Seed plants (Chapter idfk)
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
what are the key characterisitcs of seed plants?
Are the most extant plant species
Have reduced male and female gametophytes
Are heterospores as they have male and female gametophytes
what are the two types of seed plants?
gymnosperms
angiosperms
what do all seed plants have?
reduced gametophytes
what are the two types of spores produced by seed plants?
Microspores (male)
Megaspores (female)
what does each microspore develop into?
A grain of pollen
what is pollen?
A male gametophyte enclosed within a wall of sporophyte cells
what is pollination?
the transfer of pollen to the part of a seed plant containing the ovules
ovules being the female part of a plant
how can pollen be transferred?
It can be transferred long distances by wind or animals
what is an ovule?
A megaspore within a megasporangium surrounded by one or more integuments
Angiosperm has two integuments
gymnosperms have one integuments
what develops from a megaspore?
female gametophyte
what are seeds?
Embryos packaged with nutrients supply inside a protective coat
all seed plants produce these (wow really????? :0)
what are some characteristics of seeds?
Can disperse over long distances by wind or other means
ex: animals
Provides protection from harsh conditions and can remain dormant for years until favorable conditions are met
Have food supply to nourish seedlings
what is a function advantage that seeds have compared to spores?
contain a nutrient store for a developing sporophyte
what are gymnosperms (“naked seed”)?
A type of seed plant that produces seeds that dont mature within enclosed chambers
what are some characteristics of gymnosperms?
Most are wind pollinated
Dominated during the mesozoic era (circa 250 to 60 mya) and were food for dinosaurs
Still dominate in some regions
Ex: coniferous forests in northern latitudes
Consists of four phyla
what are the four phyla that gymnosperms consist of?
Cycads
Ginko’s
Gnetophytes
Conifers
what are the characteristics of cycads?
They have large cones and palm like leaves
they have flagellated sperm unlike most seed plants
Tend to be pollinated by beetles
Thrived during the mesozoic era
but there aren’t many today and are endangered
what are the characteristics of Ginko’s?
There are only one living species: Ginkgo biloba
Have flagellated sperm
They are popular in cities due to their high tolerance to air pollution
what are the characteristics of Gnetophytes?
Some are tropical and some live in deserts
Have three genera that appear very different, but are linked molecularly
Genera: a taxonomic rank used to group closely related species (dont have to know this but here so you know what it means :p)
what are the characteristics of conifers?
The largest group of gymnosperms
Most of them are evergreen and retain leaves year round
what are angiosperms (“covered seed”)?
A type of seed plant that produces seeds that mature inside chambers within flowers
what are characteristics of angiosperms?
Originated around 140 million years ago in the cretaceous era
90% of extant plant species are angiosperms
They are animal, wind or self pollinated
They all belong to one phylum (anthophyta)
what are the 2 key adaptations of angiosperms?
flowers
fruits
what are flowers? (yeah i gotta ask this-)
they are specialized shoots used for sexual reproduction with most parts being modified leaves that evolved into specialized structures
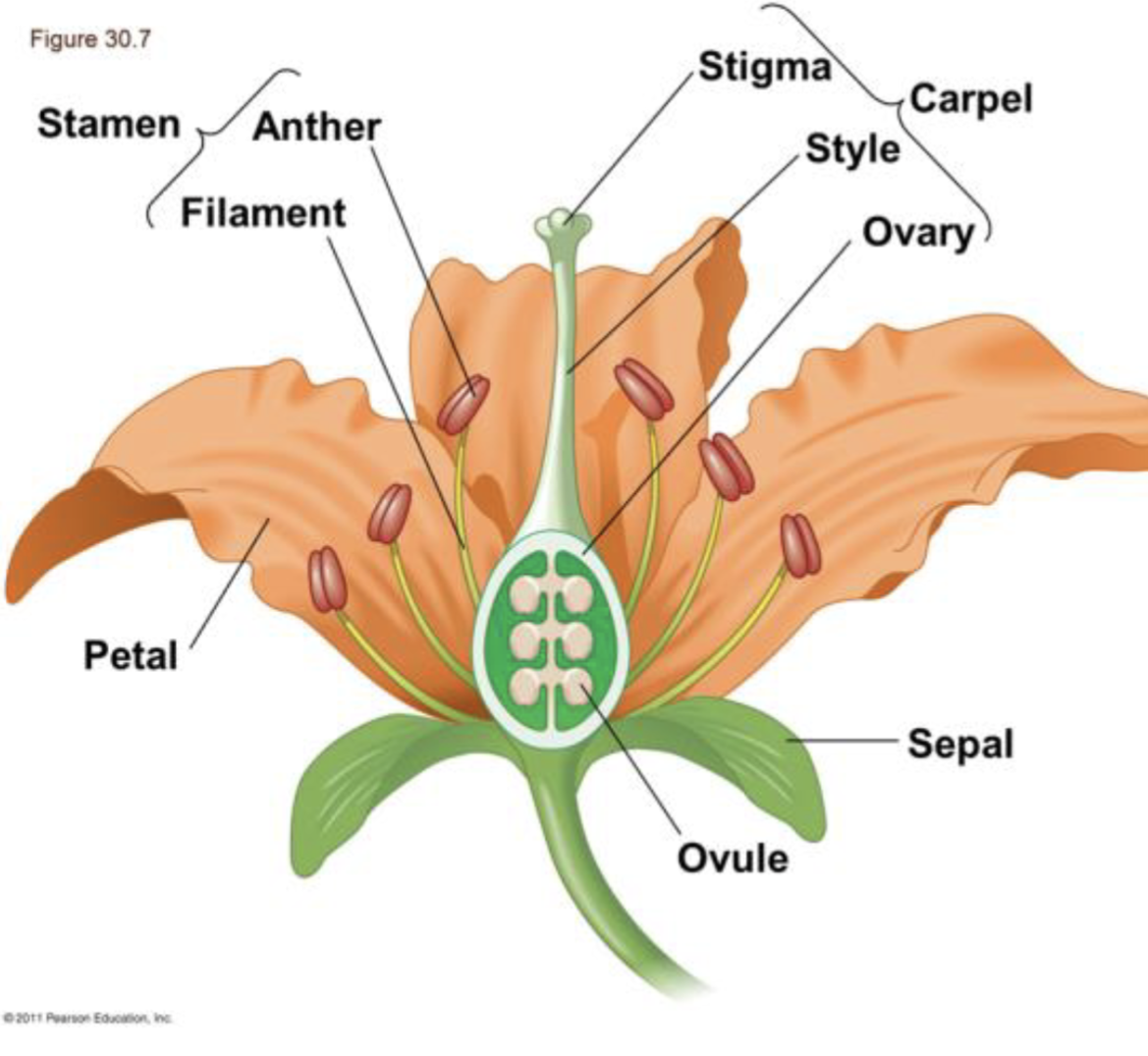
what are a flowers specialized structures?
Sepal: Encloses flower buds
Petals: Have bright colors to attract pollinators
Stamen: microsporophyll’s and are the male reproductive parts
consists of filament and anther
Carpel: megasporophyll’s and are the female reproductive parts
consists of stigma, style, ovary
Stigma being sticky and receiving pollen
Ovary having ovules that develop into seeds after fertilization
what are fruits?
The mature ovary of a flower that protects seeds and aids in their dispersal
what are some various adaptations that aid fruits in angiosperm seed dispersal?
fruits with wings
seeds within berries
fruits with barbs
what are the four primary groups of angiosperms in order of evolution?
Basal angiosperms
Ex: Water lily
Magnoliids
Ex: Southern magnolia
Monocots
Ex: orchid, pygmy date palm, wheat
Eudicots
Ex: strawberries, roses
what are monocots?
Plant embryos that have one seed leaf called cotyledon
what are eudicots?
Plant embryos that have two seed leaves with most angiosperms belonging to this group of plant embryos
why are seed plants important?
they are key sources of food, fuel, and wood products
why are angiosperms important?
angiosperms (such as wheat, rice, maize, potatoes, cassava, and sweet potatoes) provide 80% of human calories
they include grains which feeds livestock
they include other edible products
such as: tea, coffee, chocolate, spices
how are seed plants helpful in medicines?
medicinally active compounds in seed plants are used directly or synthesized to produce medicines