Amino Acids
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
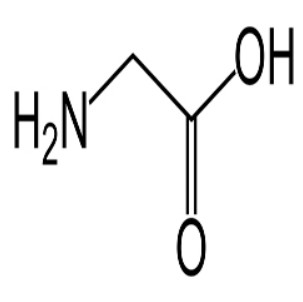
Which amino acid is this?
Glycine
Gly
Glycine
G
Glycine
What are some characteristics of glycine?
Smallest amino acid, but not simple. Single hydrogen side chain allows for high rotational freedom around the alpha carbon. Most “floppy” due to low steric hinderance. Not involved in hydrophobic interactions and can fit into various protein structures. No stereoisomers.
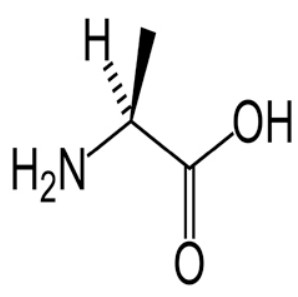
Which amino acid is this?
Alanine
Ala
Alanine
A
Alanine
What are some characteristics of alanine?
Stereochemistry: L-alanine. Side chain is a methyl group. It’s small and hydrophobic. It’s considered “vanilla,” or very generic because it is one of the simplest amino acids and commonly found in proteins.
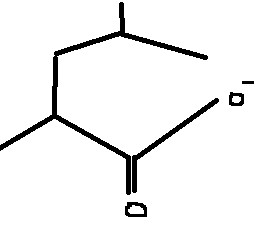
Which amino acid is this?
Leucine
Leu
Leucine
L
Leucine
What are some characteristics of leucine?
Hydrophobic and small: frequently found in protein hydrophobic core. Interchanged with isoleucine in mutations with conservative effects. Essential amino acid involved in protein synthesis and metabolism.
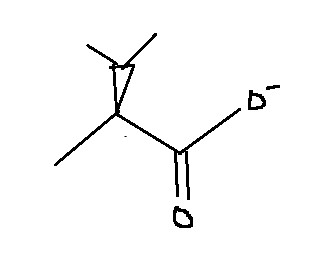
Which amino acid is this?
Valine
Val
Valine
V
Valine
What are some characteristics of valine?
Has two methyl groups on the beta carbon as its side chain. Hydrophobic, small, contributing to protein core packing.
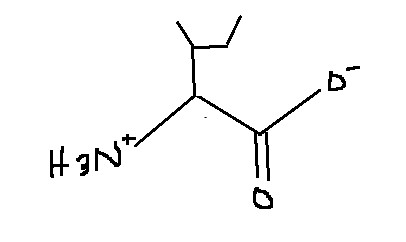
Which amino acid is this?
Isoleucine
Ile
Isoleucine
I
Isoleucine
What are some characteristics of isoleucine?
Side chain is an isomer of leucine, hydrophobic, and have common mutations with leucine - often conservative.
Carboxyl group pKa:
2.16
Amine pKa:
9.47
If pH is below 2.16, what happens to the carboxyl and amine groups?
they are protonated (pH < pKa)
If pH is between 2.16 and 9.47, what happens to the carboxyl and amine groups?
the carboxyl group is deprotonated (pH > pKa) and the amine group is protonated (pH < pKa)
If the pH is above 9.47, what happens to the carboxyl and amine groups?
the carboxyl group is deprotonated (pH > pKa) and the amine group is deprotonated (pH > pKa)
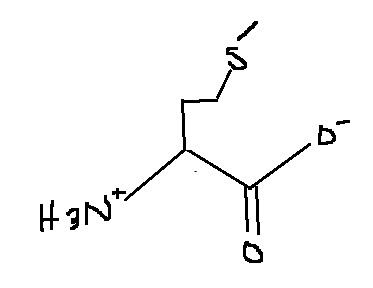
Which amino acid is this?
Methionine
Met
Methionine
M
Methionine
What are some characteristics for methionine?
Side chain contains a sulfur. Hydrophobic, not very polar. Methionine has the same codon as the start codon in protein translation (AUG), however many proteins have the initiator methionine cleaved post-translationally.
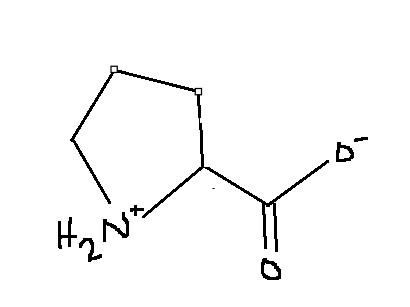
Which amino acid is this?
Proline
Pro
Proline
P
Proline
What are some characteristics of proline?
Side chain that closes back onto the amine, forming a 5-sided ring. This structure reduces flexibility, making this amino acid “kinky,” or used to create sharp turns or sudden directional changes in proteins.
Which amino acid is this?
Tryptophan
Trp
Tryptophan
W
Tryptophan
What are some characteristics of tryptophan?
The largest amino acid. W is its single letter abbreviation because the capital letter W is the largest letter in the alphabet. It is an essential amino acid and it is hydrophobic. Its side chain is a bicyclic aromatic system consisting of an indole ring. Does not accept a hydrogen bond as a typical carbonyl or amine containing donor would due to its unique structure. It also plays a role in phosphorylation and UV absoprtion.
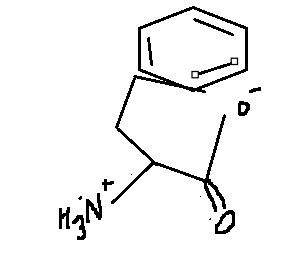
Which amino acid is this?
Phenylalanine
Phe
Phenylalanine
F
Phenylalanine
What are some characteristics of phenylalanine?
Has a benzyl side chain. F is its single letter abbrv. because of the “ph” sound. It is hydrophobic and large in size, and it plays a crucial role in protein synthesis and neurotransmitter production.
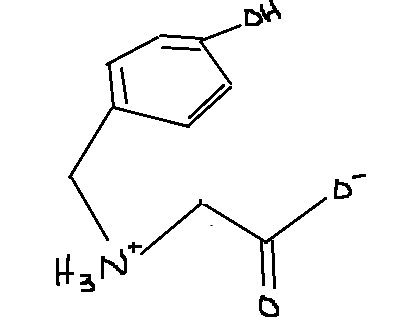
Which amino acid is this?
Tyrosine
Tyr
Tyrosine
Y
Tyrosine
What are some characteristics of tyrosine?
It is ambhipathic. Has a phenylalanine backbone with a phenolic hydroxyl group para to the side-chain. Tyrosine is an amino acid that is hydrophilic due to its phenolic hydroxyl group. It plays a key role in protein structure and function. Tyr is capable of acting as a hydrogen bond donor, and when deprotonated, an acceptor. Plays a role in phosphorylation and UV absorption.
Tyr pKa:
10.7
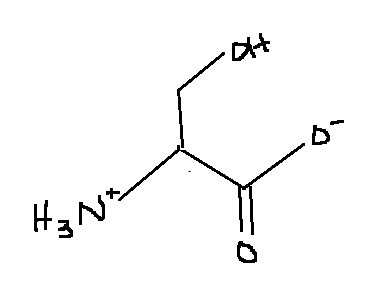
Which amino acid is this?
Serine
Ser
Serine
S
Serine
What are some characteristics of serine?
It is alcohol-containing (hydroxymethyl side chain -CH2-OH). Small, polar, hydrophobic. Capable of forming hydrogen bonds with water and other molecules. Ser can be phosphorylated in biological contexts. Not considered an ionizable side chain due to high pKa of hydroxyl group.
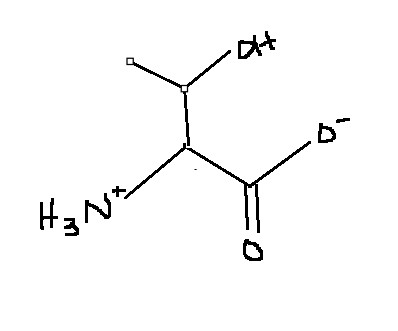
Which amino acid is this?
Threonine
Thr
Threonine
T
Threonine
What are some characteristics of threonine?
It contains an alcohol (hydrooxyl-bearing side chain, -CH(OH)-CH3). It is polar, similar to Ser but with an extra CH3 group that changes the steric profile. Can also be phosphorylated. Hydroxyl group cannot be ionized due to high pKa.
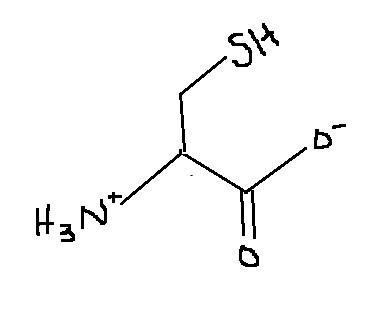
Which amino acid is this?
Cysteine.
Cys
Cysteine
C
Cysteine
What are some characteristics of cysteine?
It is sulfur containing (has a thiol side chain -CH2-SH). It is sensitive to redox conditions. Cysteine is also important for forming disulfide bonds, which stabilize protein structures. Slightly more polar than sulfur-containing groups and can act as hydrogen-bond donor when protonated.
Cysteine pKa:
8.18
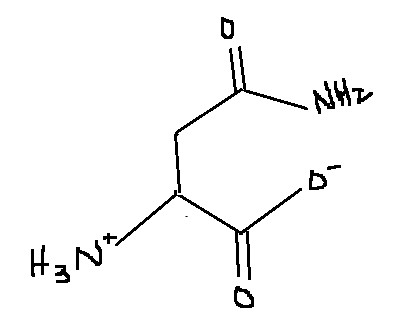
Which amino acid is this?
Asparagine
Asn
Asparagine
N
Asparagine
What are some characteristics of asparagine?
It has an amide-containing side chain (-CONH2). Asparagus gets its name from asparagine, and the extra nitrogen in asparagus causes smelly urine (think if N as its single letter code as nitrogen). It’s polar but uncharged, can form hydrogen bonds w/ water and other molecules. Particularly common in proteins and involved w/ nitrogen metalogic and transport.
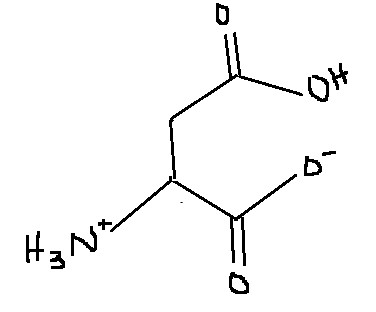
Which amino acid is this?
Aspartic acid
Asp
Aspartic acid
D
Aspartic acid
What are some characteristics of aspartic acid?
It has a carboxylate side chain (-COO-
) in physiological conditions. It is polar, hydrophilic, and charged, making it important for enzyme active sites and protein interactions. Referred to as aspartate when deprotonated.
Aspartic acid pKa:
3.65
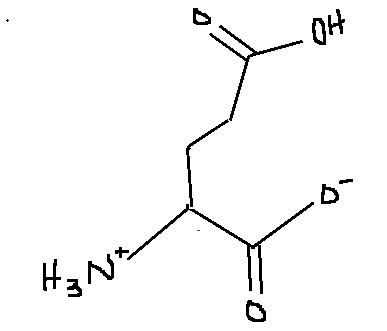
Which amino acid is this?
Glutamate
Glu
Glutamate
E
Glutamate
What are some characteristics of glutamate?
It has a carboxylate side chain (-CH2-CH2-COO-). Carboxyl side chain has pKa of 4.25, at physiological pH it is deprotonated. Influences protein stability and interactions w/ positively charged partners. Referred to as glutamic acid when protonated.
Glutamate pKa:
4.25
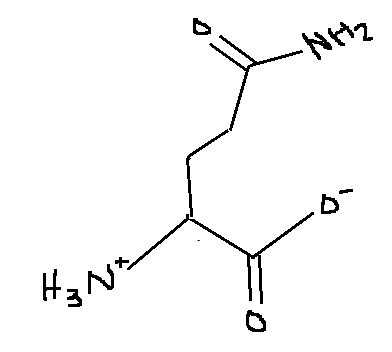
Which amino acid is this?
Glutamine
Gln
Glutamine
Q
Glutamine
What are some characteristics of glutamine?
It has an amide-containing side chain (-CH2-CH2-CONH2). It is polar, uncharged, and can form hydrogen bonds with water and other molecules. Common in protein regions that interact with water or other polar environments.
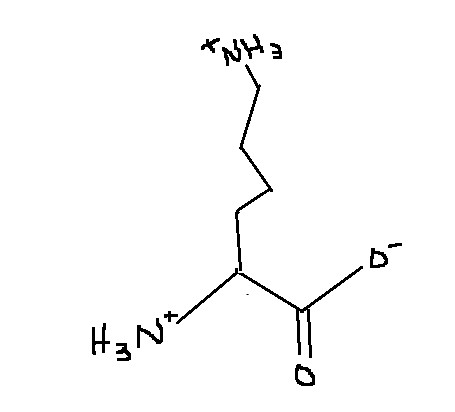
Which amino acid is this?
Lysine
Lys
Lysine
K
Lysine
What are some characteristics of lysine?
It is long and snakey, which is good to couple or shuttle cofactors between distant active sites; the extended reach bridging functions in enzymes
Lysine pKa
10.53
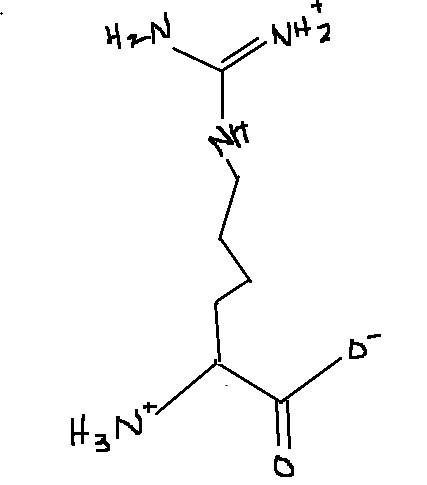
Which amino acid is this?
Arginine
Arg
Arginine
R
Arginine
What are the characteristics of arginine?
It’s always positively charged due to resonance (for the purpose of this course), which delocalizes the charge across 3 nitrogens, making it very stable.
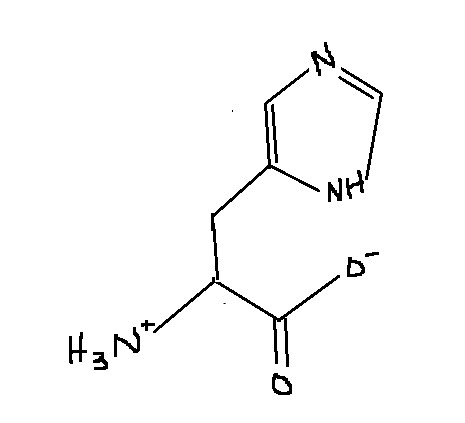
Which amino acid is this?
Histidine
His
Histidine
H
Histidine
What are the characteristics of histidine?
It has an imidazole ring with 2 nitrogens in its side chain; can both accept and donate a proton. pH around 7.0-7.4 places His in buffering range, meaning it can toggle between protonated and deprotonated forms near physiological pH, enabling roles as a proton donor/acceptor in enzymatic reactions.
Histidine pKa:
6.00