Ch 9, 11, 12, 13 FINAL EXAM PREP
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
1._______ informs us how we will define and segment our market. ________ describes specifically whom we will attempt to reach. Our ________ outlines what we will say to them.
a) Segmentation, positioning, feature-value analysis
b) Positioning statement, targeting, segmentation
c) Targeting, feature-value analysis, segmentation
d) Segmentation, targeting, positioning statement
d) Segmentation, targeting, positioning statement
2. _______ should be consistent with positioning.
_______ should support fulfilling and strengthening the positioning.
_______ decisions should be guided by positioning.
a) Targeting, Targeting, Targeting
b) Marketing mix, Marketing mix, Marketing mix
c) Segmentation, Segmentation, Segmentation
d) Marketing mix, Segmentation, Targeting
b) Marketing mix, Marketing mix, Marketing mix
Which of the following is NOT correct about target audience description?
a) It is rich and detailed and specific enough to generate a mental picture of the target audience.
b) It should be shared and validated with those charged with execution.
c) To write a target audience description we will, in essence, pluck a person from the pool that makes up our potential market and describe this person in substantial detail.
d) It includes a name, a habitat, revealing behaviors, and consumption habits, but it excludes demographics, attitudes, values and aspirations.
d) It includes a name, a habitat, revealing behaviors, and consumption habits, but it excludes demographics, attitudes, values and aspirations.
4. Ideally the value proposition
a) should be a benefit of company’s product, which overlaps with customer needs and wants but does not overlap with the benefits that competitors offer.
b) should overlap with the value proposition of competitors.
c) should be a benefit of company’s product, which does not overlap with what customers want.
d) Should be a value neither overlap with the value proposition of competitors nor with customer needs and wants.
a) should be a benefit of company’s product, which overlaps with customer needs and wants but does not overlap with the benefits that competitors offer.
5. What is the primary benefit provided by the market category that differentiates the category leader?
a) Presidential benefit
b) Main benefit
c) Dynamic benefit
d) Core benefit
b) Main benefit
1. Product in marketing mix means ______________ through developing features and benefits, adding service and branding.
a) ‘creating market position’
b) ‘creating value’
c) ‘appropriating value’
d) ‘appropriating market position’
b) ‘creating value’
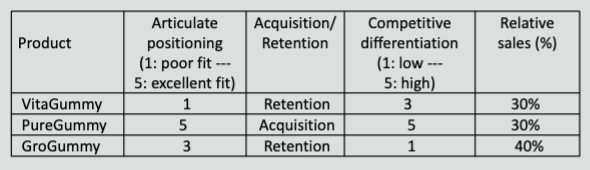
2. Gummy Nutrition Co. has three product lines - VitaGummy, PureGummy, and GroGummy. Marketing team of the company conducted product portfolio analysis as follows.
The marketing manager has to propose ideal resource allocation for the next year. Ideal resource allocation should be something like:
Product Ideal resource allocation (%) VitaGummy 20% PureGummy 50% GroGummy 30%
3. A brand can serve all of the following purposes except which of the following?
a) Serving as a memory aid for customers
b) Displaying differences between the company’s product and competitors’ products
c) Serving as a way to dissuade customers from buying a competitor’s product
d) Signaling product quality
c) Serving as a way to dissuade customers from buying a competitor’s product
4. Which branding approach is more cost efficient due to the fact that costs associated with new product launches are substantially reduced when the product and company are clearly connected?
a) Specific Branding
b)Distinct Branding
c) Hybrid Branding
d)Umbrella Branding
d) Umbrella Branding
5. _______________ of packaging should be carefully decided as it supports positioning substantially.
a) Printed information
b) Image
c) Color and background
d) Typography and font
a) Printed information
1. Whenever Melanie considers upgrading her computer gaming system, she consults with Paula , a knowledgeable friend who always has the newest technology. For Melanie, Paula is a(n)________ in the diffusion of innovation curve.
a) innovator
b) laggard
c) late majority adopter
d) early majority adopter
e) early adopters
a) innovator
2. Which group is essential for bringing the other buying groups into the market?
a) matures
b) laggards
c) late majority
d) early majority
e) early adopters
e) early adopters
3. The________ diffusion of innovation group is crucial because few new products can be profitable until this large group buys them.
a) innovator
b) laggard
c) late majority
d) early majority
e) early adopter
d) early majority
4. As soon as she saw one, Candice wanted a curved-screen television, but she was worried about making the wrong choice. She waited until there were alternatives in the market with lower prices and improved quality. Candice is part of the________ diffusion of innovation group.
a) innovator
b) laggard
c) late majority
d) early majority
e) early adopter
d) early majority
5. As a promotion technique, samples are often used for new
products when________ will influence the diffusion of the product.
a) relative advantage
b) compatibility
c) observability
d) complexity
e) trialability
e) trialability
6. Good-to-Go Corp. has a new concept for a lightweight electric scooter that can be easily folded and taken with you inside a building or on public transportation. The company is currently engaged in concept testing. The most important question during this phase of product development pertains to
a) the cost of research and development.
b) the price of the final product.
c) the cost to manufacture the product.
d) the geographic location of potential test market areas.
e) the respondent's purchase intentions if the product were made available.
e) the respondent's purchase intentions if the product were made available.
7. At which stage of the product life cycle will you find a growing number of product adopters, rapid growth in industry sales, and increases in the number of competitors and the number of available product versions?
a) innovation
b) introduction
c) maturity
d) early maturity
e) growth
e) growth
8. During the________ stage of the product life cycle, sales peak and profits begin to decline as competition becomes intense.
a) introduction
b) leveling
c) maturity
d) growth
e) decline
c) maturity
9. Lina is watching her line of organic dog treats enter the maturity stage of the product life cycle. What can you tell her about the competition at this stage?
a) Competition is nonexistent.
b) Competition begins to drop off.
c) Competition is intense.
d) Competition only exists when new products are introduced.
e) Competition tends to rise slowly and decrease dramatically.
c) Competition is intense.
10. Which of the following is NOT a reason why over-relying on product-life-cycle can
lead to problems?
a) Although we might observe that prior sales have followed the life cycle pattern to some extent, it is impossible to know how far along in the life cycle our product is, how long the plateau will last, and whether a recent sales decline is a short-term blip or the beginning of long-term sales erosion.
b) The central weakness of the traditional product life cycle approach is that it relies on products and features to drive decisions instead of consumers and benefits.
c) A specific version of a product may mature and decline; however, the product, and more importantly, the brand, may live forever.
d) All of the above are valid reasons that over-reliance on Product-life-cycle can lead to problems.
d) All of the above are valid reasons that over-reliance on Product-life-cycle can lead to problems.
A restaurant bar is a classic example of
offloading
1. Which of the following is NOT a reason for productization?
a) To capture more brand equity
b) To reduce costs and increase margin
c) To maintain consistent performance
d) To customize customers’ different needs
d) To customize customers’ different needs
2. Because services cannot be inventoried, _____________is necessary.
a) Cost control
b) Online advertising
c) Operational excellence
d) Setting a low price
c) Operational excellence
3. What becomes a critical factor when the absence of a physical product and associated cues diminish?
a) Word of mouth
b) Price of services
c) Customizing services
d) Surveying customers to make services as desired
a) Word of mouth
4. The restaurant manager asked the new chef, “can you prepare a gluten-free meal that is consistently prepared and predicable?” Which of the service dimensions was the restaurant manager expressing concern about?
a) reliability
b) responsiveness
c) assurance
d) empathy
e) tangibles
a) reliability
5. Last month, the cable service was out at Ellis’s house for four days. When Ellis called the cable company, the representative agreed to credit his next bill for a full week of service and gave him free access to a popular movie channel for the next six months. Ellis felt this was adequate compensation for the inconvenience. What is this an example of?
a) economy of scale
b) the knowledge gap
c) distributive fairness
d) empowerment fairness
e) word-of-mouth
c) distributive fairness