genetics exam 3
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
positional cloning / chromosome walk use
use for tightly linked genes. prepare genomic library, perform colony lift using known gene as probe, make new probe from end of first clone and rescreen until you find the desired gene, must have some way to recognize the gene
functional complementation use
use for temperature sensitive or fungi. prepare cDNA library from wild type in a plasmid of the organism, transform mutant and look for rescued organism
antibody probe use
use if there is a synthesized antibody. prepare cDNA library using an expression vector and perform colony
lift using antibody as probe
nucleic acid probe use
use if DNA sequence is known. screen genomic library by colony lift with gene as probe
degenerate primers use
use if protein / amino acid sequence is known. screen cDNA or genomic library by colony lift using degenerate primers synthesized based on the amino acid sequence of the protein as your probe
making a mouse
Infect ES cells from black mouse, using vector shown above
Select for recombinants in neomycin and ganciclovir
Verify that recombinants had deletion by Southern blot or PCR
Mix engineered ES cells w embryo from white mouse
Implant into pseudopregnant mouse to produce chimeric mice
Cross Chimeric X white to find mice that produce all black offspring
Cross hets to get homozygotes
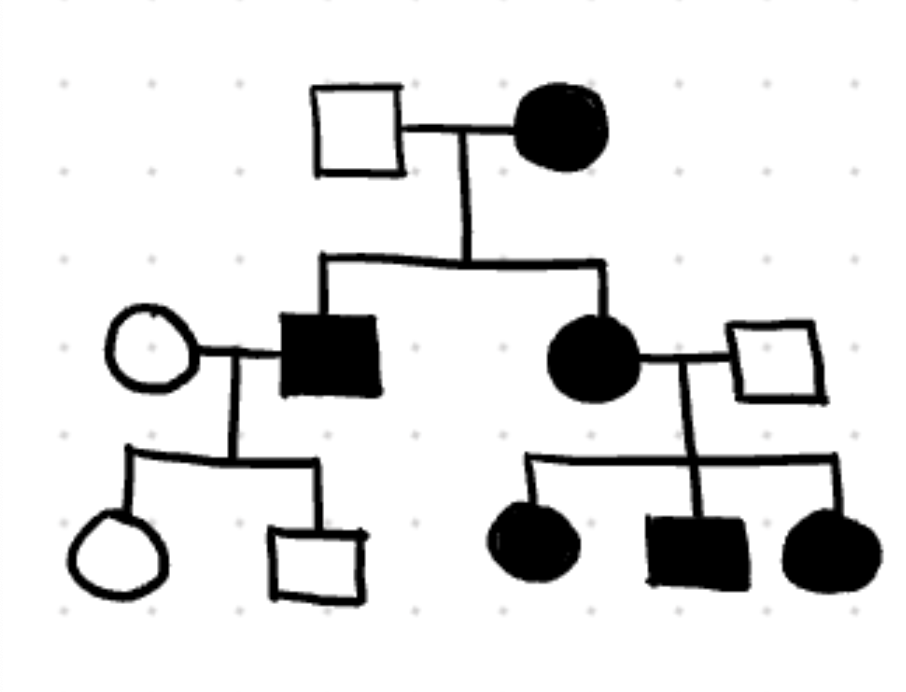
maternal effect
phenotype of offspring is based on moms genotype
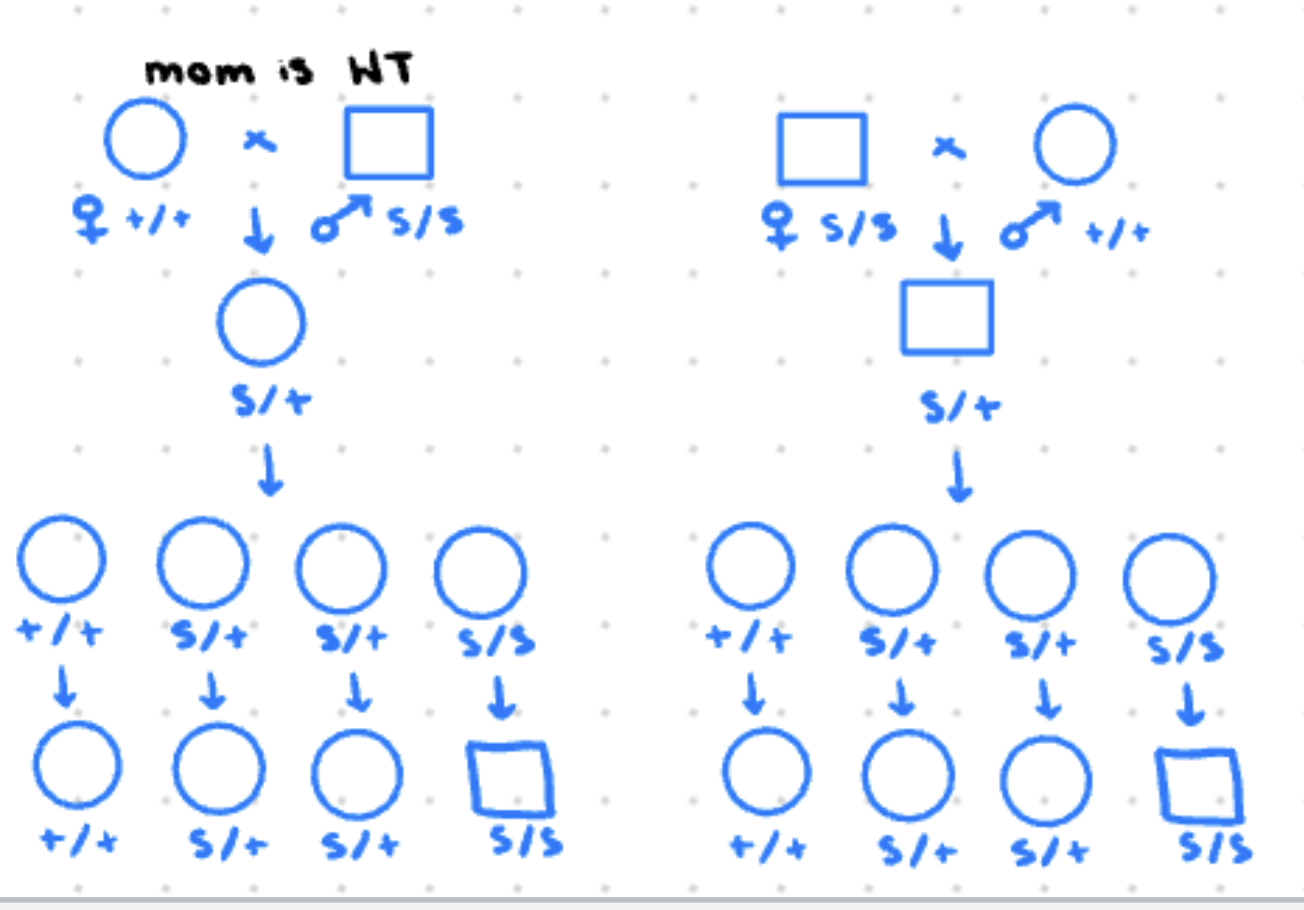
extranuclear inheritance
inheritance is determined by substances in the egg (all children of affected mother are affected)
pericentric inversion
includes centromere
paracentric inversion
does not include the centromere
deletion
removes part of a chromosome
Cri-du-chat syndrome
results from deletion of part of chromosome 5
Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome
results from deletion of part of chromosome 4
duplication
part of chromosome duplicated
balanced chromosome complement
a complete set of chromosomes where no genetic material is lost or gained, even if the arrangement of the chromosomes is altered through structural changes like translocations or inversions
reciprocal translocation
non homologous chromosomes exchange DNA
Robertsonian translocation
special type of non-reciprocal translocation that fuses 2 acrocentric/telocentric chromosomes
high frequency of spontaneous abortion and down syndrome
short arms of chromosomes lost
inversion
part of chromosome “flipped”
endopolyploidy
having extra sets of chromosomes in some cells of the body
euploidy
correct number of chromosomes
monoploidy
orgamism or cell with only one copy of each chromosome
autopolyploid
composed of multiple sets of chromosomes from the same species
allopolyploid
composed of multiple sets of chromosomes from different species
from cross fertilization between species
offspring generally infertile because homologous chromosomes are too different for synapsis, cant go through meiosis
endoreduplication
replication without nuclear division
euploidy
a state where an organism or cell has the correct number of chromosomes, or a multiple of that number
aneuploidy
chromosome # differs from normal by less or more than a full chromosome set
polysomy
extra individual chromosome
trisomy
diploid with extra copy of 1 chromosome
kleinfelter (XXY)
trisomy 21 (down syndrome)
trisomy 13 (patau syndrome)
trisomy 18 (edwards syndrome)
triploid still have balance expression, but trisomy is unbalanced
monosomy
missing one copy of a chromosome
turner syndrome (X0), sterile female
mitochondria (extranuclear inheritance)
refers to the passing of genetic information from mitochondria, which are organelles located outside the nucleus of a cell, from parent to offspring, meaning the genetic material is inherited from the cytoplasm rather than the nucleus itself; in most animals, this translates to solely inheriting mitochondrial DNA from the mother due to the egg contributing most of the cytoplasm to the zygote
human myoclonic epilepsy with ragged-red muscle (MERRF)
chloroplasts
like mitochondria, include their own genome and are maternally inherited
endosymbiont
an organism that lives within the body or cells or another organism, usually in a mutualistic relationship
heteroplasmy
the presence of more than one type of mitochondrial DNA
homoplasmy
all copies of mitochondrial DNA are identical
wolbachia
cytoplasmic endosymbiont in insects
transmitted only by female
causes male progeny to die, transforms male into female (able to reproduce without fertilization from male)
nucleoid
region in a prokaryote that contains all or most of the genetic material (not surrounded by a nuclear membrane)
conjugation
DNA transferred from donor to recipient with direct cell-cell contact
DNA transferred as episome or plasmid
plasmid - extrachromosomal circular DNA, contains F factor (fertility) and R factor (antibacterial resistance)
mating involves transfer of F (transfer of F+ to F-)
episome
genetic element that can exist free in cell or integrated into chromosome
merodiploid
a bacterial cell that has two copies of a portion of its chromosomal complement
transformation
take up of free DNA from environment
may be in form of plasmid or free dna
allows spread of drug resistance between strains
lytic
infection ruptures cell to release new phage particles
lysogenic
virus integrates into bacterial chromosome, transmitted to daughter cells
virulent phage
phage only capable of lytic growth
temperate phage
phage that are only capable of lysogeny
transduction
transfer of bacterial DNA by phage
specialized transduction
only certain portion of bacterial chromosome can be transferred between bacteria
generalized transduction
ability to transduce any bacterial genes
restriction endonuclease
enzymes that bind and cut DNA at specific sequences
genomic DNA vs. cDNA
Genomic DNA- complete DNA sequence of an organism, including both coding and non-coding regions
cDNA (complementary DNA) is a synthetic DNA molecule created from mRNA, containing only the coding regions of expressed genes
plasmid
a genetic structure in a cell that can replicate independently of the chromosomes,
southern blot definition
a lab technique used to study DNA. Using agarose gel electrophoresis, genes are separated by size.
northern blot
gel electrophoresis used to study RNA
SDS-PAGE
western blot
SDS page used to separate proteins that are transferred to a membrane, incubated with a protein-specific antibody that is detected in some way
PCR
Next generation DNA sequencing
site-directed mutagenesis
uses PCR to mutate a specific nucleotide in a plasmid vector. After cell replicates, some of the replication enzymes will have “fixed” the non-matching base pair by adding the new matching nucleotide.
reporter transgene
a gene that is introduced into an organism to report the expression of another gene or protein (lacZ - blue, gfp - fluorescent green, luciferase - produces light)
fuse regulatory sequences to reporter
transgenic organism
organisms that have had genes from other species introduced into their genome
genetically modified plant
transgenic plants
can be mutated to be herbicide resistant or to have Bt toxin that kills the insects that eat it
could have increased yield, improved crop, and reduce herbicide and pesticide use
no evidence of harm to human health, but may cause decreased biodiversity
gene therapy
a medical technique that treats or prevents disease by altering a person's genes
adult stem cell
some tissues have stem cells to replace damaged cells
less potential than the other 2 types due to the fact that it may not be able to differentiate, also can’t culture large numbers
embryonic stem cell
derived from 4-5 day old embryo, typically from infertility clinics
pluripotent (can become any type of cell)
induced pluripotent stem cell
introducing 4 genes into differentiated cells can cause them to revert to a stem like state
has more potential than adult stem cells, has extended proliferation like embryonic stem cells, can be derived from self so no chance of organ rejection
reverse genetics
general approach of moving from a cloned gene to identifying a mutation in that gene
gene knock out
used to study genes by assessing what happens when they are mutated/not functioning.
RNAi
a pathway that triggers degradation of mRNA that corresponds to the dsRNA that was introduced.
Can be used to mimic the effect of a mutation without actually causing one by causing the targeted gene to not be able to synthesize any protein.
CRISPR-Cas9
a technique involving the use of a bacterial defense mechanism that uses stored viral RNA to clip DNA that is complementary to the guide RNA. We can synthesize any RNA to target specific DNA.
Can be used to correct mutations in chromosomes, or create mutations (knock out dominant mutant allele)
not ready for use in humans due to off target events
prophage
a viral genome integrated into a host cells chromosome
basic organism cloning steps
obtain eggs, remove nucleus, fuse enucleated cells with somatic cells, let develop