Dissolved Solids, Sediments, & Turbidity
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What is TDS?
total concentration of dissolved substances in water
Inorganic salts: sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, chlorides, sulfates, silicates, bicarbonates
Small amounts of organic matter from natural sources
the "invisible" dissolved content
What TDS measures?
All dissolved ions and molecules
What does TDS not include?
suspended particles, bacteria, or anything that can be filtered out
TDS in freshwater? For drinking water?
20-1000 mg/L
50 mg/L for taste, 500 mg/L EPA recommended
is TDS unhealthy?
No
indirect indicator of contamination
How to measure TDS?
Directly: Evaporate a water sample, weigh
the remaining residue
Indirectly: Specific conductance (SpC) is a
proxy for TDS in freshwaters
Controls on TDS
Soil type
Geology/weathering
Ex. Limestone is relatively easy to mineralize
pH/temperature/DO
Discharge & Residence time
Evaporation
Decomposition & DOM
Human Activities
Wentworth Scale
defines grain size class in intervals that
increase by powers of 2
How does particle size change from upstream to downstream?
Particle size tends to decrease
moving downstream
Median size (d50)
half of the bed particles are large, half are smaller
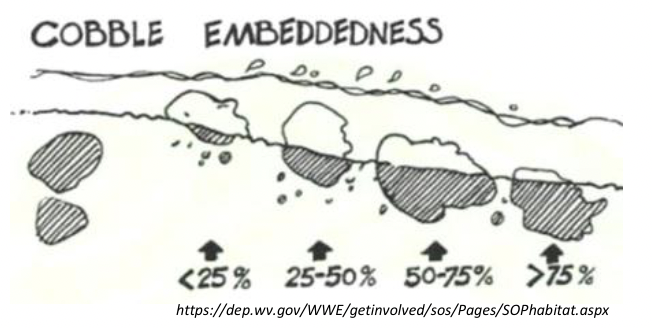
Embeddedness
degree to which particles are buried
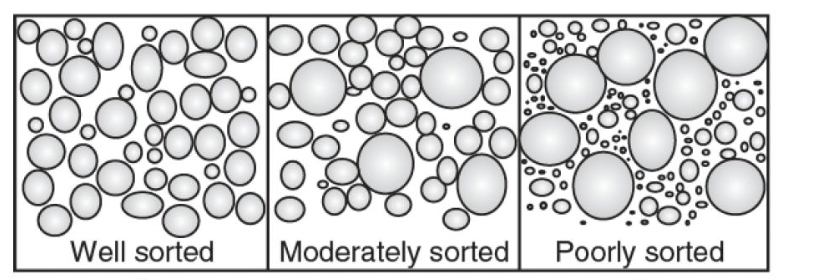
Sorting
distribution of particles in the bed
• Well-sorted = discrete patches of the same size
• Poorly sorted = mixed particle sizes
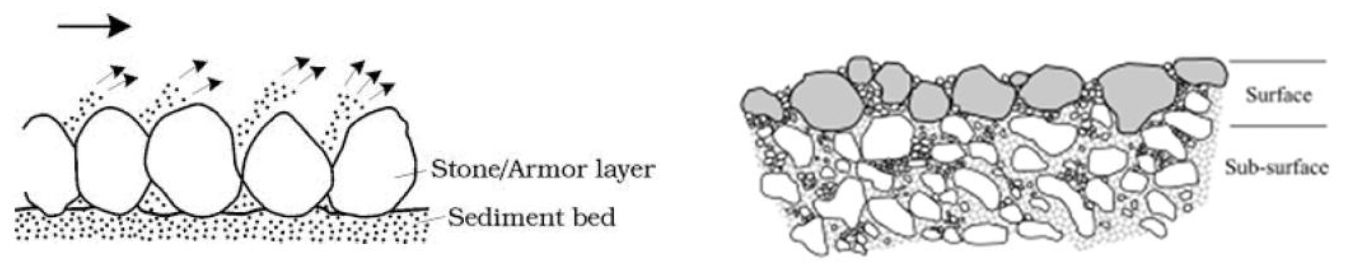
Armoring
finer sediments overlain by larger particles
• Occurs when the bed surface of gravel-bed rivers is coarsened relative to the subsurface
• Dams can exacerbate this process
How do sediments move in streams?
Stream load – transport of matter other than water by streamflow
Dissolved load
mostly dissolved chemicals (TDS!), including
nutrients
Particulate load
non-dissolved components
Suspended (solid) load, wash load, bed load
Suspended (solid) load
material in the water column (<0.5 μm)
wash load
between 0.5 μm and 0.063 mm (largely sand and silt); think about the puff of sand when you step in a stream
bed load
material that rolls along the bottom (>0.063 mm)
shear stress
The amount of tractive force (“drag”) applied parallel to a surface
Will determine if a particle enters the stream load
highest in the “thalweg” (mainthread of flow)
Critical shear stress (τc)
shear stress necessary to mobilize
a given grain size
Shear increases
with both slope and depth
main driver of sediment transport?
storms
Entrainment (erosion)
getting the sediments moving
sand is most easily entrained
sediment transport (movement)
movement down the channel;
requires a lower velocity
Deposition (sedimentation)
settling out; as velocities decrease, grains settle out
Heaviest/largest sediments fall out first
Channel Modifications
erosion
accretion
sediment routing
Measuring sediments
Total suspended solids (TSS) – filtering a water sample until filter clogs
Direct turbidity measurement - beam of light is passed through a water sample; measure amount of light scattered (units = NTU)
↑ scattered light with ↑ turbidity
Secchi Disk – common in lakes