Biology GCSE
1/153
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
154 Terms
Community
Group of living interdependent organisms
Plants produce food by photosynthesis (producers)
Herbivores eat plants
Insects pollinate plants
Animals use plant and animal material to build nests and shelter
Plants need nutrients from faeces and decay
Abiotic factors
Non-living elements of the environment
Interdependence
When different populations rely on each other to thrive and survive
Biotic factors
Interaction of living things
Habitat
An area where organisms live
Distribution
Where particular types of organisms are found within an environment
Ecosystem
interacting organisms and their environment
Abiotic factors affecting communities
Light intensity
Temperature
Moisture levels
Soil pH
Wind intensity
For aquatic organisms, oxygen availability
CO2 levels
Biotic factors affecting communities
Food availability
New pathogens or parasites could wipe out the population
New predators
Competition from other species
Trophic levels
TL 1 - Producers that make their own food via photosynthesis (autotrophs)
TL 2 - Primary consumers - herbivores that eat plants or algae
TL 3 - Secondary consumers - carnivores that eat herbivores
TL 4 - Tertiary consumers - carnivores that eat other carnivores. Apex predators have no predators
Biomass
the total dry mass of living organisms at each level in a food chain
How is biomass lost through TLs?
Biomass is lost through trophic levels due to metabolic processes and excretion. It is also lost as the animal cannot consume all of the dead one ie. bones, claws, hooves etc., and energy is used in respiration. Only a fraction of energy is passed on to the next level.
Arteries
Structure: Thick walls containing muscles and elastic fibers to withstand high pressure, narrow lumen.
Function: Carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to organs, except in the case of pulmonary arteries. They stretch with every heartbeat and have a lot of pressure.
Veins
Structure:Thinner walls than arteries with less muscle and elastic tissue, wider lumen, often assisted by valves to prevent backflow
Function: Carry deoxygenated blood away from the organs back to the heart, except for pulmonary veins. Do not have a pulse and have lower pressure compared to arteries.
Capillary
Structure: Very thin walls, only one cell thick, very small lumen
Function: Link the veins and arteries, enable substances like oxygen and glucose to diffuse out of your blood and into your cells easily
Double circulatory system
The circulation of blood from the heart to the lungs is separate from the circulation of blood to the rest of the body.
Benefits of Double circulatory system
Blood pressure is higher, especially to the body
Higher blood flow to the body tissues
Oxygenated and deoxygenated blood flow separately
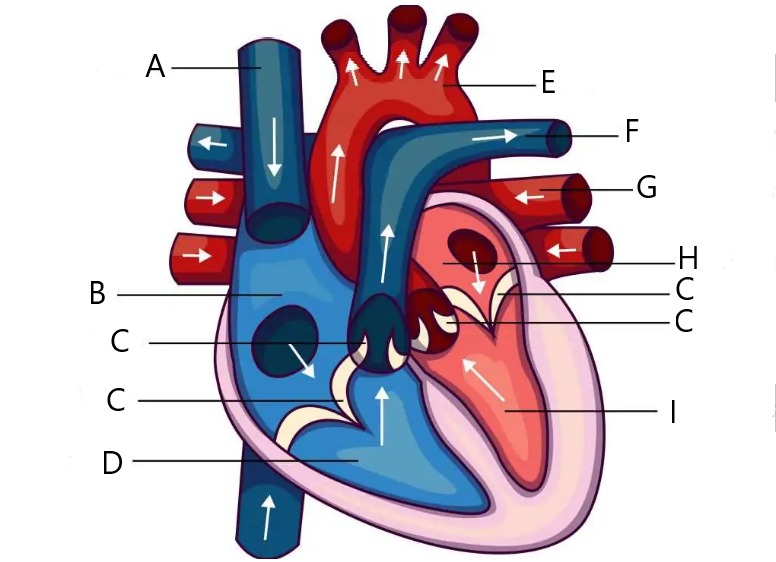
Heart
A: Vena Cava
B: Right atrium
C: the valves
D: Right ventricle
E: Aorta
F: Pulmonary artery
G: Pulmonary vein
H: Left atrium
I: Left ventricle
Stent
A metal mesh placed in a blocked or partially blocked artery. They are used to open up the blood vessel via the inflation of a tiny balloon
Surgery is very easy to install✅
Is effective most of the time ✅
Can get stuck and block the artery or burst it ❌
Quick recovery time✅
Low risk of heart attack ✅
Restore blood and last long ✅
Can form blood clots and risk of infection ❌
Statin
Drugs used to lower blood cholesterol and improve the balance of HDLs to LDLs
Proven to reduce risk of heart attacks and strokes✅
Muscle pain or weakness as common side effect ❌
Increased risk of type 2 diabetes as can slightly raise blood sugar levels ❌
Platelets
Small fragments of cells with no nucleus
They assist with clotting progress as they get stuck in the mesh of fibres called fibrin when the skin is damaged
Plasma
Transports blood components and dissolved substances - CO2 and digestion products
Transports urea to kidneys for excretion and it is removed from the blood to make urine.
Red blood cells
Bi-concave disc shape to maximise SA:V ratio for diffusion
No nucleus for maximum haemoglobin capacity
White blood cells
Form part of the body’s defence system against harmful microorganisms
Some form antibodies, some form antitoxins, some consume pathogens
Bypass surgery adv+dis
Very effective against severe blockages✅
Higher infection risk ❌
Long recovery time ❌
Expensive ❌
General anaesthetic needed
Valve replacements: Mechanical vs Tissue
Mechanical
Last very long ✅
Very effective and tough ✅
Need to take medication for the rest of your life which prevents blood clotting ❌
Tissue
No medication needed ✅
Very effective ✅
Only lasts 12-15 years ❌
Big surgery ❌
Pacemaker
Electrical device implanted to replace pacemaker cells
Used to correct irregularities in the heart rate, implanted in the chest
Sends strong, regular electrical signals to the heart to stimulate it to beat properly
Some only activate when natural rhythm goes wrong
Cancer
Disease caused by uncontrolled division (proliferation) of abnormal cells in a part of the body
Malignant tumours
Invades neighbouring tissues and spread to other parts of the body via the blood
Creates secondary tumours (metastases)
Benign tumours
Growth of abnormal (slow growing) cells contained in one area
Health problems with tumours
Can cause pressure or damage to an organ so can be fatal if the brain is involved as there is no space for the tumour to grow into
Malignant tumour can cause serious health problems as can form secondary tumours and often completely disrupt normal tissue and if left untreated, will often kill the person
Very difficult to treat
Communicable disease
A disease caused by pathogens that can be passed from one organism to another eg. HIV/AIDS, Salmonella, Cholera, COVID-19
Non-communicable disease
A non infectious disease that cannot be passed from one organism to another eg.Diabetes, Coronary heart disease, stroke, heart attack
Pathogen
A disease-causing microorganism (microscopic living thing)
Ways pathogens are spread - by water/food
Diseases can be transmitted via infected water, raw or undercooked meat or contaminated food
eg. diarrhoeal diseases, salmonella or cholera
By air (droplets)
Transmitted from droplets expelled when breathing
eg. influenza, tuberculosis or common cold
Direct contact
An infected organism coming into contact with a healthy one via sexual or skin-to-skin contact
eg. HIV, AIDS or hepatitis
Bacteria
Bacteria can cause infection and illness
Also in our body and are helpful, some decomposers
Smaller than plant and animal cells but much larger than viruses
Generally less than 10μm (micrometers)
Living single-celled organisms
Prokaryotic, without nucleus
Mostly treatable with antibiotics
Viruses
Very small, ~20-200nm (nanometers)
Not classified as living organisms
Only have protein coating and genetic material inside, coating is instead of the cell membrane
Double or single strand DNA or RNA
Cannot be treated
Fungi
Range from 2-80μm
Most common route of infextion is via inhalation of spores which cause respiratory infections
Most commonly reproduce asexually but can reproduce sexually
eg. ringworm, athlete’s foot, fungal nail
Preventing infections - Hygiene
Measures include handwashing at certain times, using disinfectants on dirty surfaces, keeping raw meat separate, coughing or sneezing in tissues and maintaining hygiene of people and agricultural machinery
Isolation
If someone has an infectious disease, they should be kept on their own away from uninfected people to prevent the spread of the disease to more vulnerable people
Destroying/controlling vectors
Some diseases are passed on through vectors like mosquitoes or houseflies
If they are destroyed, it can prevent the spread of disease
Vaccination
This is done by introducing a small, harmless amount of a disease to your body so your immune system knows how to quickly fight and overwhelm the disease before it can cause damage
Measles
Enters from nose, mouth and eyes
Immune system responds intitially with natural killer cells
Infects dendritic cells and uses them to enter deeper into the body
Symptoms of measles
High fever, rash, headache and bronchitis
Spreads easily and destroys the immune system
Long term effects include very weak immune system taking long to recover
Skin defences
Physical barrier to prevent pathogens from reaching tissues underneath
If skin is breached, it can leave the body exposed but recovers quickly using platelets, also prevents severe blood loss
Produces antimicrobial secretions to destroy pathogens
Covered with extra microorganisms as and extra barrier
Antibiotics
Inhibit cell wall synthesis
Interrupt DNA/RNA synthesis
Disrupt protein production by blocking ribosome action
Damage cell membranes
Monoclonal antibodies
Produced in a lab and made from a single clone of immune cells
Cloned immune cells are identical and so are the antibodies they produce
Specific to one binding site on one protein (antigen) and so are able to target a specific chemical/cells
+ and - of MAbs
Very high specificity ✅
Can be used to diagnose diseases ✅
Cancer treatments/therapy ✅
Time consuming❌
Expensive ❌
Ethical concerns ❌
Side effects ❌
Can be too specific as it only targets 1 disease/1 person❌
Hybridoma
A cell created during the production of MAbs by the fusion of an antibody-specific lymphocyte and a tumour cell
Uses of MAbs - Pregnancy tests
Reliant on MAbs that bind to HCG hormone that is produced in early stages of pregnancy
MAbs in pregnancy test bind to the hormone if its present and produce colour change
Small amounts of the hormone are passes through urine
Disease diagnosis
Eg. Used in blood test for prostate cancer
Becoming more important in modern disease detection
Made to bind to specific antigens, on blood clots or cancer cells
MAbs carry markers to help see doctors where disease has spread
Measuring and monitoring
Used in hospitals and labs to measure hormone levels and other chemicals in the blood
Eg. donated blood for HIV infection, detecting illegal athlete drug use
Disease treatment
Can be used to treat specific diseases
Used to trigger immune responses, carry toxic drugs for chemo or to block receptors on cancer cells
Used to treat cancers
Research
Used to identify or locate specific molecules in a cell/tissue
MAbs linked a molecule of fluorescent dye can be used to observe build up of disease or cancer
How MAbs are made
Mouse lymphocytes stimulated by introducing the antigen by injection
Lymphocytes extracted from mouse’s spleen
Lymphocytes combined with a tumour cell (myeloma cell)
Hybridoma cell made so the tumour cell divides quickly but can still make the antibody
A single hybridoma cell can be cloned to produce many identical cells that all produce the same antibody
A large amount of the antibody can be collected from mouse’s spleen
Uses of monoclonal antibodies
Direct use of MAbs to trigger the immune system to recognise, attack and destroy cancer cells
MAbs can be used to carry toxic drugs or radioactive substances for radiation therapy, or chemicals that stop cells growing and dividing to attack the cancer cells directly without harming other cells in the body
Using MAbs to block receptors on the surface of cancer cells and so stop the cells growing and dividing
Pregnancy test process
Urine applied
Reaction zone - Mobile Abs specific to HCG here, can move and have dye attached
Result window - Immobilised Abs specific to HCG
Control window - Immobilised Abs specific to mobile Abs from reaction zone
No line in result or control - INVALID
Line only in control window - NEGATIVE
Line in control and result window - POSITIVE
Synthetic vs Plant antibiotics
Synthetic
Can be manufactured on a larger scale more easily so more product can be manufactured
Easier to edit for fewer side effects
More stable and dosage can be controlled
Safer for rigorous testing of synthetic drugs
Plant
Only small amounts of active chemical can be found
Plant extracts can be impure
Antibiotics from living organisms
Evidence of medicinal properties means a lot less time and expenses for research ✅
Long term usage suggests few side effects✅
More biodegradable - less harmful environmental effects✅
Sourcing the living material may be difficult (eg. low yield, low availability etc.) ❌
Concentrations may be low❌
Might be difficult isolating the chemical that has the antibiotic effect❌
Developing drugs
In-vitro testing - New drugs tested on cells, tissues and organs. Many drugs fail at this point.
Animal testing - Tested on animals to see how they work in whole living organisms. Side effects and dosage established here. Done one rabbits, mice, monkeys
Human testing
Phase 1 - Testing on a small number of healthy male volunteers. Very low doses are used
Phase 2 - Testing on a small number of humans with the disease. It determines if the drug is safe and effective.
Phase 3 - Similar to Phase 2 but much larger numbers are used
Approval and publishing results
Results of tests and trial published in journals after have been peer reviewed - other scientists working in same field check results
If tests are passed, drug is licensed and doctors can begin using it
Drug is monitored when in use and checked by NICE (National Institute for Clinical Excellence)
Placebo
A medicine that doesn’t contain the active drug, used in clinical trials of new drugs
Double blind trial
Neither researcher or patient know who has had the real medicine or the placebo
Detecting diseases in plants
Malformed stems and leaves (due to aphid infestation)
Stunted growth (eg. nitrate deficiency)
Spots on leaves (rose black spot)
Decay or rotting (rose black spot)
Growth (eg. crown galls)
Discolouration (yellowing in Mg deficiency)
Presence of visible pests (aphids, caterpillars)
Plant diseases - Virus
Eg. Cauliflower/ tobacco mosaic virus
Symptoms - Mosaic patterns, vein clearing, stunted growth
Virus destroys cells, reducing plant growth because the affected areas of the leaf do not photosynthesise
Bacteria
Eg. Crown gall
Symptoms - Abnormal galls (rough tumours) on the roots, trunk or crown of a plant
Galls can encircle stem or trunk, cutting off flow of sap to cause stunted growth and eventual death
Fungus
Eg. rose black spot
Black spots on leaves become larger blotches and then leaves turn yellow and fall off
Causes defoliation and weakening of the plant, reducing its ability to flower and makes it more susceptible to other diseases
Parasitic
Eg. root knot nematodes
Damaged roots
Prevents the plant getting the water and mineral ions it needs so it fails to grow
Insects
Eg. aphids
Discoloration, leaf curling, yellowing, stunted growth, visible green insects around stem
Sharp mouth parts penetrate phloem vessels to feed on sugar rich sap, damaging and weakening the plant, aphids also act as vectors
Nitrate ion deficiency
Stunted growth
Nitrate ions not present to convert the sugars made in photosynthesis into proteins needed growth
Magnesium ion deficiency
Leaves turn yellow between veins but veins remain green, called interveinal chlorosis
Mg ions not present to make chlorophyll so leaves become yellow and growth slows as plant cannot fully photosynthesise
Identifying plant diseases
Testing kits using MAbs
Taking samples to a lab
Gardening manuals or online manuals
Plant defences - Chemical
Chemicals that the plant can secrete
Lots of medicines are derived from plants, like aspirin from willow bark or caffeine
Poisons
Anti-microbial chemicals
Physical defences
Physically prevent entry of pathogens
Layers of dead cells eg. bark
Cellulose cell walls
Waxy cuticle on leaves and stems
Mechanical defences
Similar to physical but more of a function rather than just a barrier
Leaves that curl up/ droop when touched
Thorns/ hairs stop animals eating or touching
Photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O —> C6H12O6 + 6O2
reactants products
Carbon dioxide + Water —> Glucose + oxygen
Light and chlorophyll
Endothermic reaction as it takes in energy from the environment
Chloroplasts
Organelles of plant cells that contain a green substance called chlorophyll
Chlorophyll
Absorbs light energy and this is transferred into chemical form in glucose molecules
Optimum conditions for plant growth
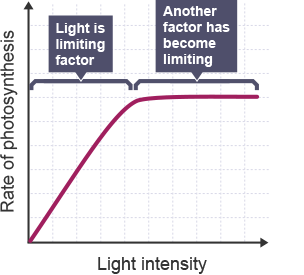
Lots of sunlight
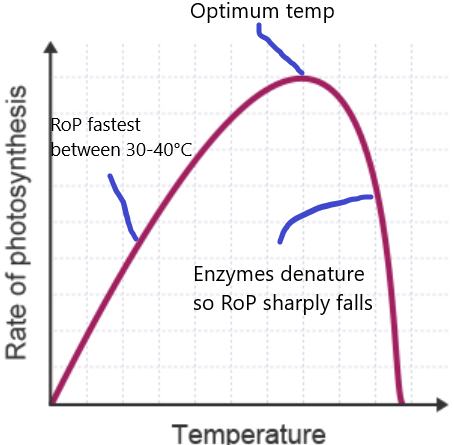
Warm temperature, not too hot as enzymes would denature
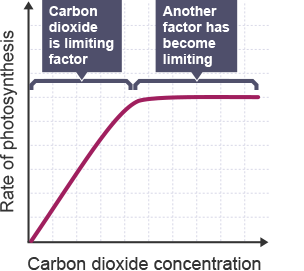
High CO2 concentration
if one of these is in short supply, we call this a limiting factor
RoP graph for CO2 concentration
RoP grpah for light intensity
RoP graph for temperature
Hydroponics
A method of growing plants using mineral nutrient solutions in water without soil in order to optimise growth rate
Uses of glucose
Can be converted into fats and oils for storage
Converted into proteins for plant growth
Stored as starch for storage
Used as an energy source for respiration
Used to make cellulose in plant cell walls
Aerobic respiration
glucose + oxygen —> carbon dioxide + water + (release of energy)
C6H12O6 + 6O2 —> 6CO2 + 6H2O (energy transferred to the environment)
Site of aerobic respiration is the mitochondria
Inner membrane is folded to increase SA for enzymes involved in aerobic respiration
Respiration is an exothermic reaction as it releases energy to the surroundings
Respiration
Allows you to keep warm
To carry out the basic functions of life
To make your muscles contract
Respiration in plants
Energy released from respiration is required to move mineral ions, such as nitrates from the soil into the roots
Plants can synthesise amino acids from glucose and nitrate ions
They can absorb nitrates from the soil and ‘fix‘ atmospheric nitrogen
Anaerobic respiration
An exothermic reaction in which glucose is broken down in the absence of oxygen to produce lactic acid in animals and ethanol and CO2 in plants and yeast
A small amount of energy is transferred for the cells
C6H12O6 —> 2C3H6O3 + ENERGY
glucose —> lactic acid (energy transferred to the environment)
IN PLANTS - glucose —> ethanol + carbon dioxide (energy transferred to the environment)
Lactic acid
The end product of anaerobic respiration in animal cells
Oxygen debt
The extra oxygen that must be taken into the body after exercise has stopped to complete the aerobic respiration of lactic acid
Response to exercise
Hormones
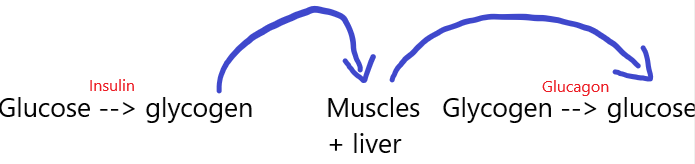
Short term effects of exercise
Heart beats faster in order to pump more blood around the body to deliver more oxygen and glucose to cells to release energy via respiration
Breathing gets heavier to get more oxygen into the bloodstream
Long term effects of exercise
Increased heart and lung volume
Resting pulse and breathing rate lowers
Cardiac output (amount of blood pumped per beat) increases
Metabolism in plants and animals
Formation of lipids from glycerol and fatty acids🐵
Respiration🐵
Breakdown of excess protein into urea 🐵
Conversion of glucose—>glycogen🐵
Conversion of glucose—> starch🌱
Synthesis of protein from glucose and nitrate ions🌱
Metabolism
Sum of all reactions that take place in a cell or the body
Affected by
Age
Muscle to fat ratio
Hormones
Genetic factors
DNA and the genome
Genome is the entire genetic material of an organism
Human Genome Project sequenced every gene in the human body
DNA provides chemical instructions about how to build an organism

Mitosis
Interphase - DNA replicates to form two copies of each chromosome
Cell grows and double the organelles
Mitosis - Prophase - Chromosomes condense to become more visible and membrane around nucleus disappears
Metaphase - Chromosomes line up along middle of the cell
Anaphase - One copy of each chromosome is pulled to each end of the cell
Telophase - A new nuclear membrane forms around each set of chromosomes
Cytokinesis - Cytoplasm and cell membrane divide to form 2 identical daughter cells
Stem cells
Unspecialised cells that have not yet differentiated into a specific role, have the capacity to become any type of cell
Stem cells in plants
Cell division in plants take place in regions of the plant called meristems. These tissues are found in the tips of roots and shoots
Plants only get taller when cells in meristems elongate following cell division
After this cells differentiate into their final form
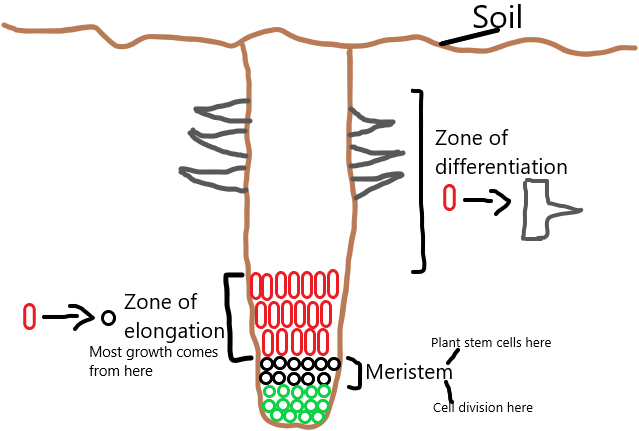
Re-differentiation
Plant cells can become a different specialised cell, even after they have first differentiated