BSCI202 lab practical 1
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
The 3 cellular components that blood is composed of
RBCs/Erythrocytes, WBCs/leukocytes, platelets
5 types of WBCs
agranulocytes: (lymphocytes, monocytes) and granulocytes: (neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils)
function of erythrocytes
use hemoglobin to carry oxygen to tissues throughout body
function of leukocytes
immune functions
function of platelets
blood clotting
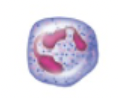
name, amount in blood, and function
neutrophil. 3000-7000. phagocytize pathogens or debris
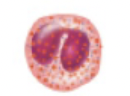
name, amount in blood, function
eosinophil. 100-400. kill parasitic worms, slightly phagocytic, role in allergy and asthma

name, amount in blood, function
basophil. 20-50. releases histamine and other mediators of inflammation. contains heparin (anticoagulant)

name, amount in blood, function
lymphocyte. 1500-3000. immune response through direct cell attack or antibody production. recognizes antigens
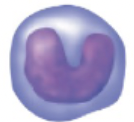
name, amount in blood, function
monocyte. 100-700. develop into macrophages in tissues and phagocytize
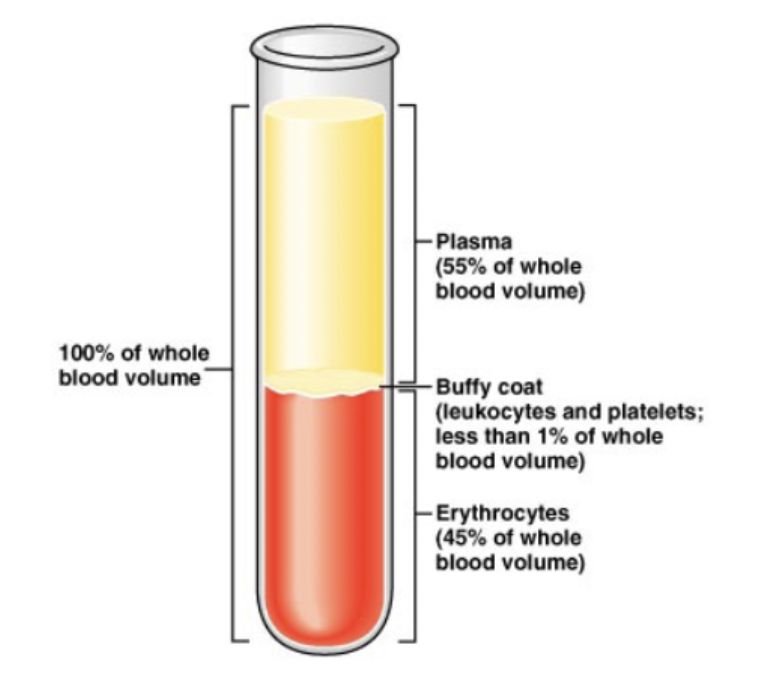
formula for hematocrit
(height of RBC/height of all components of blood) x 100
what is a buffy coat
fluid that is >1% of blood that contains leukocytes and platelets
normal hematocrit ranges
adult female: 37-47%
adult male: 42-52%
newborn: 49-61%
whats leukocytosis
leukocyte count too high. buffy coat is over 1%. caused by infection and some types of leukemia. detected by hematocrit
whats anemia
erythrocyte count too low. hematocrit value below average
whats aplastic anemia
bone marrow doesn’t produce enough new erythrocytes
whats iron deficiency anemia
erythrocytes are smaller
whats hemolytic anemia
erythrocytes are destroyed too quickly
whats sickle cell anemia
sickle shaped erythrocytes
hemorrhagic anemia
caused by blood loss. not detected by hematocrit
why do individuals that live at high altitude have higher hematocrits
low oxygen levels, so body produces more erythrocytes to increase blood oxygen levels
function of lymphatic system and the 2 parts
2 parts are lymphatic vessels and lymphoid tissues and organs.
function: transports ecaped fluids back to the blood. aids in body defense and disease resistance/ helps digestion
whats lymph fluid
fluid within bodily tissues that leaks out capillaries of cardio system. picked up by lymphatic vessels
properties of lymphatic vessels
one way system that moves lymph back towards heart (right lymphatic duct and thoracic duct). skeletal muscle pump. valves prevent backflow of lymph
function of lymph nodes
filters lymph fluid before its returned to blood.
2 defense cells within lymph nodes
macrophages: engulf and destroy foreign substances
lymphocytes provide immune response to antigens
cortex
outer part of lymph node that contains follicles that house collections of lymphocytes
medulla
inner part of lymph node that contains macrophages
how does lymph enter and exit
enters through the 4 afferent lymphatic vessels and exits out the 2 efferent lymphatic vessels
the 2 primary lymphoid organs
bone marrow and thymus
6 secondary lymphoid organs and tissues
spleen, lymph nodes, tonsils, adenoid, appendix, and peyers patches
red bone marrow
site of lymphocyte production. B cells and T cells originate from here but only B cells mature here.
spleen function
left side of abdomen. filters blood and destroys worn out blood cells. forms blood cells in fetus and acts as blood resevoir.
thymus
T cells mature here. produces hormones to program lymphocytes. functions at peak levels during childhood
tonsils
trap and remove bacteria.
peyer’s patches
capture and destroy bacteria in the intestine.
appendix
reservoir for gut bacteria. assists in B cell maturation
B cell function
lymphocyte that resides in the lymph nodes, spleen or other lymphoid tissues.
plasma cells produce…
antibodies
5 major classes of antibody
IgM, IgG, IgD, IgA, IgE
structure of antibodies
Y shaped and antigen binding sites on arms.
antibody functions
bind to specific antigen. aids in inactivation or destruction of antigens
antigen antibody complex is inactivated by
neutralization, agglutination, precipitation which enhances phagocytosis
how is blood typed
by using antibodies that cause blood with certain proteins to clump. classified based on antigens found on the plasma of erythrocytes
2 groups that blood is classfied by
ABO blood groups
Rh blood groups
difference between arteries and veins
arteries carry blood away from the heart. veins carry blood to the heart.
4 chambers of the heart and function
2 atria: receive blood from the vena cavae and pulmonary vein
2 ventricles: receive blood from atria and pumps blood into aorta and pulmonary artery
septa includes
interatrial septum: separates atria into the left and right atrium
interventricular septum: separates ventricles into left and right ventricle
what is lub dub
sounds of blood hitting SL and AV valves as they close. lub is the closure of av valves at the start of ventricular systole. dub is closure of sl valves at the end of ventricular systole,
4 heart valves
2 semilunar: pulmonary and aortic
2 atrioventricular valves: tricuspid and mitral
location and function of SL valves
located at openings to arteries. prevent backflow of blood into ventricles when they relax.
function of AV valves
prevents backflow of blood into atria
right av valve: tricuspid
left av valve: bicuspid/mitral
chordae tendinae
cords prevent av valve inversion
papillary muscle
anchors the chordae tendinae
3 layers of the heart wall
epicardium: outermost layer of heart wall
myocardium: middl layer made of cardiac muscle.
endocardium: innermost layer
2 circulatory systems
systemic circulation: carries blood to tissues for nourishment. transport deoxygenated blood back to heart. left ventricle to aorta to other arteries to arterioles to capillaries to venules to veins to venae cavae to right atrium
pulmonary circulation: carries oxygenated blood to lungs for gas exchange then brings oxygenated blood back to the heart. right ventricle to pulmonary trunk to pulmonary arteries to capillaries within the lungs to left atrium
natural pacemaker
SA node. sets rate of depolarization
affect of sns and pns on heart activity
sns accelerates heart rate while pns decelerates heart rate
p wave
depolarization of the atria before atrial contraction
QRS complex
depolarization of ventricles before ventricular contraction. atrial repolarization
t wave
repolarization of ventricles
explain the route of conduction in the heart
impulse at SA node
impulse is delayed at the AV node
electrical conduction through ventricles: bundle of His/AV bundle, bundle branches, purkinje fibers)
whats depolarization
contraction of cardiac muscles
PR interval
signal travel from SA node to AV node. if >0.2 seconds, that indicates partial heart block
QRS complex
ventricular depolarization and atrial repolarization. prolonged interval means partial blockage of right or left bundle branch
QT interval
from ventricular depolarization through repolarization. faster heart rate is shorter QT interval. prolonged interval can cause ventricular arrhythmias
whats this
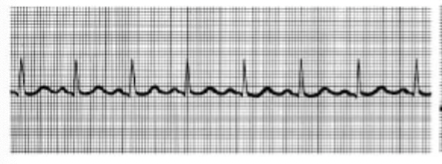
normal sinus rhythm
whats this
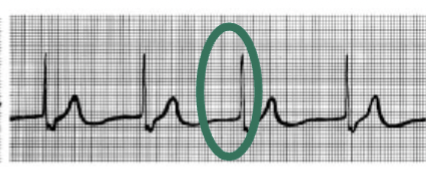
junctional rhythm. no P wave. SA node is not acting as the pacemaker and AV node is pacing the heart
whats this
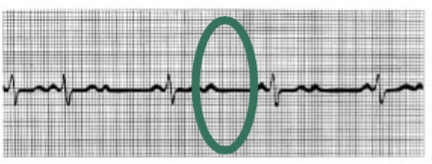
second degree heart block. not all p waves followed by qrs complex. damage to AV node
whats this
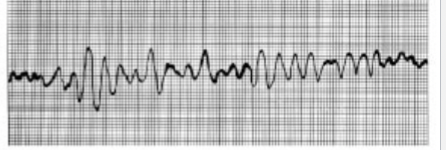
ventricular fibrillation. acture myocardial infarction. impulses generated in atria do not pace ventricular contractions
fibrillation
rapid uncoordinated contractions. renders heart useless as a pump
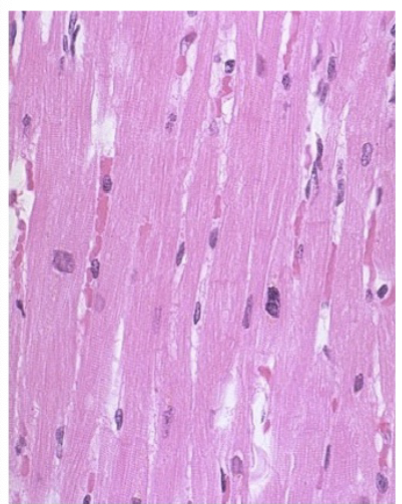
whats this
normal cardiac muscle. striated and uninucleate cells.
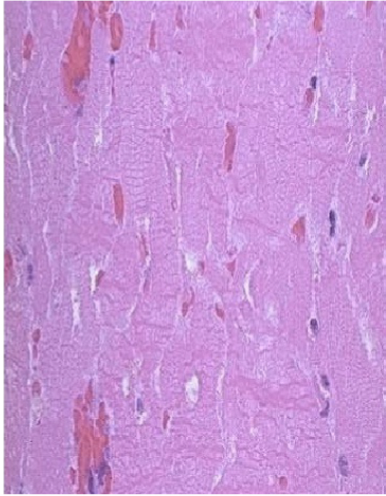
whats this
immediately after infarction (12hrs). loss of striations and nuclei
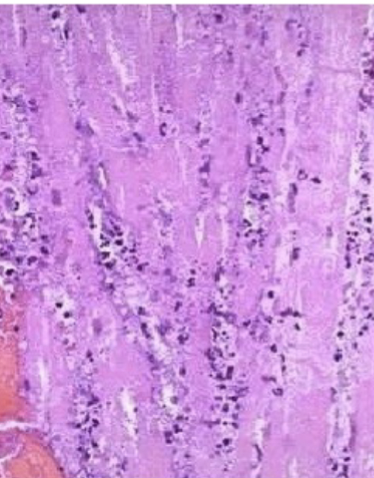
whats this
healing the tissue. (1-4 days0. necrosis of cardiac tissue. invasion of neutrophils
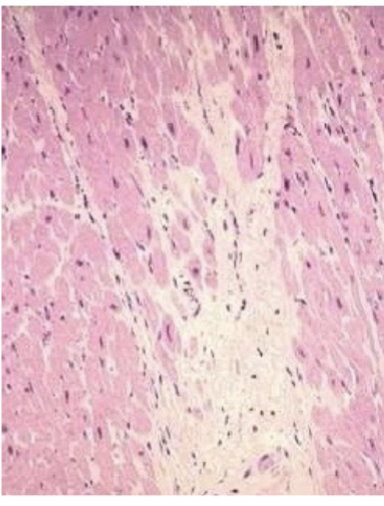
whats this
healed tissue. scarring and noncontractile scar tissue
average blood volume
females is 4-5 L and males is 5-6 L
why are RBCs different from other blood cells
anucleate so unable to repair damage/reproduce. limited lifespen of 100-120 days and break down in spleen
diapedesis
how leukocytes move in and out of blood vessels and wnder through body tissues with amoeboid motion
leukocytosis
wbc count over 11,000. indicates bacterial/viral infection.
leukopenia
wbc number under 4000
leukemia
malignant disorder of lymphoid tissues. uncontrolled proliferation of wbcs accompanied by reduction of rbcs and platelets.
causes of polycythemia (inc in # of rbcs)
bone marrow cancer or living in high altitudes.
finding differential wbc count formula
percent= #observed/total # counted times 100.
hemostasis
protective mechanism when blood vessel breaks to stop bleeding
what are the 3 events that happen during homeostasis
vascular spasm platelet plug formation, coagulation
what triggers coagulation mechanism
when the injured issues and platelets release tissue factor and platelet factor 3.
what do antibodies do
act against RBC carrying antigens that arent present on the persons own rbcs
blood type A antigens and antibodies
antigens A, antibodies anti B
blood type B antigens and antibodies
B antigens, Anti A antibodies
blood type AB antigens and antibodies
A and B antigens, no antibodies
blood type O antigens and antibodies
O antigen, anti a and anti b antibodies
atherosclerosis
body’s blood vessels become blocked by plaques
2 functions of the lymphatic system
transports tissue fluid that leaked out of the vascular system and returns it to the blood vessels
protects body by removing foreign material
lymphatic capillaries
pick up leaked fluid and carry it to larger vessels
right lymphatic duct function
drains lymph from right upper extremity, head, and thorax. large thoracic duct receives lymph form rest of the body.
location and function of lymph nodes
found in inguinal, cervical, and axillary regions. filters lymph fluid
2 types of defense systems
innate: surface barriers like skin and mucous membranes. born with it
adaptive defenses. lock and key for foreign molecules
3 characteristics of adaptive immune response
memory, specificity, self tolerance
whats autoimmunity
our immune system/s ability to recognize our own tissues (self) from foreign antigens (nonself)
clonal selection
when antigen binds to the specific cell surface receptors of a T or B cell