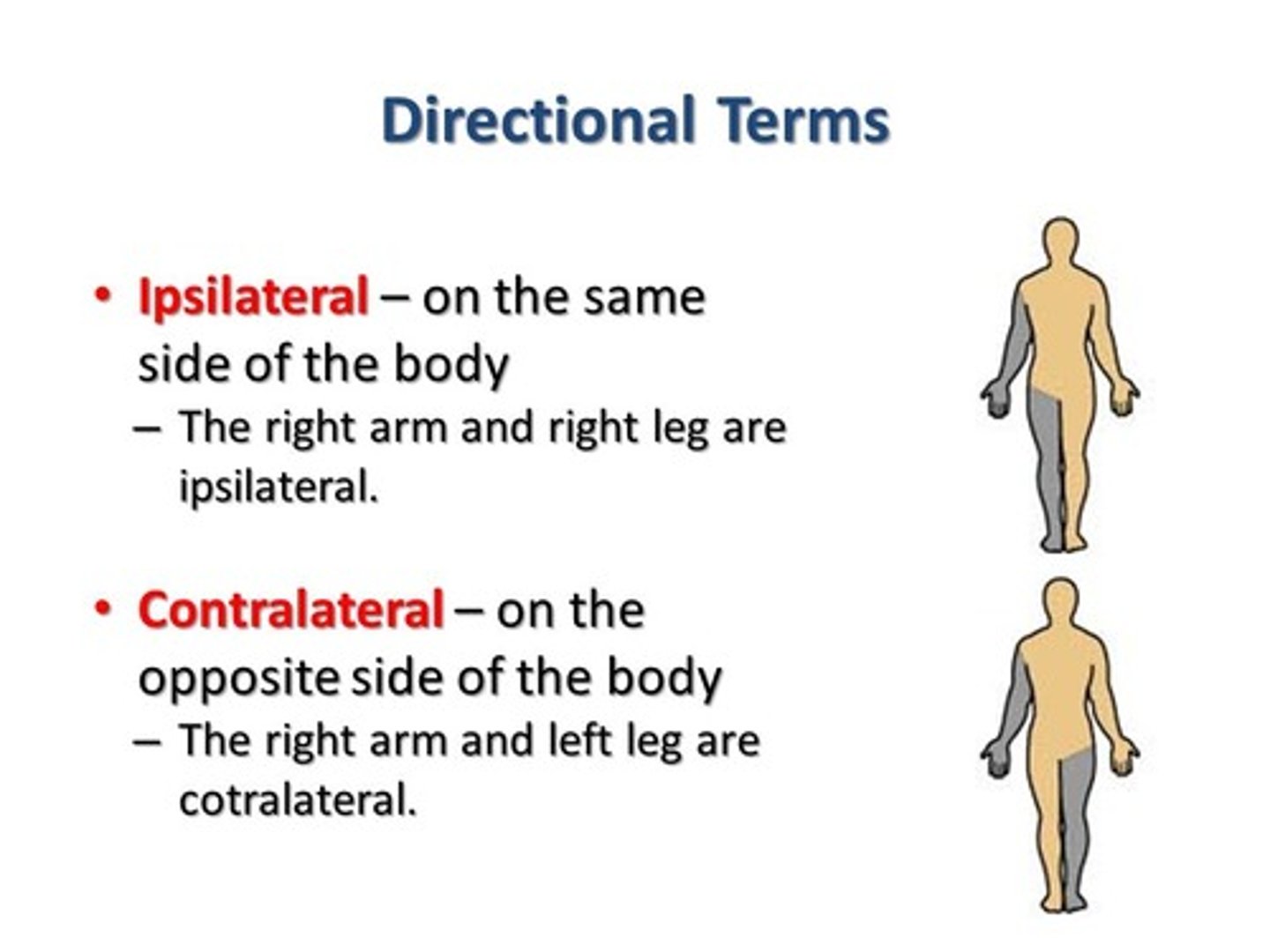
ipsilateral/contralateral
same side/opposite side
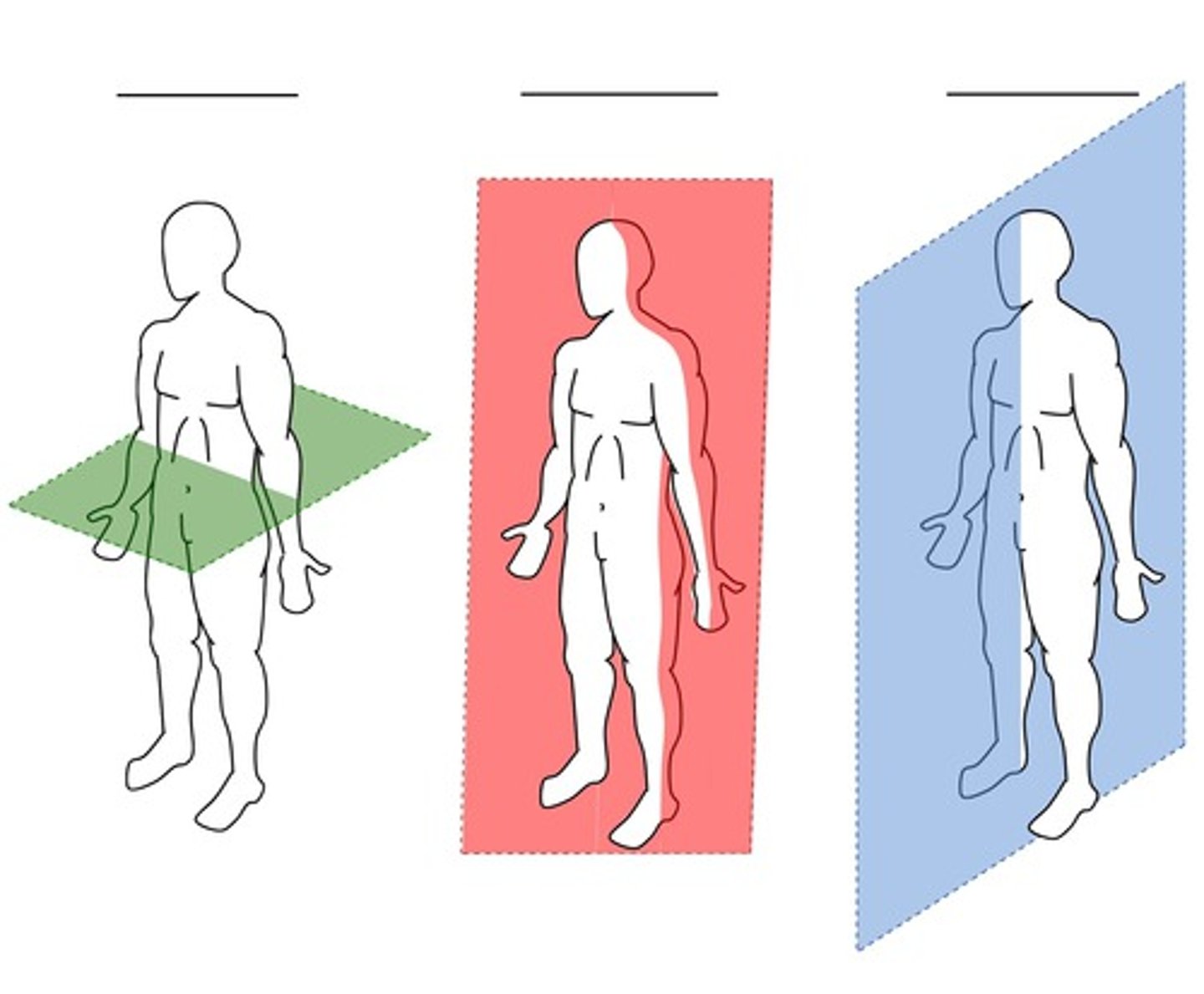
sagittal, frontal, transverse
3 body planes
bilateral symmetry
Body plan in which only a single, imaginary line can divide the body into two equal halves.

nucleus
A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction
Brainstem
the oldest part and central core of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull; the brainstem is responsible for automatic survival functions
Medulla
the base of the brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing
Pons
A brain structure that relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
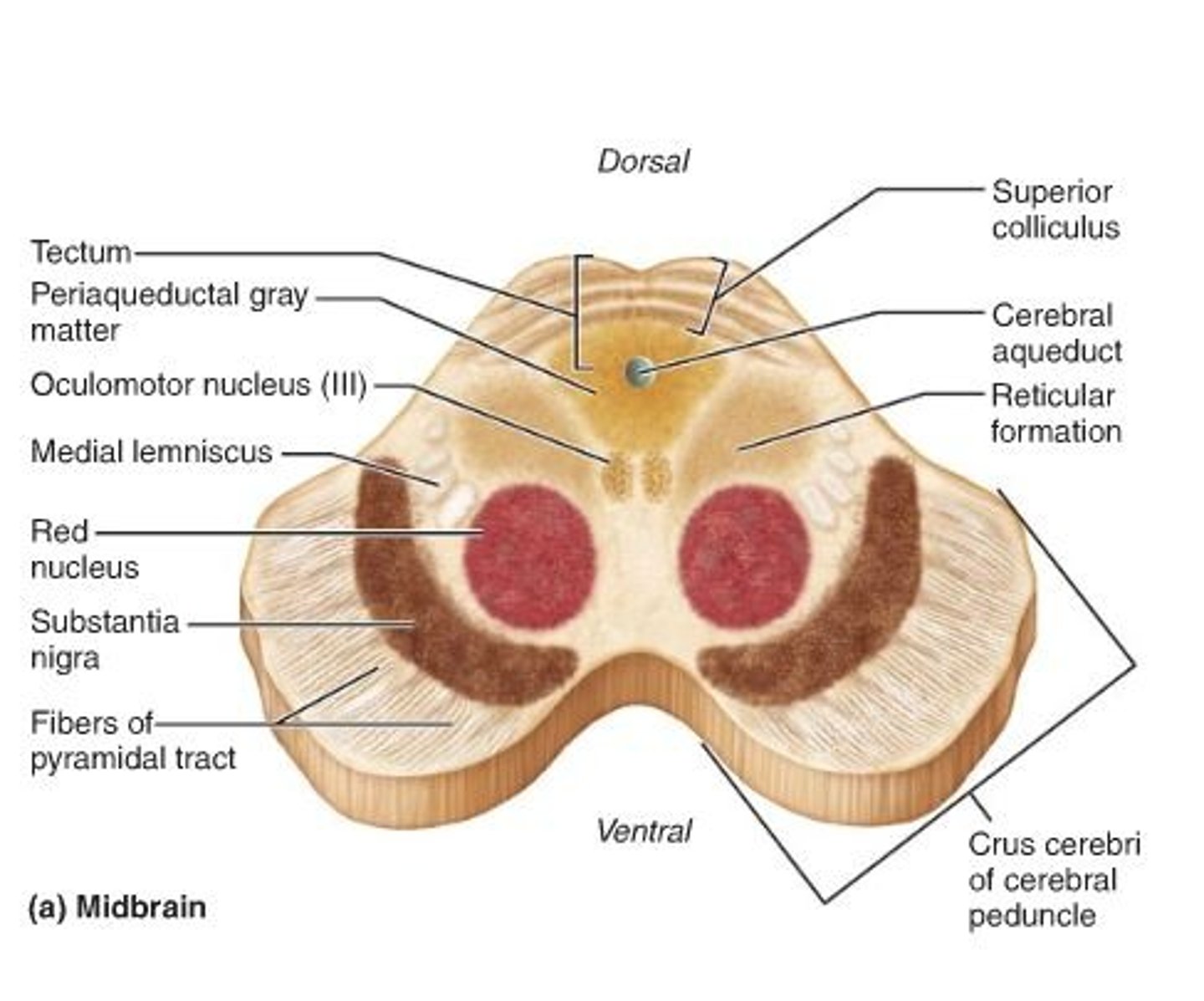
Midbrain
A small part of the brain above the pons that integrates sensory information and relays it upward.
Diencephalon
thalamus and hypothalamus
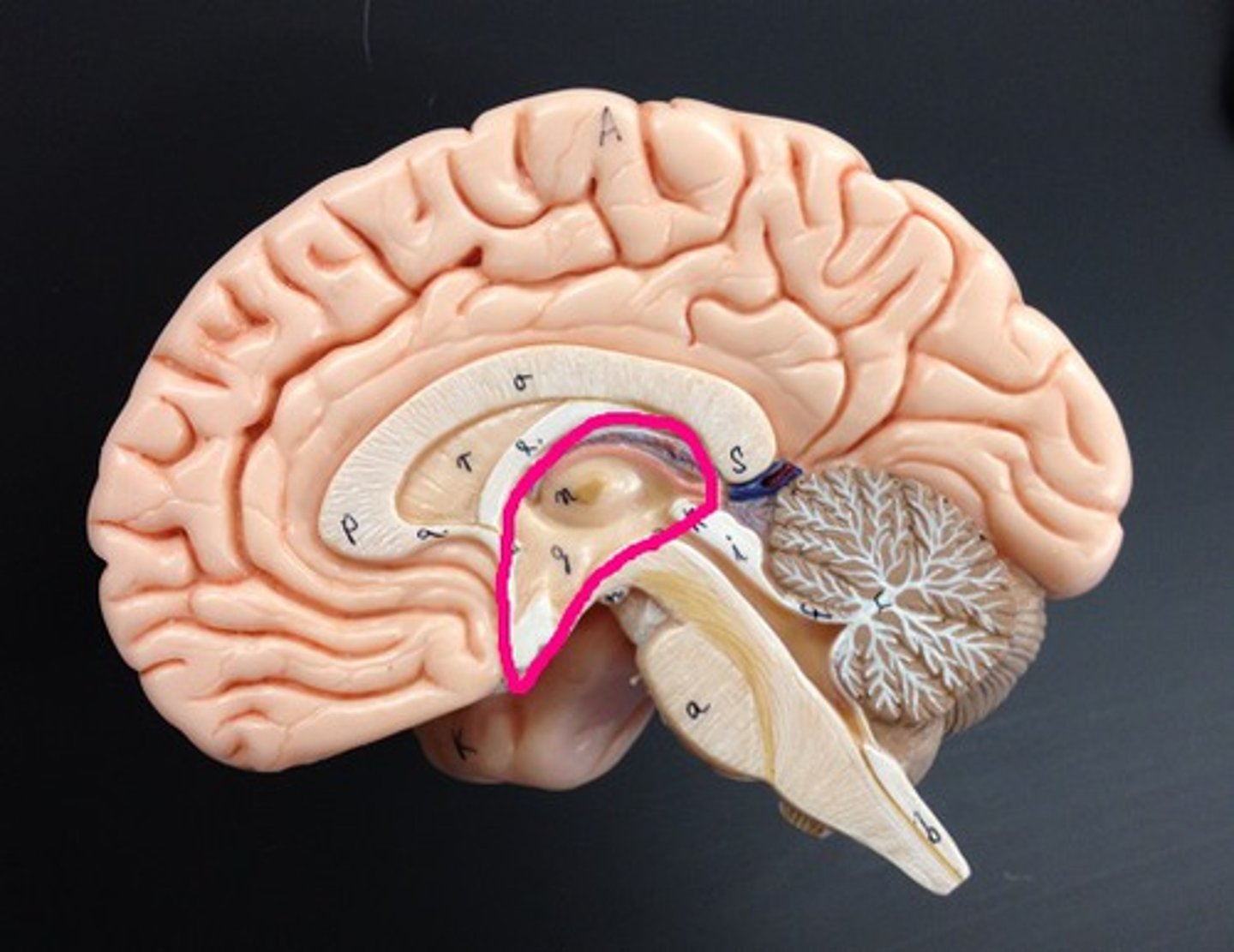
Telencephalon
cerebrum
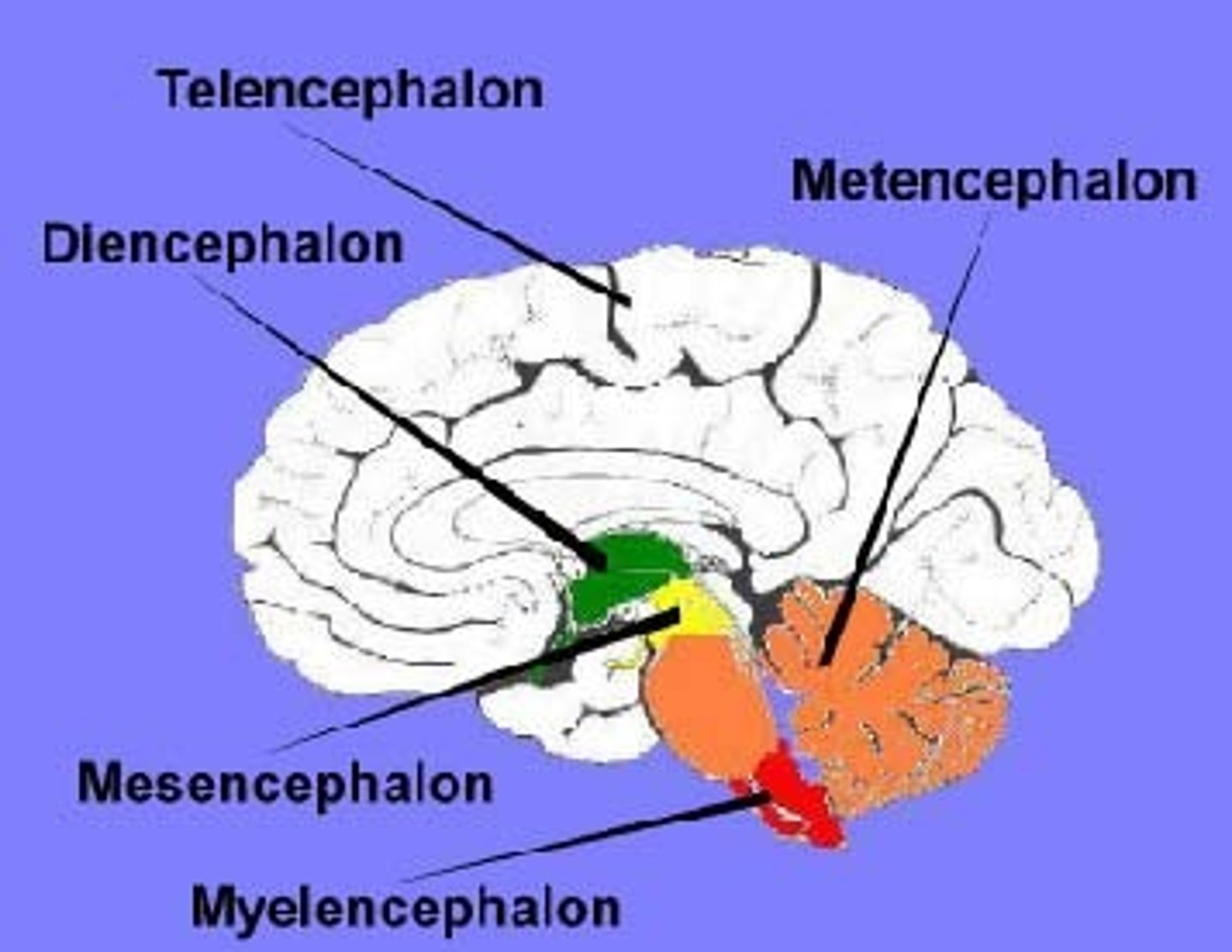
Thalamus
the brain's sensory switchboard, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
Hypothalamus
A neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward.
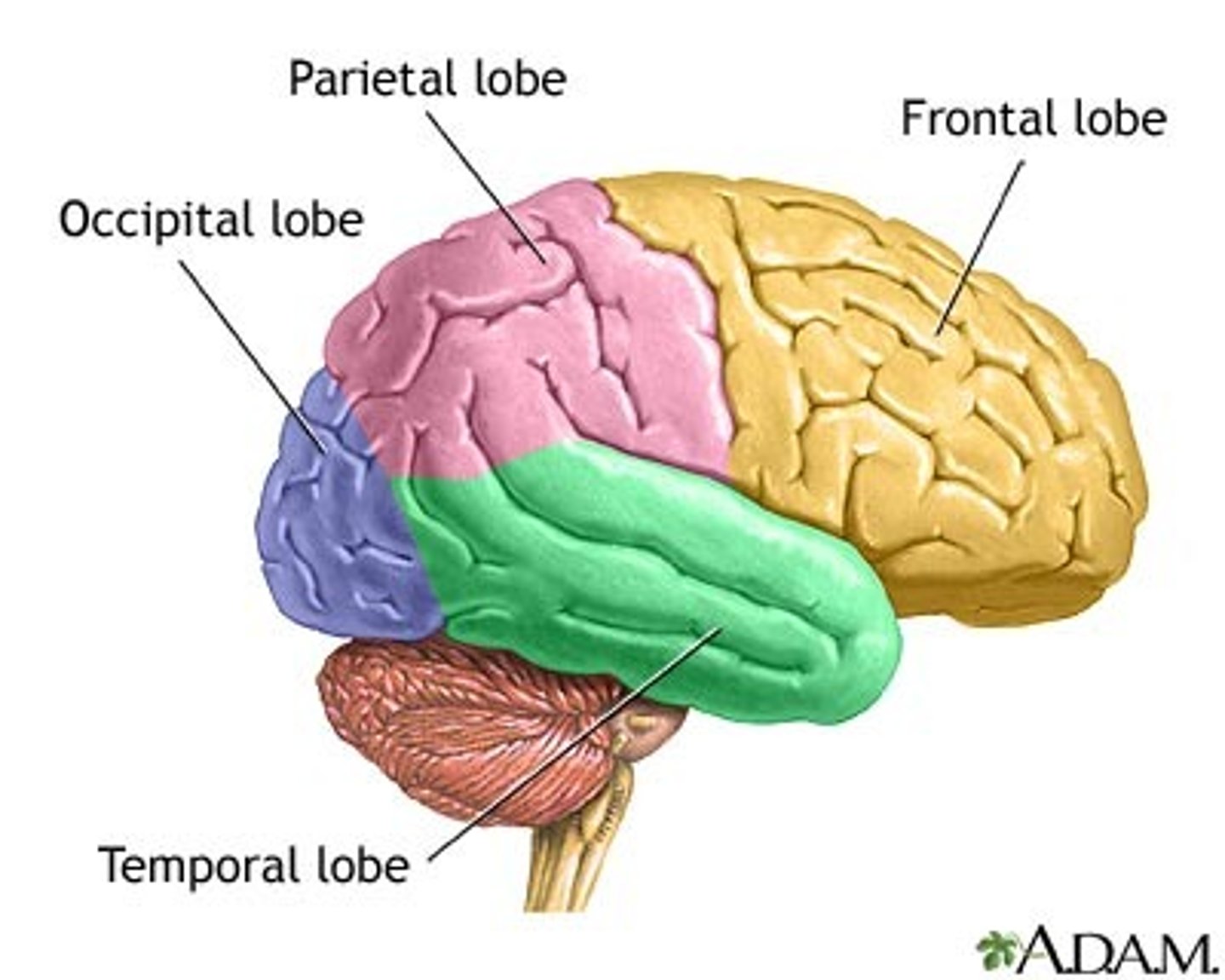
Lobes of the brain
frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal
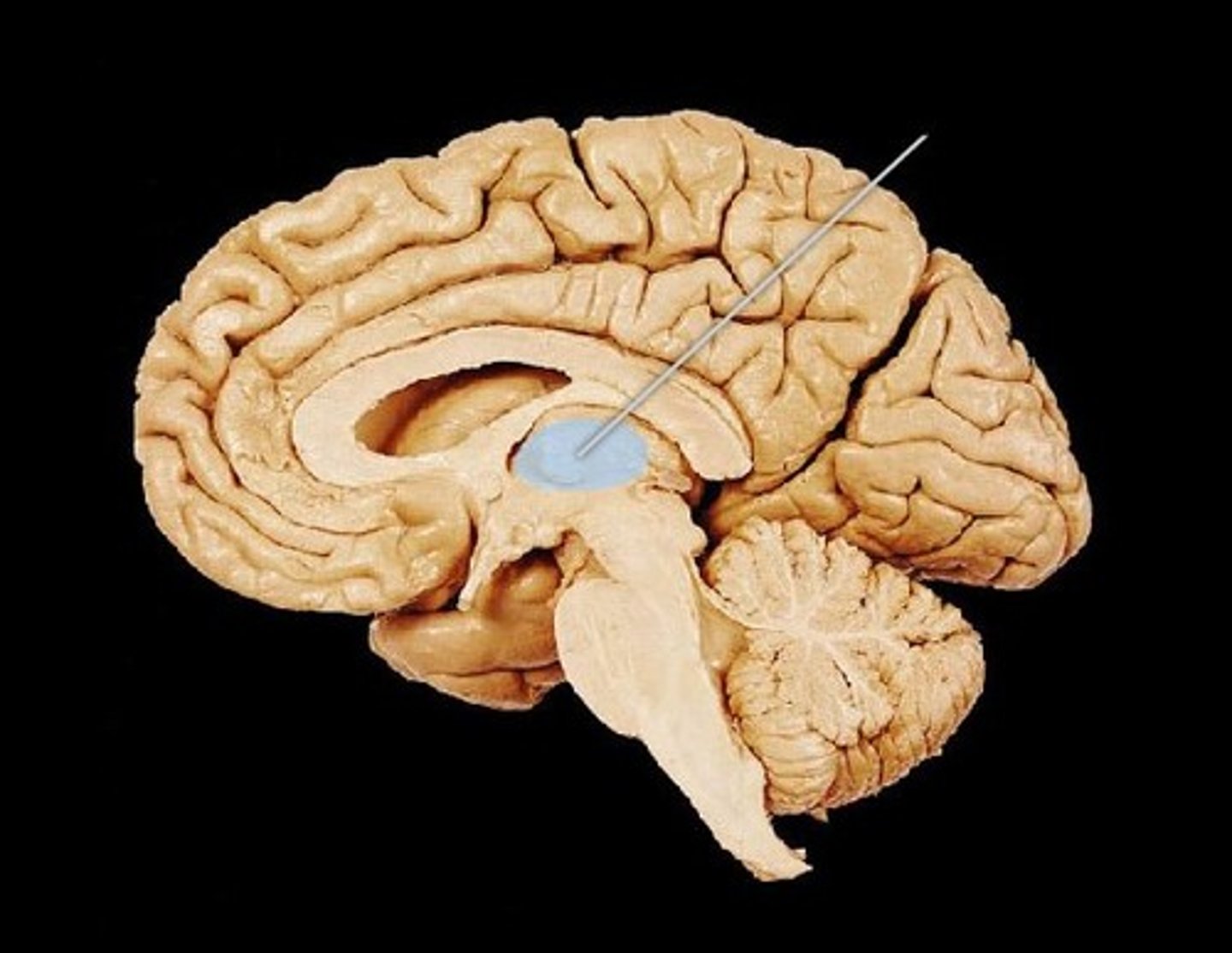
subcortical structures
areas of the forebrain housed under the cerebral cortex near the very center of the brain
association cortex
regions of the cerebral cortex that integrate simpler functions to perform more complex functions
cognitive skills
A leader's ability to understand the internal and external environments, make decisions with sound reasoning, and communicate effectively
control of attention
the increasing ability to tune into certain stimuli, while tuning out others
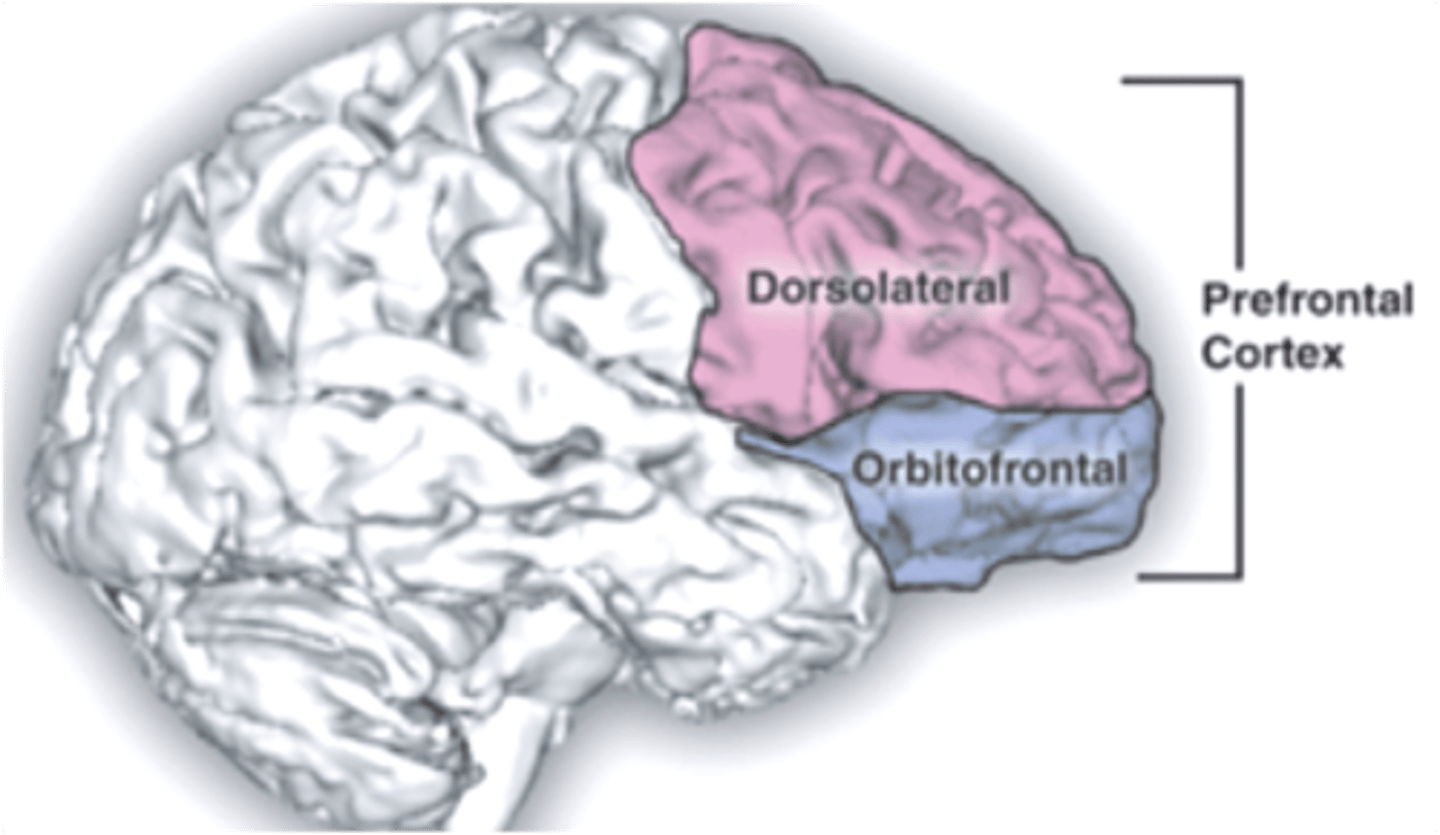
prefrontal cortex
part of frontal lobe responsible for thinking, planning, and language
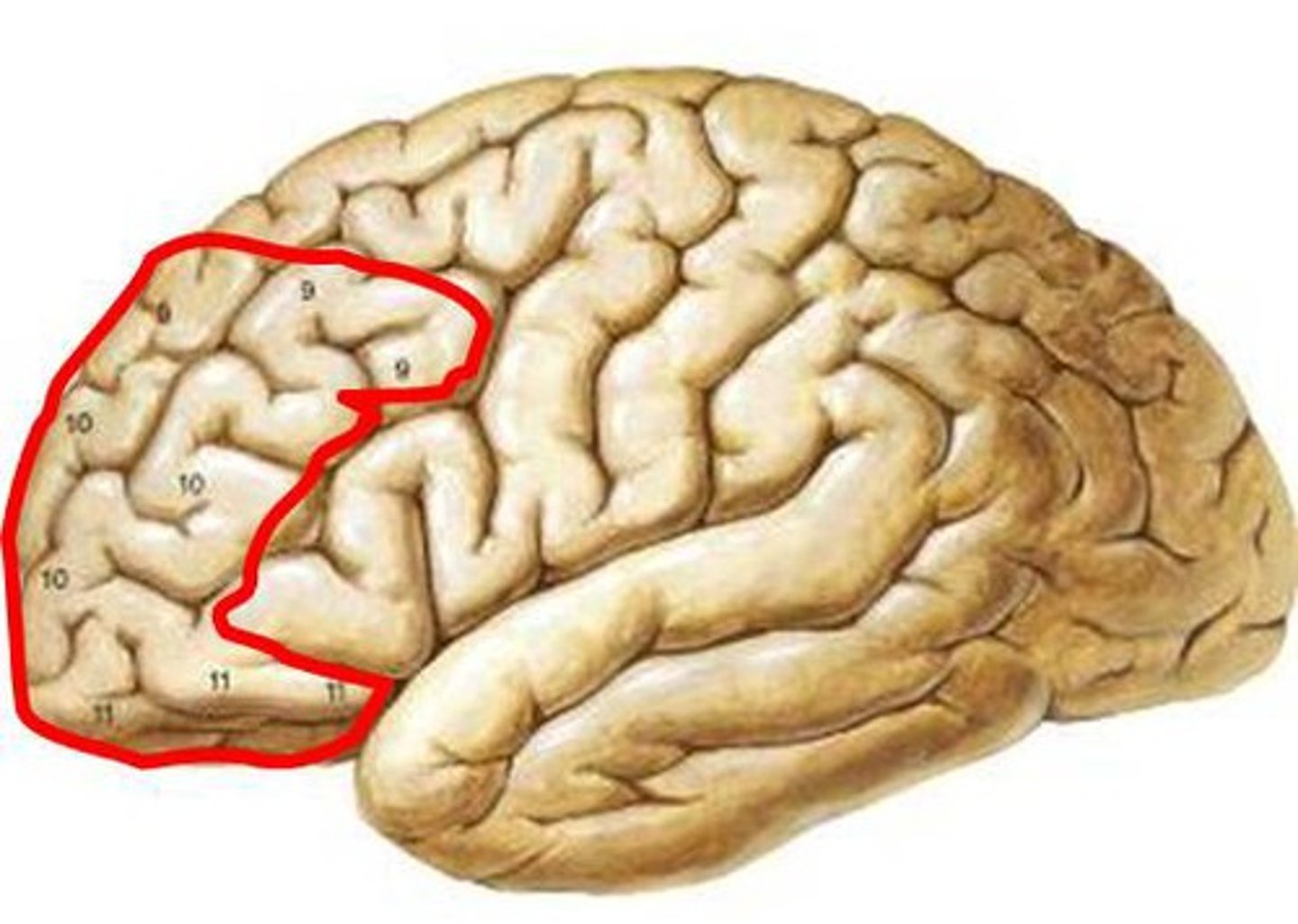
orbital cortex
part of the brain in which the combination of odor and taste information helps create the perception of flavor
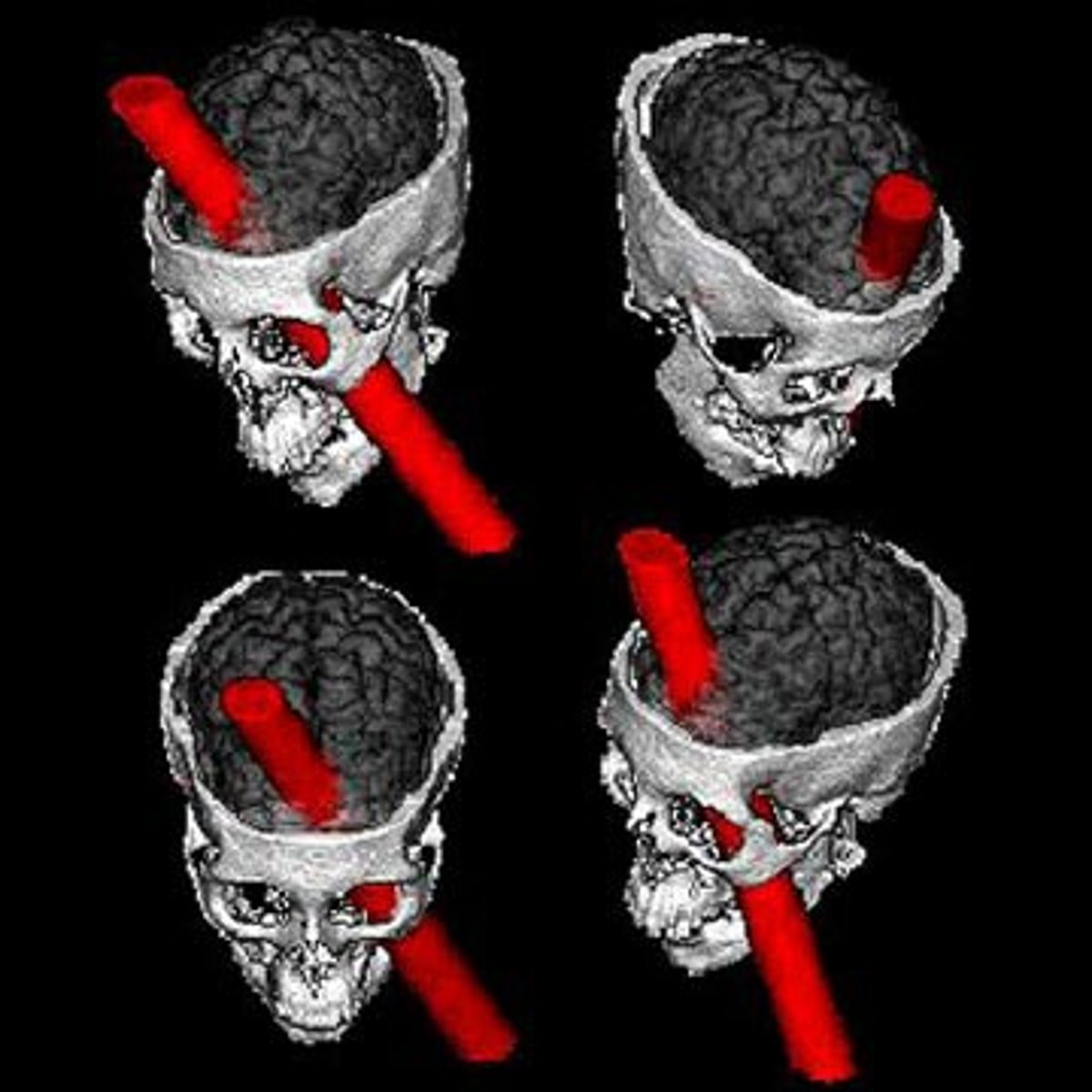
Phineas Gage
railroad worker who survived a severe brain injury that dramatically changed his personality and behavior; case played a role in the development of the understanding of the localization of brain function
Hippocampus
A neural center located in the limbic system that helps process explicit memories for storage.
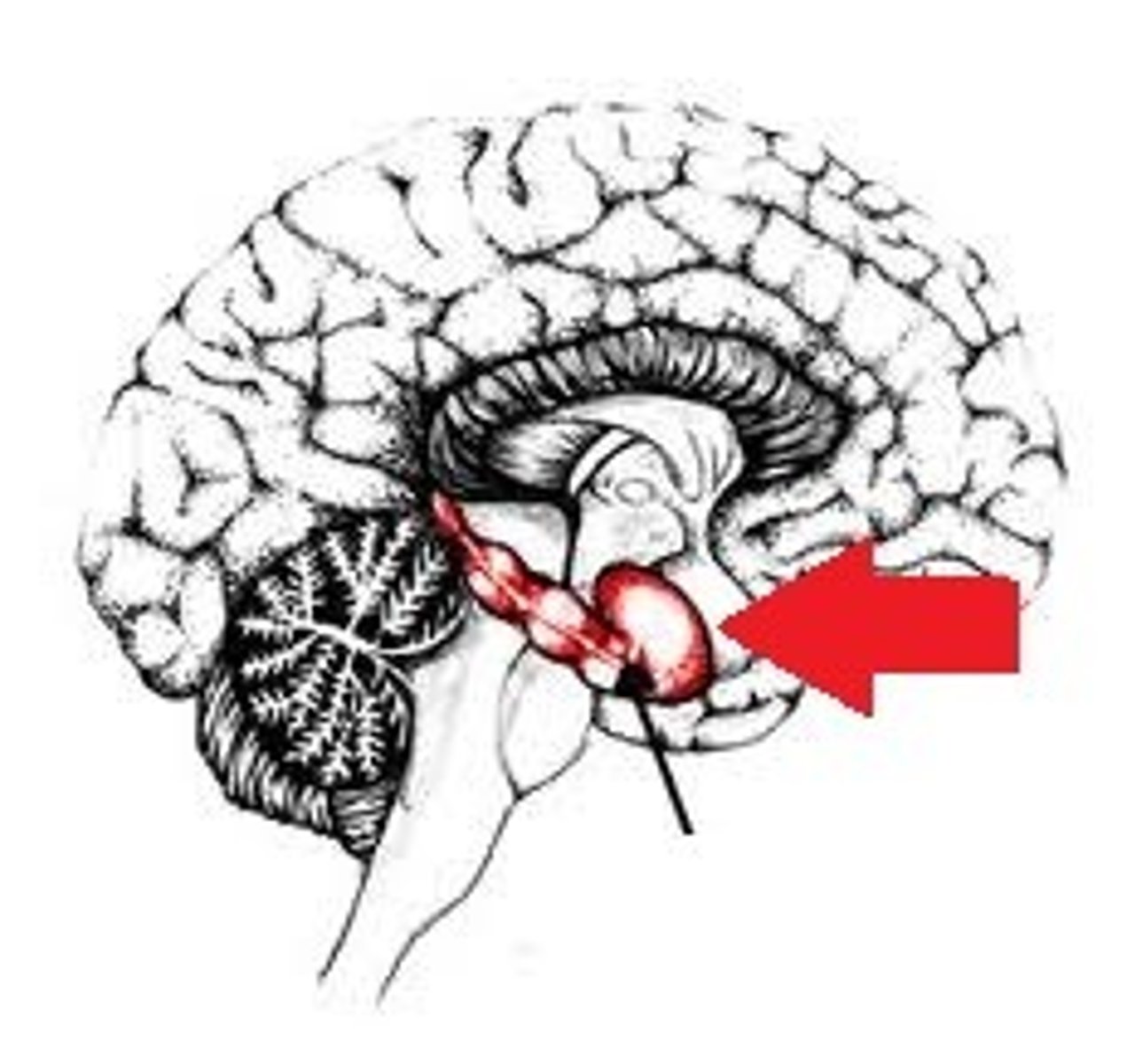
limbic system
neural system located below the cerebral hemispheres; associated with emotions and drives

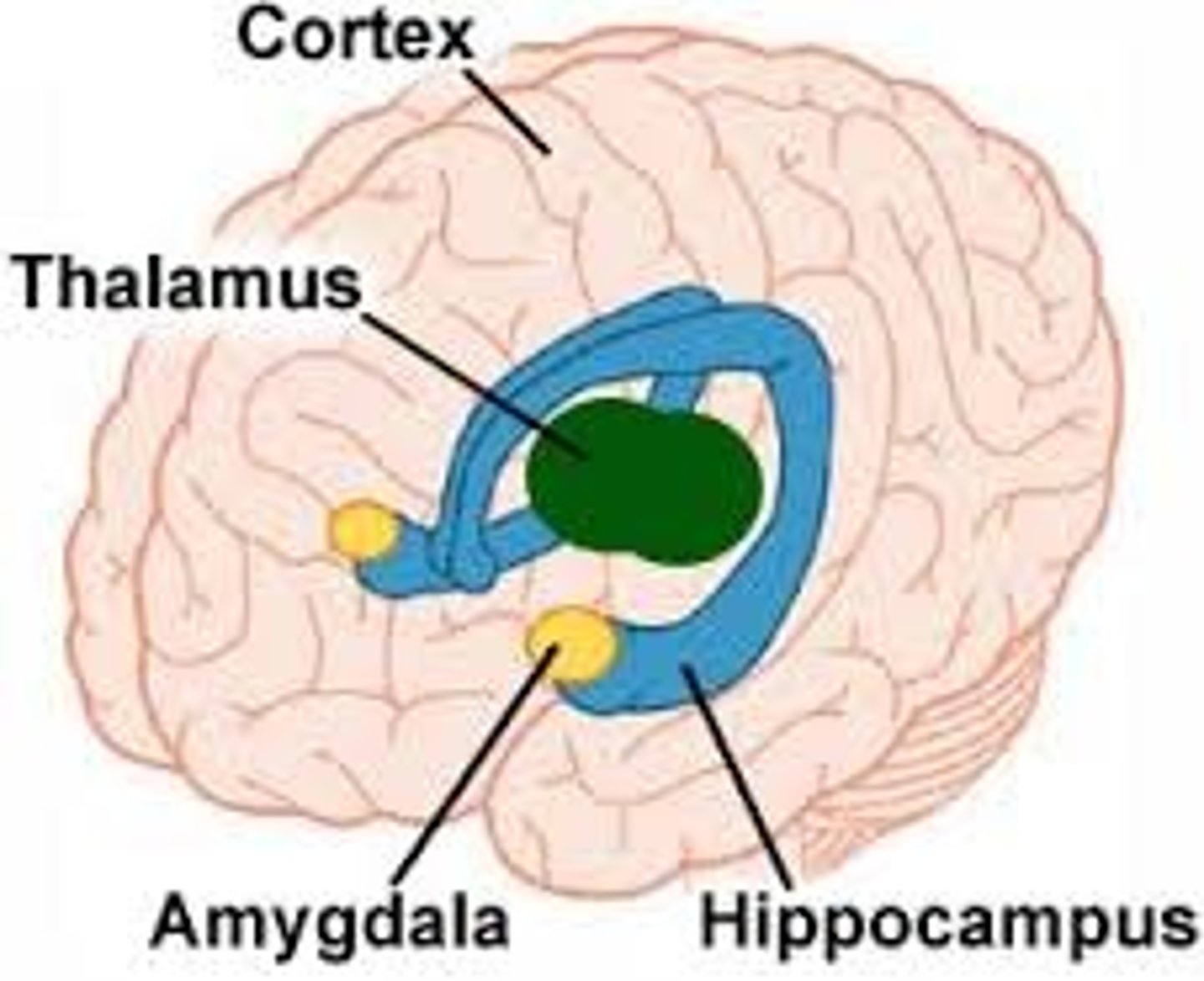
Amygdala
A limbic system structure involved in memory and emotion, particularly fear and aggression.
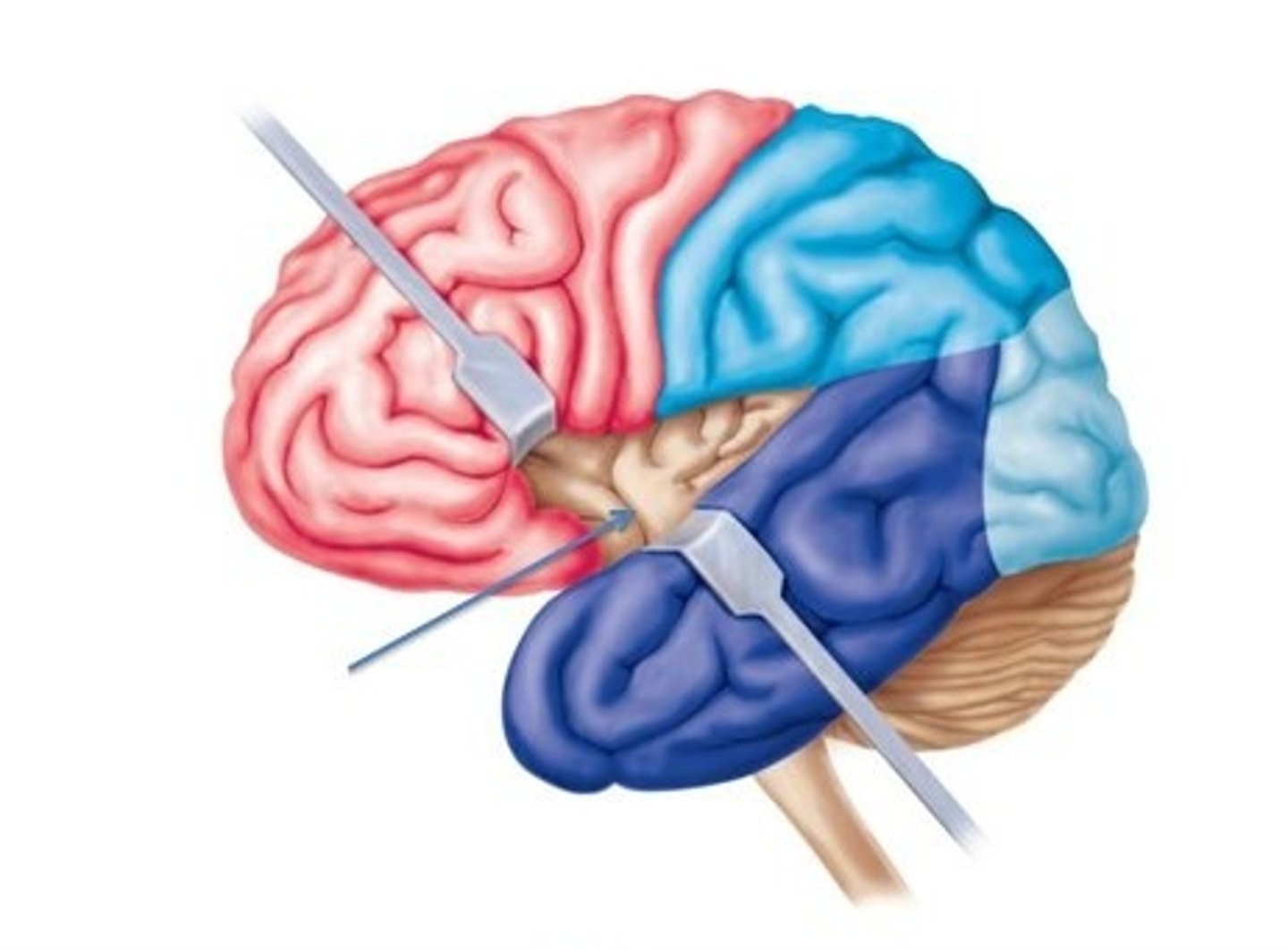
insula
regions of cortex located at the junction of the frontal and temporal lobes
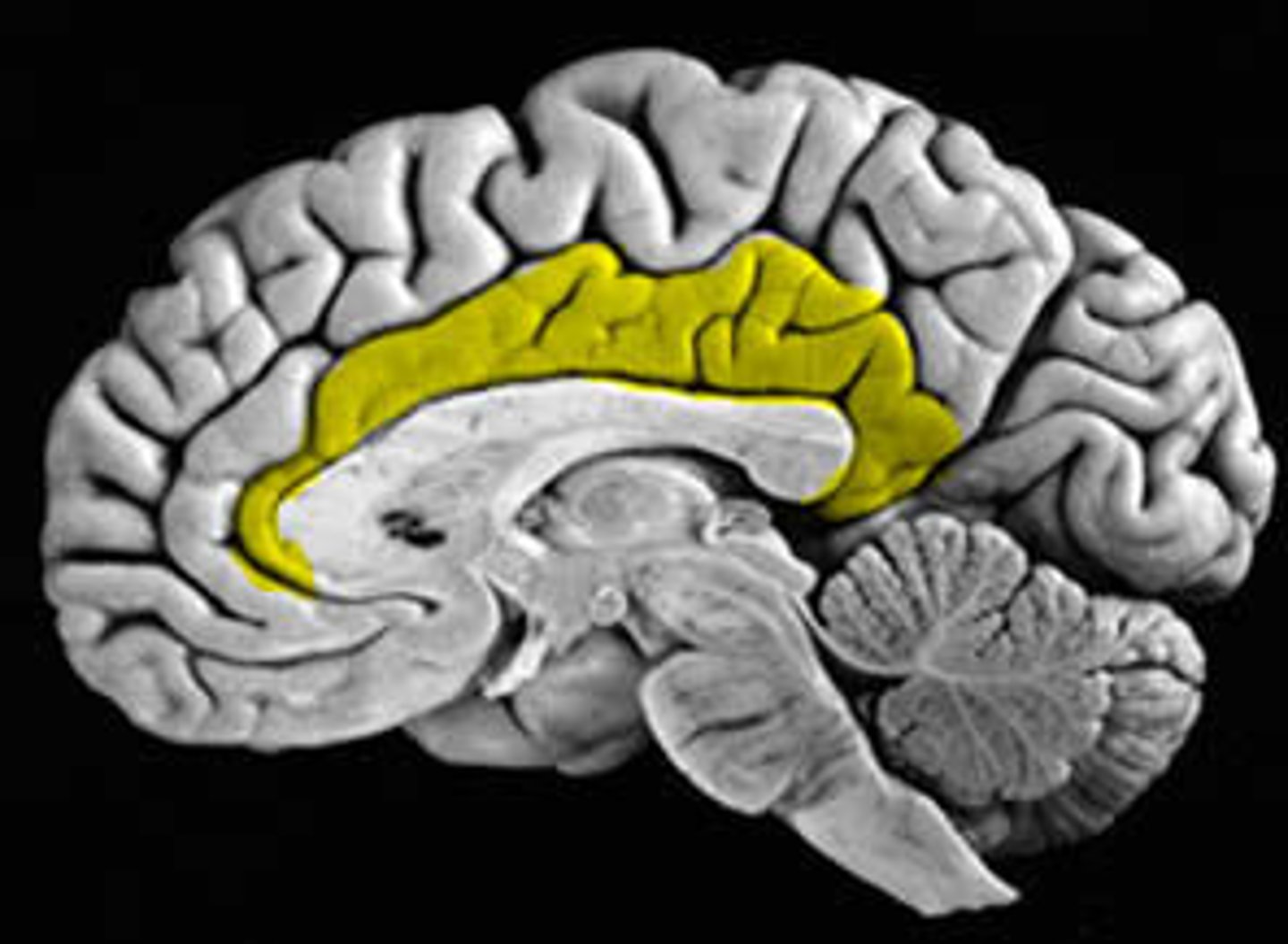
anterior cingulate gyrus
brain region involved in the supervisory attentional system that inhibits automatic responses and selects the correct response
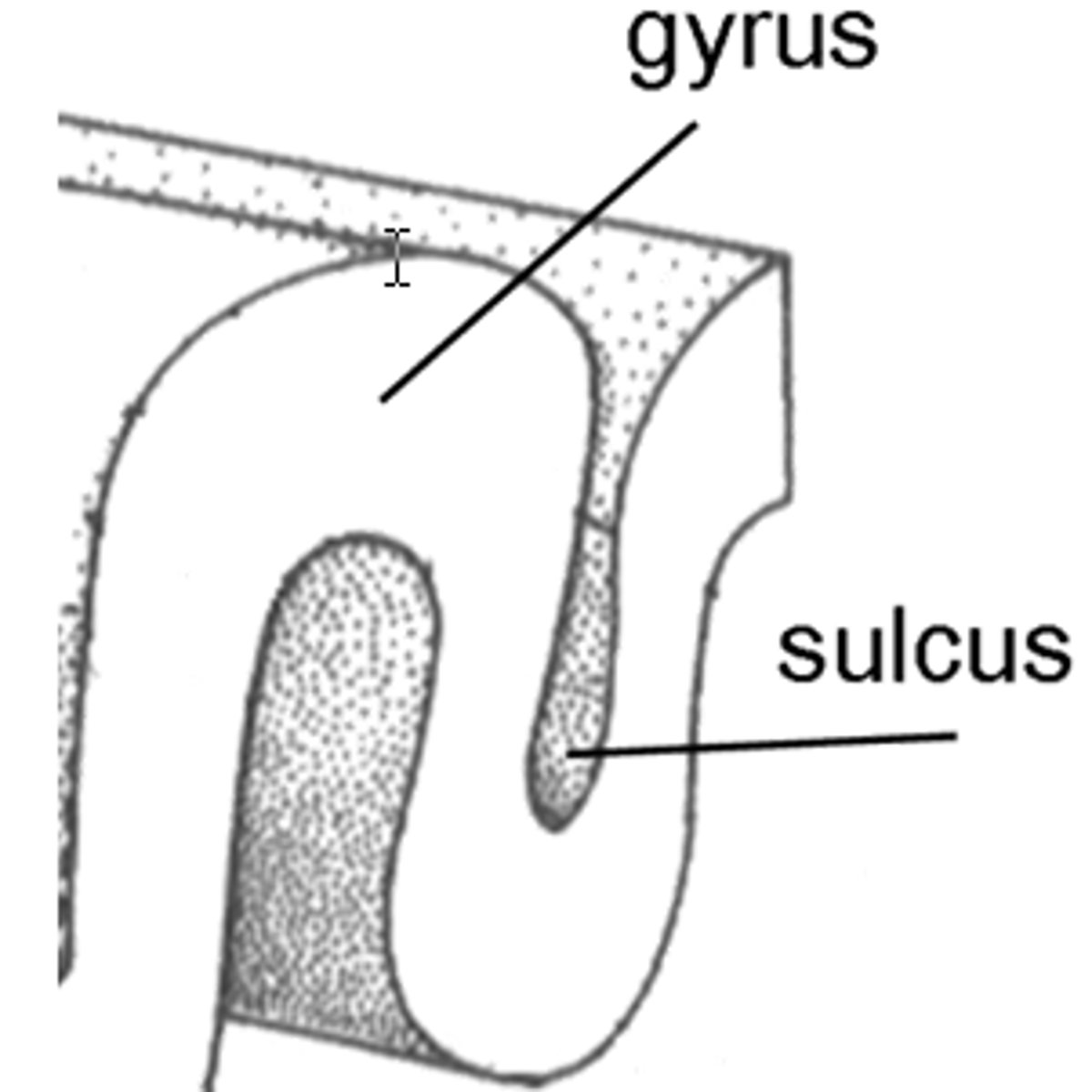
gyrus, sulcus, fissure
bump, groove, deeper groove
reptilian brain
The Portion of the brain that controls vital functions like heart rate, breathing, body temperature and balance. (medulla, pons, cerebellum, midbrain, globus pallidus, and olfactory).
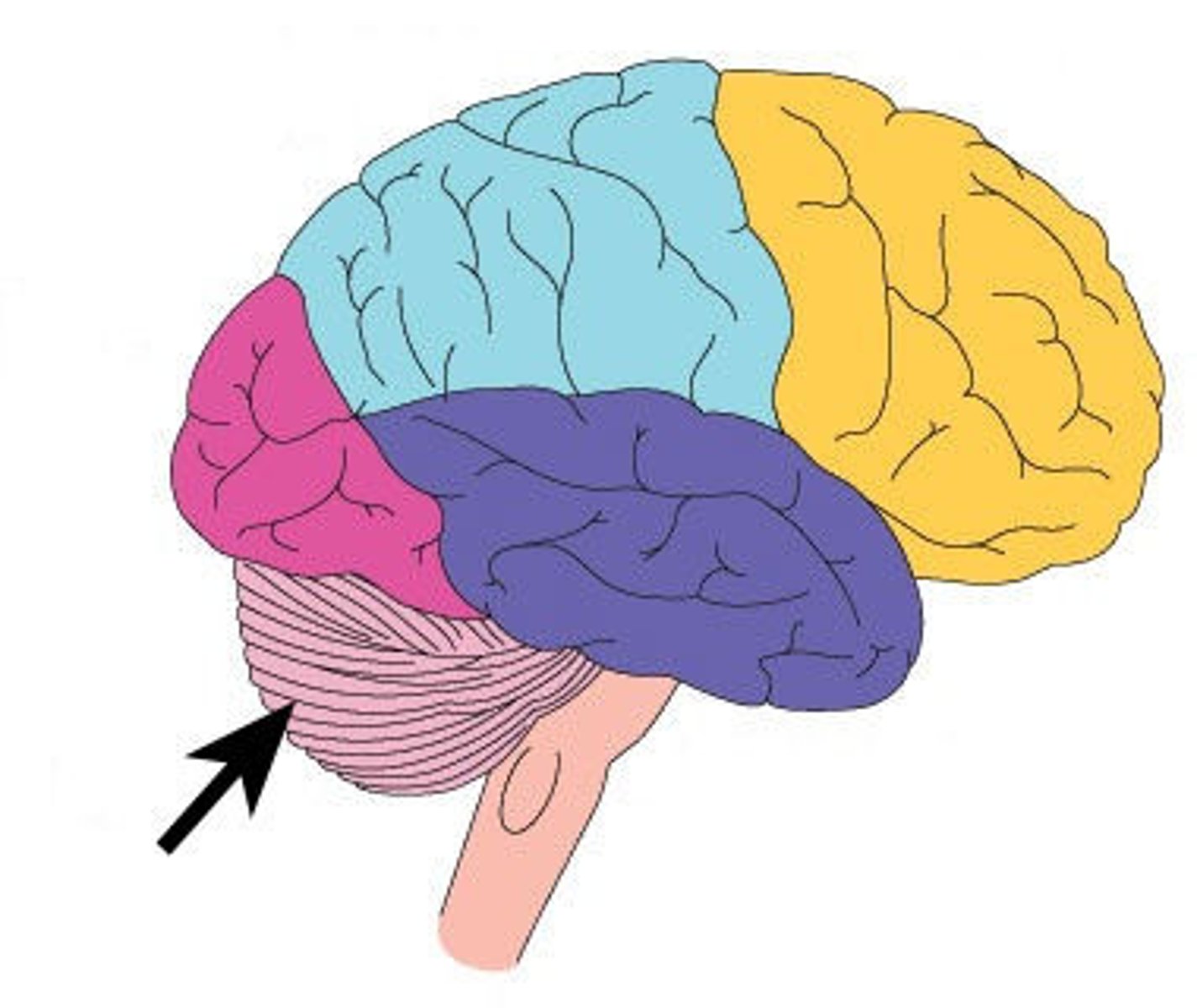
Cerebellum
A large structure of the hindbrain that controls fine motor skills.
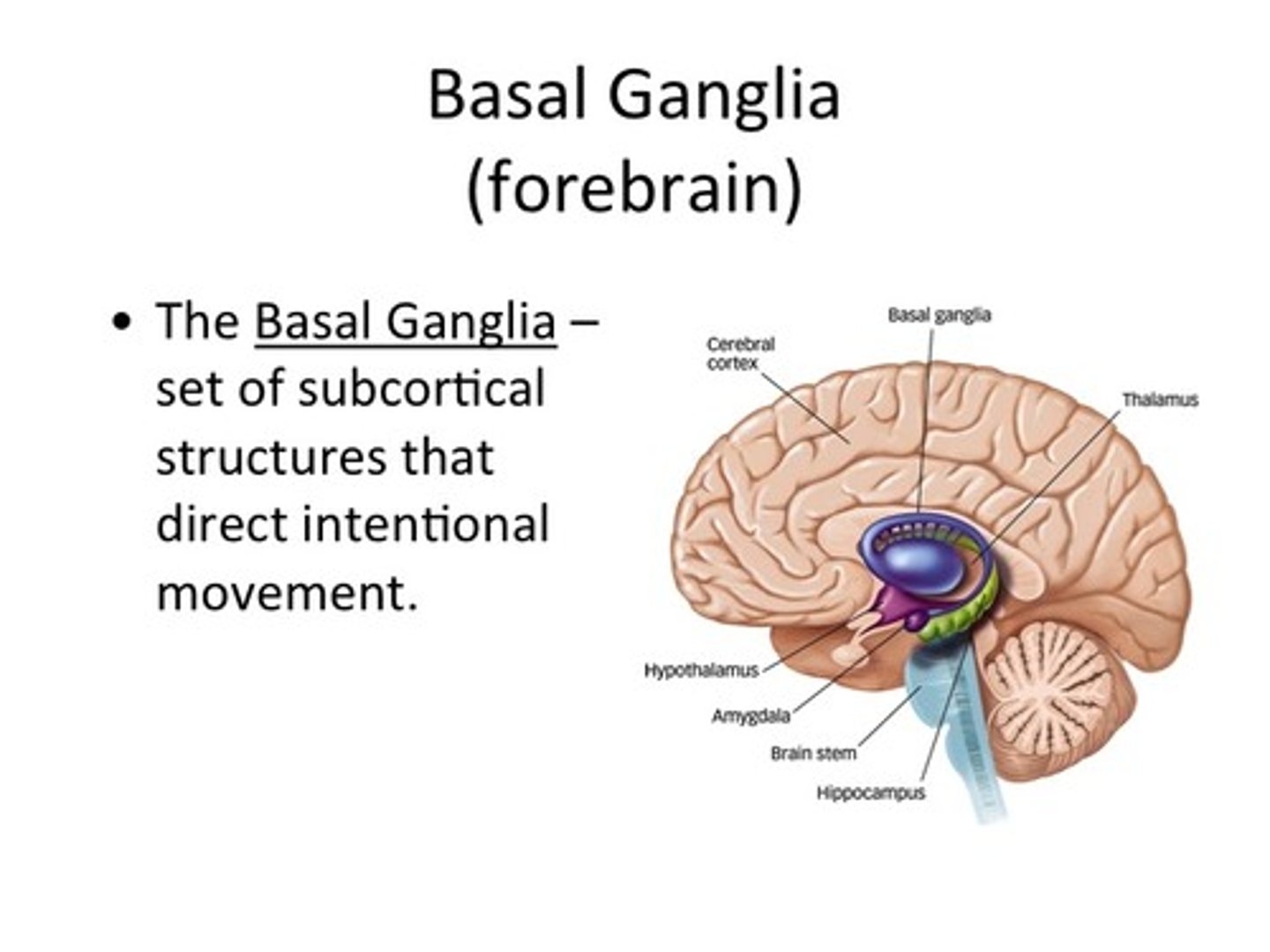
basal ganglia
a set of subcortical structures that directs intentional movements
Parkinson's disease
A disorder of the central nervous system that affects movement, often including tremors.
colliculi (superior and inferior)
two paired bumps on back of midbrain containing the visual and auditory reflex centers
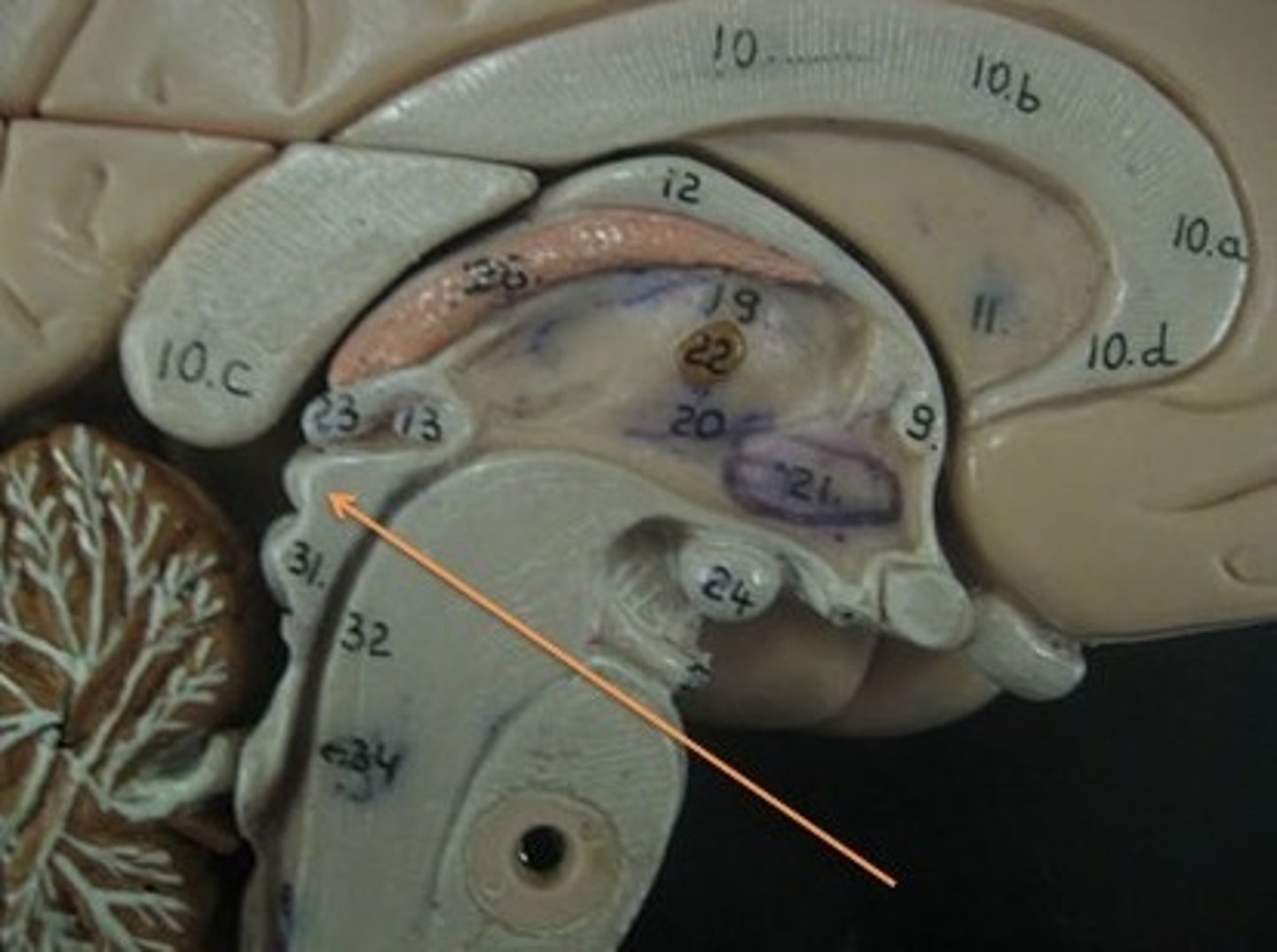
substantia nigra
An area of the midbrain that is involved in motor control and contains a large concentration of dopamine-producing neurons
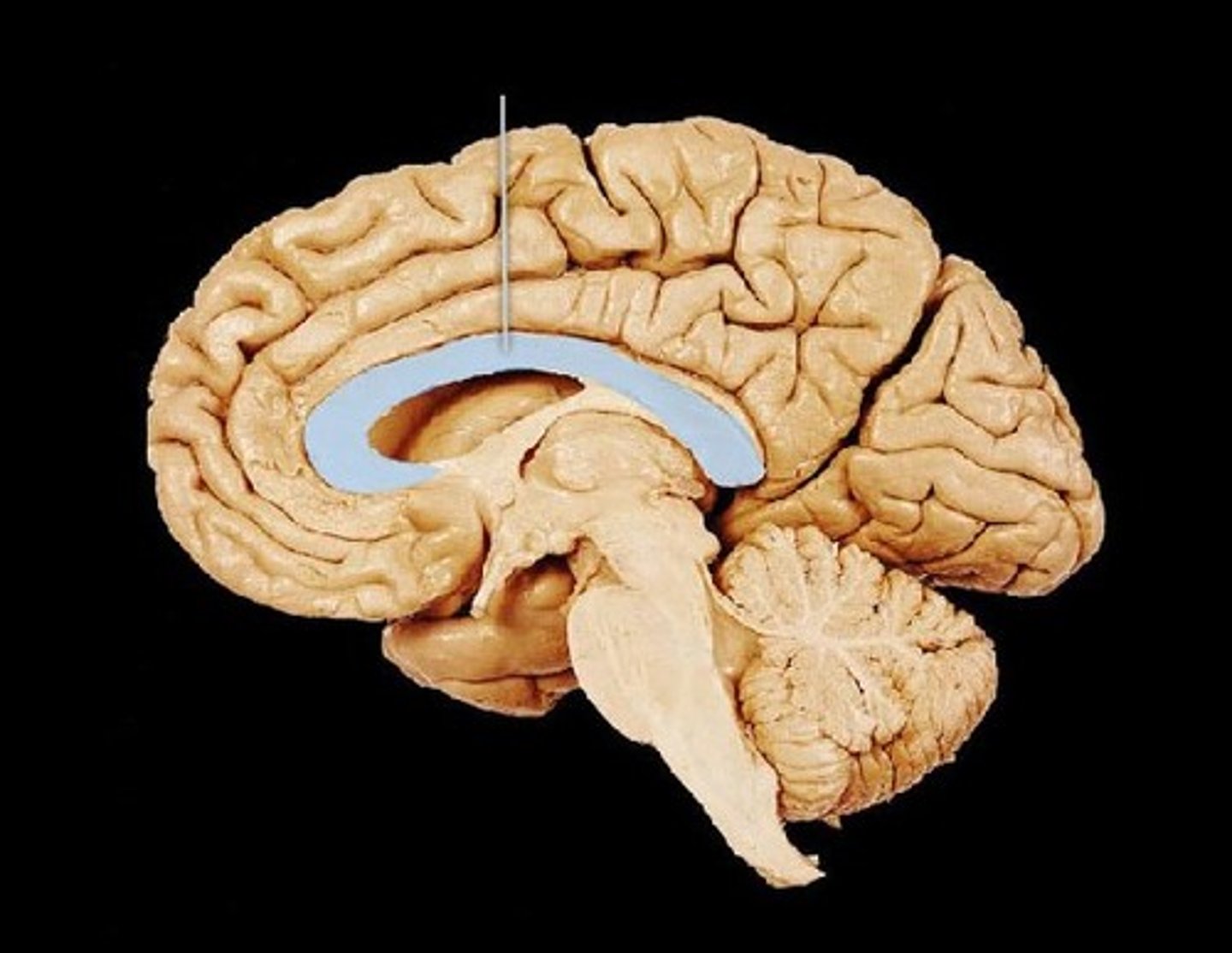
corpus callosum
the large band of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them
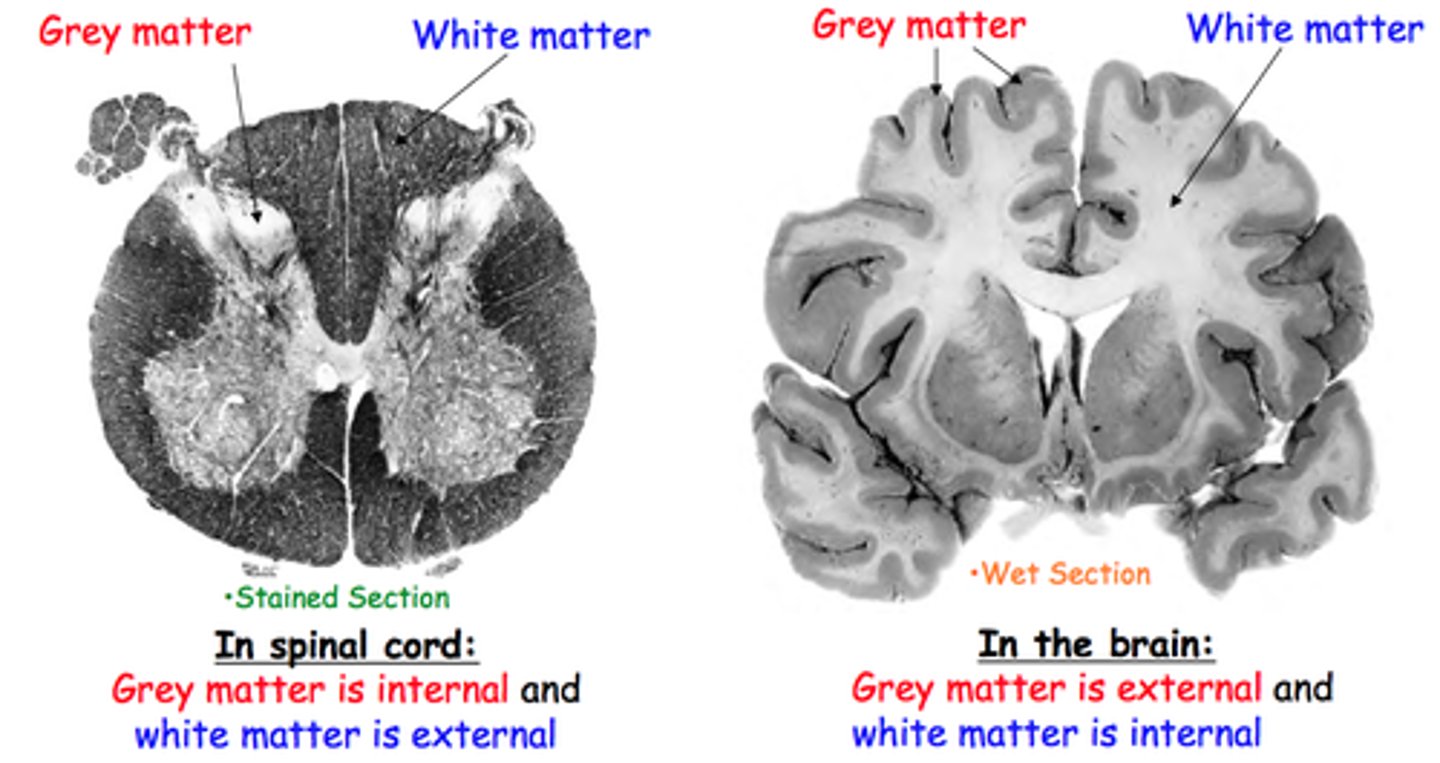
Grey and white matter
Area of the Spinal Cord (as seen in cross-section) consisting of soma vs. myelinated axons
precuneus
visual spatial processing
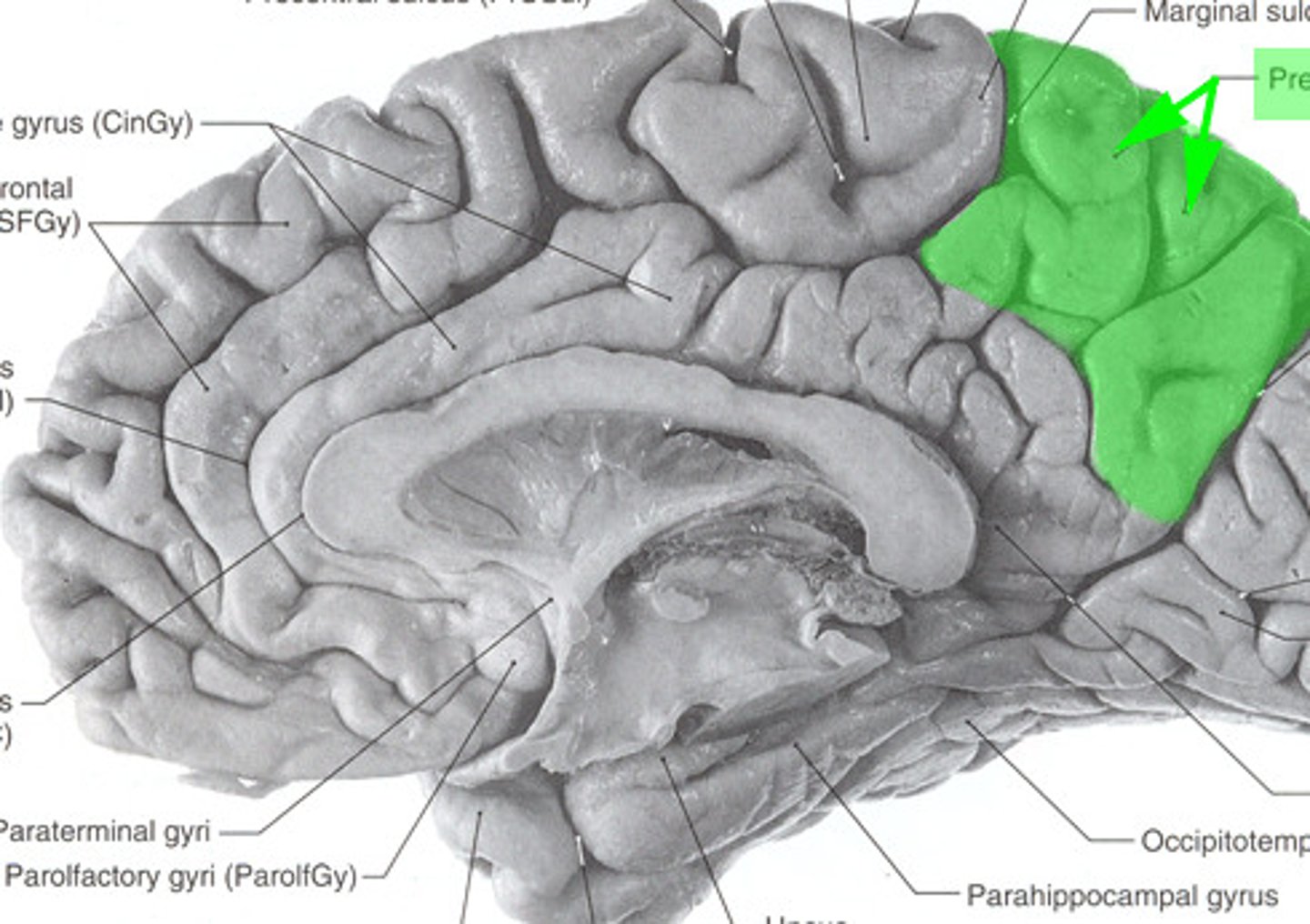
cortex
outermost covering of the brain consisting of densely packed neurons, responsible for higher thought processes and interpretation of sensory input
cerebral hemispheres
The right and left halves of the cerebrum.
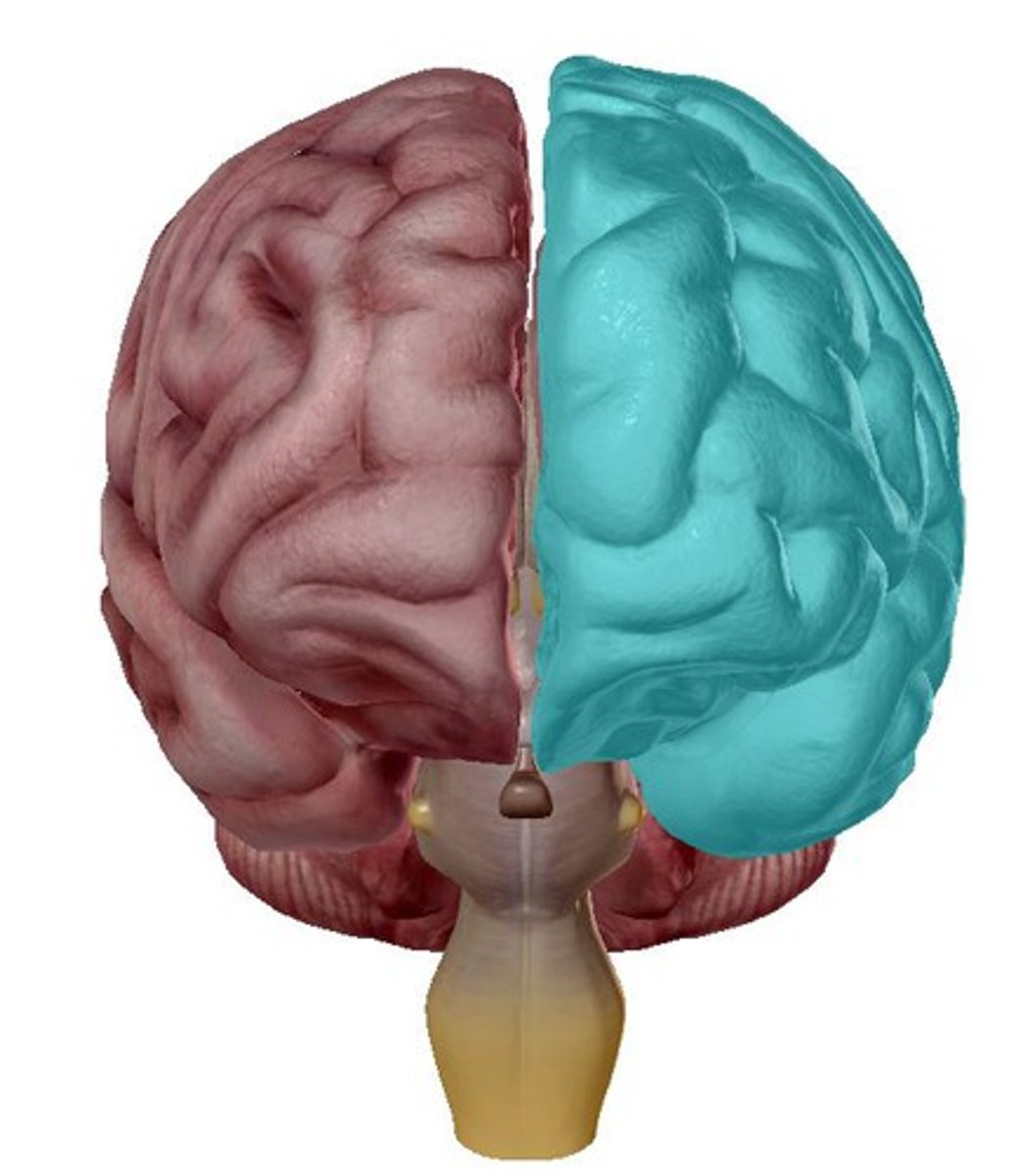
contralateral neglect
A disturbance of the patient's ability to respond to visual, auditory, and somatosensory stimuli on the side of the body opposite to a site of brain damage, usually the left side of the body following damage to the right parietal lobe.
short range signals
EPSP, IPSP
long-range signals
AP