3.1, 3.3 and 3.4
What is the equation for number of moles
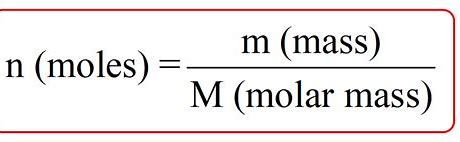
How many cm3 are in a ml
1
How many cm3 are in a litre
1000
How many cm3 are in a dm3
1000
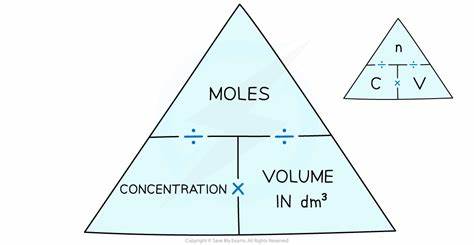
What is the formula for concentration
What is a standard solution
A standard solution is a solution of known concentration
How are standard solutions prepared
Standard solution are prepared by dissolving an exact mass of the solute in a solvent and making up the solution to an exact volume
What is the molar gas volume
Molar gas volume is the volume per mole of gas molecules at stated temperature and pressure
What is formula of number of moles of gas at RTP

What 4 assumption are made for the ideal gas equation
Random motion
Elastic collisions
Negligible size
No intermolecular forces
What is the ideal gas equation
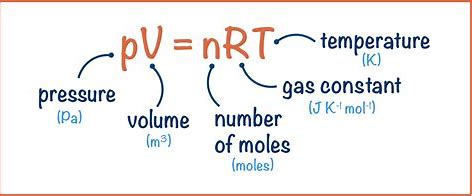
Describe the conversions necessary for the ideal gas equation
cm3→ m3 x10-6
dm3→ m3 x10-3
C → K +273
kPa → Pa x103
Why is it not possible to achieve 100% percentage yield
Reaction may not have gone to completion
Side reactions may have taken place
Purification may have resulted in loss of product
What is the formula of percentage yield

What is the limiting reagent
Limiting reagent is the reactant that is not in excess and will be used up first thus will stop the reaction
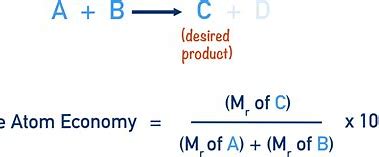
What is atom economy
Atom economy of a chemical is a measure of how well atoms have been utilised
What are 2 features of reactions with high atom economies
They produce a large proportion of desired products and few unwanted waste products
They are important for sustainability as they make the best use of natural resources
What is the equation of atom economy