Chemical Spill and Injury Response in Laboratory Safety (extended)
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
What should you do immediately after a small liquid spill on your skin?
Flush the skin with flowing water for at least 15 minutes (30 minutes for bases) and notify your instructor.
Why should jewelry be removed after chemical exposure?
To facilitate removal of residual liquid that may be trapped between the skin and jewelry.
What is the recommended action if solid chemicals spill on your skin?
Brush the solid off before applying water, then wash the area with soap and water.
What should you do if your skin or clothing is contaminated with a large liquid spill?
Go to the nearest safety shower, remove contaminated clothing, and flood the area with water for at least 15 minutes.
What is the importance of notifying your instructor after a chemical incident?
To ensure proper medical attention and documentation of the incident.
What should you do if you are splashed in the eye with chemicals?
Go to the nearest eyewash station and flush the eye for at least 15 minutes (30 minutes for bases).

How should you hold your eyelids while flushing an eye contaminated with chemicals?
Use your thumb and forefinger to hold your eyelids away from the eyeball.
What should you do if an eyewash fountain is not available?
Use the nearest source of running water and pour it gently into the corners of the affected eye.
What special treatment is required for hydrofluoric acid (HF) exposure?
Apply calcium gluconate gel or cream and seek emergency medical treatment immediately.
What are some common types of personal injuries in a laboratory setting?
Slips, trips, falls, electrical shock, chemical ingestion, inhalation, and cuts.
What should you do if someone is overcome with smoke, vapors, or fumes?
Move to fresh air, warn others, and seek medical assistance immediately.
What is the recommended action for contaminated clothing after a chemical incident?
Wash separately from other clothing or discard it as recommended in the Safety Data Sheet (SDS).
How long should you flush an eye affected by chemical exposure?
At least 15 minutes (30 minutes for bases).
What is the risk of putting neutralizing chemicals on skin contaminated with acid?
The heat of neutralization can increase an injury.
What should you do if pain returns after flushing a contaminated area with water?
Resume flushing the area with water.
What should you do with the brushed-off solid chemical after cleaning your skin?
Put it into the appropriate waste container.
What is the purpose of wearing chemical splash goggles?
To eliminate the chance of chemicals splashing into the eyes.
What should you do if you are assisting someone with chemical exposure?
Lead them to the appropriate safety equipment and notify the instructor.
What is the recommended action if you experience chemical inhalation?
Move away from the area to fresh air and seek medical assistance.
What should you do if someone ingests hazardous chemicals?
Call 911 (or your institution's emergency number) and follow first aid treatment shown on the label or in the SDS.
What is the first step if someone is in contact with a live electrical circuit?
Do not touch them; the circuit must be disconnected by unplugging the device or turning off the circuit breaker.
What should you do if an injured person is not breathing and has no pulse?
Provide CPR if trained, or use an AED if available, and call 911 immediately.
How should severe bleeding be controlled?
Place a cloth on the wound and apply firm pressure; elevate the injury above heart level if possible.
What precautions should you take when dealing with blood?
Avoid contact with someone else's blood and use gloves available in most chemistry laboratories.
What is the first action to take if a chemical spill occurs?
Move away from the spill and warn others in the area.
What should you do if a flammable liquid is spilled?
Warn others to extinguish all flames and turn off electrical equipment if safe to do so.
What is the proper response if a chemical spill occurs in a chemical hood?
Close the hood sash to allow vapors to be removed more effectively.
What should you do if a small solid spill occurs?
Use a dustpan and brush to clean up the material as directed by your instructor.
How should small liquid spills be cleaned up?
Use paper towels or another absorbent to soak up the liquid as directed by your instructor.
What should you use to pick up broken glass?
Use tongs or wear leather or cut-resistant gloves; a small brush and dustpan can also be used.
What defines a minor or simple spill?
A spill that can be managed by one person, does not spread rapidly, and does not pose immediate danger.
What defines a major or complex spill?
A spill that involves injury, is highly toxic or flammable, or requires immediate evacuation.
What should be done if a large spill occurs?
Follow your institution's formal procedure for handling spills, as they are not managed by students in introductory labs.
What materials can be used to neutralize spilled acids?
Limestone or sodium carbonate can be used to neutralize spilled acids.
What is the importance of preparing for a laboratory emergency?
It minimizes injury and damage by ensuring you know how to respond appropriately.
What are the most likely emergency situations in a chemistry laboratory?
Ignition of flammable solvents, chemical exposure, cuts from broken glassware, and chemical spills.
Why is prevention education important in laboratory safety?
It helps to prevent incidents and spills, which is crucial for maintaining safety.
What should you do if you observe obstructions in the laboratory aisles?
Notify your instructor immediately.
How should chemicals be transported in the laboratory?
Support the beaker or flask with one hand under the container and alert others to your presence.
What is secondary containment in chemical transport?
Using a rubber carry bucket or plastic tote to transport chemicals out of the laboratory.
What should you do if you are unsure about cleaning up a spill?
Consult your instructor or trained personnel for guidance.
What should be done with materials used to clean up a spill?
Dispose of them as directed by your instructor.
What is the role of personal protective equipment (PPE) during a spill?
PPE helps protect workers from exposure to hazardous materials during a spill.
What is the significance of understanding hazards in the laboratory?
It helps in assessing and minimizing risks, which is essential for safety.
What should be used if a safety shower is immediately available?
It should be used for decontamination.
What are the types of automatic fire-extinguishing systems commonly used in laboratories?
Water sprinkler, foam, carbon dioxide, halon, or dry chemical systems.
What precaution should laboratory workers take when an automatic fire-extinguishing system is activated?
They should evacuate before a carbon dioxide total-flood system is activated to avoid asphyxiation.
What is the primary method for protecting laboratory personnel from airborne contaminants?
Minimizing the amount of contaminants entering the laboratory air.
When should respiratory protection be used in a laboratory?
During experimental procedures, handling hazardous chemicals, responding to spills, or hazardous waste handling.
Which organizations' regulations must be followed for respiratory protective equipment?
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), Mine Safety and Health Administration (MSHA), and National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
What must be implemented at each site where respiratory protective equipment is used?
A respirator program including training and medical certification.
What are the main types of respirators available for laboratory use?
Chemical cartridge respirators, nonemergency respirators, and emergency or rescue respirators.
What is a key limitation of chemical cartridge respirators?
They can only be used for specific vapors or gases and cannot be used in low oxygen environments.
What indicates that a chemical cartridge respirator may be ineffective?
Difficulty in breathing or detection of odors.
How should chemical cartridges be stored?
In sealed containers to prevent chemical contamination.
What is necessary for a respirator to be effective?
It must fit snugly on the face to ensure a proper seal.
What should be done if a user has facial hair when using a respirator?
They should use powered air-purifying or supplied-air respirators instead.
What must be conducted before selecting a respirator?
Tests for a proper fit must be conducted.
What is the purpose of a respirator program under OSHA regulations?
To ensure safe use of respiratory protective equipment through training and medical certification.
What is a potential risk of using chemical cartridge respirators?
Significant breakthrough of contaminants can occur if the cartridge is not replaced regularly.
What additional protection may be required when handling certain airborne contaminants?
Full-body suits and full-face masks may be necessary for skin and eye protection.
What types of vapors cannot be filtered by organic vapor cartridges?
Vapors that are not readily detectable by odor or irritating effects, or those that generate substantial heat upon reaction with the sorbent materials.
What are particulate-removing respirators used for?
Protection against specific classes of dusts, fumes, and mists as specified by the manufacturer.
What is a limitation of particulate-removing respirators?
They are not 100% efficient in removing particles and afford no protection against gases or vapors.
What must be done before using supplied-air respirators?
Fit testing is required before selection and use.
What is the function of supplied-air respirators?
They supply fresh air to the facepiece at a pressure that prevents contaminated air from entering.
When can supplied-air respirators be used in dangerous environments?
When the protection factor is not exceeded and OSHA's Respiratory Standard provisions are followed.
What is the purpose of self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA)?
They are suitable for emergency or rescue work.
What training is required for personnel using respirators?
Thorough training in fit testing, use, limitations, and care of the equipment, including demonstrations and practice.
What does OSHA require before a worker can use a respirator?
The worker must be medically certified.
How often should respirators for routine use be inspected?
Before each use by the user and periodically by the laboratory supervisor.
What should safety showers be used for?
Immediate first aid treatment of chemical splashes and extinguishing clothing fires.

What features should safety showers have?
A quick-opening valve, capability to drench the subject immediately, and drains to reduce water risks.
What is the requirement for eyewash fountains in laboratories?
They should be present if substances used pose an eye hazard or if unknown hazards may be encountered.

How long should an eyewash fountain provide water?
For an extended period of at least 15 minutes.
Where should eyewash fountains be located?
Close to safety showers for simultaneous use if necessary.
Secondary labels
OSHA requires secondary containers to be labeled with at least two key pieces of information:
The chemical name or product identifier.
A general indication of the chemical's hazards (e.g., words, pictures, or symbols).
Manufacturer Labels
These labels contain comprehensive information about the chemical and its hazards. Manufacturer labels must never be removed, altered, or defaced.
Superfund Law (from the Environmental Protection Agency
Any producer of a hazardous compound must pay a premium for producing and selling this chemical. All the money from these premiums goes into a fund monitored by the EPA called the “Superfund”. This fund is then used to treat/clean up any hazardous waste that is not the responsibility of any individual or company, and is also used to clean up hazardous waste sites from the past
“Cradle to grave” Tracking (Congressional Act, Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA))
All Hazardous Waste must now be accounted for from the moment a product is produced through all transactions until it is disposed of. In other words, you cannot pass on a hazardous product without proper paperwork on where it has gone.
What is safety?
Safety is Planning and organization NOT responding to a situation
It can be difficult to know how to handle the accidental release of hazardous substances, so two things should be done before you work:
Design experiments with as low risk as possible
Familiarize yourself with safety hazards and what to do in case of spills or accidents.
If an accident (or spill happens) you should:
Notify the instructor
Tend to the injury: treatment of injured or contaminated person must be a priority, but remove yourself and them from the area if there is a continued hazard to either of you
Take steps to confine the spill or hazard
Clean up if possible
Notify anyone who may be affected: Everyone in the area

warning symbol?
poison

warning symbol?
explosive

warning symbol?
corrosive

warning symbol?
flammable

warning symbol?
environmental hazard
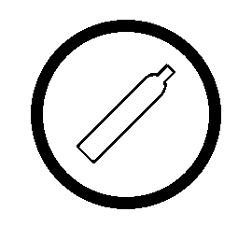
warning symbol?
compressed gas

warning symbol?
radioactive
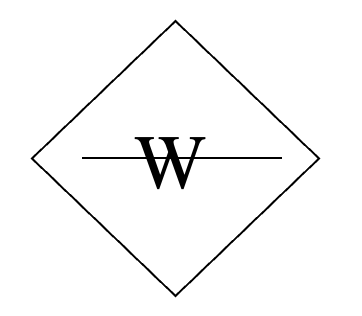
warning symbol?
water reactive

warning symbol?
general health hazard

warning symbol?
biological hazard

warning symbol?
oxidizing agent
In laboratories, the main cause of fires is…
flammable liquids.
Flammability: Flashpoint is…
the temperature at which a spark will ignite a vapor
Flammability: Auto-ignition temperature is…
the lowest temperature at which a substance will spontaneously ignite
Flammability: Flammable range of the solvent is…
Temperature range in which a substance will ignite
Flammability: Incompatible chemicals are…
Chemicals that produce a hazardous reaction or product when combined
National Fire Protection Agency…
Sets the standards for the flammable storage of substances, including the standards for flammable storage cabinets