States of matter y9
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Density
The mass in a given volume of a substance (solids are denser than liquids, which are
denser than gases)
Temperature
The measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance
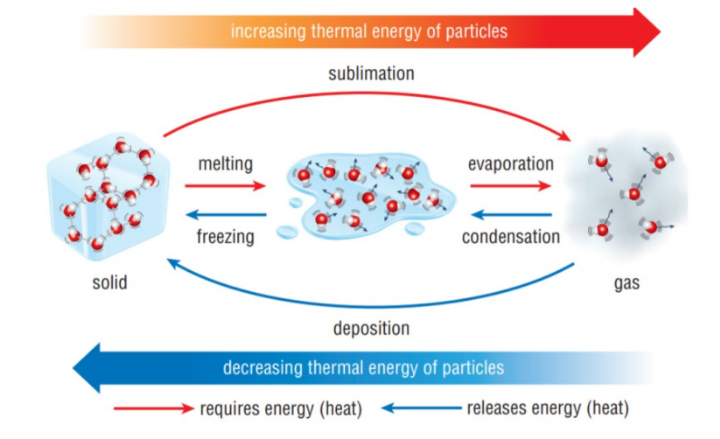
Melting
is the process where a solid turns into a liquid as it absorbs heat, resulting in increased particle movement.
Melting point
the specific temperature at which a solid transitions to a liquid. (ice melts at 0°C)
Boiling
The change of state from a liquid to gas, due to an increase in temperature (also called vaporisation)
Condensing
The change of state from a gas to a liquid, due to a decrease in temperature
Freezing
The change of state from a liquid to a solid, due to a decrease in temperature
Sublimation
The process by which a solid turns into a gas without melting (at normal pressure)
Deposition
The process by which a gas turns into a solid without condensing (also called de-sublimation)
Evaporation
The change of state from a liquid to a gas over a range of temperatures. Evaporation happens at the surface of a liquid
Solvent
The liquid in which a solute will dissolve
Solute
The soluble substance that dissolves in the liquid to form a solution
Solution
The mixture formed when a solute dissolves in a solvent
Saturated solution
A solution with the maximum amount of solute dissolved in solvent at a particular temperature
Solubility
The maximum amount of solute (in grams) that can be dissolved in 100g of solvent (100cm3 of water) at a particular temperature.
How is Evaporation is different to boiling?
The average kinetic energy of particles will vary in a sample, hence at a particular temperature some particles will have an energy higher than the average kinetic energy, some lower
• Very fast particles at the surface of the substance have enough kinetic energy to overcome the forces of attraction between the particles and so turn to a gas (they evaporate)
• As more particles evaporate, the average kinetic energy of the sample decreases, so the temperature also decreases
• Evaporation occurs over a range of temperatures at the surface of a liquid; boiling occurs at a specific temperature throughout he whole of the liquid

Properties of a solid
Arrangement of particles : Packed closely together, all touching in a regular repeating pattern of ordered rows
Movement of particles: Vibrate around a fixed position
Kinetic energy of particles : Lowest
Forces between particles: Strong forces of attraction holding particles together
Shape, volume and density: Fixed shape and fixed volume; most dense

Properties of a liquid
Arrangement of particles : Fills from the bottom, close together, touching, some gaps between particles, randomly arranged
Movement of particles: Particles can move past each other; medium speed
Kinetic energy of particles : Higher
Forces between particles: Forces of attraction less effective than in solid, but still present
Shape, volume and density: No fixed shaped but fixed volume; less dense

Properties of a Gas
Arrangement of particles : Far apart, large spaces between particles, irregular and random arrangement
Movement of particles: Random movement at high speed in all directions
Kinetic energy of particles : Highest
Forces between particles: Negligible forces of attraction
Shape, volume and density: No fixed shape or volume; least dense
Endothermic
Processes that need energy (take in energy from the The kinetic energy of the surroundings)
The kinetic energy of the particles is increased. These processes are melting, boiling/evaporation and sublimation.
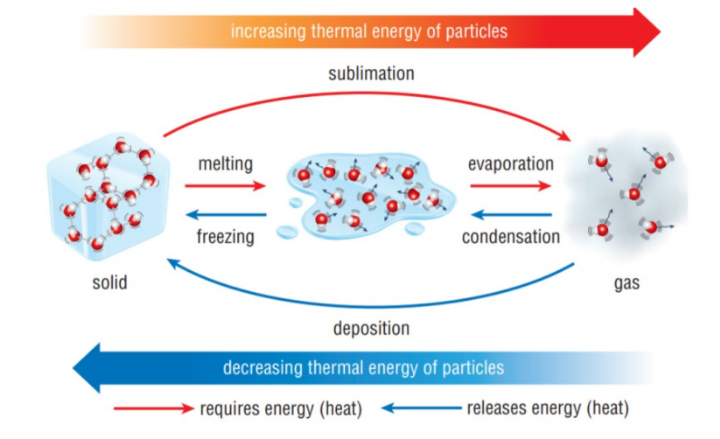
Exothermic
Processes that give out energy (release energy to the
surroundings)
The kinetic energy of the particles is decreased. These processes are condensing, freezing and deposition.
Changes of state graph
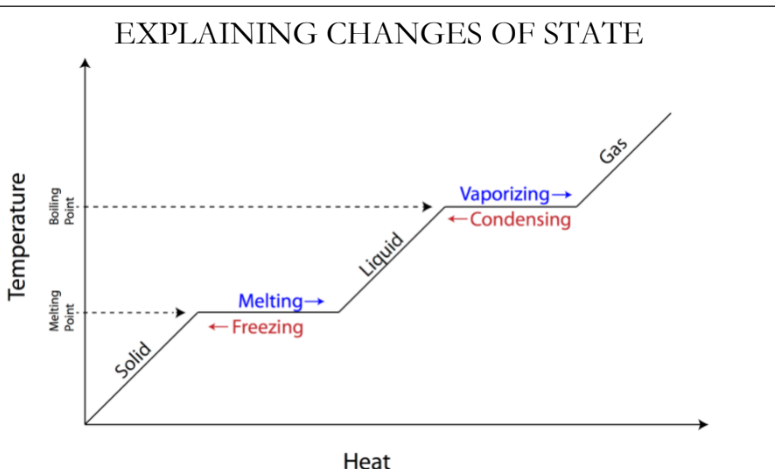
The physical state of a substance at a given temperature (solid)
If the given temperature is below the melting point of the substance, the substance is a solid
The physical state of a substance at a given temperature (liquid)
If the given temperature is between the melting and boiling point of the substance, the substance is a liquid
The physical state of a substance at a given temperature (Gas)
If the given temperature is above the boiling point of the substance, the substance is a gas
Diffusion
The spreading out (random movement) of particles from an area of
high concentration to an area of low concentration