punnet squares and that kinda thing quiz
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
how are traits passed from one generation to the next, and what determines which trait will be expressed?
traits are passed through genes and sexual reproduction
why are there so many different forms of life?
because we all came from the same common ancestor and slowly over time we expressed traits through sexual reproduction that in some species worked and in other it did not (i really don’t know)
what makes each of us unique?
our expressed traits
agglutination
clumping in blood types that occurs when you do not get the correct blood type and antigens in your body attack the blood because they recognize it as a foreign entity
allele
a form of a gene
you inherit equal amounts of genetic information from both parents and one allele will be expressed over the other most of the time
autosomal linkage
some genes being found on the same chromosome
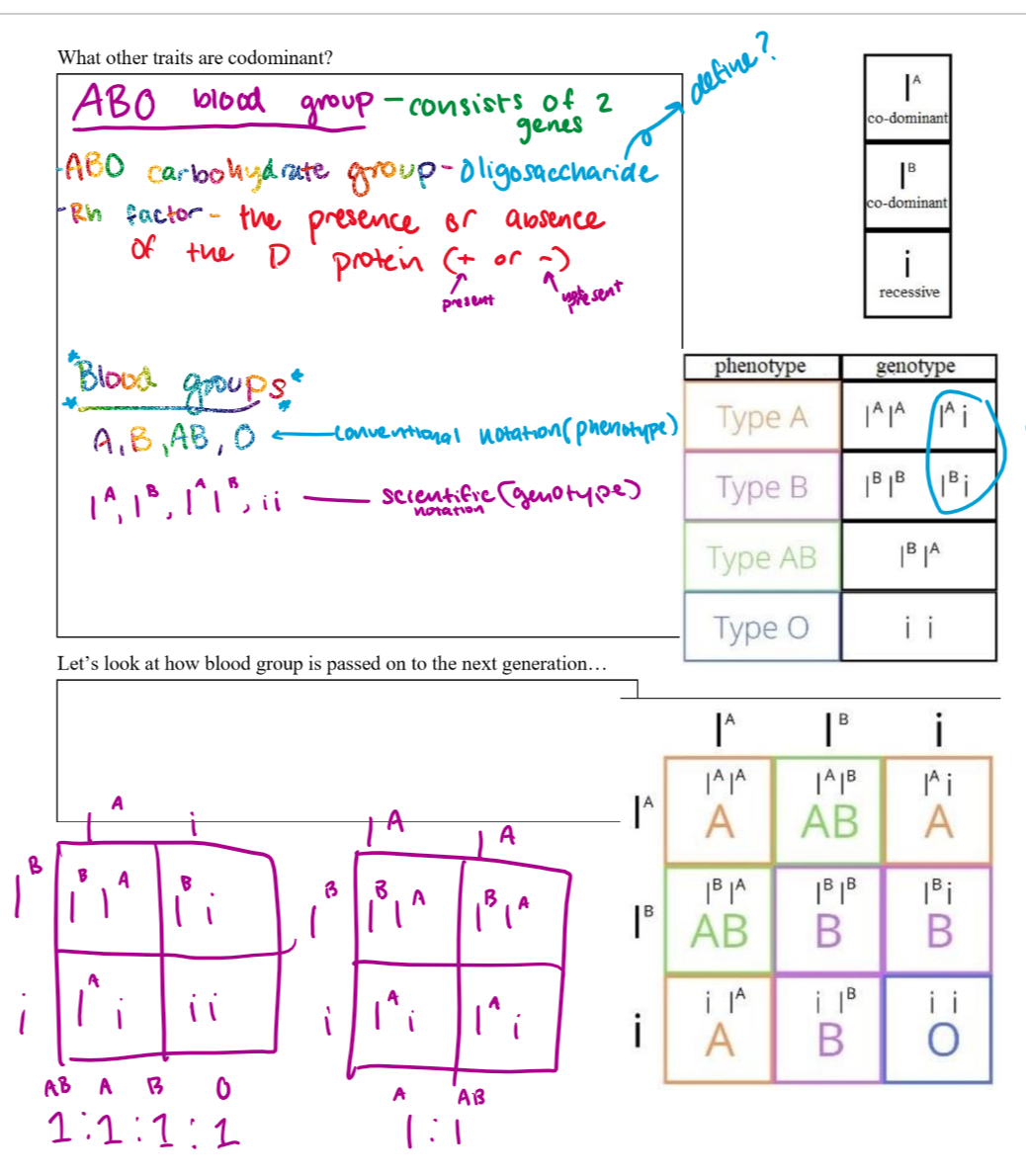
blood types (ABO)
consists of two genes
AB is codominance
O is recessive
carrier
carrying a trait (not the same as affected, which means expressing the trait)
in sex-linked traits, only females can be carriers. this is because (using an example)
is hemophilia is a recessive trait, a woman can either have hemophilia (X^hX^h) be a carrier (X^HX^h) or just not have hemophilia (X^HX^H). men either express the trait or they don’t, because they only have one X chromosome.
codominance
when more than one allele is dominant, so both are expressed to varying degrees
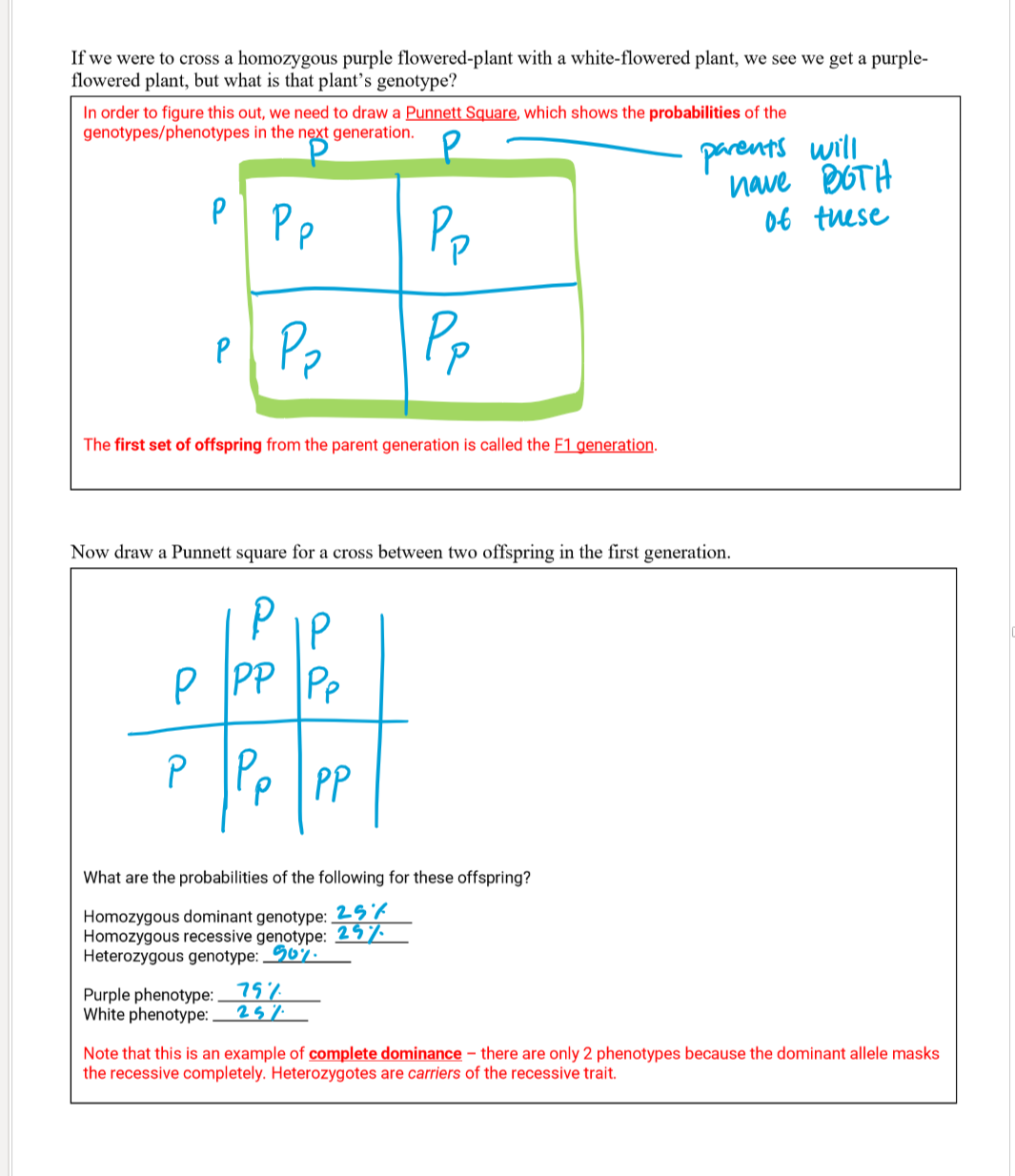
complete dominance
when the dominant allele always masks the recessive allele in heterozygous conditions
if H=curly and h=straight and complete dominance is exhibited, then the hair would be curly
discrete/discontinuous
traits that are inherited in distinct, seperate units and don’t blend with anything else (mendelian traits are discrete and polygenic are not)
continuous traits have ranges like weight, blood pressure, and height. blood types would be an example of discontinuous because there are no intermediate values
homozygous dominant
two capital letters
gene
a segment of DNA that codes for a functional product
generation (F1, F2, etc.)
F1=first set of offspring from the parent generation
process of reproduction
genotype
the genetic information or letters that code for observable traits
heterozygous
when you have a lowercase and a capital letter (example: Hh). therefore, it will always be the dominant trait expressed
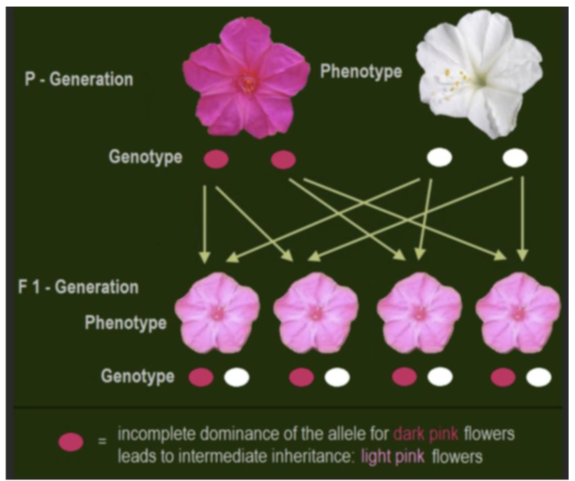
incomplete dominance
when the dominant allele only partially masks the recessive allele
if H=curly and h=straight, then you would get wavy hair
inherited traits
traits passed on from generation to generation
mendelian traits
a trait governed by a single gene. discrete (you have the trait or you don’t)
examples: heritable alopecia, attached/detached earlobes
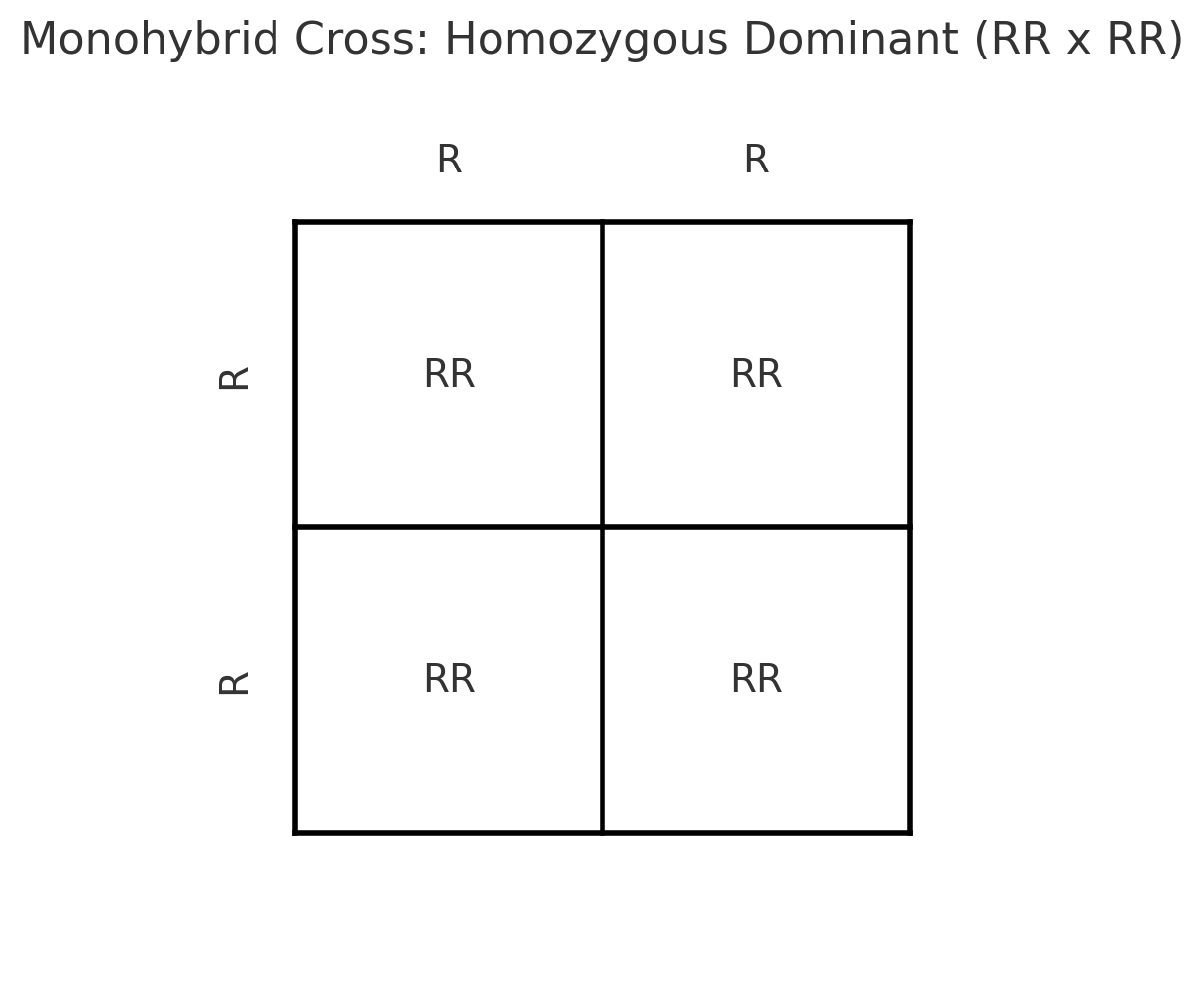
monohybrid cross
punnet square with 4 squares
phenotype
the observable, physical trait that comes from your genotype
for example, if the genotype options are Hh, HH, and hh, you could have blonde or brown hair as your phenotype.
pleiotropy
one gene affecting mutliple traits
polygenic traits
a trait governed by multiple genes, such as hair color and freckles
probability
expressed with either genotype or phenotype
punnett square
a way to see what two parents crossed will form (what will be expressed)
homozygous recessive
two little letters
recombination
when two homologous chromosomes exchange genetic information through crossing over
sex linkage (X-linked)
traits controlled by genes in the X-chromosome (aka most of your traits)
trait
a characteristic or feature
true-breeding
True breeding happens when an organism is homozygous dominant (e.g., RR) or homozygous recessive (e.g., rr) for a trait. Since both copies of the gene are the same, the offspring will always inherit the same version of the gene
X-inactivation
if X chromosomes have linked genes, why don’t 2 X chromosomes in females cause overproduction?
during development one of the X chromosomes is condensed into heterochromatin and methylated (covered by carbon groups)
these inactive chromosomes are called barr bodies
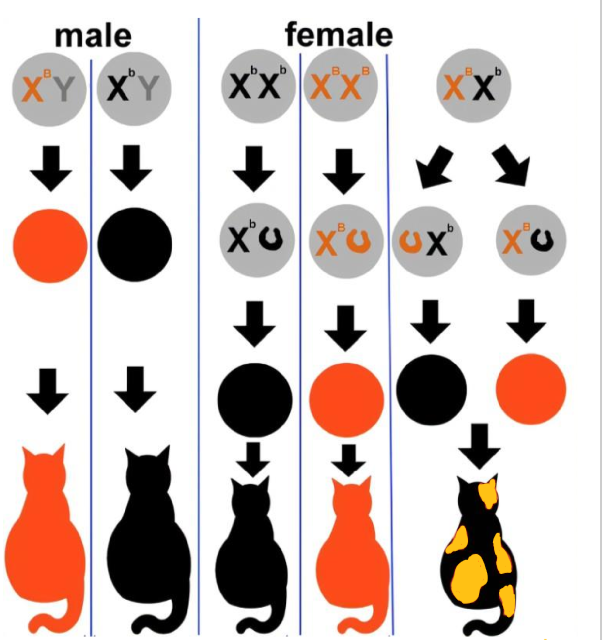
how are chromosomes and genes related?
Each chromosome contains many genes and each gene may have a number of different versions called alleles.
how do sets of chromosomes and alleles relate to each other?
Sexually reproducing organisms usually have paired sets of chromosomes, one set from each parent. They carry equivalent sets of genes, but there is potential for different alleles to exist within an individuals genome and within a population.
how do gametes pair up and why does it matter
The way in which gametes pair up is random, therefore the offspring will carry a random combination of alleles from the mother and the father.
what determines the outcome of a cross
The outcome of any cross depends on the parental genotypes. A true-breeding parent is homozygous for that trait.
what is a monohybrid cross’s purpose
A monohybrid cross studies the inheritance pattern of one gene, and the offspring of these crosses occur in predictable ratios.
what determines the phenotype that is expressed?
The dominance of an allele will determine what phenotype is expressed in an individual.
why can males not mask recessive alleles?
Many genes on the X chromosome do not have a match on the Y chromosome. Therefore, in males, a recessive allele cannot be masked by a dominant allele.
are sex-linked traits and autosomal traits (everything else, every other chrosome other than the sex chromsomes) the same? why or why not?
Sex-linked traits and autosomal traits have different inheritance patterns.
many phenotypes are determined by…
more than one gene and show continuous variation in a population.
what is pleiotropy?
Some genes affect multiple biochemical pathways and their genotype affects more than one trait
one gene affects multiple traits
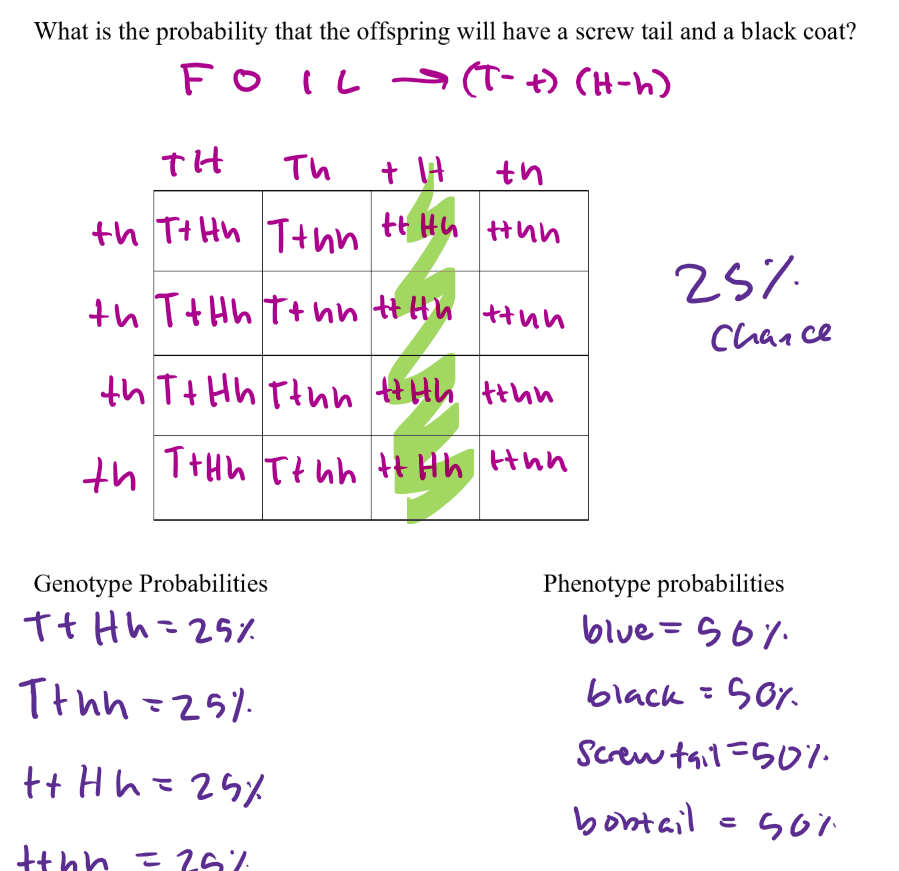
how to do dihybrid crosses
j look at pic
what two genes does the ABO blood group consist of?
ABO carbohydrate group-oligosaccharide
-Rh factor—presence or absence of the D protein (- or + blood type)
how can we figure out someone’s blood type
blood type is determined by the sugar on the outside of a red blood cell (A B or O). this sugar is considered an antigen—a marker that allows the body to recognize something as friendly or foreign
the Rh factor is another antigen your body looks for