final exam dalman geol 1403 pt. 2
1/197
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
198 Terms
________ is a volcanic rock that is extremely vesicular and glassy.
Pumice
________ is characterized by very coarse mineral grains?
Pegmatite
Which of the following igneous rocks has a pyroclastic texture?
rhyolitic tuff
A ________ is an open cavity in a volcanic rock that was filled by a gas bubble when the lava was still mainly liquid.
vesicle
A(n) ________ texture represents a single, long period of cooling and crystallization.
phaneritic
Visible quartz and potassium feldspar grains are the main constituents in a ________.
granite
________ is the dominant lava erupted from volcanoes on Hawaii and Iceland.
Basalt
The sizes, shapes, and arrangements of mineral grains in an igneous rock are known as ________.
texture
What do pumice and obsidian have in common?
glassy texture
In a porphyritic volcanic rock, which mineral grains are the last to crystallize?
matrix or groundmass
Which one of the following best describes volcanism in the Cascade Range, northwestern United States?
related to plate subduction
________ are usually the most abundant gases emitted during basaltic volcanism.
Water and carbon dioxide
Which one of the following statements is not true?
When magma reaches the surface, its dissolved gas content increases.
Mount St. Helens is ________.
an explosive stratovolcano
Pockets of magmas can be formed by the melting of deep continental crust heated by the intrusion of other magmas. Which of the following correctly describes this process?
Intrusion of basaltic magma causes deep crustal rocks to melt, producing andesitic or rhyolitic magmas.
Which of the following is associated with deep mantle hot spots?
the volcanoes of Hawaii and Quaternary activity in Yellowstone National Park
Which one of the following shows the correct order (left to right) of decreasing magma viscosity?
rhyolite, andesite, basalt
Which kind of volcanism is typical of mid-oceanic ridge systems?
submarine; basaltic lava flows
Which type of basaltic lava flow has a fairly smooth, unfragmented, ropy surface?
pahoehoe
Which one of the following statements concerning volcanic blocks and bombs is true?
Bombs are ejected as magma lumps; blocks are ejected as solid fragments.
The ________ is an example of an active, continent-continent collision.
northward movement of India into Eurasia
________ was never proposed as evidence supporting the existence of Pangaea.
Islands of Precambrian rocks along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge
Which of the following energy sources is thought to drive the lateral motions of Earth's lithospheric plates?
export of heat from deep in the mantle to the top of the asthenosphere
A typical rate of seafloor spreading in the Atlantic Ocean is ________.
2 centimeters per year
The former late Paleozoic super continent is known as ________.
Pangaea
In the early part of the twentieth century, ________ argued forcefully for continental drift.
Alfred Wegener
The Himalayan Mountains are the tectonic product of a collision between India and Eurasia that began in Eocene time and still continues.
True
Which one of the following is an important fundamental assumption underlying the plate tectonic theory?
Earth's diameter has been essentially constant over time.
Deep ocean trenches are surficial evidence for ________.
sinking of oceanic lithosphere into the mantle at a subduction zone
All of the following are evidence supporting the theory of plate tectonics except for ________.
changes in the Moon's orbit due to shifting plates
The ________ is thought to be a liquid, metallic region in the Earth's interior.
outer core
The lithosphere, asthenosphere, and mesosphere are all layers of Earth defined by their composition.
False
The asthenosphere is a relatively cool and rigid shell that overlies the lithosphere.
False
________ rocks always originate at the surface of the solid Earth.
Sedimentary
The composition of the core of Earth is thought to be ________.
solid iron-nickel alloy
________ is the process by which rocks breakdown in place to produce soils and sediments.
Weathering
The Geologic Time Scale divisions are based on ________.
equal divisions of 1 million (era), 50,000 (period), and 5,000 (epoch) intervals
The ________ is the thinnest layer of the Earth.
Crust
Igneous rocks are produced largely by the deposition and consolidation of surface materials like sand and mud.
False
The ________ proposes that the bodies of our solar system formed at essentially the same time from a rotating cloud of gases and dust.
Nebular Hypothesis
Which one of the following describes a mineral's response to mechanical impact?
Cleavage
A cubic centimeter of quartz, olivine, and gold weigh 2.5, 3.0, and 19.8 grams respectively. This indicates that ________.
gold has a higher density and specific gravity than quartz and olivine
What in the name given to an atom that gains or loses electrons in a chemical reaction?
Ion
All silicate minerals contain which two elements?
silicon, oxygen
The ion at the center of a silicate tetrahedron is surrounded by ________.
4 oxygen ions
The strong tendency of certain minerals to break along smooth, parallel planes is known as ________.
Cleavage
Which of the following minerals is in the mineral group known as mica?
Muscovite
Which of the following best characterizes ferromagnesian silicates?
They are black to dark-green silicate minerals containing iron and magnesium.
Hornblende and the other amphiboles have what type of silicate structure?
double chains
Which of the following best defines a mineral and a rock?
In a mineral the constituent atoms are bonded in a regular, repetitive, internal structure; a rock is a lithified or consolidated aggregate of different mineral grains.
Overall, this type of seismic wave is the most destructive.
Surface Wave
Which of the following sedimentary features can each be used to determine paleocurrent directions?
ripple marks and cross stratification
Which of the following lists the rocks in the order of increasing grain size and increasing grade of metamorphism?
Slate, Phyllite, Schist
Which of the following do feldspars weather to form?
Clay minerals
The continental rise is located ________.
between an abyssal plain and continental slope
________ proposed a hypothesis (that later became a theory) on the creation of atolls.
Charles Darwin
On a typical seismogram, ________ will show the highest amplitudes.
Surface Waves
________ forms from the metamorphism of limestone or dolostone.
Marble
________ are NOT associated with a mid-ocean ridge.
Deep Ocean Trenches
________ is formed when carbon dioxide is dissolved in water.
Carbonic Acid
The ________ lies at the base of the continental slope.
Continental Rise
The ________ is an example of the earliest stage in the formation of a new ocean basin.
East African Rift
________ is another name commonly used by scientists to denote seismic sea waves induced by earthquakes.
Tsunami
An echo sounder operates by measuring the time required for a ________.
sound pulse to travel from a ship to the seafloor and back
Sedimentary rocks account for about what percentage of the Earth's outermost 10 kilometers of rock (first percentage). Also, what percentage of the Earth's continental area is covered by sedimentary rocks (second percentage)?
5% and 75%
What is the major source of heat for contact metamorphism?
heat from a nearby magma body
When strata are displaced so that a dipping reservoir rock abuts an impermeable bed, a ________ is formed.
fault trap
Which of the following places these coral reefs in order from youngest to oldest?
fringing reef, barrier reef, atoll
Which of the following is not one of the agents of metamorphism?
calcium-rich liquids
What is the main difference between a conglomerate and a sedimentary breccia?
Breccia clasts are angular; conglomerate clasts are rounded.
________ is the most common type of chemical sedimentary rock.
Limestone
The primary basis for distinguishing among detrital sedimentary rocks is ________.
Particle Size
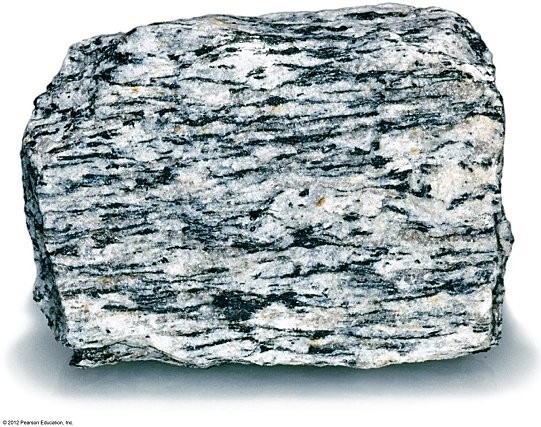

This rock's texture resulted from pressure that was applied ________.
from top to bottom
Which metamorphic rock, widely used for monuments and buildings, would deteriorate significantly in contact with acid rain?
marble
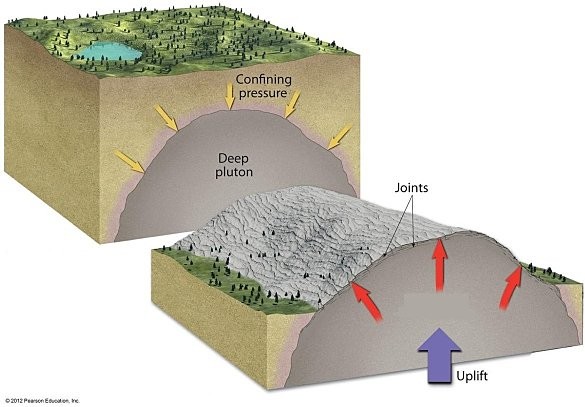
What process does the diagram below illustrate?
sheeting
________ have the highest velocities.
Primary waves
The two basic categories of weathering are ________.
mechanical and chemical
________ can provide good indication of the metamorphic environment in which a rock formed.
Index minerals
Which of the following is/are most susceptible to chemical weathering by dissolution?
calcite
The metamorphic grade refers to ________.
the degree to which the parent rock changes during metamorphism
The gently sloping submerged surface extending from the shoreline toward the ocean is termed the ________.
continental shelf
________ is the principle ore of aluminum.
Bauxite
From the land surface downward to the unweathered bedrock, which of the following is the correct order of the different soil horizons?
O, A, E, B, C, bedrock
The layer of rock and mineral fragments, produced by weathering, that cover most of Earth's land surface, is called ________.
regolith
Which type of metamorphism alters the basaltic rocks of the seafloor?
hydrothermal
________ is the layer of warm rock below the crust and uppermost mantle that readily deforms and flows plastically.
The asthenosphere
Seamounts ________.
are volcanoes that form on the ocean floor
Major earthquakes are often followed by somewhat smaller events known as ________.
aftershocks
Sedimentary rocks formed from the accumulation of material that is transported as solid particles derived from both mechanical and chemical weathering are known as ________ sedimentary rocks.
detrital
Oceans cover approximately ________ of Earth's surface area?
70%
Which of the following components of granite are more resistant to chemical weathering?
Quartz
Which of the following sedimentary features would typically be found in shales but not in sandstones?
Mud Cracks
The position on Earth's surface directly above the earthquake source is called the ________.
epicenter
________ is a nonfoliated rock formed by contact metamorphism of a shale or mudstone.
Hornfels
Which of the following sedimentary rocks would you expect to have originally been deposited by fast-moving streams?
conglomerate
The mechanism by which rocks store and eventually release energy in the form of an earthquake is termed ________.
elastic rebound
The instrument that records earthquake events is termed a ________.
seismograph
Oxidation plays an important role in the weathering of ________.
ferromagnesian minerals
Which of the following mass movements is most likely to occur in a geologic setting where the rock strata are inclined?
Rockslide
A drainage pattern comprised of streams that diverge from a central area like spokes is called ________.
Radial