lab final - intro to molecular diagnostics (cls 607)
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
molecular lab areas
Pre-PCR area
Reagent preparation
Specimen preparation
slight positive air pressure to keep contaminants from going into room
Post-PCR area
Amplification
Detection
slight neg air pressure to prevent products from going out of the room
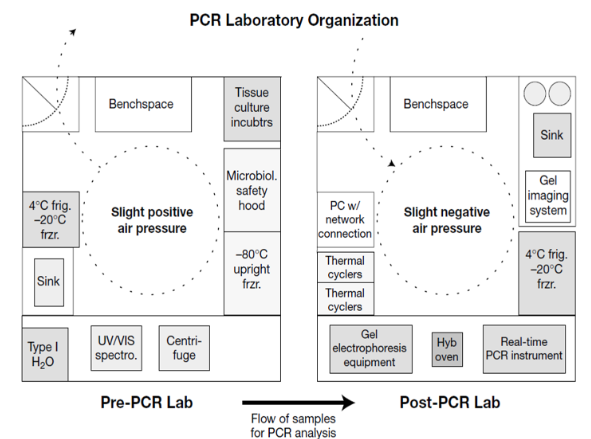
(PCR lab rules & regulations) work surfaces & workflow
Always work in a one-way direction from pre-PCR to post-PCR to avoid carryover contamination from PCR products
Post-PCR should be kept as far away as possible from pre-PCR to avoid aerosol contamination
working surface in each area must be decontaminated with 10% sodium hypochlorite followed by 70% ethanol before performing assay procedures in that area
Specimens must be stored separately from reagents so as not to contaminate open reagents
(PCR lab rules & regulations) attire & specimen handling
Lab coats must be worn in all areas; the coat worn in post-PCR must never be worn in pre-PCR
When handling material containing DNA/RNA or amplicon, always use a pipettor with aerosol-barrier tips (or a positive displacement pipettor). Post-PCR pipettors must never be used in pre-PCR
Centrifuges should be kept at a distance from areas where master mixes are prepared
(PCR lab rules & regulations) glove safety
Gloves must be worn at all times for operator safety as well as for control of contamination from one area to another
Gloves must be changed before moving to the next work area
Gloves worn in the specimen preparation area must never be worn in the reagent preparation area
Gloves worn in post-PCR must never be worn in pre-PCR
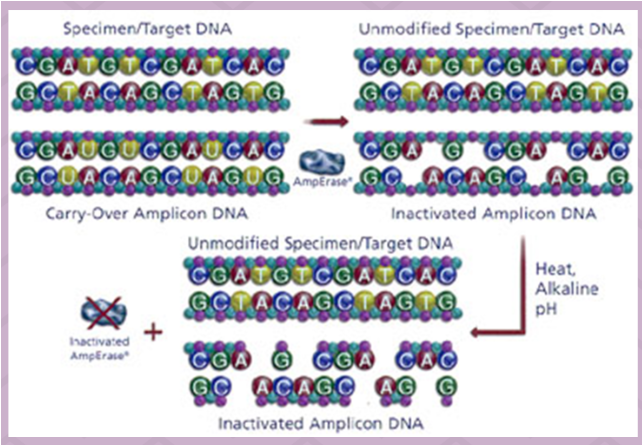
preventing contamination: AMP erase
When setting up PCR reactions, substitute deoxyuridine (dUTP) for deoxythymidine (dTTP)
Any contamination amplicons will contain U rather than T
When setting up subsequent PCR reactions, AmpErase (uracil-N-glycosylase, or UNG) is included as a reagent
UNG cleaves the deoxyuridine in the contaminating amplicon, preventing the contamination from being amplified
template unaffected since it doesn't contain deoxyuridine
UNG is heat-inactivated during the first PCR cycle, so the desired PCR product is protected
negative controls
a known negative specimen that monitors for contamination
positive controls
A known positive specimen (high, low) monitors for assay activity, contamination
A known positive specimen + patient specimen monitors for inhibitors
internal controls
Control target added to a patient sample prior to extraction (often present in extraction reagents in FDA-approved kits) monitors extraction efficiency and presence of inhibitors
No template (reagent control) monitors for contamination
quality control
Commercially available kits:
The number of kit-based tests (both with and without FDA approval) is rapidly increasing
Manufacturers provide reference samples and reagent sets that have been tested for accuracy, precision, detection limits, interfering substances etc
New lot numbers of kits must be analyzed with reference samples prior to use on patient samples
lab developed tests (LDTs)
diagnostic tests created and used within a single laboratory
Must be proven effective by in-house validation studies, e.g., sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, precision
2024: FDA claimed regulatory authority over LDTs (makes approval more difficult)
2025: a federal court struck down this rule
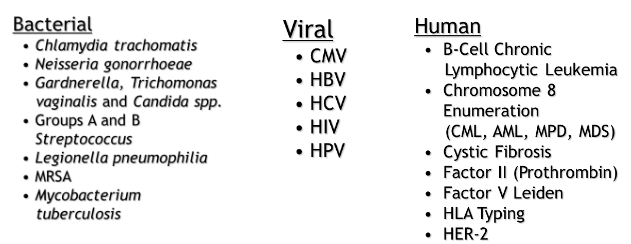
FDA approved molecular tests (pic)
hereditary hemochromatosis
Genetic condition that causes too much iron to be absorbed
Iron overload—build-up of iron in tissues and organs
Two common mutations in HFE gene:
C282Y & H63D
Most likely to have symptoms C282Y homozygotes and C282Y/H63D compound heterozygotes
hereditary hemochromatosis general procedure
DNA extraction & dilution
2 PCR reactions for amplification of C282Y & H63D
restriction enzyme digest of C282Y & H63D
run products & PCR reactions on gel electrophoresis
analyze

interpretation of hereditary hemochromatosis results
C282Y mutation ADDS a restriction enzyme site
homozygous C282Y = three bands
H63D mutation REMOVES a restriction enzyme site
homozygous H63D = two bands
normal result for hereditary hemochromatosis
C282Y = bands at 74 & 176 bp
band at 74 bp is diagnostic of normal allele
uncut DNA will be at 250 bp
H63D = bands at 53, 55, 99
band 99 is diagnostic of normal allele
uncut DNA will be at 207
heterozygote result for hereditary hemochromatosis
C282Y = bands at 29, 45, 74, 176 bp
band at 45 bp is diagnostic of mutant allele
H63D = bands at 53, 55, 99, 152
band 152 is diagnostic of mutant allele & 99 is normal
homozygote result for hereditary hemochromatosis
C282Y = bands at 29, 45, 176 bp
band at 45 bp is diagnostic of mutant allele
H63D = bands at 55, 152
band 152 is diagnostic of mutant allele
hepatitis C virus
Causative agent hepatitis C, viral infection of the liver that can lead to liver disease
Enveloped positive sense RNA genome
Serology and/or PCR used for diagnosis
(HCV) how to handle RNA?
RNA is more sensitive to degradation compared to DNA
Rnases are very stable enzymes
Only use supplies/reagents that have been treated to inactivated RNAses
Ideally, have a set of pipettors dedicated to RNA work
Aseptic technique
HCV RNA extraction kit steps
For purification of viral RNA from plasma, serum, urine, cell culture media or cell-free body fluids
General steps:
Lysis of viral particles
Buffering conditions adjusted so that RNA binds to column
Contaminants are washed away
RNA is eluted
how does the QIAamp viral RNA kit separate DNA and RNA?
buffering conditions are adjusted so that the viral RNA preferentially binds to the column
PCR will use primers specific for the RNA
minimizes human DNA/RNA by getting rid of human cells—serum is used instead of other cellular samples
two step vs one step vs end point reverse transcriptase PCR
two step RT-PCR: reverse transcribe RNA to DNA in one reaction, then set up PCR
one step: RT-PCR: reverse transcription and PCR all take place in one tube
end point RT-PCR: only looking for end product (is product present or absent)
quantitative RT-PCR
amount of DNA generated in each cycle can be used to quantify RNA in original sample
HCV gel electrophoresis results
positive result--band at 298 bp
CANNOT tell viral load
rxn lane w/o reverse transcriptase should NOT have product
unexpected bands may mean contamination or nonspecific amplification