Electrode Potential
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
why does zinc dipslaces copper
because zinc stronger reducing agent than copper
what is electrochemical series
a ranking of half equation based on reducing power
what happens as the gap in electrochemical sereies is bigger
the more energy is given out
what is a half cell / electrode
A metal dipped into a solution of its own ions
when is displacement not redox
double displacement
equilibrium position and its affects on reducing agent
position of reducing agent equilibrium is to the left of the oxidising agent equilibrium
increase concentration of delocalised electron in metal that acts as reducing agent
which directions will electrons move if wire added
away from reducing agent towards oxidisng agent
what happens to reducing agent as conc of reaction changes
conc of 2e- decreases
equilibrium position left
sending more electrons throwugh wire
what happens to oxisidising agent as conc of
conc of 2e- increases
equilibrium postion to the right
more ions come out of solutions , balancing out some of new electrons
what potential diffrencence and unit
diffrenece between reducings agent and oxidisng agent
voltage
diffrence between P.D and Electrotimotive force
electromotive force rules out factors like resistenece wire to get maximum possible voltage
why use hydrogen to compare
readily available and cheap
why us platinium
conduct electricity and will not reaact
since hydrogen is not metal how we use it
connect wire to platinium
dip into solution containtg H+ ions
bubble H2 gas through solution
what happens to hydrogen if other stronger reducing agent
hudrogen ions pick up electrons from platiumin to form H2 gas
what happens if other weaker reducing agent
hudrogen gas oxides to hydrogen ions
electrons flow throguh platinuim strip
what is electrode potential
comapring each reducing strenght to hydrogen
what is a more negative electrode potential mean
stronger redusinc agent
what is more positive electrode potential mean
stronger oxidising agent
what happens to electrode potential when pressure decreases
decrease in pressure , decrease in conc of H2 gas , equilibrium position to the right so electrode potential more positive
if equilibirum shifts left what happens to electrode potential
electrode potential more negative
if equilibirum shifts rights what happens to electrode potential
electrode potential more positive
what does it mean if electrode potential is negative
electrons flow right to left
positive on left
what does it mean if electrode potential is positive
electrons flow left to right
positive on right
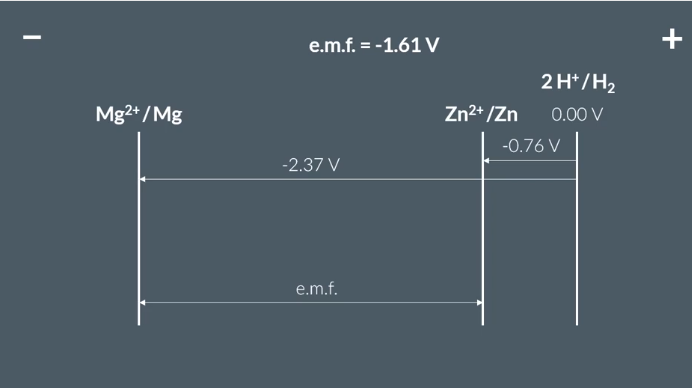
how to work out electrode potential cell
electrode potential of right - electrode potential of negative