Week 5 Anatomy 2025 sem 1
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
What is an action potential defined as?
Nerve signals that cause a sudden change the resting membrane potential
What are the three stages of an action potential?
Resting
Depolarisation
Repolarisation
What are arteries?
Vascular tubes that conduct oxygenated blood from the heart to the capillary beds
Arteries typically become progressively smaller and form into what?
Arterioles
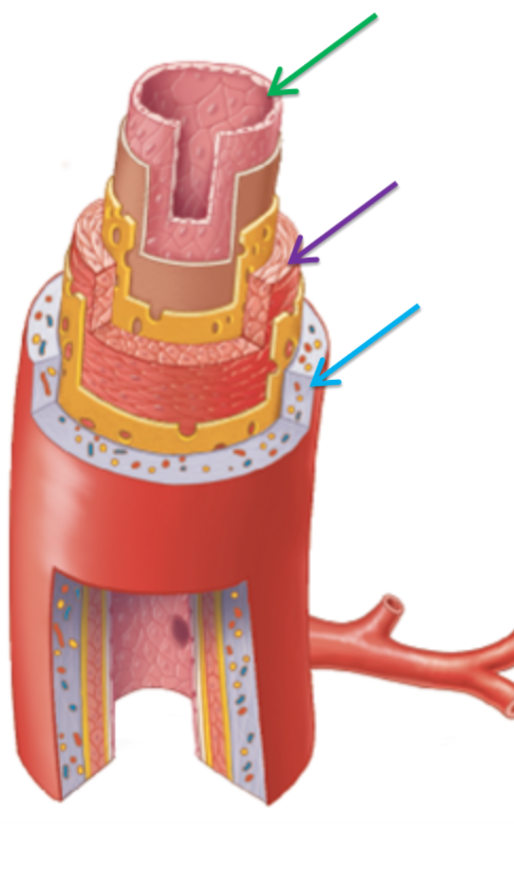
Label the following dissection of an artery in order from green to blue
Tunica interna
Tunica media
Tunica externa
Words such as branch, diverge and fork are associated with what vascular structures? and why?
Arteries as they form smaller divisions in comparison to veins
Arteries typically have what wall structures in comparison to veins? What is the exemption?
Thicker walls with smaller diameters except for pulmonary veins
What are veins defined as?
Vascular tubes that conduct poorly oxygenated blood from the capillary beds to the heart
What do veins begin as before they form larger vessels?
Venules
Words such as join, merge or converge are used to describe what vascular structures? how come?
Veins as the form larger vessels
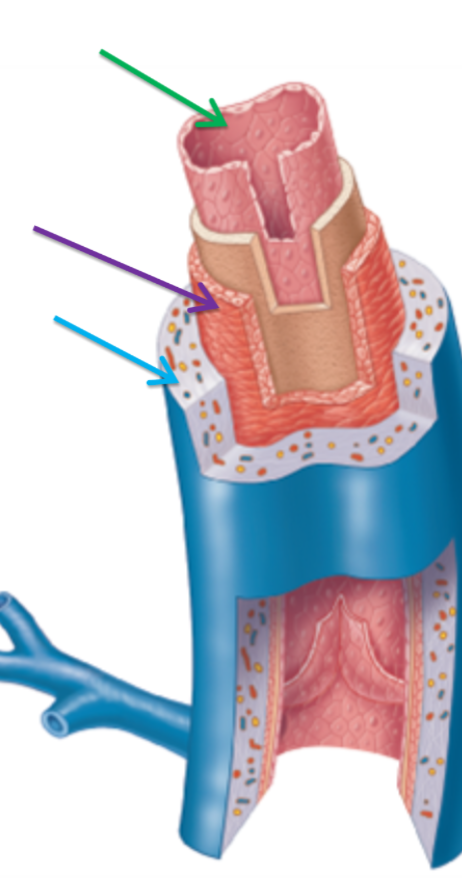
Label the following dissection of a vein purple green to blue in order
Tunica interma
Tunica media
Tunica extrerna
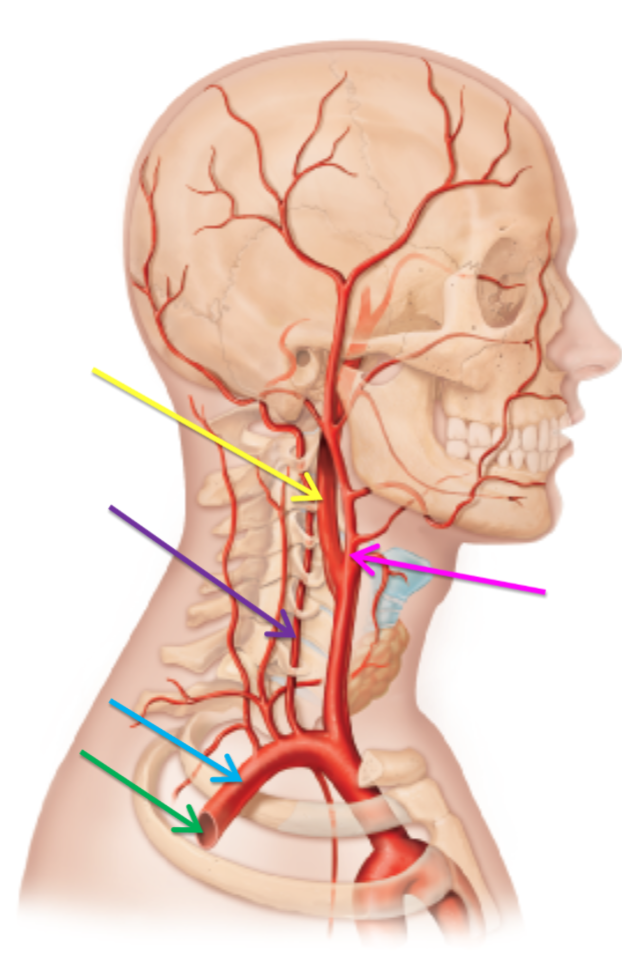
What artery is highlighted green?
Axillary artery
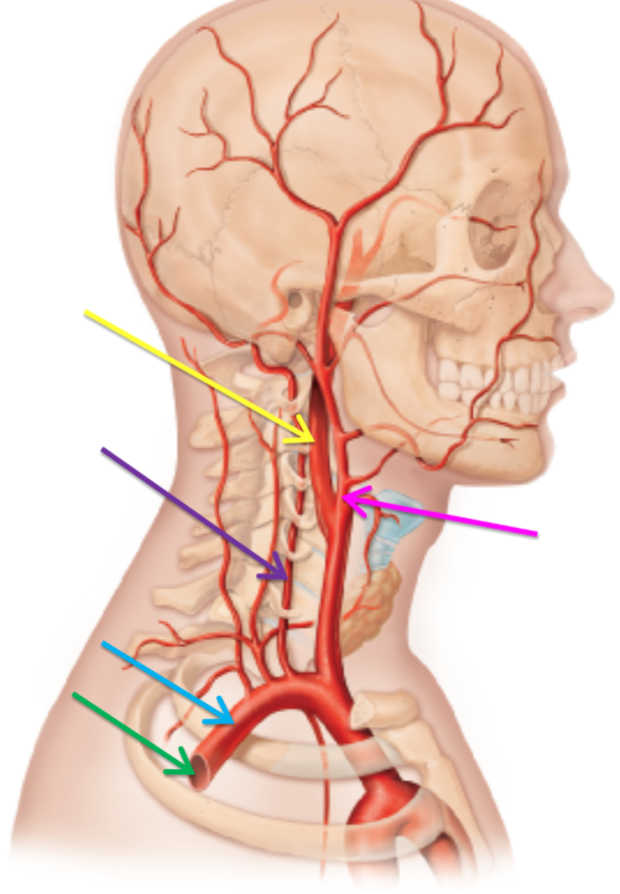
What artery is highlighted blue?
Subclavian artery
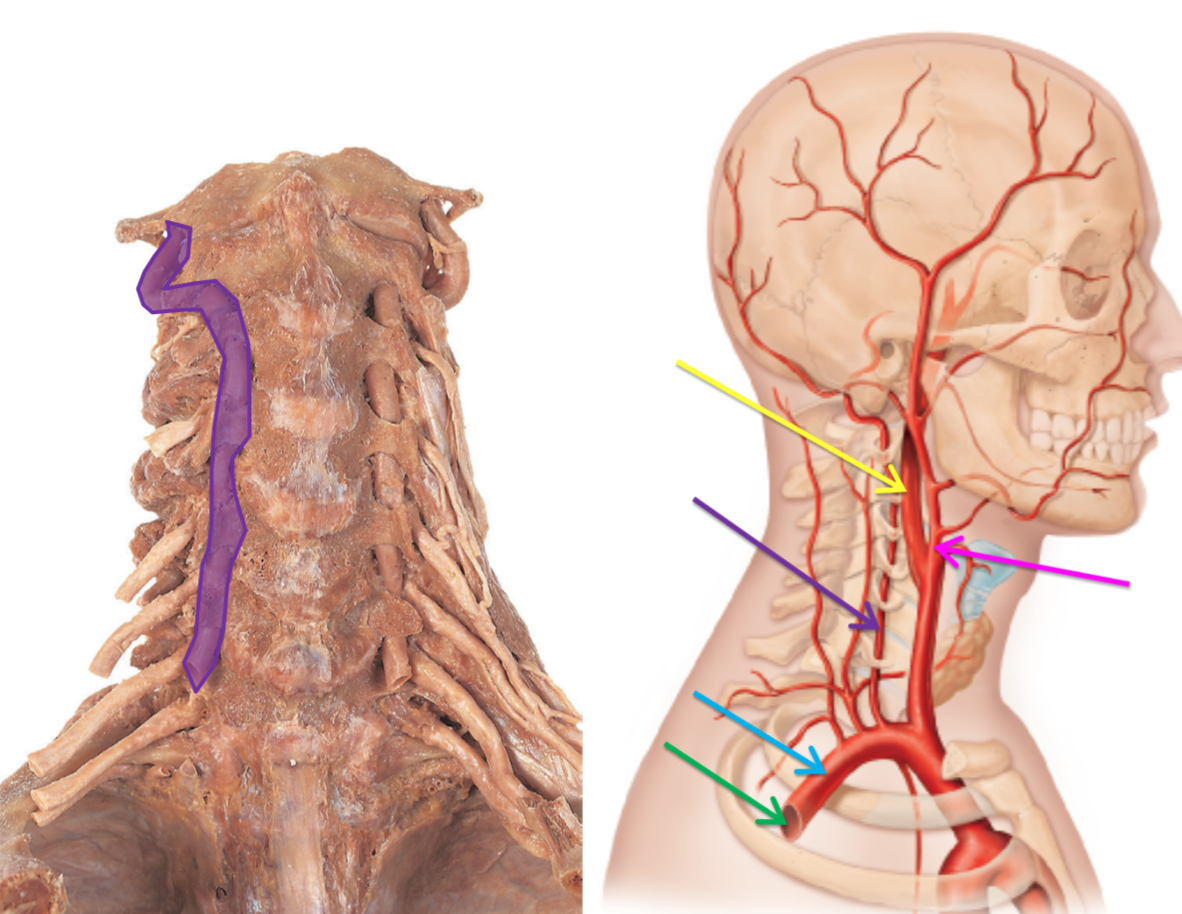
What artery is highlighted purple?
Vertebral artery
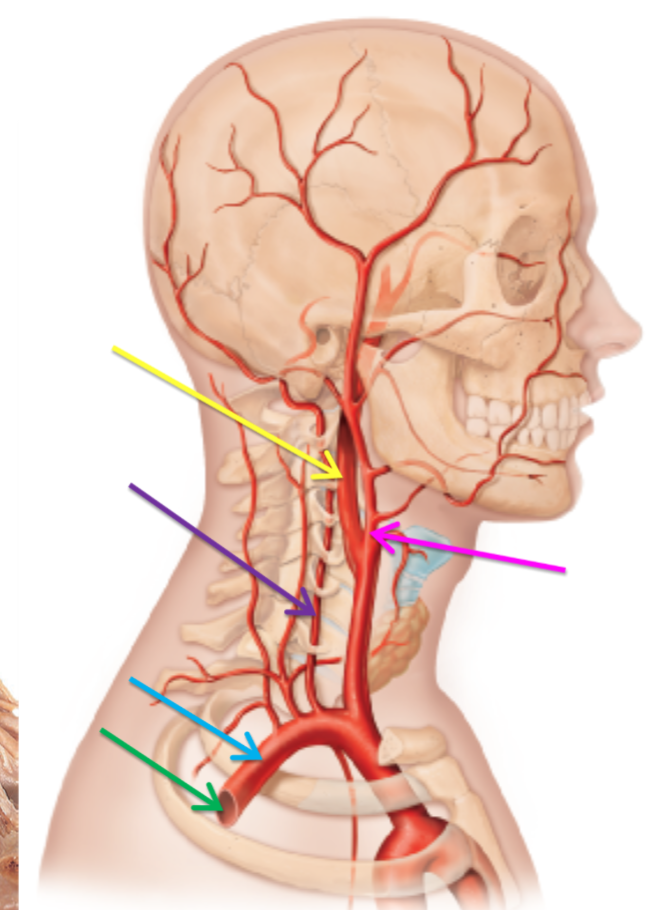
The arteries highlighted pink and yellow have stemmed off from which artery?
Common carotid artery
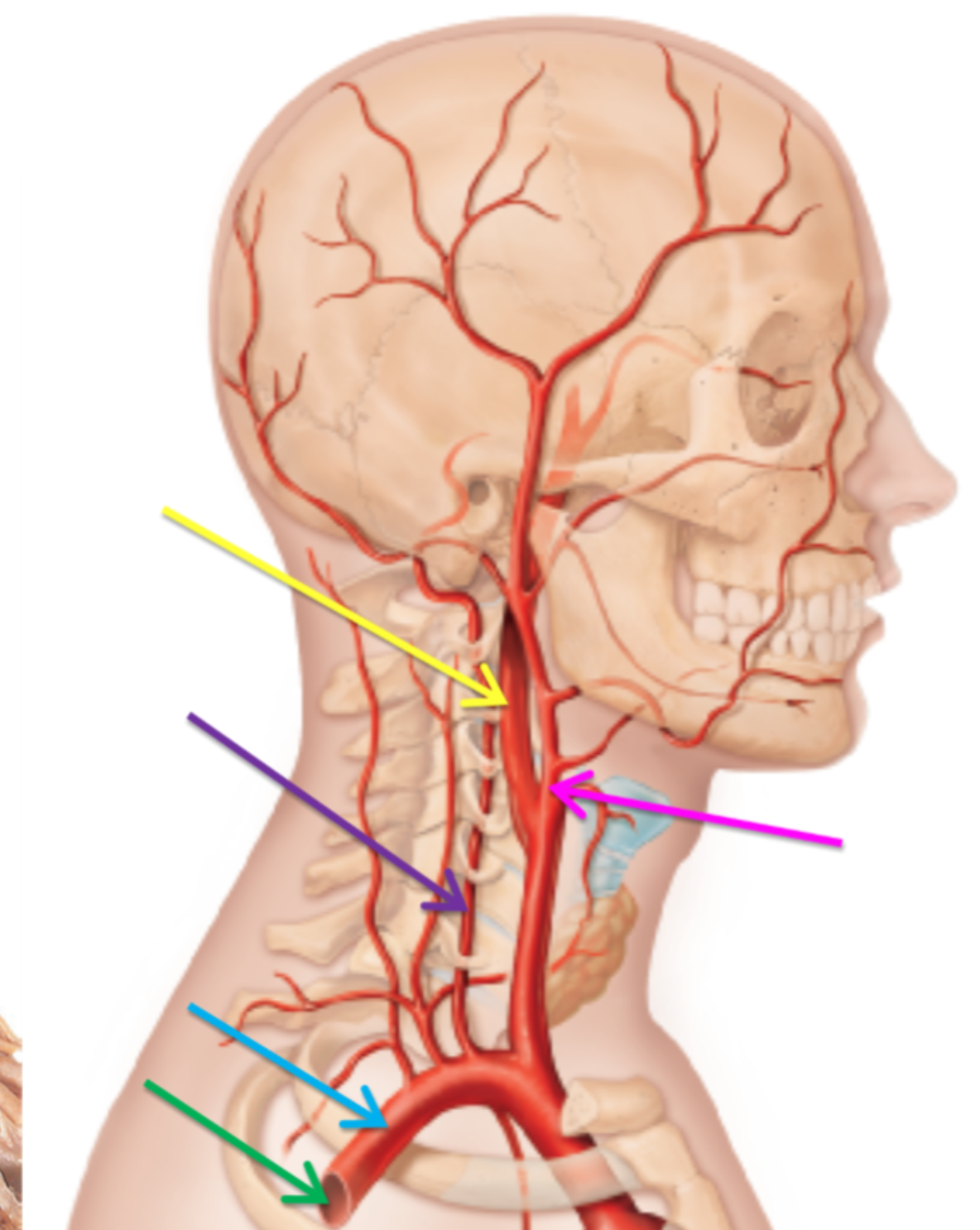
What is the artery highlighted pink?
Internal carotid artery
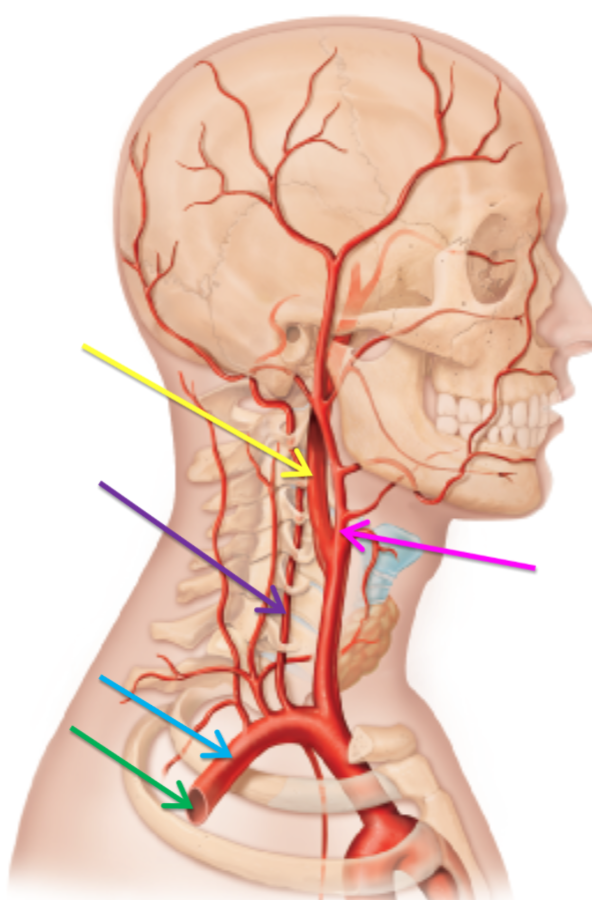
What is the artery highlighted pink?
Internal carotid artery
What are the steps of neurotransmission?
Synthesis
Release
Action
Reuptake
What are the two main classes of neurotransmitter?
Small and large molecule transmitter
What is cranial nerve I
Olfactory
What are the competes of cranial nerve I?
Special sensory olfaction
Where are the cell bodies of cranial nerve 1 located?
Olfactory epithelium
Where does cranial nerve I exit?
Foramina in cirbiform plate of ethmoid bone
What are the main actions of cranial nerve I?
Sense of smell, allowing the perception of odors and chemical stimuli in the environment
What is cranial nerve II?
Optic
What are the components of cranial nerve II?
Special sensory vision
Where are the cell bodies of cranial nerve II located?
Ganglion cells of retina
Where does cranial nerve II exit?
Optic canal
What is the main action of optic nerve II?
Transmits visual information from the retina to the brain
What is cranial nerve III?
Oculomotor
What are the components of the cranial nerve III?
Somatic
Visceral
Where are the cell bodies located in for the somatic component of cranial nerve III?
Midbrain
Where are the cell bodies located in for the visceral component of cranial nerve III?
Presynaptic in the midbrain (Edinger Westphal nucleus)
Postsynaptic in ciliary ganglion
Where does cranial nerve III exit from?
Superior orbital fissure
What is the main action of the somatic motor component of cranial nerve III?
Allows eye movement upward, downward, inward, and elevation of the upper eyelid.
What is the main innervation of the somatic motor component of cranial nerve III?
Innervates superior rectus, inferior rectus, medial rectus, inferior oblique, and levator palpebrae superioris.
What is the main actions of the visceral motor components of the cranial nerve III?
Constricts pupil and accommodates lens
What is the main innervation of the visceral motor components of cranial nerve III?
Sphincter pupillae and ciliary muscles
What is cranial nerve IV?
Trochlear
What are the comments in cranial nerve IV?
Somatic motor
Where are the cell bodies of cranial nerve IV located?
Midbrain
Where does cranial nerve IV escape?
Superior orbital fissure
What is the main action of cranial nerve IV?
Turning your eye inferolaterally
What is the main innervation of cranial nerve IV?
Superior oblique
What is cranial nerve V?
Trigeminal
What is cranial nerve V1?
Opthamalic
What is cranial nerve V2?
Maxillary
What is cranial nerve V3?
Mandibular
What are the components of cranial nerve V1-V2
Somatic sensory motor
What are the components of cranial nerve V3?
Somatic sensory motor
Somatic motor
Visceral motor
Where are the cell bodies of somatic sensory motor CN V1-V3 located?
Trigeminal ganglion synapse
Where does the somatic sensory motor component CN V1 exit?
Superior orbital fissure.
Where does somatic sensory motor component CN V2 exit?
Foramen roduntum
Where does CN V3 exit? (no its not competent specific)
Foramen ovale
Where are the cell bodies of the somatic motor comment of cranial nerve V3 located?
Pons
Where are the cell bodies of the visceral motor component of cranial nerve V3 located?
Hitch-hiking fibres of CN VII
What is the main action of somatic sensory motor components of CN V3?
Sensation of anterior two thirds of tongue and skin over mandible
What is the main action of somatic motor component of CN V3?
Motor innervation of muscles of mastication
What is the main action of visceral motor components of CN V3?
Submandibular and lacrimal gland
What is the main action of CN V1?
Sensation of forehead, upper eyelid, and nose
What is the main action of CN V2?
Sensation of the maxillary region, including cheeks, upper lip, and palate
What is cranial nerve VI?
Abducent
What is the comment of cranial nerve VI?
Somatic motor
Where are the cell bodies of CN VI located?
Pons
Where does cranial nerve VI exit from?
Superior orbital fissure
What is the main action of cranial nerve VI?
Motor innervation to lateral rectus to turn eye laterally
What is cranial nerve VII?
Facial
What are the components of CN VII?
Somatic motor
Special sensory
Somatic sensory
Visceral motor
Where are the cell bodies for the somatic motor component of cranial nerve VII located?
Pons
Where are the cell bodies of the special sensory component of cranial nerve VII located?
Geniculate ganglion synapse nuclei of solitary tract
Where are the cell bodies of the somatic sensory component of cranial nerve VII located?
Geniculate ganglion synapse sensory nucleus of trigeminal nerve
Where are the cell bodies of the visceral motor component of cranial nerve VII located?
Presynaptic from pons
Postsynaptic from pterygopalatine ganglion and submandibular ganglion
Where does cranial nerve VIII exit?
Internal acoustic meatus, facial canal and stylomastiod foramen
What is the main action of the somatic motor component of CN VII?
Innervates muscles of facial expression
What is the main action of the special sensory component of CN VII?
Taste from anterior two thirds of tongue
What is the main action of the somatic sensory components of CN VII?
Sensation of skin of external acoustic meatus
What isn the main action of the visceral motor components of CN VII?
Innervation of salivary and lacrimal glands and nasal mucosa
What is CN VIII?
Vestibulocochlear nerve
What are the two categories of CN VIII?
Vestibular and cochlear divisions
What are the components of CN VIII?
Special sensory hearing and balance
Where is the location of cell bodies of CN VIII vestibular?
Vestibular ganglion synapse
Where is the location of the cell bodies of CN VIII cochlear?
Spiral ganglion synapse
Where does CN VIII exit?
Internal acoustic meatus
What’s the main action of CN VIII vestibular?
Transmit information about balance and spatial orientation from the inner ear to the brain.
What’s the main action of CN VIII cochlear?
Transmit auditory information from the cochlea to the brain.
What is CN IX?
Glassopharyngeal
What are the components of CN IX?
Somatic sensory
Special sensory (taste)
Somatic sensory
Visceral motor
Where is the somatic motor component cell bodies of CN IX located?
Medulla
Where is the special sensory component cell bodies of CN IX located?
Sensory ganglion (nuclei of solitary tract)
Where is the somatic sensory component cell bodies of CN IX located?
Sensory ganglion synapse
Where is the visceral motor component cell bodies of CN IX located?
Presynaptic at medulla
Post synaptic otic ganglion
Where does CN IX exit?
Jugular foramen
What is the main action of somatic motor CN IX?
To innervate the stylopharyngeus muscle, aiding in swallowing.
What is the main action of special sensory CN IX?
To provide taste sensation from the posterior one-third of the tongue.
What is the somatic sensory CN IX?
Sensory to external ear, pharynx and middle ear
What is the visceral motor CN IX?
Parasympathetic innervation to parotid gland
What is CN X?
Vagus
What are the components of CN X?
Somatic motor
Special sensory (taste)
Somatic sensory
Visceral motor
Visceral sensory
Where is the cell bodies for the somatic motor components of CN X located?
Medulla
Where is the cell bodies for the special sensory (taste) components of CN X located?
Sensory ganglion