Chapter 3: A Tour of the Cell
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for vocabulary review of cells, microscopy, cell theory, cell structures, cell division, and cellular transport.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Cells
Fundamental units of life and the building blocks of the body, responsible for various functions like providing strength (bone cells), protection (immune cells), and oxygen transport (red blood cells).
What is a Cell?
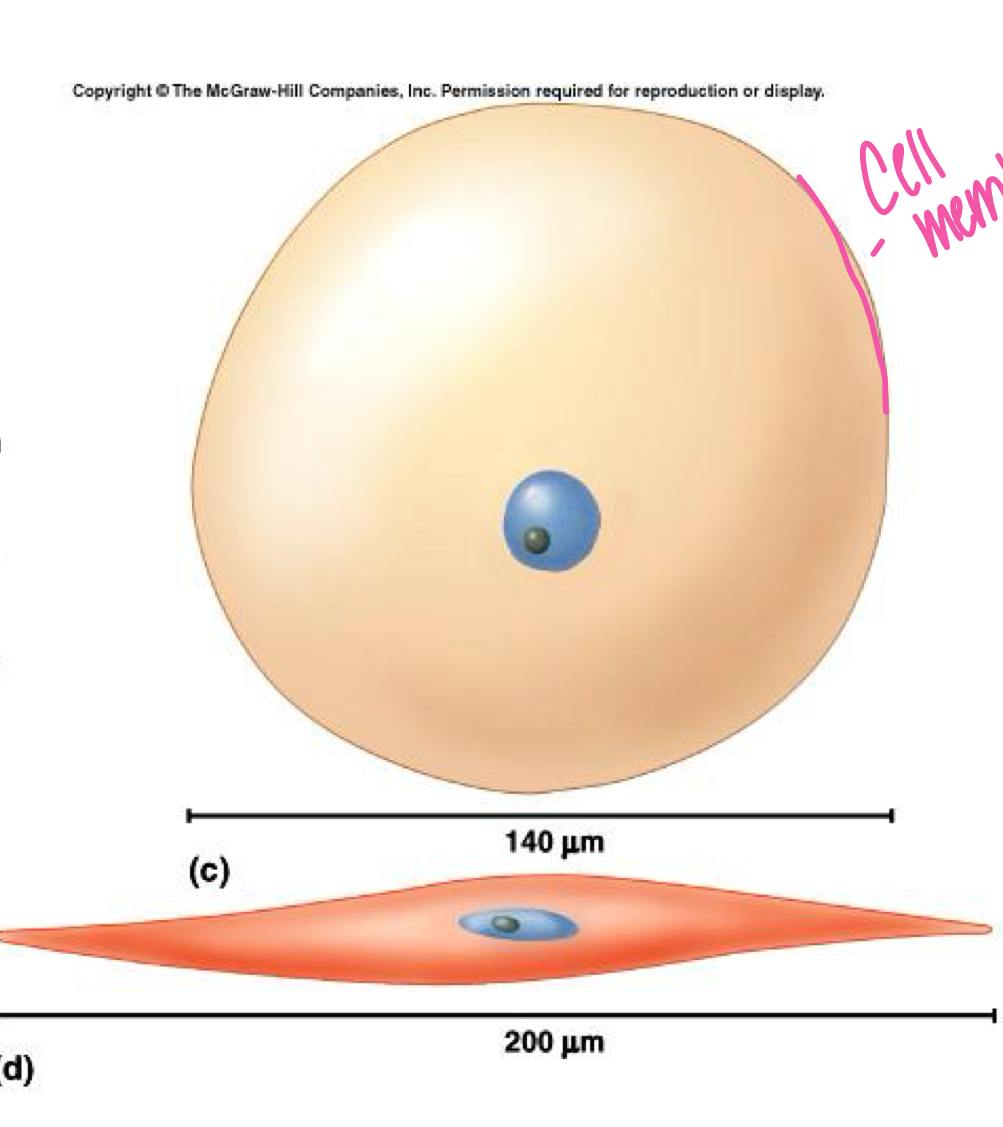
Smallest unit of life, varying in size and shape, measured in micrometers, and differentiated into various types (e.g., stem cells). Major parts include the nucleus, cytoplasm, and cell membrane.
Microscopy
Technique that allows us to observe cells and cellular structures using magnifying lenses, light and electron microscopes.
Cell Theory
States that all living things are composed of cells, the cell is the basic unit of life, and all cells come from preexisting cells.
Eukaryotic Cells
Cells with a complex structure containing organelles that float in the cytoplasm and are usually larger in size compared to prokaryotic cells.
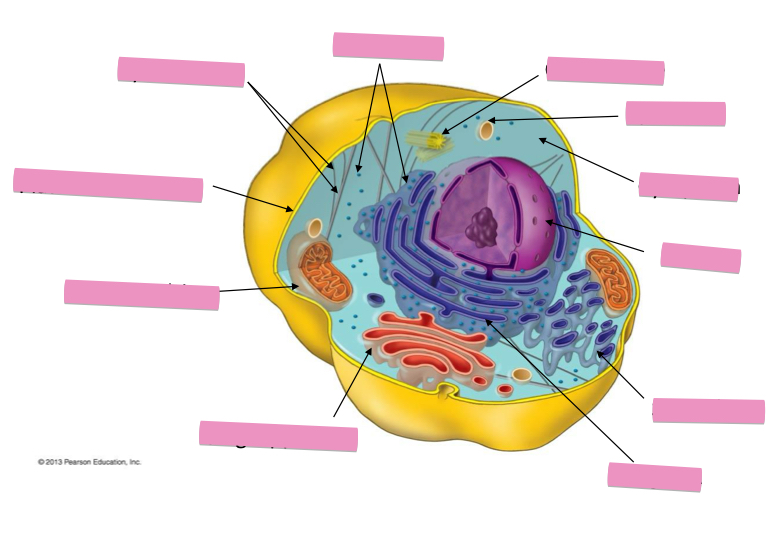
Identify the cytoskeleton
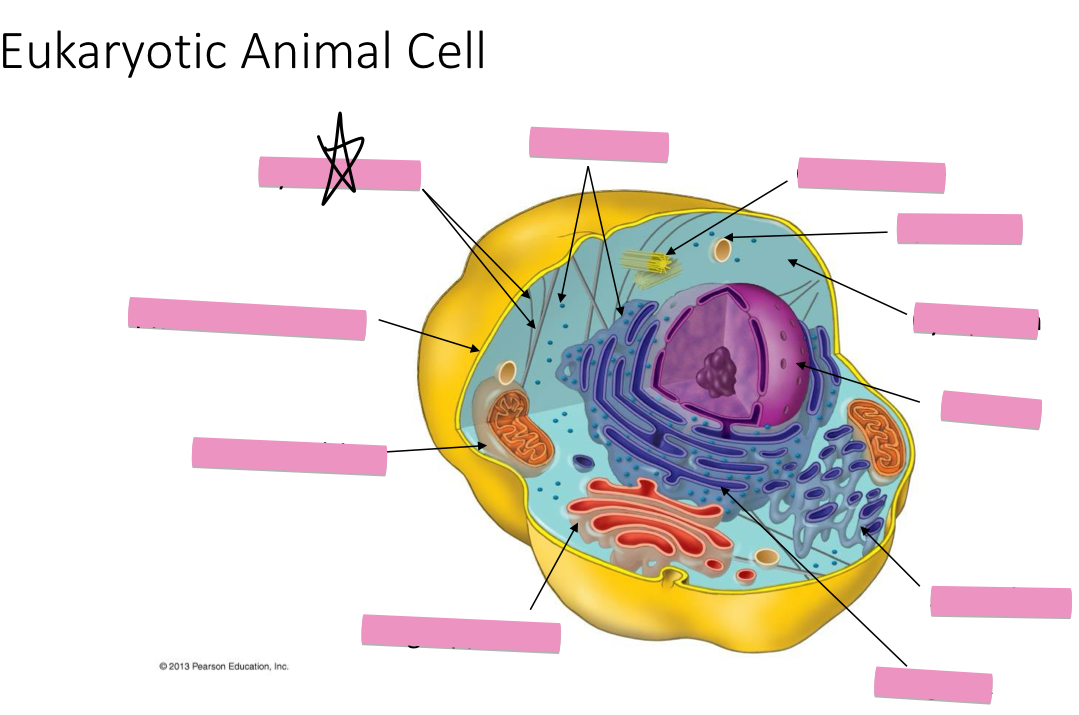
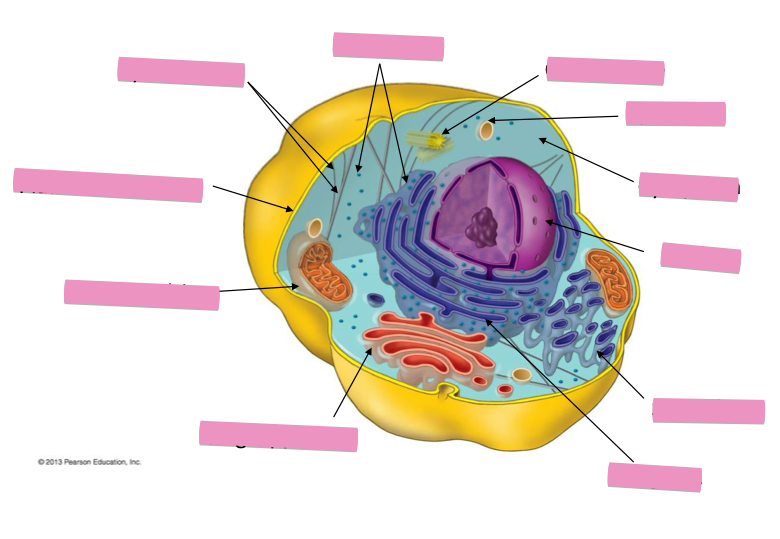
Identify the ribosomes
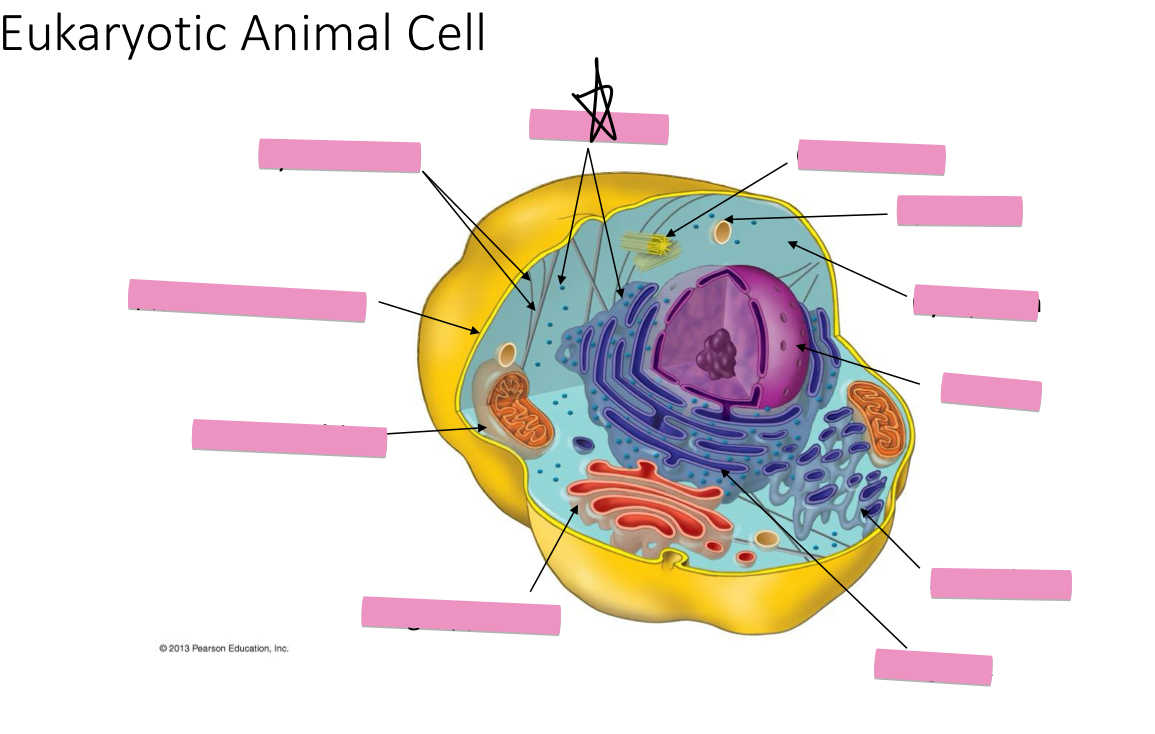
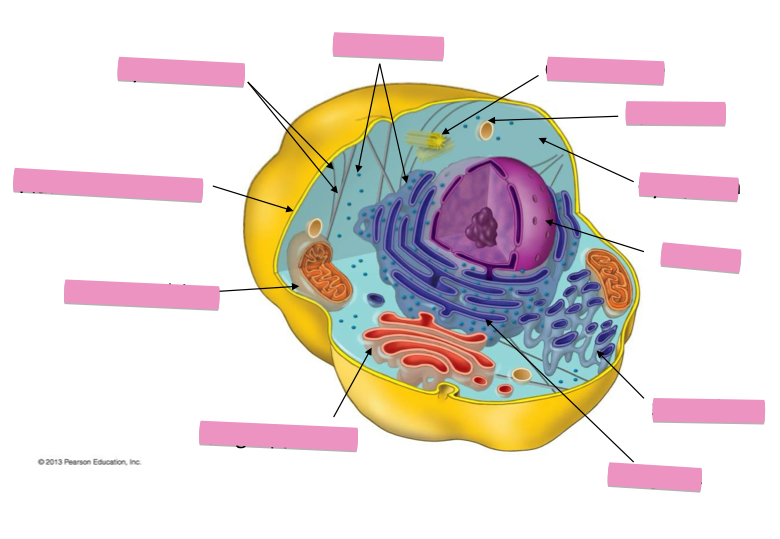
Identify the centrosome also called the centriole
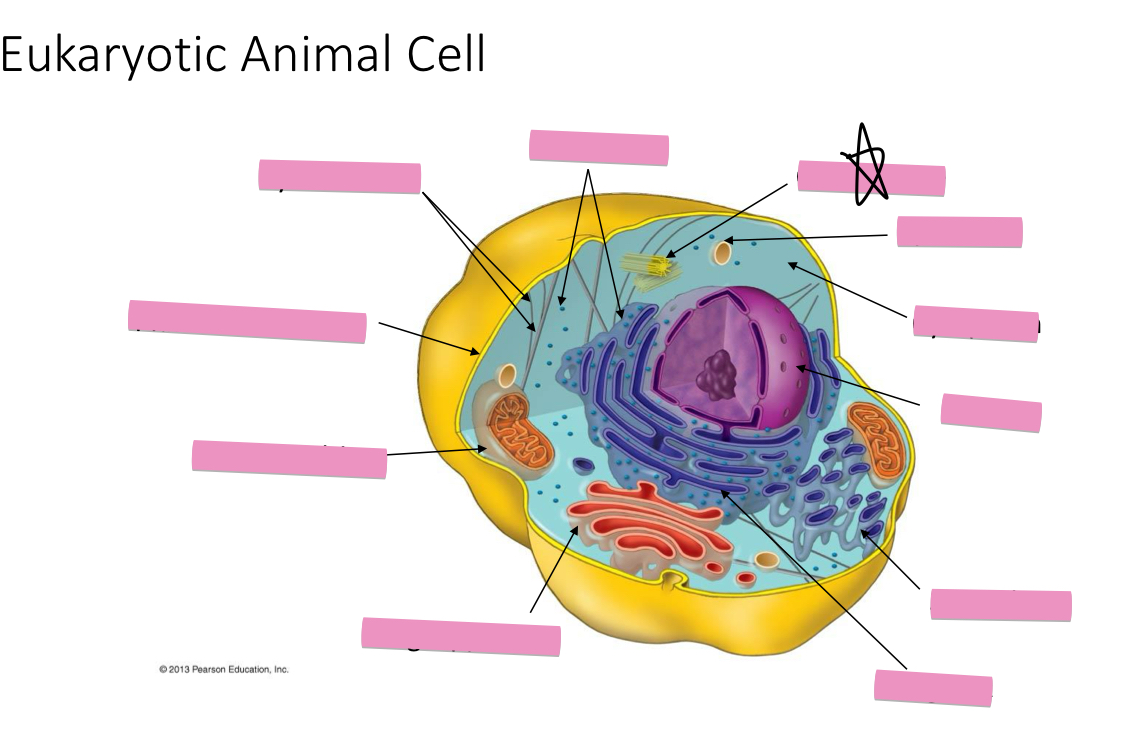
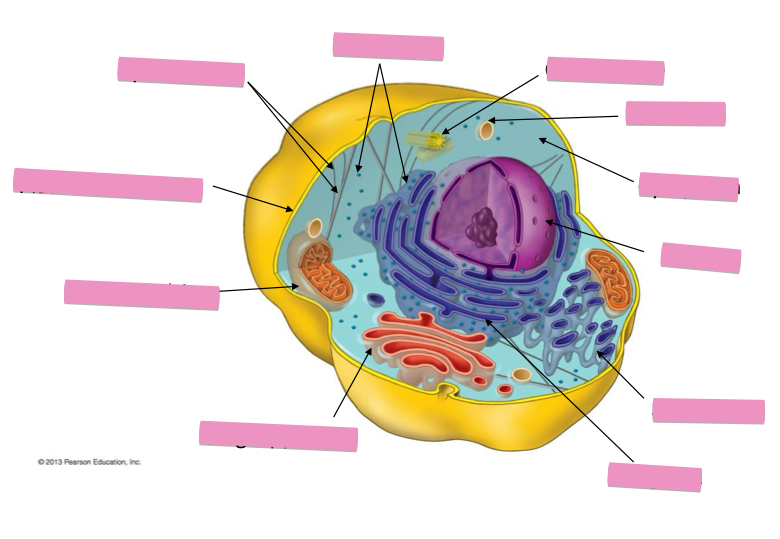
Identify the lysosomes
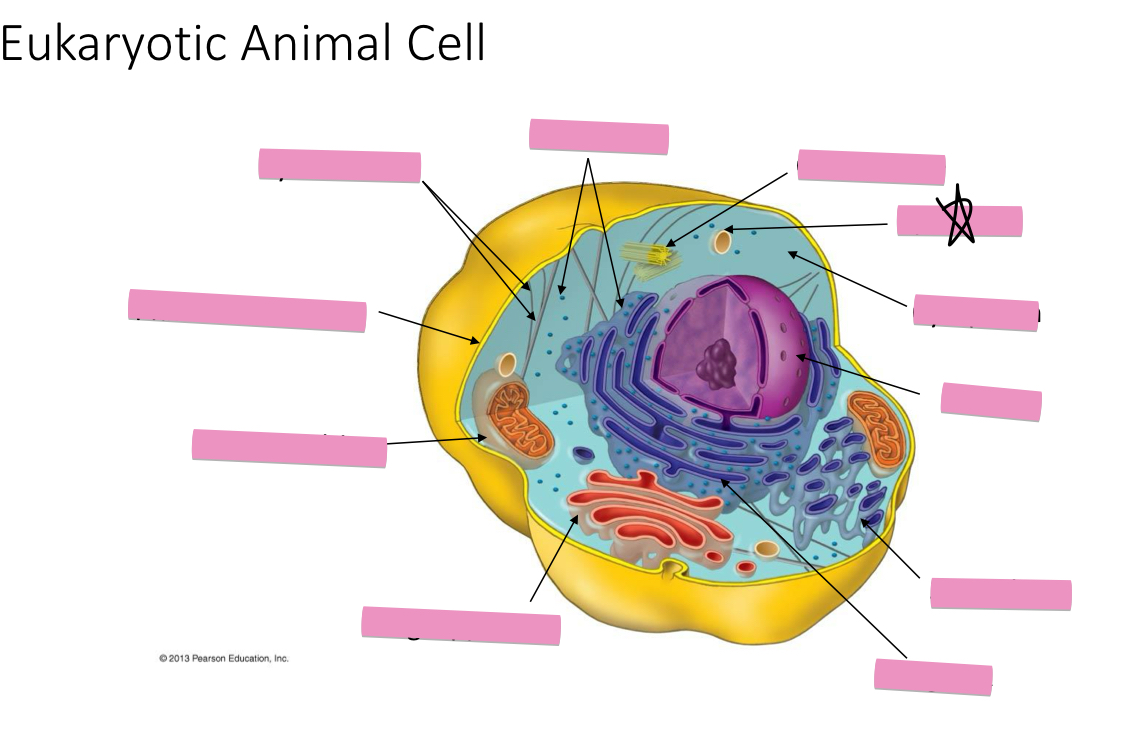
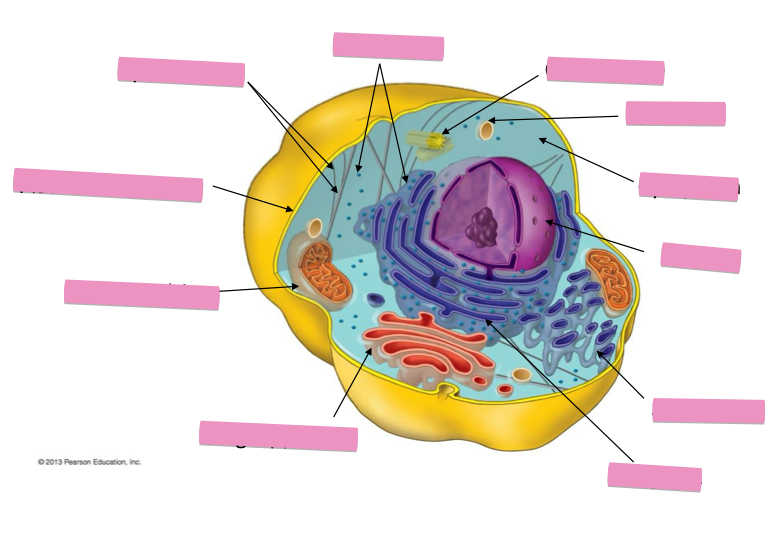
Identify the cytoplasm
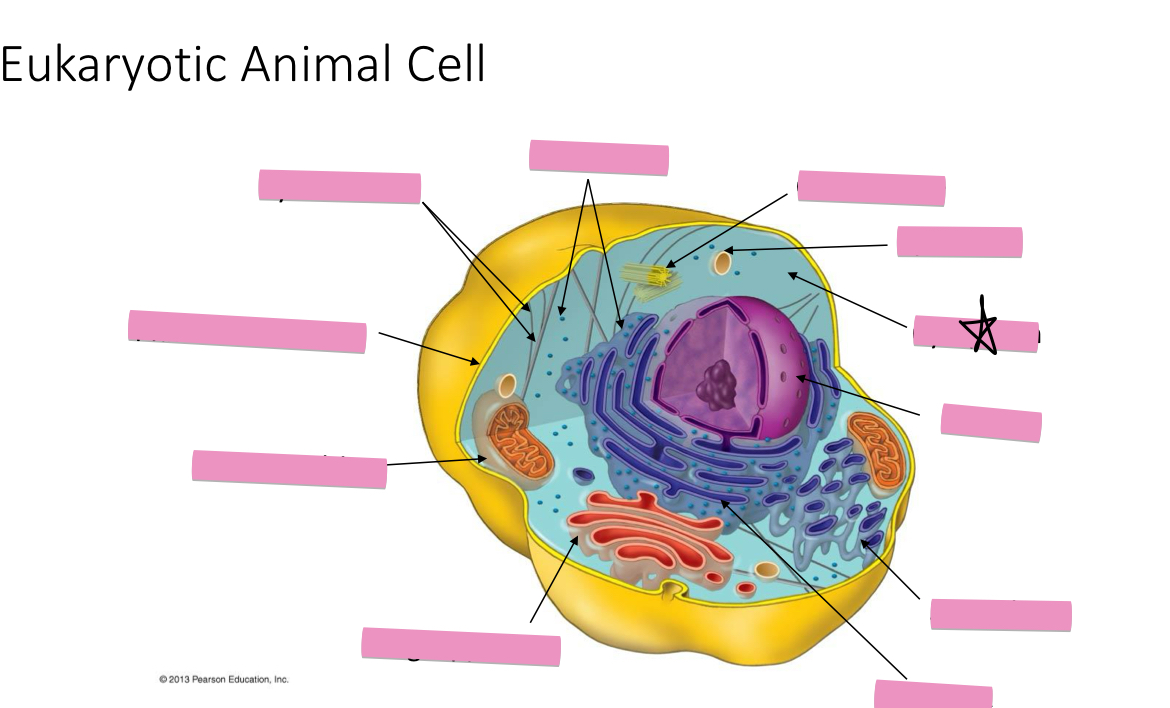
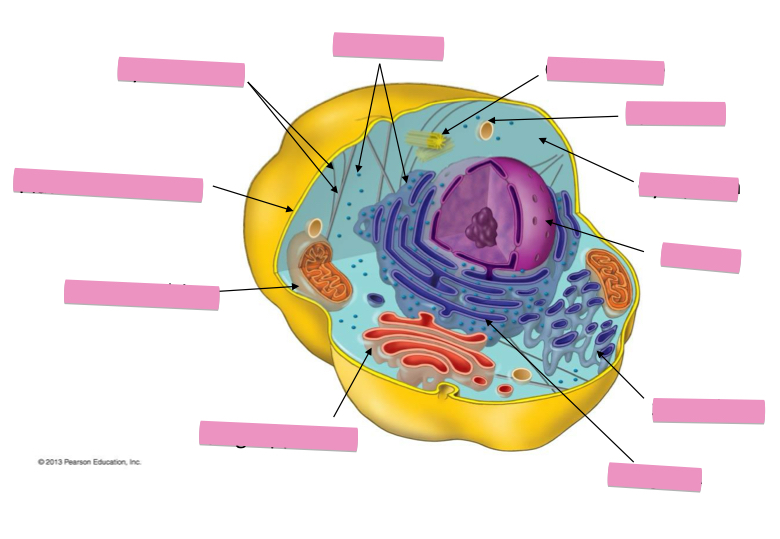
Identify the Smooth ER
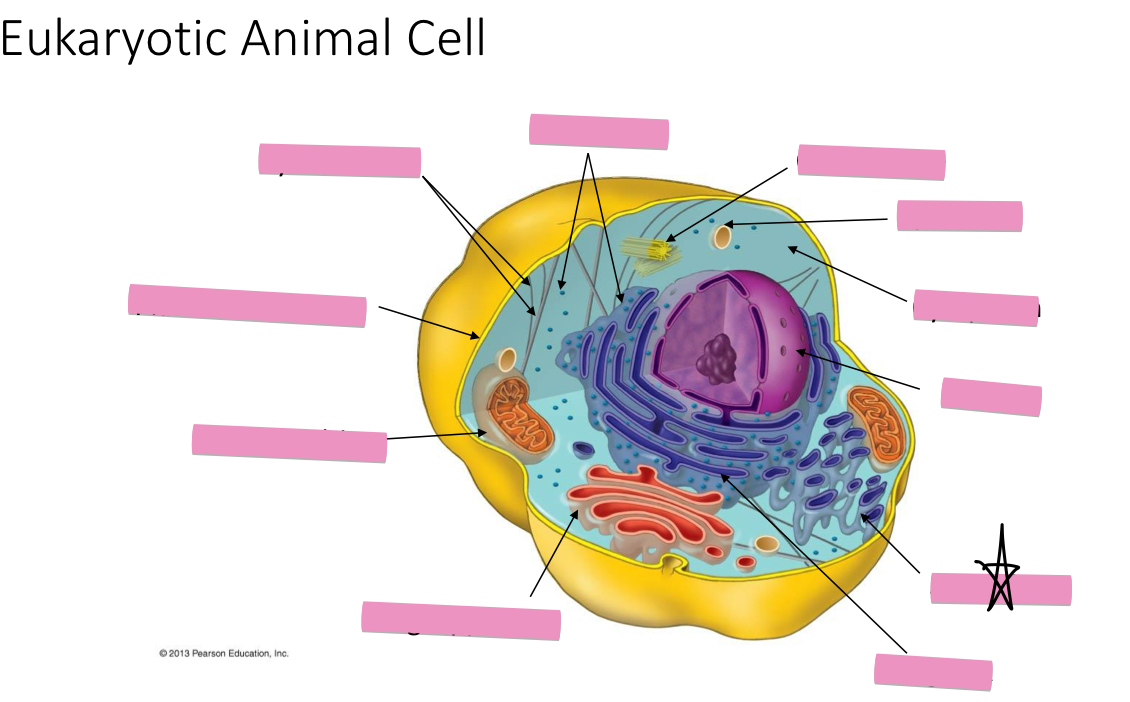
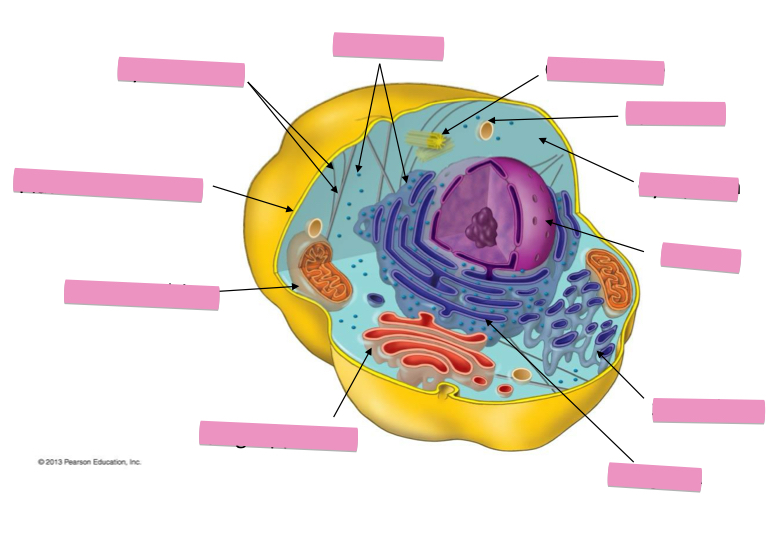
Identify the Rough ER
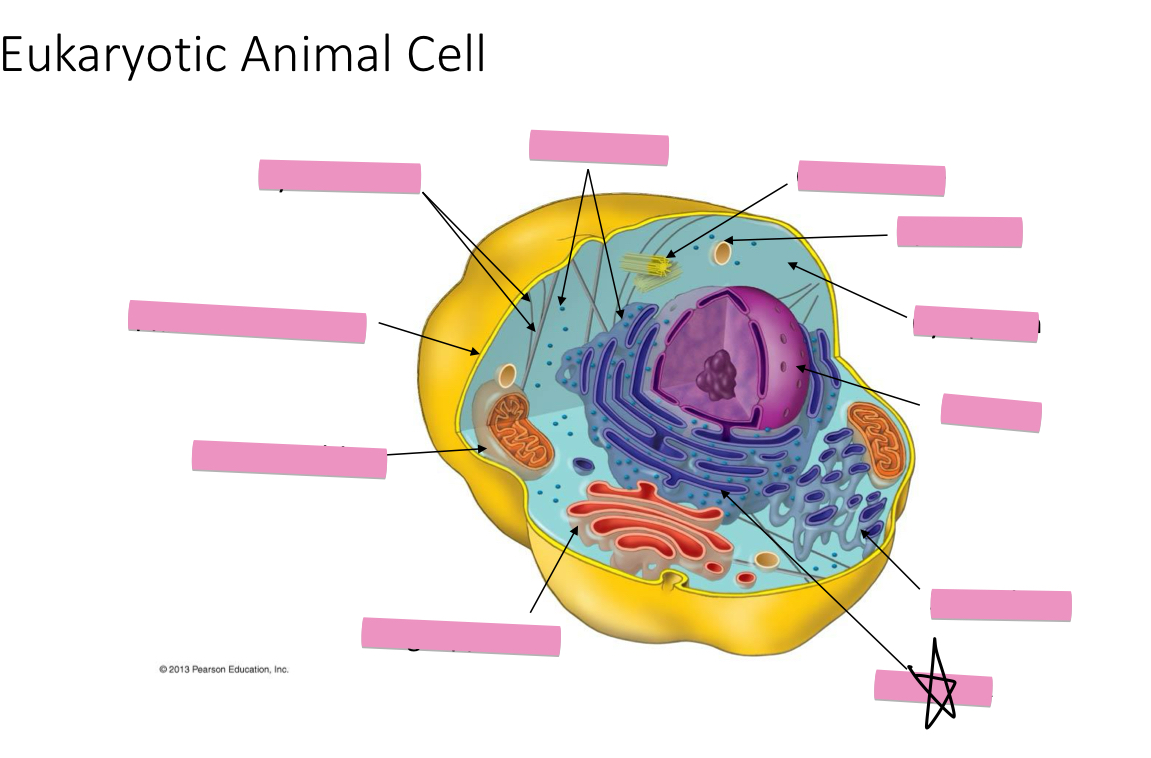
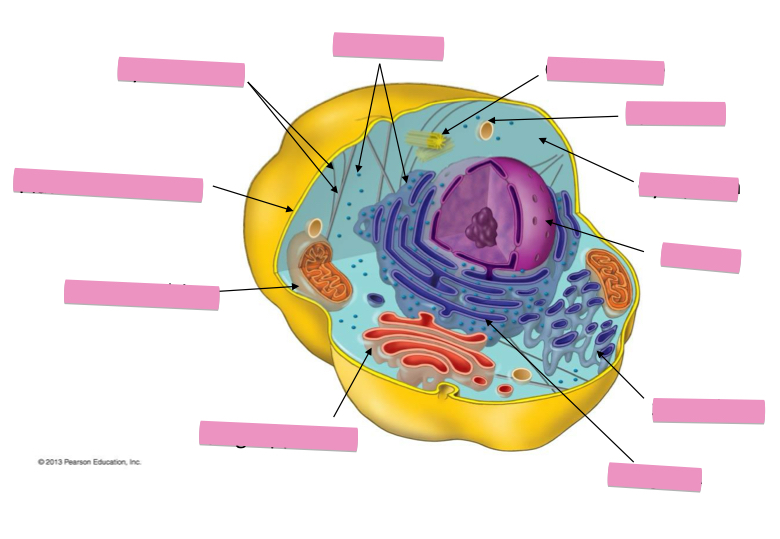
Identify the Golgi apparatus
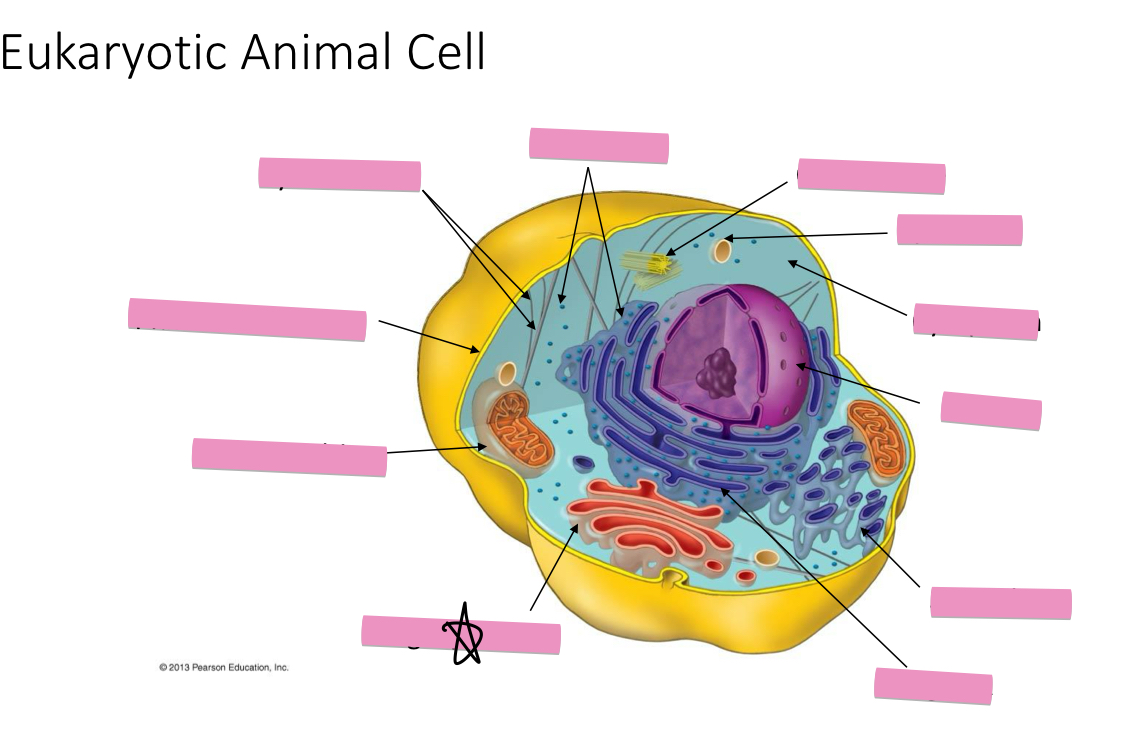
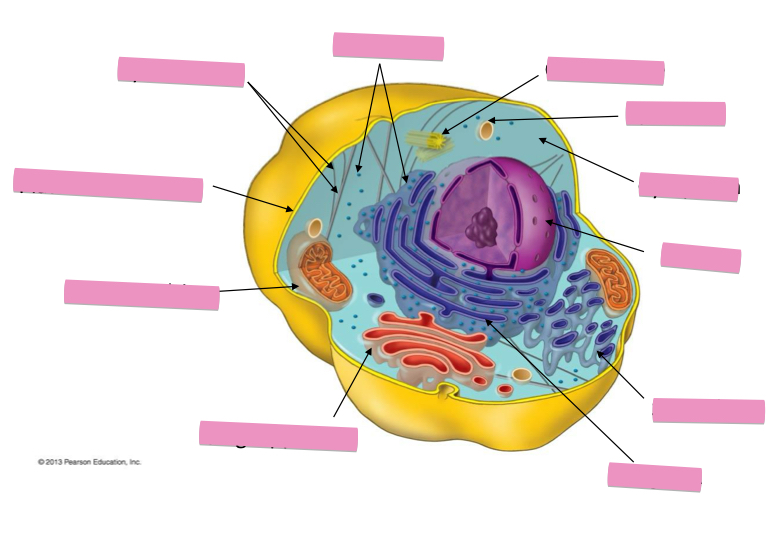
Identify the mitochondria
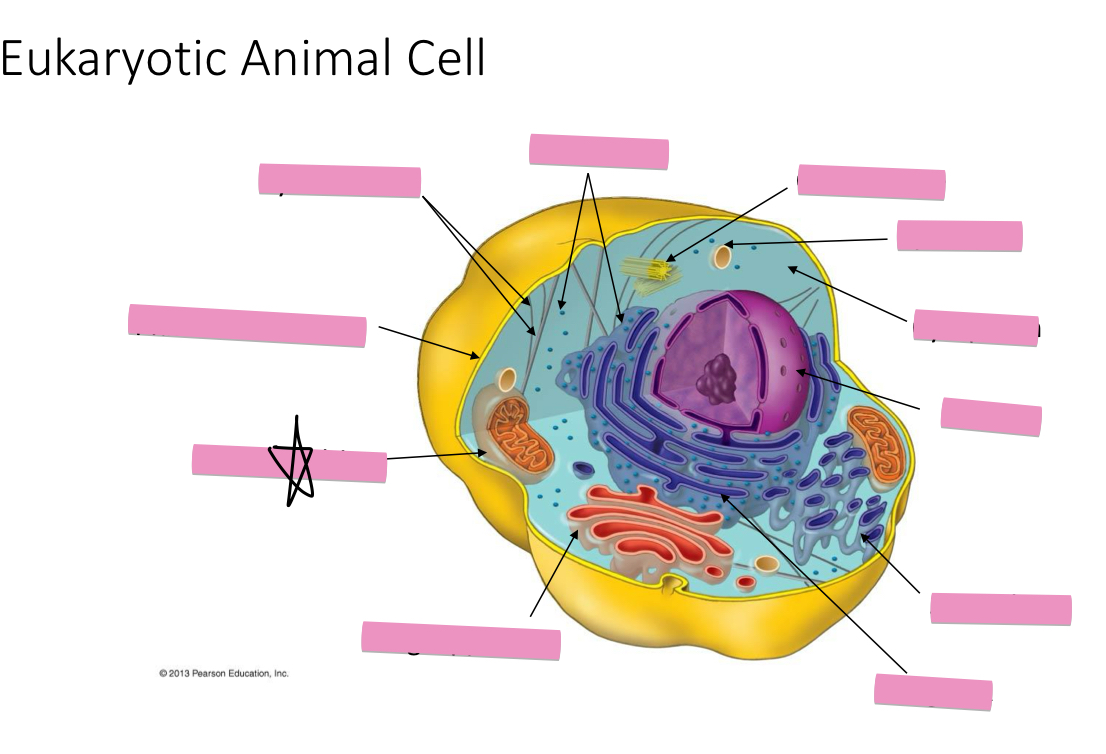
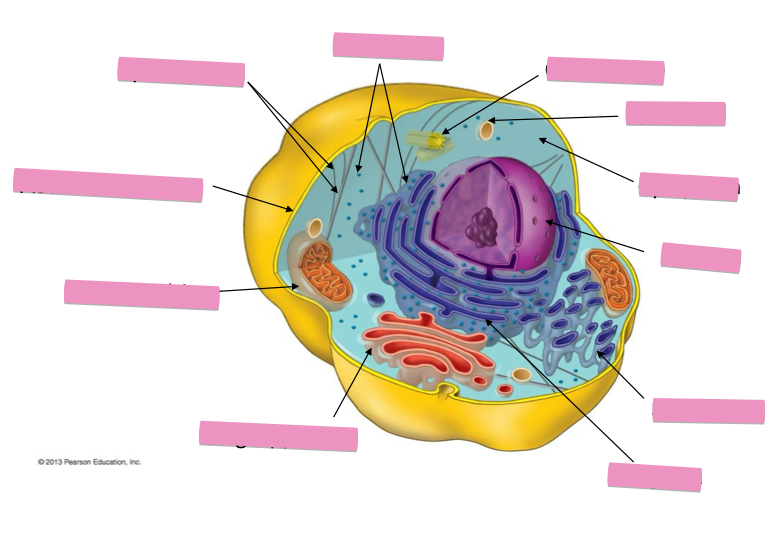
Identify the plasma membrane
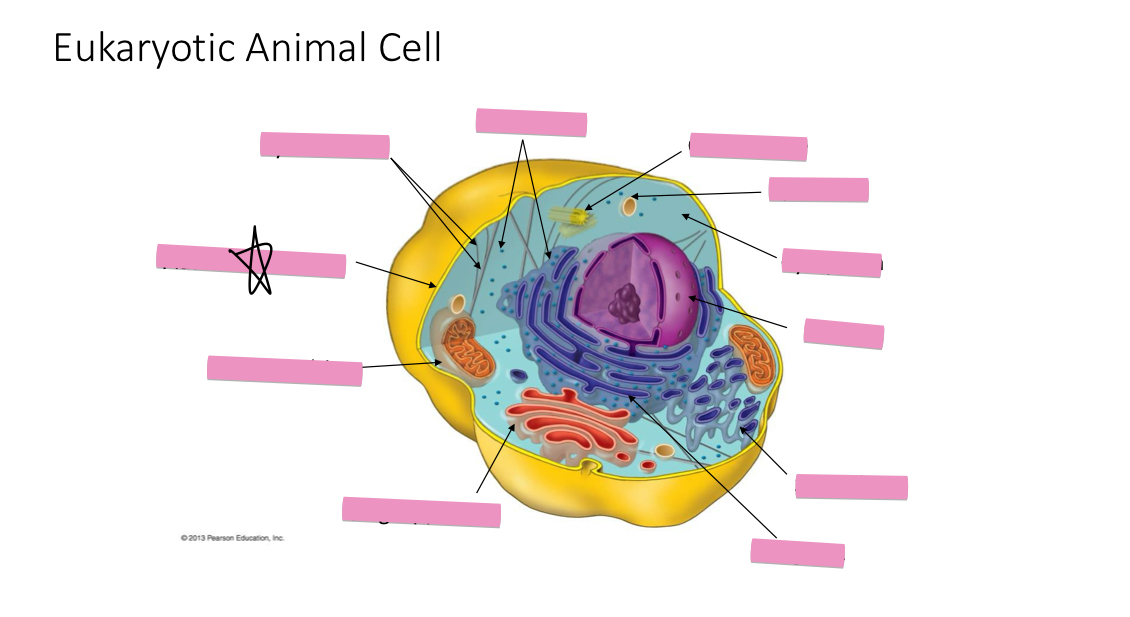
Plasma or Cell Membrane
Encloses the cell interior and controls what substances enter and exit the cell. “Selectively permeable”. Made of a double-layer of phospholipids. It is also embedded with cholesterol and proteins. Is also called a fluid mosaic
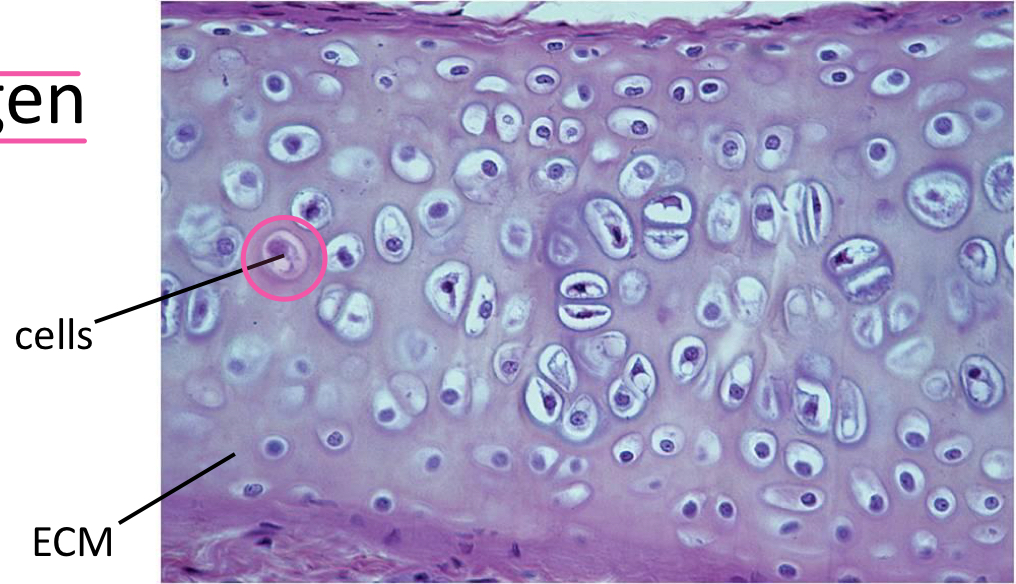
Extracellular matrix (ECM)
A sticky coat made of protein collagen. Holds cells together in tissues. Provide protection and support.
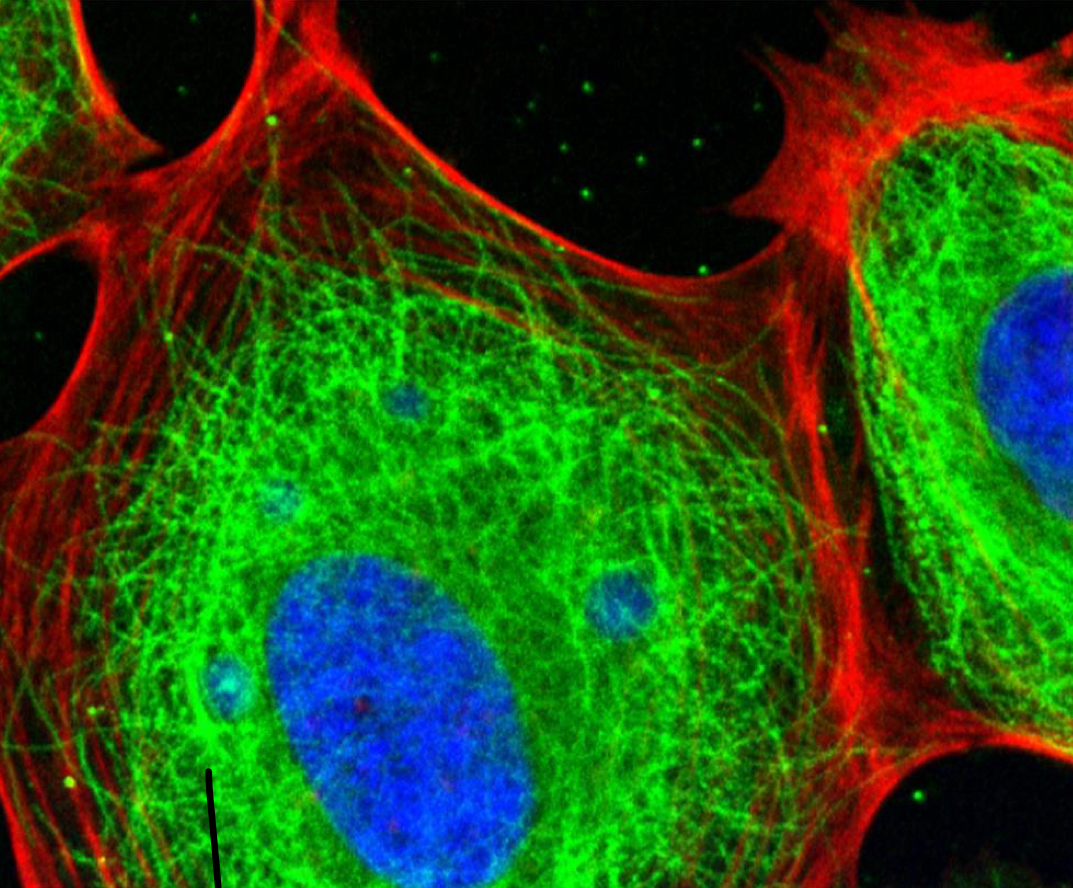
Cytoskeleton
Network of fibers which acts as mechanical support to the cell. Helps a cell maintain its shape. Provides anchorage and reinforcement for many organelles.
Cytosol
Interior of the cell; comprised of cytoplasm, which contains organelles
Nucleus
DNA-containing organelle; control center of the cell
Cytoskeleton
Internal framework for the cell; provides structure and shape to the cell
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
One of the main manufacturing facilities in a cell. Modifies proteins (rough ER) and synthesizes lipids within a cell (smooth ER). Interconnected with the nuclear envelope.
Rough ER
Has ribosomes on the outside of its membrane. These ribosomes produce proteins. This ER manufactures and packages proteins which are transported via vesicles.
Smooth ER
Lacks surface ribosomes. Produces lipids (steroids, hormones). Can also help liver cells detoxify circulating drugs.
Golgi apparatus
Modifies and packages proteins and lipids for distribution via transport vesicles around and outside of the cell.
Vesicles
Are membranous sacs that store and transport substances inside a cell.
Centrosome
Two rod-like centrioles. Used to produce cilia and flagella. They also play a role in manipulating and moving chromosomes during cell division.
Phospholipid bilayer
Made of a double layer of phospholipids. Embedded with proteins and cholesterol.
Flagella
Long extensions of the cell that produce whip-like motions. Gives the cell the ability to move.
Cilia
Finer and shorter extensions of the cell that produce back-and-forth motions. Allows the cell the ability to move.
Ribosomes
Responsible for making proteins (Protein Synthesis). Some of them are suspended in the sytoplasm while others are attached to the outside of the nucleus and the Rough ER.
The endomembrane system
Organelle membranes that interact with each other. Includes the: nuclear envelope, both ER, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles.
Lysosomes
Membrane-bound sacs of digestive enzymes found in animal cells that break down large biomolecules and damaged organelles.
Mitochondria
Organelle that performs cellular respiration, breaking down sugars to make ATP (energy for the cell).
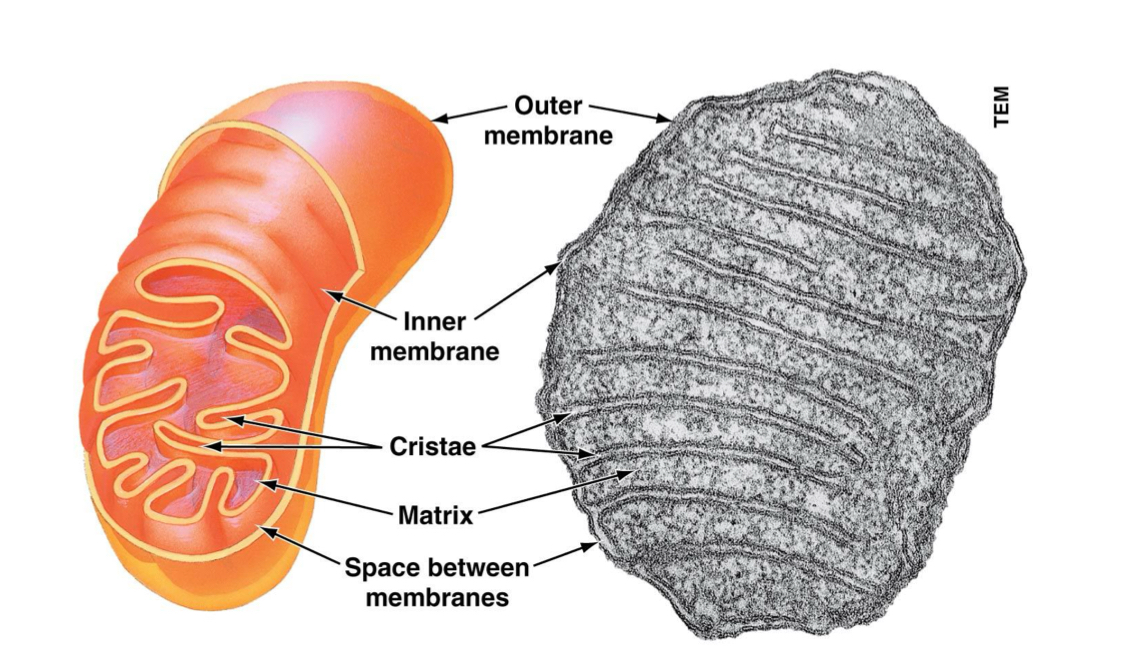
Nuclear envelope
Made of a phospholipids bilayer. Pores allow for materials to more between the nucleus and cytoplasm.
Nucleolus
Is where ribosomes are made
For most of a cell’s lifetime (cell cycle) DNA is stored as ________.
Chromatin
Chromatin
Consists of long, uncondensed DNA molecules and associated proteins.
Each chromatin strand or fiber makes up a single ________.
Chromosome
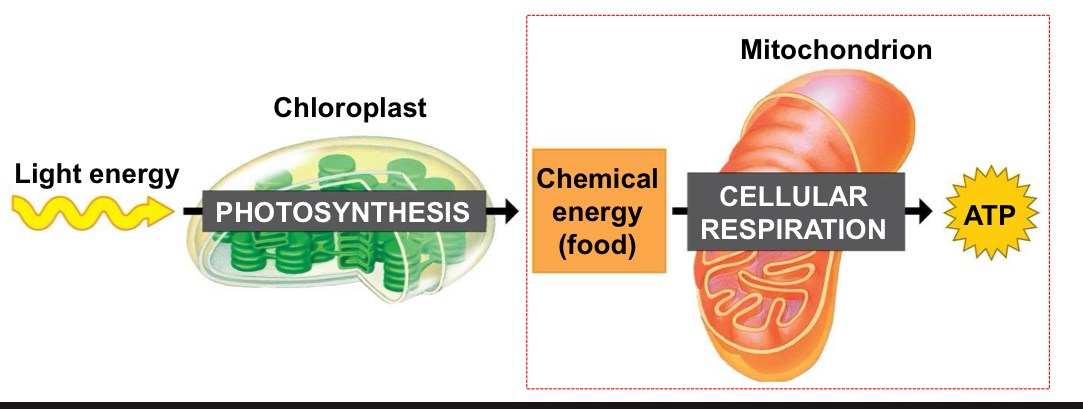
Cellular respiration
Breakdown of sugars to make ATP (energy for the cell). Both plant and animal cells preform this.
ATP: Adenosine Triphosphate
Acts like an energy shuttle. Stores energy obtained from food (GLUCOSE) then releases it later as needed.
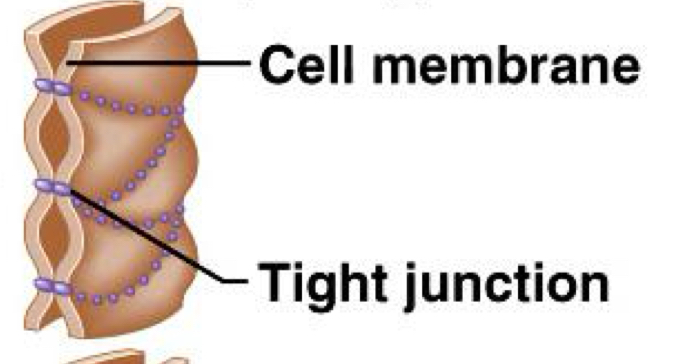
Tight Junctions
Close space between cells; usually among cells that form linings. Cell membranes fuse together.
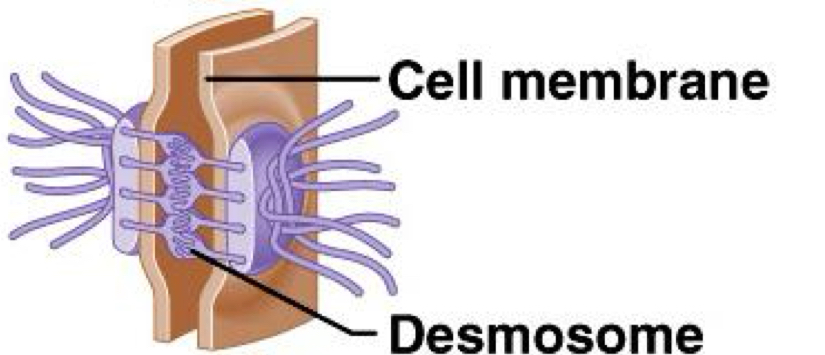
Desmosomes
Form ‘spot welds’ between cells; located among outer skin cells
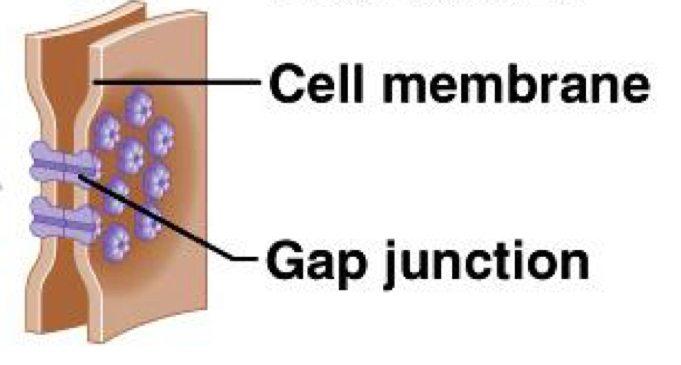
Gap Junctions
Tubular channels between cells; located in cardiac muscles cells. Allows materials to pass between neighboring cells.
Simple Diffusion
Movement of substances from regions of higher concentration to regions of lower concentration
Facilitated Diffusion
Diffusion across a membrane with the help of a channel or carrier molecule. Larger molecules.
Osmosis
Movement of water through a selectively permeable membrane from regions of higher concentration to regions of lower concentration. Water moves toward a higher concentration of solutes.
Filtration
Smaller molecules are forced through porous membranes; hydrostatic pressure important in the body.
Active Transport
Carrier molecules (act as doorways) transport substances across a membrane from regions of lower concentration to regions of higher concentration. Goes against the concentration gradient.
Endocytosis
Cell engulfs a substance by forming a vesicle around the substance. Three types: pinocytosis, phagocytosis, and receptor-mediated endocytosis.
Exocytosis
Reverse of endocytosis; substances in a vesicle fuse with cell membrane and contents released outside the cell.
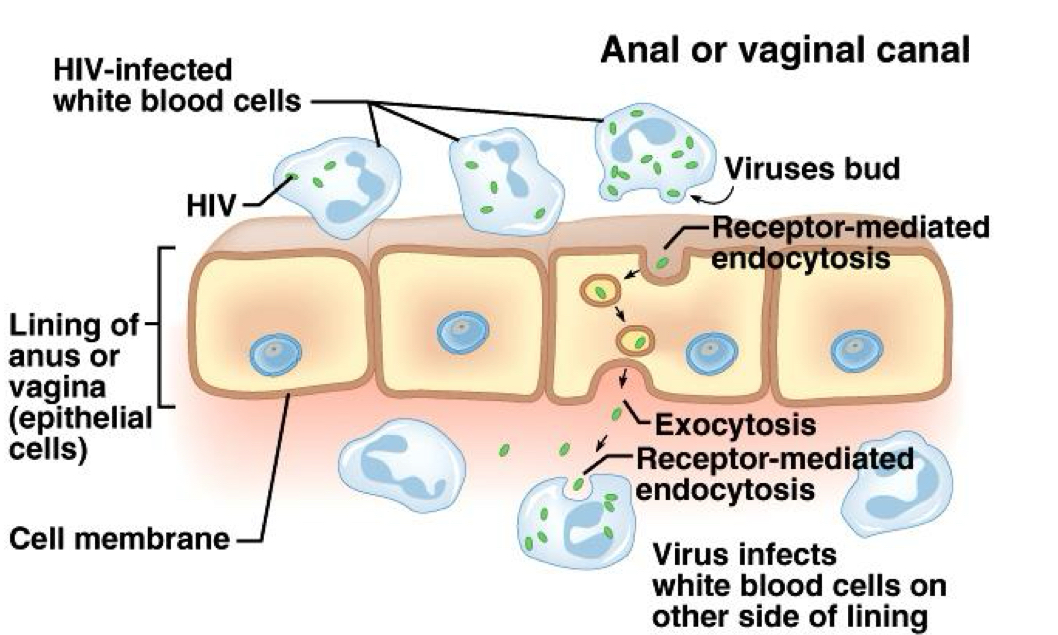
Transcytosis
Endocytosis followed by exocytosis; transports a substance rapidly through a cell.
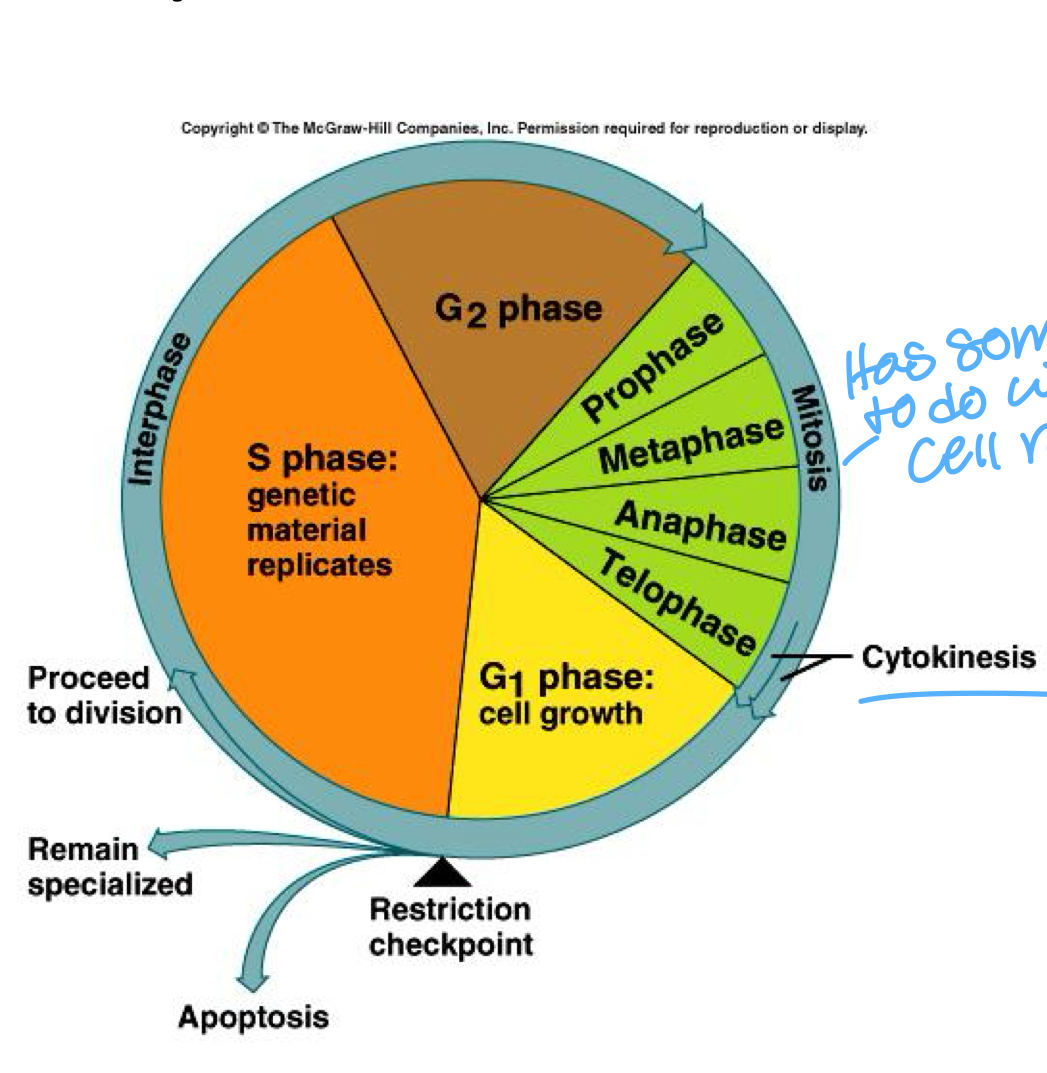
Cell Cycle
Series of changes a cell undergoes from the time it forms until the time it divides involving stages such as interphase (longest stage), mitosis, and cytoplasmic division (shortest stage).
Interphase
Very active period. Cell grows, maintains routine functions, cell replicates genetic material to prepare for nuclear division. Cell synthesizes new organelles to prepare for cytoplasmic division. Phases: G phase and S phase
Mitosis
produces two daughter cells from an original somatic cell; nucleus divides – karyokinesis; cytoplasm divides – cytokinesis. Phases: Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Cytoplasmic Division
Also known as cytokinesis. Begins during anaphase continues through telophase. Contractile ring pinches cytoplasm in half.
Stem cell
Can divide to form two new stem cells; self-renewal; can divide to form a stem cell and a progenitor cell. Totipotent- can give rise to every cell type. Pluripotent- can give rise to a restricted number of cell types.
Progenitor cell
Committed cell; can divide to become any of a restricted number of cells; pluripotent