5.2.1 Lattice Enthalpy
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
enthalpy change
heat energy transferres in a reaction at constant pressure
enthalpy change symbol
ΔH
units of enthalpy change
kJ mol^-1
enthalpy change of atomisation of an element
enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous atms is formed from an element under standard conditions
enthalpy change of atomisation symbol
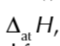
enthalpy change of atomisation of cl
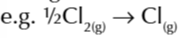
enthalpy change of atomisation of a compound
enthalpy change when 1 mole of a compound is converted to gaseous atoms under standard conditions
enthalpy change of atomisation of NaCl
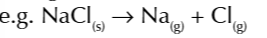
second ionisation energy
energy needed to change 1 mole of gaseous 1+ ions atoms into 1 mole of gaseous 2+ ions
first electron affinity
energy needed to change 1 mole of gaseous atoms into 1 mole of gaseous 1- ions
second electron affinity
energy needed to change 1 mole of gaseous 1- into 1 mole of gaseous 2- ions
lattice enthalpy
enthalpy change when 1 mole of a solid ionic compound is formed from its gaseous ions under standard conditions
lattice enthalpy symbol
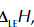
lattice enthalpy of NaCl
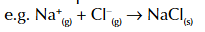
enthalpy change of hydration
enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous ions is dissolved in water under standard conditions
enthalpy change of hydration symbol
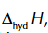
enthalpy change of hydration of Na
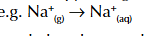
enthalpy change of solution
enthalpy change when 1 mole of solute is dissolved in a solvent such as water under standard conditions
enthalpy change of solution symbol
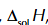
enthalpy change of solution of NaCl
what is lattice enthalpy a measure of
ionic bond strength
Factors affecting lattice enthalpy
ionic charge
ionic radius
how does ionic charge affect lattice enthalpy
the higher the charge on the ions
the stronger the electrostatic attraction between the ions
so the more energy is released when an ionic lattice forms.
more energy released meand lattice enthalpy will be more negative
so lattice enthalpy for compounds with 2+ or 2- iions are more negative than 1+ or 1- ions
how does ionic radius affect lattice enthalpy
the smaller the ionic radii of the ions involved the higher the charge density of the ion this means the electrostatic attraction between the ions is greater so the lattice enthalpy is mor exothermic
born haber cycle example
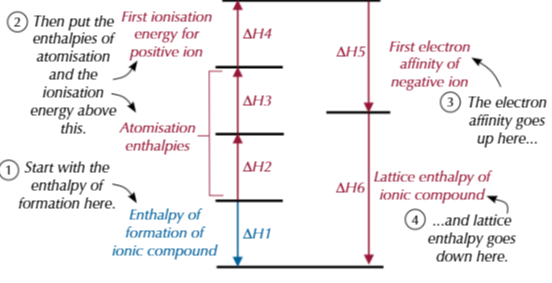
what happens if there is 2 of a molecle in bohn haber cycle
times enthalpy change of atomisation for element by 2 and either is ionisation energy or electron affinity by 2
what happens when a solid ionic lattice dissolves in water
bonds between ions break to give gaseous ions which is endothermic,enthalpy change is opposite of lattice enthalpy
bonds between ions and water and made-exothermic,enthalpy change of hydration
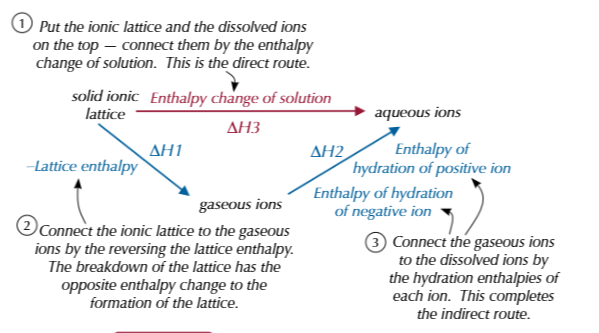
enthalpy change of solution equation
enthalpy of hydration-lattice enthalpy
enthalpy change of solution enthalpy cycle
factors affecting enthalpy of hydration
ionic charge
ionic radius
how does ionic charge affect enthalpy of hydration
ions with a greater charge have a greater enthalpy of hydration
because ions with a higher charge are better at attracting water molecules than those with lower charges
more energy is released when the bonds are made giving them a more exothermic enthalpy of hydration
how does ionic radius affect enthalpy of hydration
smaller ions have greater enthalpy of hydration
as smaller ions have a higher charge density than bigger ions
they attract water molecules better and have more exothermic enthalpy of hydration
is lattice enthalpy endo or exothermic
exothermic
bond enthaly
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of a particular covalent bond in the gaseous state is broken.
why is the second and third electron affinities endothermic
incoming electron is added to an already negative ion so energy is required to overcome the repulsive forces between the incoming electron and negative ion