periodic table grouping and vocab
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:40 AM on 12/1/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
1
New cards
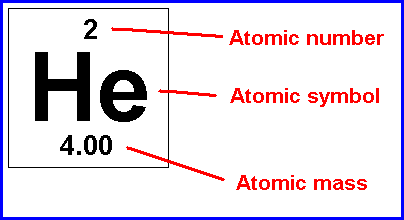
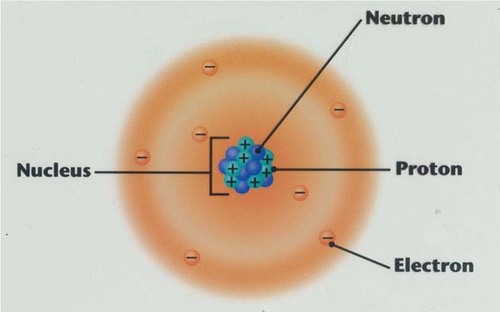
atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of an element

2
New cards
mass number
the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom's nucleus

3
New cards
element
pure substance that consists entirely of one type of atom
4
New cards
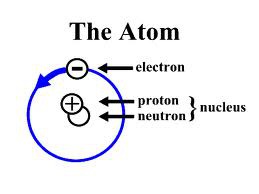
atom
the smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element
5
New cards
luster
ability to reflect light

6
New cards
malleable
able to be hammered into thin sheets

7
New cards
reactivity
the ease and speed with which an element combines, or reacts, with other substances
8
New cards
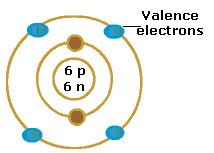
valence electrons
electrons on the outermost energy level of an atom (determines and elements reactivity)
9
New cards
physical property
a characteristic of a substance that can be observed without changing the identity of the substance
10
New cards
electron cloud
a region around the nucleus of an atom where electrons are likely to be found
11
New cards
isotope
one of two or more atoms with the same atomic number but with different numbers of neutrons
12
New cards
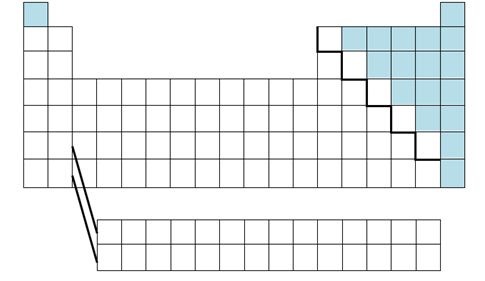
three groups of the periodic table
non-metals, metals and metalloids
13
New cards
properties of metals
☆ good conductors of electricity and heat
☆ ductile and malleable
☆ reaction with water is corrosion
☆ ductile and malleable
☆ reaction with water is corrosion
14
New cards
properties of non-metals
☆ poor conductors
☆ not ductile or malleable
☆ brittle and dull
☆ many are gasses
☆ not ductile or malleable
☆ brittle and dull
☆ many are gasses
15
New cards
properties of metalloids
☆ properties of metal and non-metals
☆ solids that are shiny or dull
☆ conduct heat but not as good as metals
☆ ductile and malleable
☆ solids that are shiny or dull
☆ conduct heat but not as good as metals
☆ ductile and malleable
16
New cards
family
they have similar properties, organized into columns
17
New cards
period
horizontal rows, don’t have similar properties
18
New cards
hydrogen
Hydrogen has 2 valence electrons and is a gas at room temperature. It's very reactive and is never found uncombined.
19
New cards
group 1
☆ alkali metals
☆ 1 valence electron
☆ react with air to form caustic metal oxides
☆ shiny, consistency of clay
☆ 1 valence electron
☆ react with air to form caustic metal oxides
☆ shiny, consistency of clay
20
New cards
group 2
☆ alkaline earth metals
☆ 2 valence electrons
☆ very reactive, (not as much as group1)
☆ never found uncombined in nature
☆ shiny, soft (but harder than group 1 metals)
☆ 2 valence electrons
☆ very reactive, (not as much as group1)
☆ never found uncombined in nature
☆ shiny, soft (but harder than group 1 metals)
21
New cards
groups 3-12
☆ transition metals
☆ 1 or 2 valence electrons
☆ moderate (ex: Fe) to low reactivity (ex: Au)
☆ good conductors of heat and electricity
☆ compounds are usually brightly colored
☆ 1 or 2 valence electrons
☆ moderate (ex: Fe) to low reactivity (ex: Au)
☆ good conductors of heat and electricity
☆ compounds are usually brightly colored
22
New cards
group 13
☆ boron family
☆ 3 valence electrons
☆ moderately reactive
☆ includes a metalloid (boron) and the rest are metals
☆ 3 valence electrons
☆ moderately reactive
☆ includes a metalloid (boron) and the rest are metals
23
New cards
group 14
☆ carbon family
☆ 4 valence electrons
☆ unreactive
☆ includes a non-metal (carbon), metalloids and metals
☆ 4 valence electrons
☆ unreactive
☆ includes a non-metal (carbon), metalloids and metals
24
New cards
group 15
☆ nitrogen family
☆ 5 valence electrons
☆ tend to share electrons when they bond
☆ moderately reactive
☆ 5 valence electrons
☆ tend to share electrons when they bond
☆ moderately reactive
25
New cards
group 16
☆ oxygen family
☆ 6 valence electrons
☆ moderately reactive (oxygen is very reactive)
☆ most elements in this family share electrons when forming compounds
☆ 6 valence electrons
☆ moderately reactive (oxygen is very reactive)
☆ most elements in this family share electrons when forming compounds
26
New cards
group 17
☆ halogen family
☆ 7 valence electrons
☆ react with alkali metals to form salts
☆ strong odors and interesting colors
☆ halogen atoms only need to gain 1 electron to fill their outermost energy level
☆ 7 valence electrons
☆ react with alkali metals to form salts
☆ strong odors and interesting colors
☆ halogen atoms only need to gain 1 electron to fill their outermost energy level
27
New cards
group 18
☆ noble gases
☆ 8 valence electrons
☆ extremely unreactive
☆ inactive because their outermost energy level is full, called inert because they aren’t ready to combine with other elements
☆ 8 valence electrons
☆ extremely unreactive
☆ inactive because their outermost energy level is full, called inert because they aren’t ready to combine with other elements
28
New cards
stable isotopes
they stay the same over time
29
New cards
unstable isotopes
will eventually decay into a different nucleus
30
New cards
when a nucleus emits a particle and changes identity, that process is called
radioactive decay
31
New cards
Isotopes that are unstable and undergo radioactive decay are called
radioactive isotopes
32
New cards
1:1
the most stable neutron to proton ratio
33
New cards
elements with a large number of protons are most stable when their neutron to proton ratio is ____. The more protons an element has, the ____ this ratio needs to be for the nucleus to be stable.
higher, higher
34
New cards
types of decay
alpha, beta - , and beta +
35
New cards
β− decay
too many neutrons compared with protons
36
New cards
β+ decay
too many protons compared with neutrons
37
New cards
positron
charge of +1, no mass, when they collide with an electron, both this particle and the electron get annihilated
38
New cards
α-decay
when the nucleus is too big overall, it can become more stable by losing both protons and neutrons
39
New cards
alpha particle
has 2 protons and 2 neutrons, same as the nucleus of a helium-4 atom
40
New cards
fission
splitting a nucleus into smaller parts, ex: power plants
41
New cards
fusion
combining nuclei to make something bigger, ex: stars
42
New cards
How many valence electrons does fluorine (F) have?
7
43
New cards
How many valence electrons does aluminium (Al) have?
3
44
New cards
How many energy levels does phosphorus (P) have?
3
45
New cards
Iron-50 has ___ protons and ___ neutrons.
26, 24
46
New cards
A calcium ion has a charge of +2 and a mass of 40. How many electrons does it have?
18
47
New cards
An oxygen ion has a charge of -2 and a mass of 17. How many protons does it have?
8
48
New cards
Strontium (Sr) shares common properties with what other element?
Barium (Ba)
49
New cards
All of the following are properties of metals EXCEPT
a. brittle
b. conducts elecricity well
c. malleable
d. lustrous
a. brittle
b. conducts elecricity well
c. malleable
d. lustrous
brittle
50
New cards
An isotope will undergo beta minus (electron) decay when
Its neutron to proton ratio is too high to be stable
51
New cards
A positron decay occurs, and the daughter isotope is Manganese-55. What was the parent isotope?
Iron-55
52
New cards
What particle is emitted when Barium-140 decays to Lanthanum-140?
electron
53
New cards
What particle is emitted when Potassium-38 decays to Argon-38?
positron