BIOL 461 Neurobiology Midterm
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
dorsal
up toward top of head
ventral
down toward base of head
rostral
toward front (nose)
caudal
toward back (occipital lobe)
medial
middle
lateral
away from middle
anterior
front
posterior
back
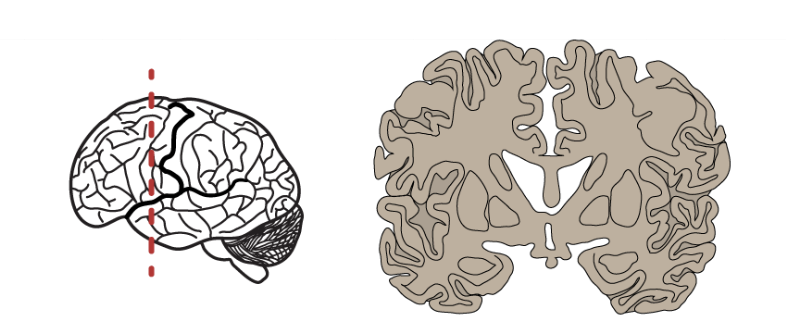
coronal plane
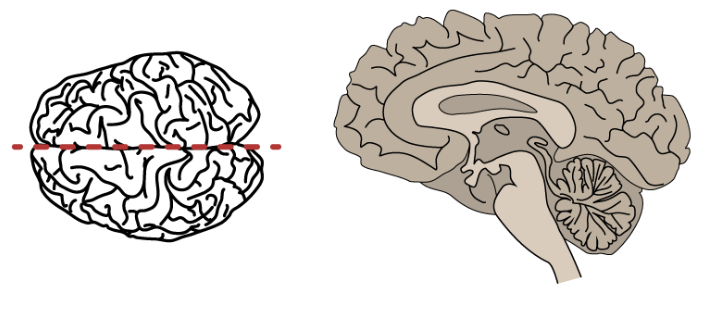
saggital plane
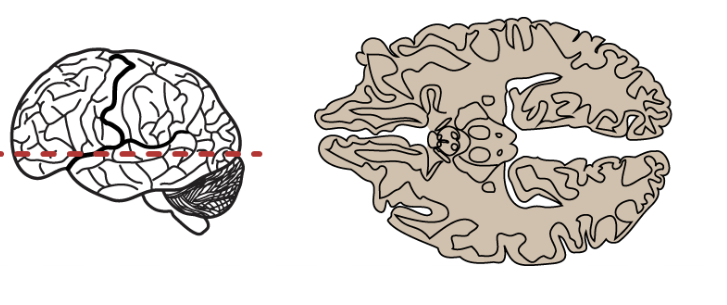
horizonatal plane
why use intracellular recording?
you need precise real time Vm, EPSP/IPSP
pros/cons of intracellular recording?
get the voltage, see sub-threshold events
one cell at a time, invasive, fragile seal no movement
why use extracellular recording?
to listen in on multiple nearby neurons while animal behaves
pros/cons of extracellular recording?
multiple cells, during behavior, more stable than intracellular
no sub-threshold events, artifact signals, spike shape depends on geometry between electrode and neuron
why use tetrodes/arrays?
you need more spikes or separation of neighbor cells
pros/cons of tetrodes/arrays?
many simultaneous neurons
invasive, depth trade offs
why use neuropixels?
want big and dense recordings across structures
pros/cons of neuropixels?
orders of magnitude scale, large datasets
lots of data but less than 1% of brain, analysis bottleneck
why use spike raster plots?
see link between firing and stimulus
pros/cons of spike raster plots?
good population timing view
hides sub-threshold events, needs sorting and alignment
why use patch clamp?
prove channel function or kinetics
pros/cons of patch clamp?
single protein precision, clear mechanism
cannot collect much data at once, specific preparation
why use calcium imaging?
need large field of view, cell type targeting, movie of many neurons
pros/cons of calcium imaging?
big field, genetic targets, record during behavior
measuring Ca and not voltage directly, Ca slower than AP deconvolve
why use protein calcium sensor?
cell type specificity, chronic imaging
pros/cons of protein calcium sensor?
targeted, stable, multi-color
needs viral or transgenic delivery
why use voltage imaging?
want fast voltage events and optical readout
pros/cons of voltage imaging?
direct measure, higher fidelity than calcium imaging
less mature, finicky
why use optogenetics?
want to activate cells
pros/cons of optogenetics?
high temporal and spatial resolution, animals can behave during
viral and transgenic delivery is hard
why use MRI?
need anatomy
pros/cons of MRI?
whole-brain volume, non-invasive
does not show neural activity
why use fMRI?
want to map whole brain while it is engaged
pros/cons of fMRI?
non-invasive, see deep structures
slow, subject must lay still, variation in interpretation
why use MEG?
need good temporal resolution without a magnet
pros/cons of MEG?
faster than fMRI, non-invasive
weaker signal, less depth than fMRI
why use EEG?
want to measure while person does moving tasks, cheap
pros/cons of EEG?
good temporal resolution, portable
artifacts, poor spatial resolution, averaging of signals
cerebrum
thought, memory, voluntary movement, sensory perception and made up of frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital lobe
corpus callosum
connects left and right cerebral hemispheres to communicate
cerebellum
balance, movement, posture
brain stem
breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, sleep-wake cycles
spinal cord
transmits messages between brain and body
gray matter
neuron cell bodies, dendrites, synapses
white matter
myelinated axons
neural inhibition
any process that reduces a neurons chance of firing action potentials
cocaine
-natural coca plant
-agonist
-blocks dopamine reuptake via DAT
-targets dopamine (pleasure) and noradrenaline (readiness) system
-increases synaptic dopamine, euphoria
amphetamine
-synthetic
-false substrate/releaser
-releases dopamine instead of reuptake
-targets dopamine (pleasure), noradrenaline (readiness), serotenergic system
-increase synaptic dopamine and serotonin, alertness
caffeine
-natural coffee bean
-antagonist
-blocks A1/A2A receptor from binding adenosine to calm
-targets adenosine, dopamine, noradrenaline systems
-prevents neural inhibition, alertness
THC
-natural cannabis plant
-partial agonist
-activates CB1 GPCR which leads to decreased GABA and glutamate release
-targets endocannabinoid, perception, neural activity systems
-relaxation, altered time sense, mild euphoria
LSD
-semi-synthetic from fungus
-agonist
-activates 5-HT2A metabotropic receptor
-targets serotinergic system
-hallucination, sensory perception altered
PCP
-synthetic
-antagonist
-blocks NMDA ionotropic receptor
-glutamate, dopamine, perception, neural activity systems
-dissociation, psychosis, hallucination
psilocybin
-natural mushrooms
-agonist
-activates 5-HT2A receptor
-targets serotinergic system
-hallucination, sensory cross talk
morphine
-natural opium poppy
-agonist
-activates u-opiod GPCR
-targets opiod, dopamine, neural activity systems
-sedation, pain relief, euphoria
heroin
-semi-synthetic from morphine
-agonist
-converts to morphine and binds to u-opiod GPCR’s that block GABA neurons
-euphoria, highly addictive
nicotine
-natural tobacco
-agonist
-activates ACh ionotropic receptor
-targets dopamine and noradrenaline systems
-increased dopamine release
-stimulation and mild dependency
alcohol
-natural fermentation
-depressant
-enhance GABA-A by blocking NMDA receptor and fluidizing membrane
-targets dopamine and neural activity systems
-sedation, motor impairment
aspirin
-semi-synthetic willow bark
-enzyme inhibitor
-inhibit COX enzymes which blocks prostaglandin synthesis
-targets peripheral prostaglandin system
-pain relief, anti-inflammatory
naloxone
-synthetic
-antagonist
-competes u-opiod receptor without activating it
-reverses opiod overdose
MDMA
-synthetic
-false substrate/releaser
-blocks serotinergic system
-targets dopamine, perception, serotinergic system
-euphoria, neurotoxic at high dosage
acetylcholine (ACh) ionotropic
ionotropic nicotinic ACh receptor allows Na+ in and K+ out
neuromuscular junction, depolarizes cell for muscle contraction
acetylcholine (ACh) metabotropic
metabotropic muscarinic ACh GPCR receptor opens resting K+ channels
vagus nerve in heart, hyperpolarizes cell to slow heart rate
GABA (mature)
ionotropic GABA-A receptor permeable to Cl-
hyperpolarizes cell to inhibit action potentials
GABA (developing)
ionotropic GABA-A receptor permeable to Cl-
depolarizes cell to excite action potentials by increasing intracellular Cl- (to flow out)
glycine
ionotropic glycine receptor permeable to Cl-
hyperpolarizes cell to inhibit action potentials in the spinal cord
glutamate AMPA
ionotropic AMPA receptor allows Na+ in and K+ out to quickly depolarize cell for EPSPs
glutamate NMDA
ionotropic NMDA receptor permeable to Na+, K+, Ca2+ to depolarize cell and allow Ca2+ entry
adrenaline (epinepherine)
metabotropic beta-adregenic GPCR receptor turns on cAMP—>PKA—>Ca2+ to allow more Ca2+ entry to increase heart rate and strengthen contraction
what 2 things does an NMDA receptor need to open?
1) glutamate binds to NMDA receptor
2) post-synaptic membrane must be depolarized to remove the Mg2+ ion blocking NMDA receptor at rest
what happens once the NMDA receptor is open for binding?
Ca2+ influx triggers LTP (stronger synapses) and more AMPA receptors are inserted into postsynaptic membrane for more EPSPs
associative learning
when two neurons are regularly active at the same time, their communication becomes stronger
AMPA vs NMDA receptors
AMPA: only needs glutamate binding, fast, initial cell depolarization
NMDA: glutamate binding AND Mg2+ block removal, slow, LTP
what neurotransmitter does curare (paralysis) block?
ACh via nicotinic ACh receptor
what neurotransmitter does acetylcholinesterase block?
ACh via degrading ACh in synaptic cleft
what neurotransmitter does atropine block?
ACh via muscarinic ACh receptor
what drugs effect mature GABA?
barbituates
muscimol
benzodiazepines
picrotoxin (blocks Cl- channel)
what neurotransmitter does picrotoxin block?
mature GABA
what neurotransmitter does strychnine block?
glycine receptor in spinal cord/brainstem
what does length constant 𝜆 represent?
how far a potential spreads before dropping to 37% of initial amplitude
larger 𝜆 = further spread
𝜆 is proportional to radius, bigger axonal radius = further spread
what is the quantal hypothesis?
each vesicle unit releases as an integer multiple
what are v-SNARE (vesicle docked) and t-SNARE (presynaptic membrane docked) proteins?
upon Ca2+ binding in presynaptic membrane, they twist together to fuse vesicles to membrane
what is botulinum toxin?
cleaves SNARE blocking ACh NT release thus muscles cannot contract called flaccid paralysis (botox)
what is tetanus toxin?
targets SNARES in inhibitory spinal neurons blocking GABA and glycine release thus cell uncontrollably excites and rigid paralysis (lockjaw)
what do experiments conclude about the role of Ca2+ in synaptic transmission?
1) removing extracellular Ca2+ stops NT release even w/ AP
2) increasing intracellular Ca2+ invokes NT release w/o AP
3) EPSPs occur in integer mulitples
what are mEPPs? (mini endplate potentials)
tiny postsynaptic depolarizations that occur spontaneously without stimulation in low Ca2+ environment
what is tetrodotoxin (TTX)?
drug that blocks voltage-gated Na+ channels to kill AP (fatal)
what is myelin?
fatty sheath that wraps around neuronal axons to speed AP
time constant 𝜏 (𝜏=RC)
sets how fast membrane voltage changes after a current
smaller 𝜏 = faster voltage response
2 criteria for ion to cross PM?
1) open channel/transporter
2) electrochemical gradient driving force
what is Eion?
balance when chemical and electric gradient cancel
mamallian E values (K+, Na+, Cl-, Ca2+)
Ek+= -80 mV
Ena+= +60 mV
Ecl-= -65 mV
Eca2+= +120 to +130 mV
what happens when Vm=Eion (reversal potential)
no net flux of ions
ionotropic receptor
neurotransmitter gated ion channels
faster than metabotropic
metabotropic receptor
GPCRs activated by neurotransmitter binding
slower than ionotropic
amplifies signals
long-lasting effects
reinforcement
what you EXPECT versus what actually HAPPENS
drugs hijack brains natural reinforcement learned by altering dopamine reward prediction error signal
e.g. cocaine use leads brain to interpret taking drug as a positive prediction error (good surprise)
reward system
-dopamine rich areas
-VTA, NAc, medial forebrain
-direct stimulation is VERY pleasurable
serotonergic system
-raphe nuclei
-neurons project every way, reason why ser target drugs affect mood everywhere
glutamate/GABA system
-balance excitation/inhibition
-suppress dopamine to reduce APs