ch 12 – central visual pathways
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
sensory systems
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
information collected by the retina allows for:
perception of the scene
induces reflexes
pupil dilation
turning eyes towards object of interest
influences behaviors linked to circadian rhythms
occipital
primary visual cortex is in the _______ lobe
occipital, parietal, and temporal
what lobes are involved in vision?
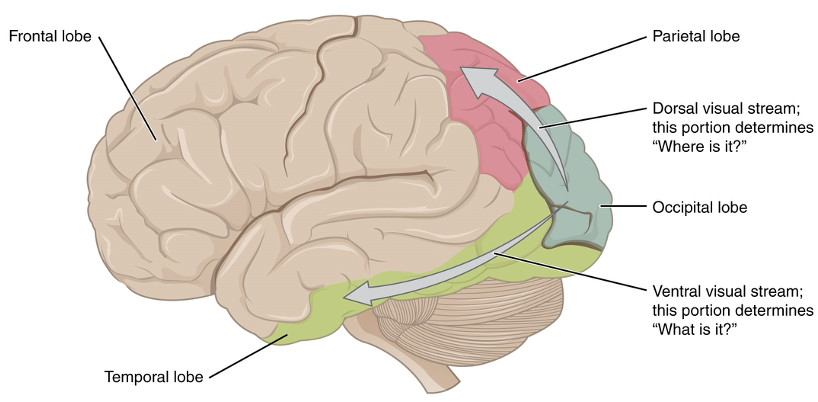
parietal
lobe for motion and location
temporal
lobe for object recognition
optic nerve
where do axons of ganglion cells bundle to exit the retina?
optic chiasm
60% of neurons cross to the other hemisphere and enter the optic tract
optic tract
contains neurons from both sides
dorsolateral geniculate nucleus (DGN)
where do ganglion cell axons project to?
thalamus
where is the DGN located?
thalamus
relay for several sensory systems to the cortex
primary visual cortex
where do thalamic neurons send axons to?
optic radiation
how thalamic neurons send axons to primary visual cortex
30
how many different types of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs)?
different functions of RGCs:
send info about objects/writing that requires high-resolution
send info about circadian rhythms/pupil adjustment
need to assess changes in light intensity
sense light changes without rods and cones
inverted and left-right reversed
how are images projected onto retina?

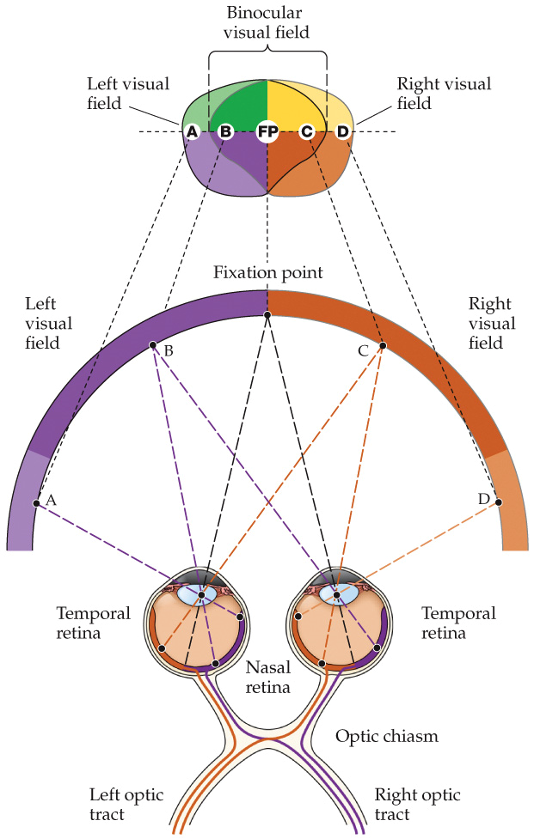
binocular visual field
two symmetrical hemifields
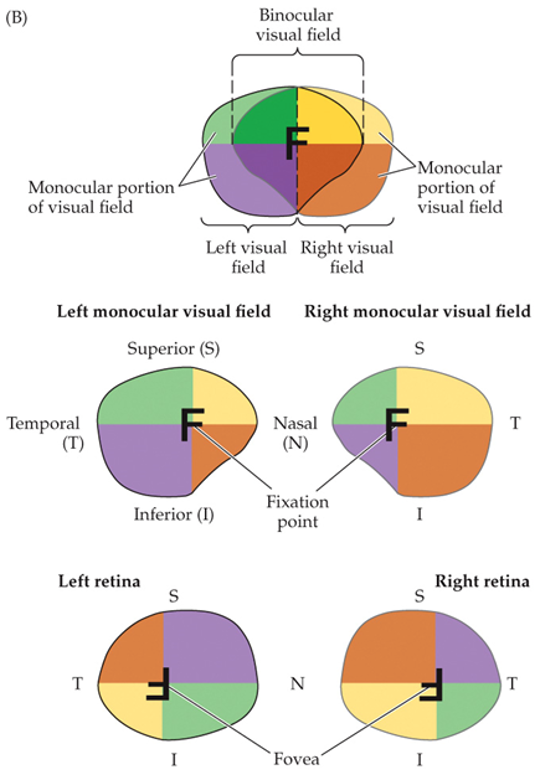
right hemifield
right temporal visual field and left nasal visual field
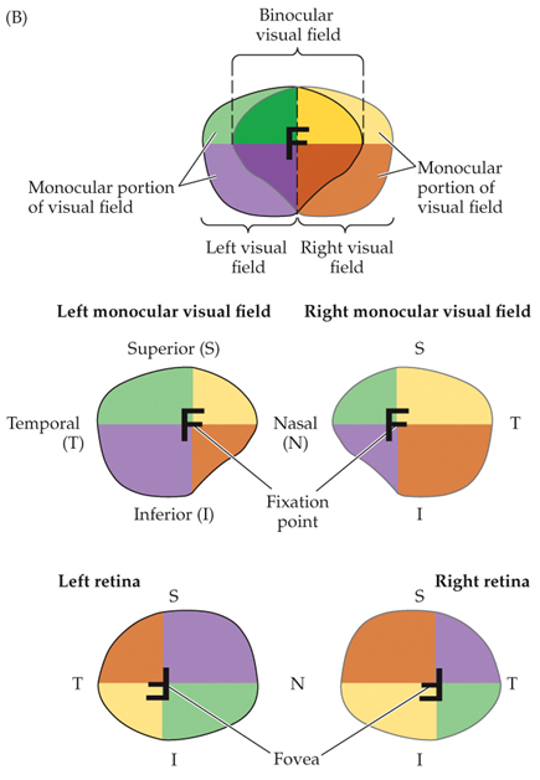
temporal field
larger
peripheral vision
peripheral vision
monocular
shape of nose blocks them more
why are inferior fields smaller than superior fields?
nasal
an object in the temporal visual field will be perceived in the _____ part of the retina
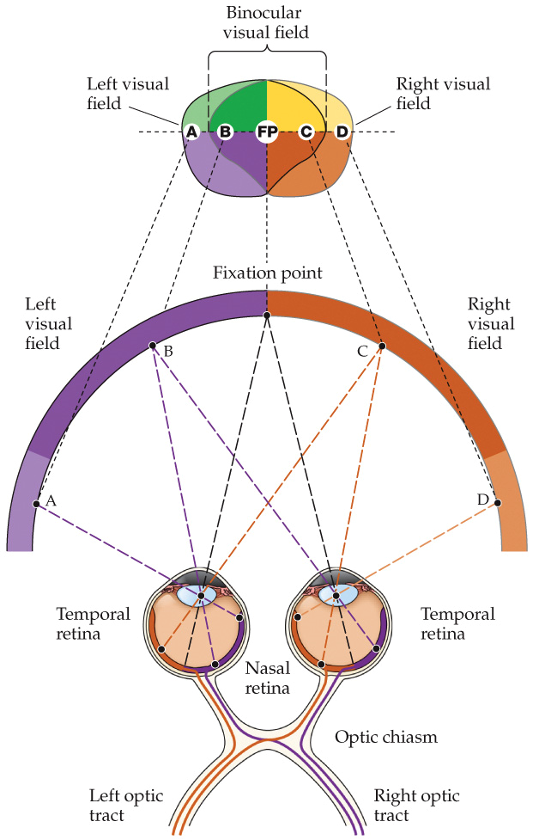
cross through optic chiasm
RGC axons on nasal side will cross through optic chiasm or stay on same side?
stay on same side
RGC axons on temporal side will cross through optic chiasm or stay on same side?
fovea
what delineates the boundary between nasal and temporal axons?
object on left of visual field
nasal retina of left eye
temporal retina of right eye
all axons go through right optic tract
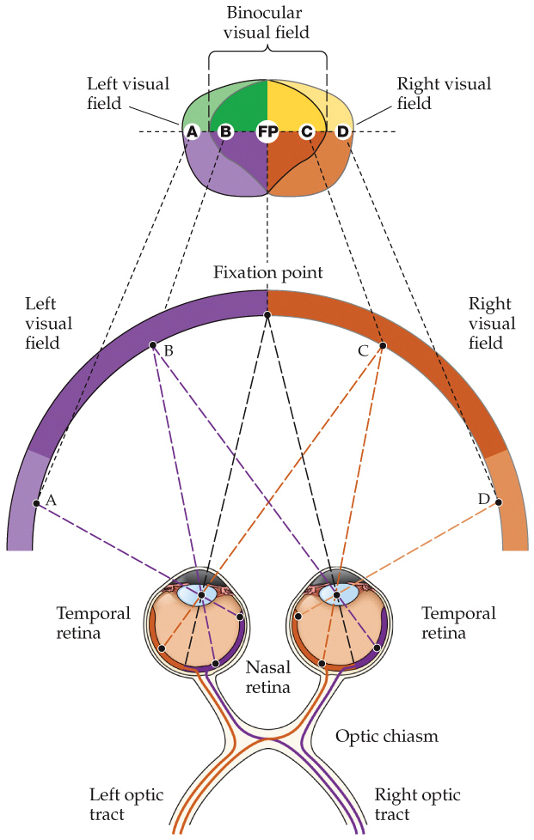
object on right of visual field
nasal retina of right eye
temporal retina of left eye
all axons go through left optic tract
retinotopic maps
RGC projections are maintained as __________ _____ in the brain
DGN and striate cortex
where are the maps of contralateral field maintained?
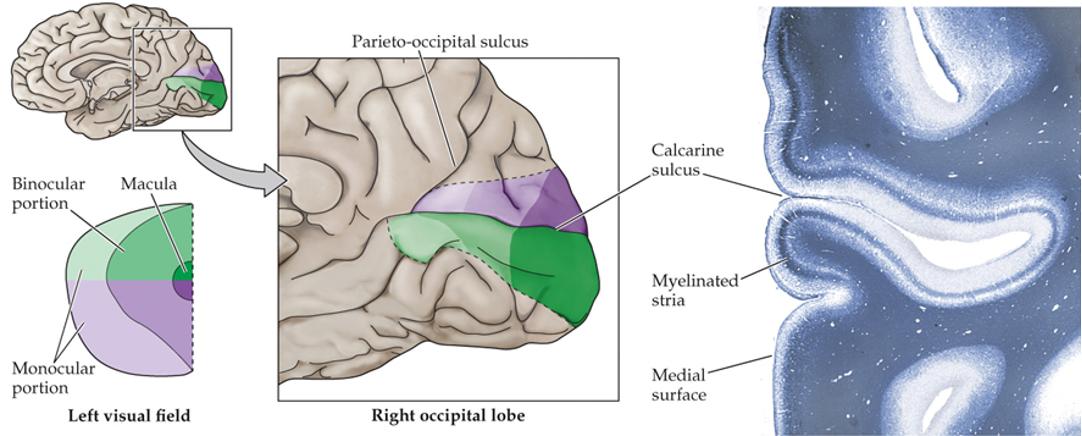
striate cortex
presence of myelinated layer around the calcarine sulcus (groove)
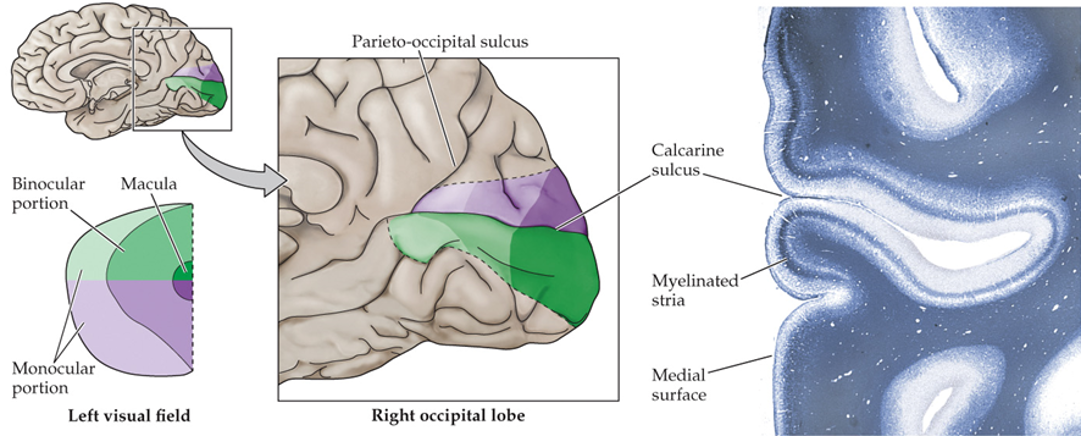
superior visual field
below the calcarine sulcus
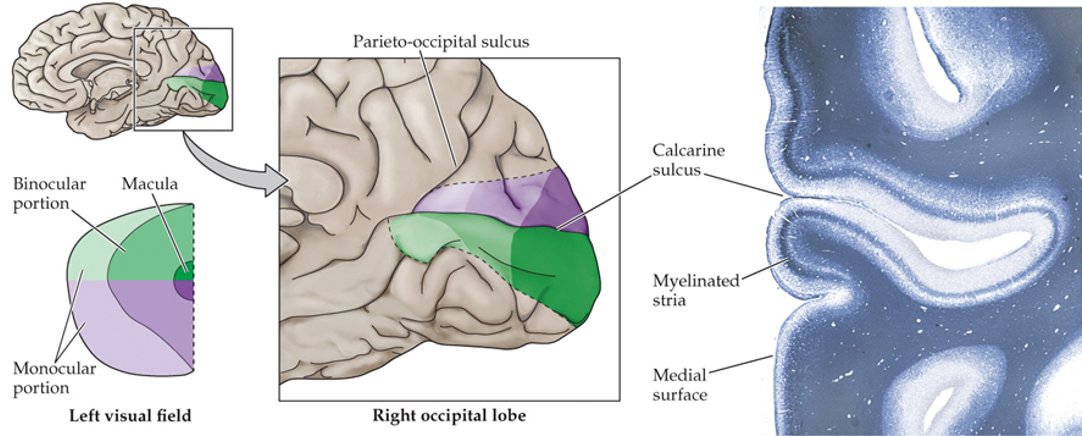
inferior visual field
above the calcarine sulcus
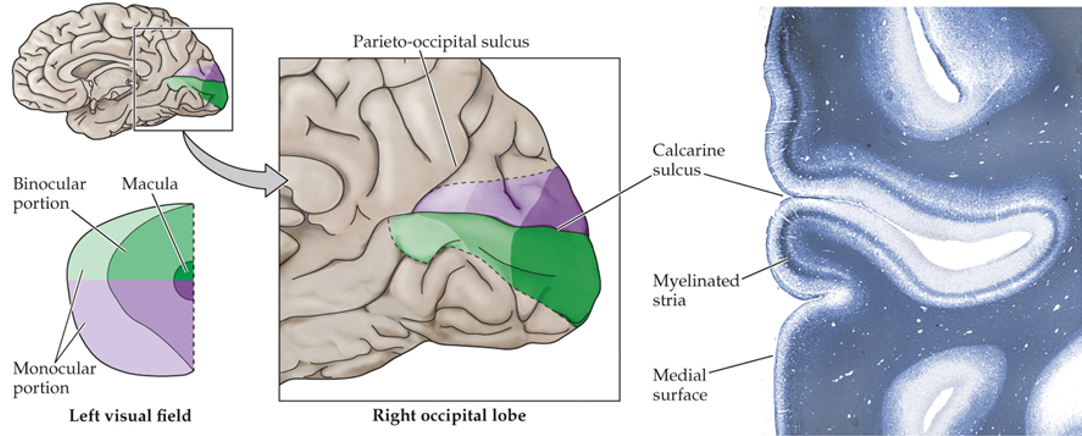
fovea
posterior (most occipital) of the visual cortex

peripheral retina
anterior parts of the visual cortex
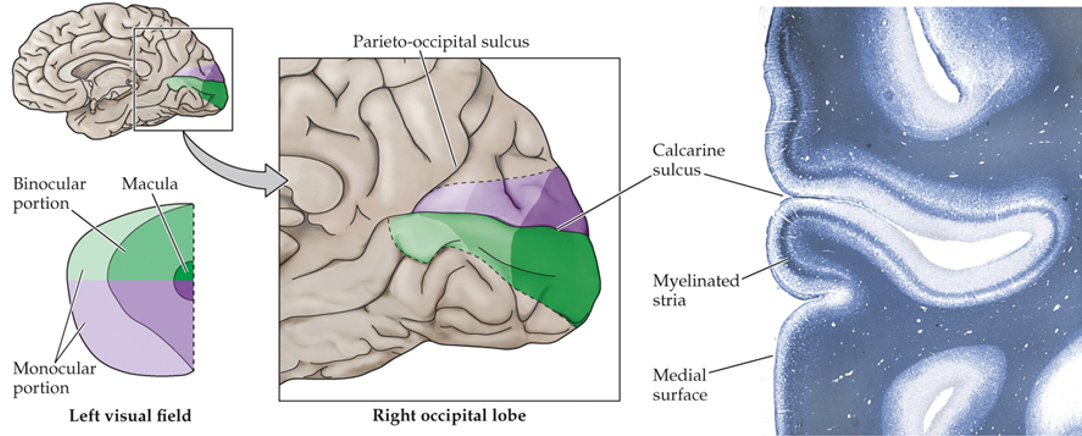
density of photoreceptors and sensory axons
what does the area in the visual cortex correlate with?
highest acuity (highest density of photoreceptors and sensory axons)
why is the area of the fovea/macula disproportionally large?
retina
stimulation of neurons in the DGN elicits responses similar to ones triggered in the ______
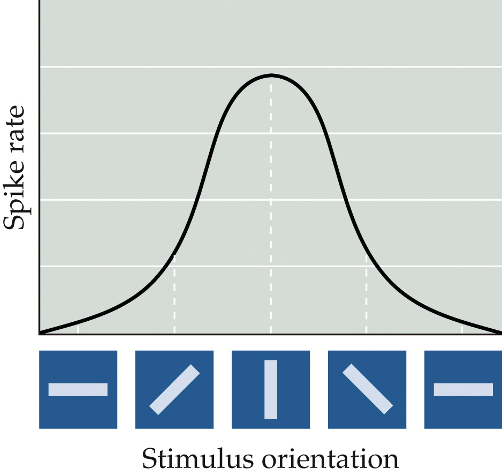
bars with distinct orientations
(spatiotemporal tuning) in the visual cortex, the neurons respond to different stimuli than the DGN + retina; instead, they respond to:
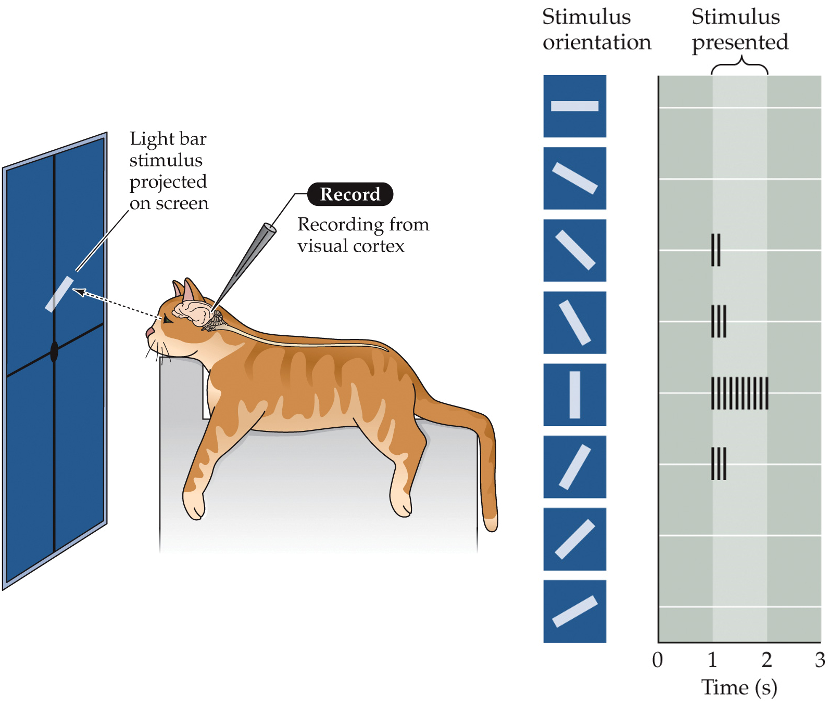
preferred orientation
each neuron is sensitive to a _______ ________
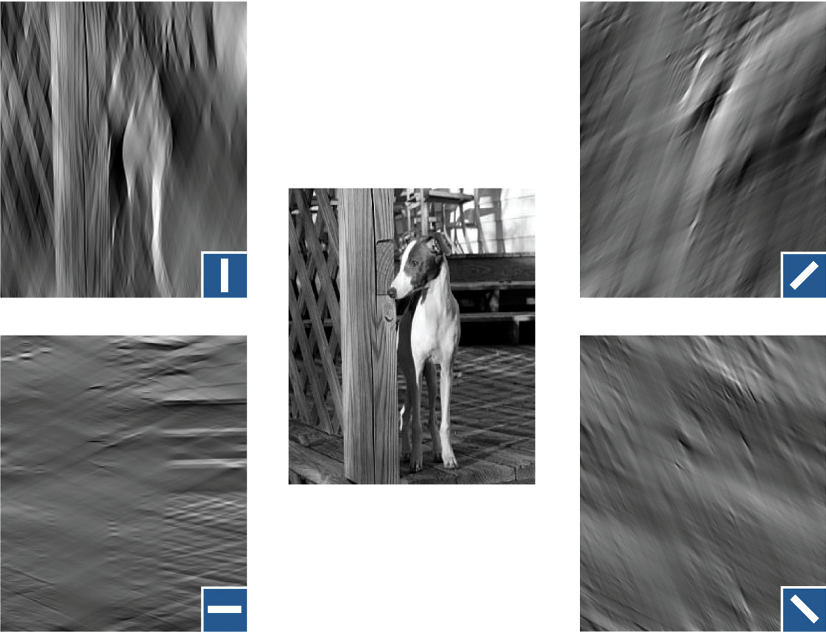
Fourier transform
images are decomposed in frequency components
each neuron only passes on a part of the total information of a scene
other neurons in the visual cortex respond the the motion of the stimulus

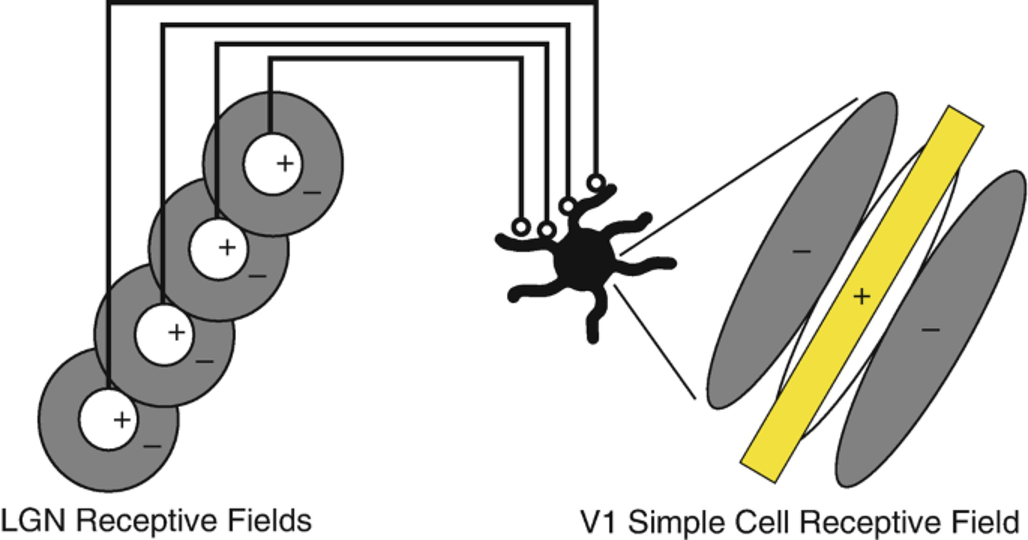
oriented receptive field
model: orientation selectivity in the visual cortex results from the integration of previous steps
thalamic neurons with aligned concentric perceptive fields project to a neuron in the primary visual cortex
the ________ ________ _____ comes from the receptive field alignment of the inputs
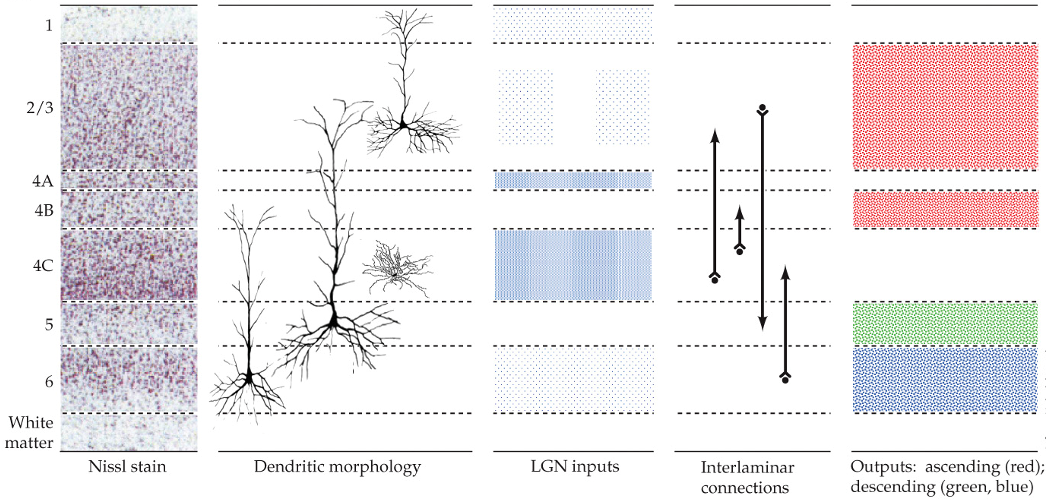
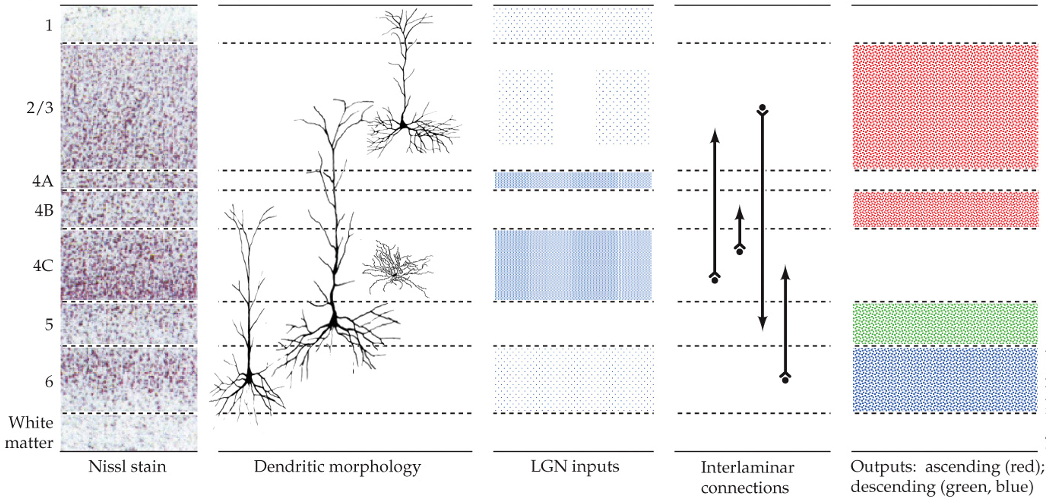
spiny neurons (dendrites) and aspinous (smooth) neurons
what types of neurons are in the primary visual cortex?
spiny neurons (dendrites)
neurons in the primary visual cortex
use glutamate as a neurotransmitter
consist of pyramidal neurons and stellate neurons
pyramidal neurons
spiny neurons in the primary visual cortex
have dendrites
in all layers except 4C
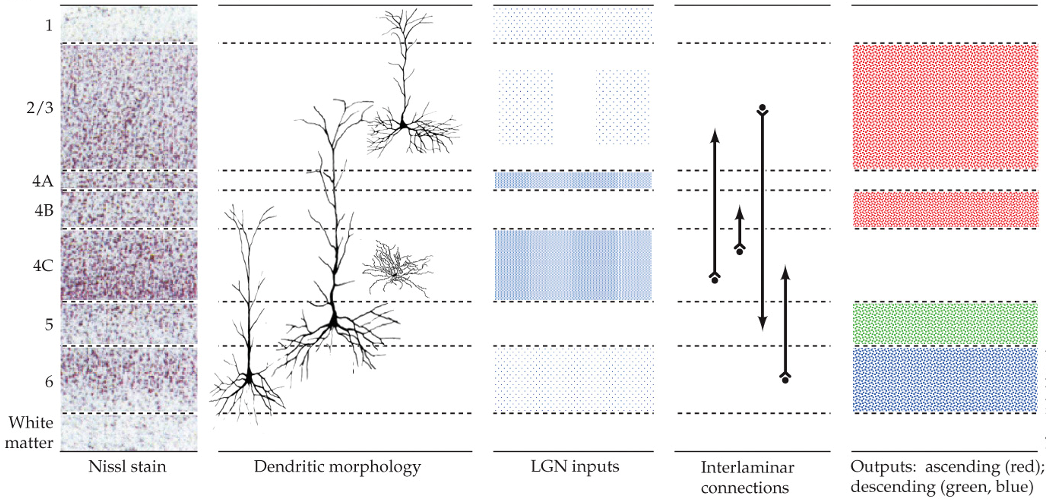
stellate neurons
neurons in the primary visual cortex
don’t have dendrites
use GABA as a neurotransmitter
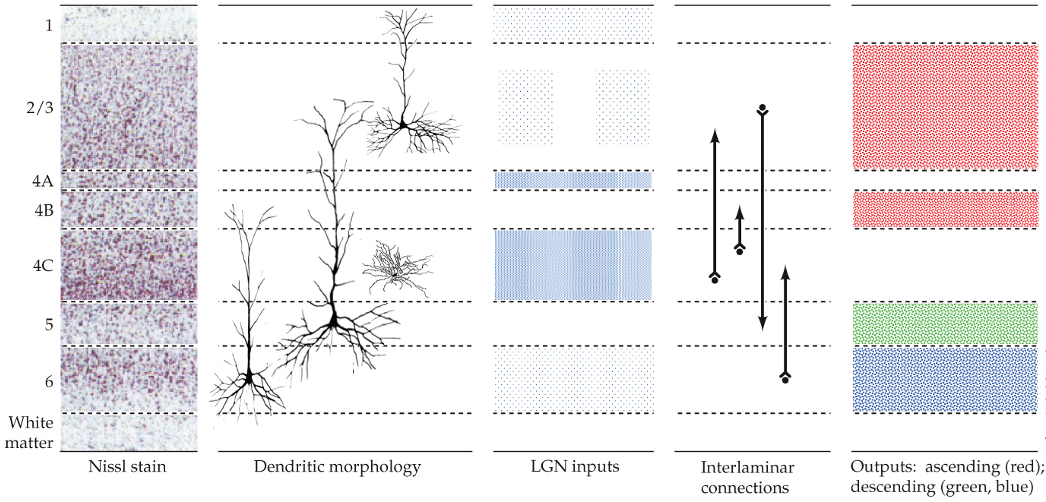
aspinous (smooth neurons)
spiny neurons in the primary visual cortex
have dendrites
in all layers except 4C
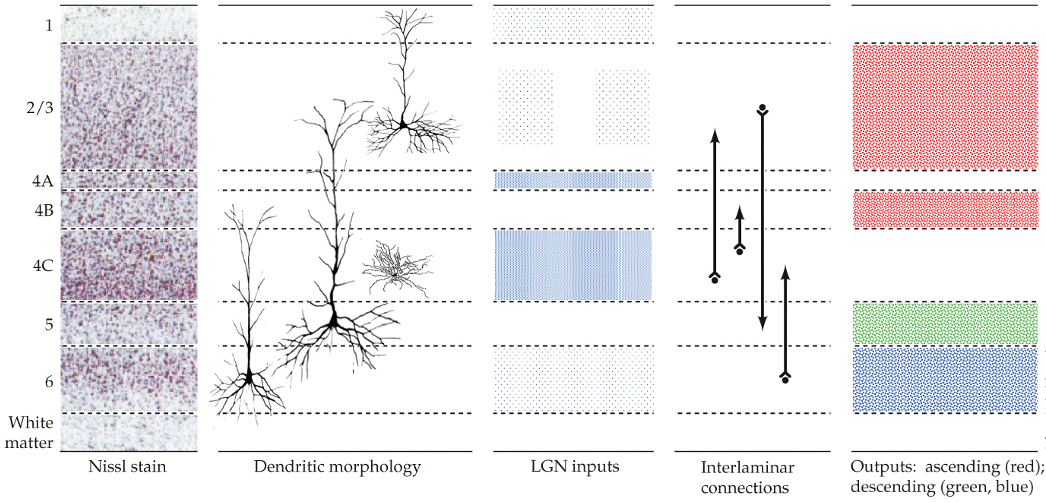
layer 4C
what layer do DGN axons terminate in the primary visual cortex?
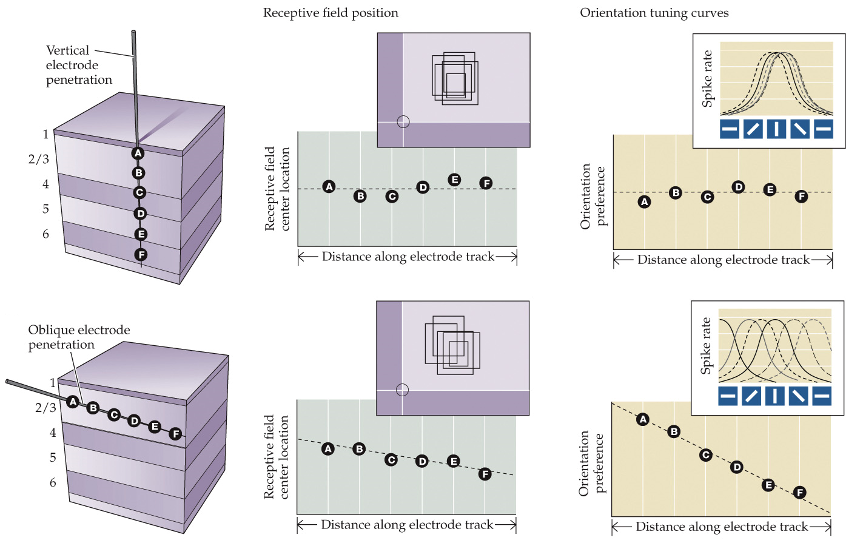
electrode inserted perpendicular to P.V cortex surface:
neurons form radial columns centered on the same field with similar orientation preferences
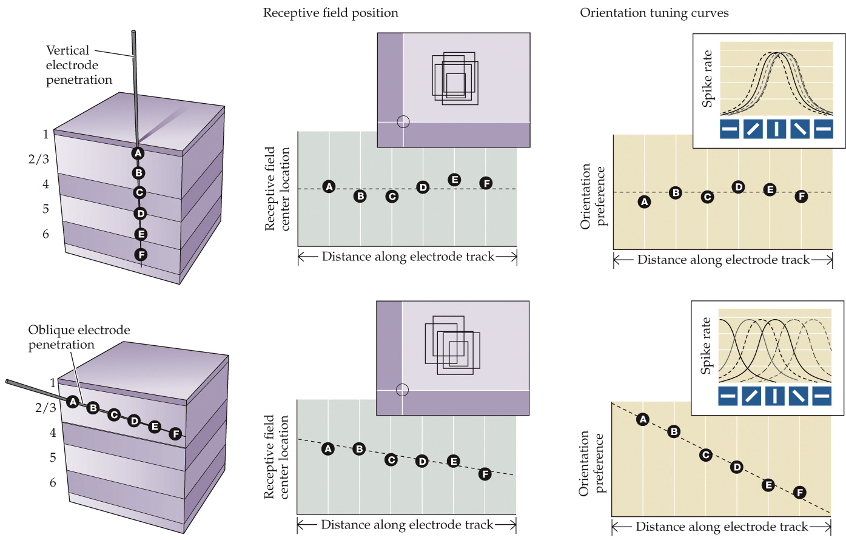
electrode inserted tangential to P.V cortex surface:
encounters neurons with different receptive fields and orientations that shift progressively
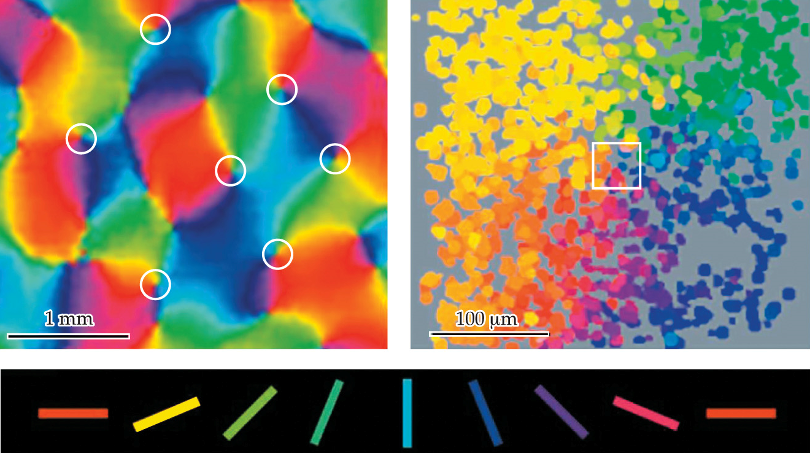
functional imaging
orientation maps are drawn from ________ _______
separate; monocular
in the DGN, inputs from both eyes arrive in ________ layers, and the neurons are _________
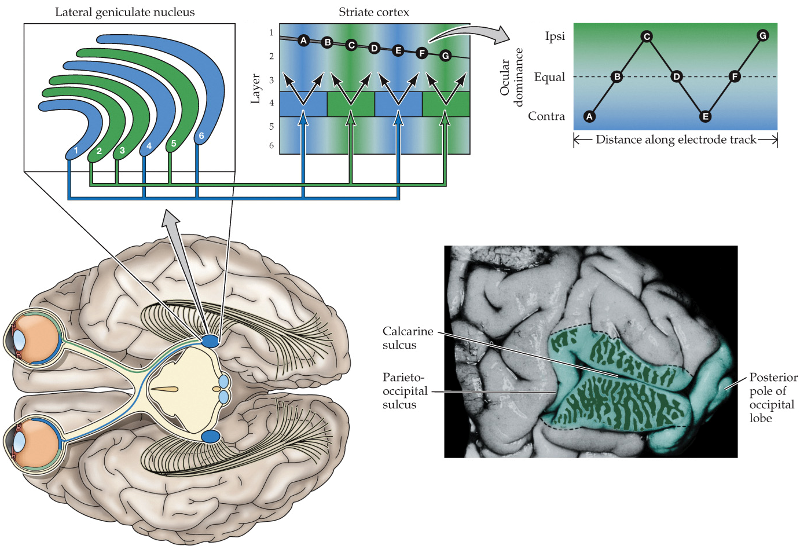
layer 4; ocular dominance columns; convergent
in the striate cortex, neurons of ______ receive inputs in separate _______ ________ _______, and then send ________ outputs in other layers
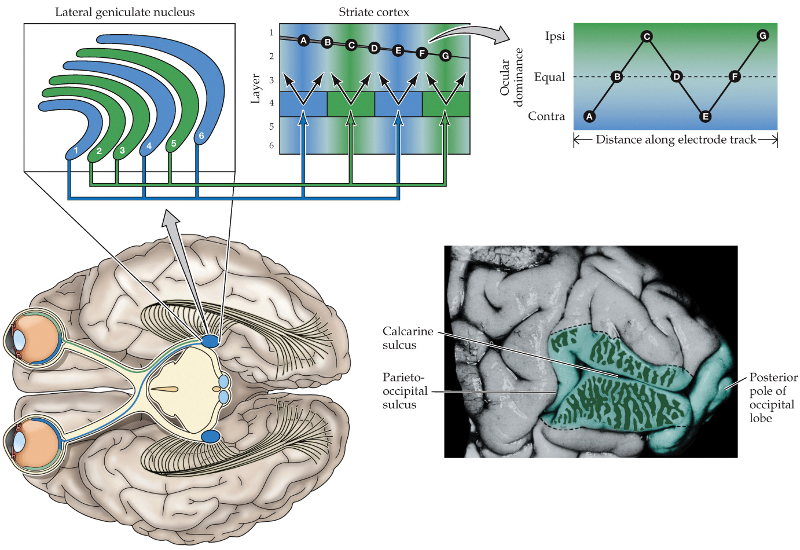
respond to one eye
do outputs on neurons at the center of ocular dominance columns respond to one eye or have equal contribution from both eyes?
have equal contribution from both eyes
do outputs on neurons at the borders between ocular dominance columns respond to one eye or have equal contribution from both eyes?
outside of the striate cortex
where is vision processed?
MT (middle temporal area)
processes movement of an object, not color
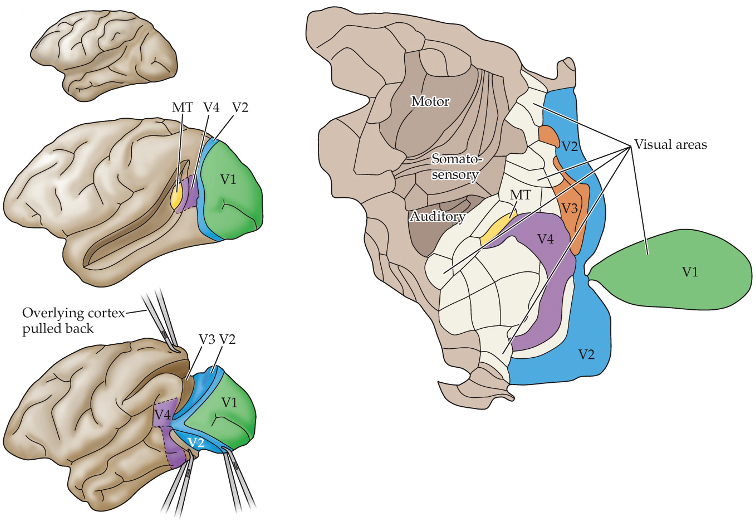
V4
processes color of an object, not movement

cerebral akinetopsia
damage to MT area
patient can’t pour liquid easily
fluid looks frozen
can’t detect that liquid has reached the top
when crossing the street, cars appear far away and suddenly appear very near