Lec 19 Sleep
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
sleep is naturally recurring state characterized by
reduced or basent conciousness, suspended sensory activity, inactivity of most voluntary muscles
sleep occurs in what animals
all mammals, birds, and most reptiles
sleep is controlled by
brainstem nuclei with projections to brain and spinal cord
does brain remain active while you sleep
yes, brain is active while sleeping
humans spend … of their lives sleeping, or … hours
1/3, 7.5 hrs
how is sleep measured
EEG which records electrical activity on scalp from thousands of cells
EEG’s are ___ spatial resolution, and has leads in which parts?
low spatial res, frontal, temporal, central, parietal, occipital leads
What are the two main phases of sleep?
Non-REM and REM sleep
What are 3 major reasons for sleep?
ecological adaptation, energy conservation/restoration, memory consolidation
eco adaptation
difficult for predators to hunt in the dark at night, so prey sleep then to save energy
in terms of energy conservation/restoration, what happens to glycogen and metabolism when you sleep?
glycogen replenishes, metabolism decreases to reduce heat loss on colder nights
What effect does sleep deprivation have on the immune system?
It compromises it
how does sleep affect memory consolidation?
strengthens synaptic connections induced during waking hours, spatial location info is consolidated in rats
rat experiment sleep
experimental rat was kept awake and control rat could sleep, exp rat lost body weight and total sleep deprivation led to death in 3-4 weeks
What type of animals have single long periods of sleep?
Predators like humans, long period of nocturnal or diurnal sleep
How do prey animals sleep differently?
They sleep in short intervals of minutes to maintain vigilance
What is unique about dolphin and seal sleep?
One brain hemisphere sleeps while the other stays awake
first hour of sleep is
non-rem
What characterizes Stage I sleep?
drowsy, EEG has decreased frequency, increase in amplitude
What characterizes Stage II sleep?
Light sleep; lower frequency, increase amplitude, spike clusters/sleep spindle
What characterizes Stage III sleep?
Moderate-deep sleep; even lower frequency and higher amplitude
What characterizes Stage IV sleep?
Deep sleep; delta waves, low frequency, high amplitude
What is the EEG trend from wakefulness to Stage IV sleep?
Amplitude increases and frequency decreases
When does REM sleep occur?
After non-REM sleep stages
How long does the first REM period last?
About 10 minutes, gets longer as sleep continues
How does EEG during REM compare to wakefulness?
It looks similar to being awake
How many REM periods occur per night?
About 5
What brain waves are associated with wake?
beta eyes open, alpha eyes closed
What brain waves are associated with sleep?
Theta(stage 1) and delta waves(stage 4)
deep sleep is characterized by …. activity in….
synchronous activity in pyramidal cortical neurons
What does synchronization of neurons cause in EEG?
Increased amplitude (delta waves)
How do heart rate and respiration change in non-REM vs REM sleep?
slow down in non-REM sleep and increase in REM sleep.
REM sleep increases from 10 minutes to
50 minutes in final cycle
which stage of sleep is only present in the first 2 sleep cycles?
stage 4 non-REM
EOG
electroOCULOgram, eye movements in REM
EMG
electroMYOgram, muscle movement at onset of sleep and right before waking
When does sleepwalking and talking occur?
During non-REM sleep
When does dreaming occur?
Mostly during REM sleep, combo of memory and hallucinations
dreams last … hrs for both REM and n-REM
2 hrs, mostly in REM
What are dreams like in REM vs non-remsleep?
in REM, dreams are vivid and emotional, bizarre
in non-REM, dreams are less vivid, less emotional, more related to everyday activities, Sigmund Freu’s day residue
What are two possible functions of dreams?
Memory consolidation and unwanted memory disposal(would otherwise become intrusive+compulsive)
What is the activation synthesis theory?
Dreams result from random cerebral cortex firing during REM, forebrain creates a story to make sense of nonsensical sensory info, this explains irrationality of dreams in REM
how brain knows its night/day
Light sensed by photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (with melanopsin photopigment) sets the biological clock by sending signals to the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), then via the paraventricular nucleus(hypothalamus) and preganglionic sympathetic neurons(spinal cord) to the pineal gland, which releases melatonin.
What brain structure is central site for circadian control?
Suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of the hypothalamus, evidence is SCN lesion in rat abolished sleep-wake cycle
SCN controls which circadian rhythms
sleep • physical activity • alertness • hormone levels • body temperature • immune function • digestive activity
SCN neurons hae internal endogeneous 24-hr rhythm that persists when…
external time cues are removed
human in a cave, deprived of time clues would…
begin free-running on a cycle of 24-hrs based on internal clock.
What hormone is called the "Dracula of hormones"?
Melatonin, only comes out at night
in darkness, SCN turns on pineal gland to make melatonin starting from
9PM for 12 hrs
body temp and motor activity when we sleep is decreased due to…
melatonin
What happens to melatonin production in elderly people?
It decreases, so elderly sleep less at night
during REM sleep, which happens to limbic activity and frontal cortex activity?
increased limbic activity (amygdala, hippocampus, pontine tegmentum, anterior cingulate cortex)
decreased frontal cortex activity (dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, posterior cingulate cortex inactivated)
stimulation of what woke the cat in experiment?
Cholinergic neurons (Reticular Activating System)
low-frequency pulse stimulation of … caused cat to sleep
lamina medullaris interna of the thalamus
sleep has interactions btwn which 3 brain structures
brainstem, thalamus, cortex
role of Cholinergic nuclei near the pons-midbrain junction
low activity during non-REM, increases during REM, high when awake
What is the role of noradrenergic neurons from the locus coeruleus (LC)?
inactive during sleep, active during waking,arousal,stress
What is the role of serotonergic neurons from the raphe nuclei?
Active during waking, decreased or inactive when asleep
What is the role of histamine neurons in the TMN?
slow firing when tired, stop firing when asleep, fires rapidly when waking, modulates LC and raphe
which 2 chemicals promote wakefulness?
orexin and histamine
antihistamines cause
drowsiness
TMN is activated by ….
orexin from lateral hypothalamus
VLPO lesion causes
insomnia
VLPO of hypothalamus inhibits..
wake circuits, causes onset of sleep
Antihistamines make people drowsy because they A. inhibit the cholinergic nuclei in the brainstem. B. excite several classes of neurons in the raphe. C. mimic noradrenaline and serotonin at several metabotropic receptors. D. are selectively taken up by VLPO neurons. E. block the effects of tuberomammillary hypothalamic neurons.
E, block effects of TMN
chart of sleep wake centers
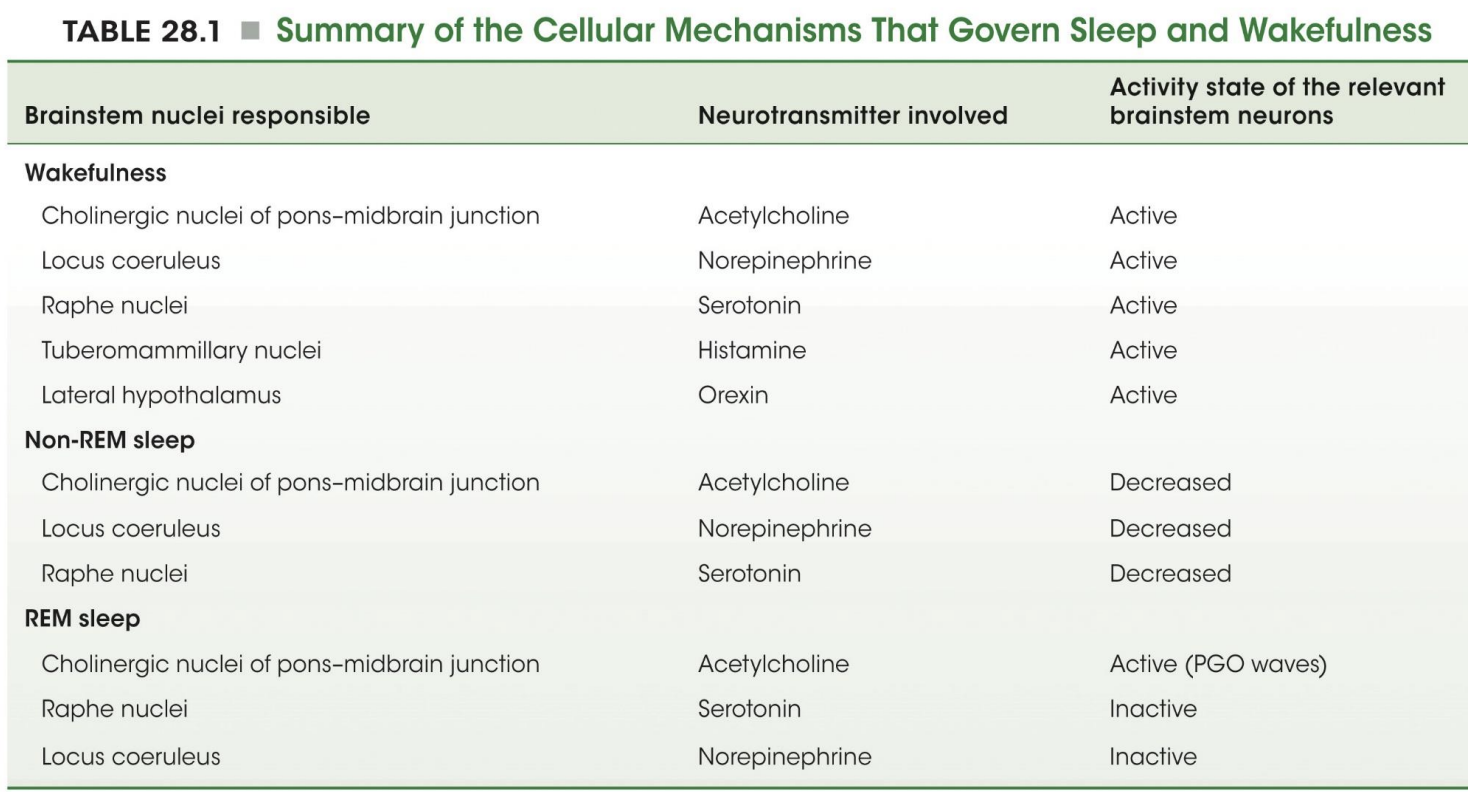
Projections from brainstem modulate activity of thalamocortical projections
Ascending projections from LC (NE), raphe (5HT), reticular activating system (ACh) and tuberomammillary nucleus (histamine) ➔ thalamocortical neurons ➔ pyramidal cortical neurons
What are the two states of thalamocortical neurons?
Intrinsic bursting oscillatory(sleep) and tonic active (wake)
What happens during intrinsic bursting of thalamocortical neurons?
sleep, thalamocortical neurons synchronize with cortex
oscillation decreased by activation of ascending systems causes what…
diminishes the high amplitude, low frequency waves of sleep
What is tonically active firing of thalamocortical neurons associated with?
awake, thalamocortical neurons depolarized by RAS, transmit info encoding peripheral stimuli to cortex
What is insomnia?
Inability to sleep long enough or deeply enough, caused by stress, jetlag, depression, caffeine, age altering NT’s
What is sleep apnea?
Breathing interruptions during sleep causes little to no slow-wave sleep and less REM, caused by pharynx muscle problems or compressed by obesity, rise in CO2 causes person to inhale by reflex and wakes person up
What is narcolepsy?
frequent 30 sec to 30 min REM sleep attacks without entering non-REM, animal studies show mutation in ORX2 gene
causes of jet lag aka desynchronosis
internal vs external clock, eating chocolate for breakfast prevents jetlag
Delayed sleep phase vs advanced sleep phase
DSPS- out of phase with 24 cycle, later everyday
ASPS- out of phase with 24 cycle, earlier everyday
What is non-24-hour sleep-wake syndrome?
Circadian rhythm not synchronized to 24-hour day
What is shift work disorder or situational circadian rhythm disorder?
Circadian disruption from work schedules
What is somniphobia?
Fear of falling asleep
What is hypopnea syndrome?
Abnormally slow respiratory rate during sleep
What is parasomnia?
Disruptive or inappropriate behaviors during sleep
What is bruxism?
Grinding or clenching teeth during sleep
What is periodic limb movement disorder (PLMD)?
Involuntary limb movements during sleep
What is restless legs syndrome (RLS)?
Uncontrollable urge to move legs, without PLMD
What is sleep paralysis?
Temporary paralysis before or after sleeping
What is nocturia?
Frequent nighttime urination
What is enuresis?
Bedwetting during sleep without waking