Derm E2: hypersensitivity/autoimmune/rheum etc
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
What is urticaria (hives)?
edema w/in cutaneous vascular plexus of papillary body
caused by: insect bites, stings, meds, foods, infx
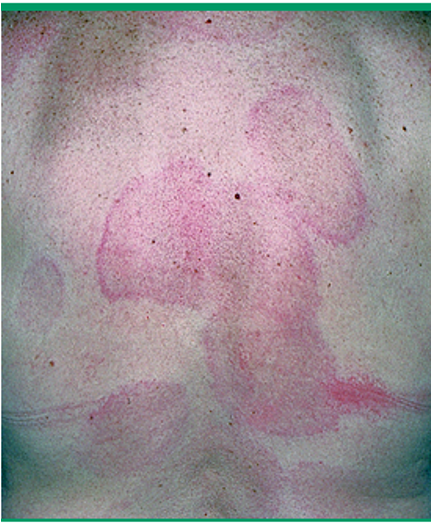
what are clinical features of urticaria?
transient pruritic edematous papules and plaques
superficial and well defined
can be assoc. w/ angioedema
location: face, lips, trunk, extremities
acute: < 6 wks, IgE dependent
chronic: > 6 wks
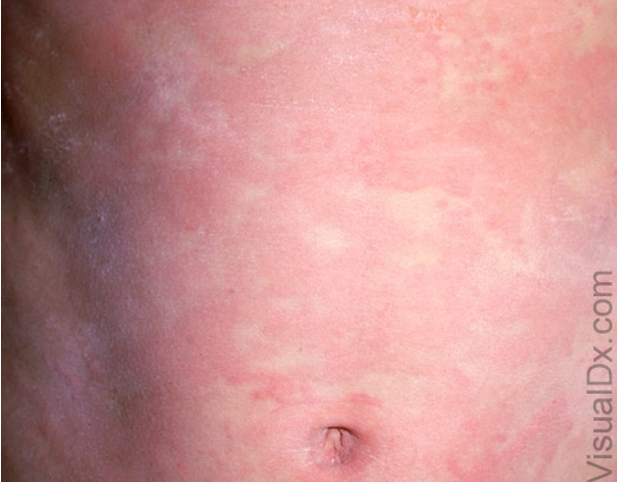
What are risk factors for urticaria?
atopy
What is the pathophysiology of urticaria?
mast cell degranulation → release immune mediators (histamine, prostaglandins, leukotrienes, cytokines, chemokines)
induce vasodilation and inc permeability of vessels → dermal edema
what type of hypersensitivity is acute urticaria?
type 1; IgE mediated
what type of hypersensitivity is chronic urticaria?
type 2-4
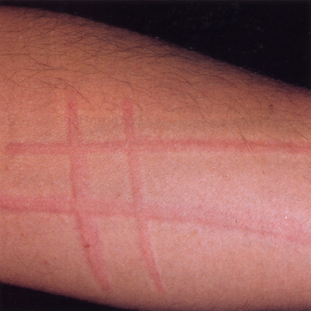
what is dermographism / urticaria factitia?
linear urticarial lesions after stroking/scratching skin; < 30 min
what is cold urticaria?
lesions confined to sites exposed to cold; special test- ice cube test
what is solar urticaria?
post solar exposure
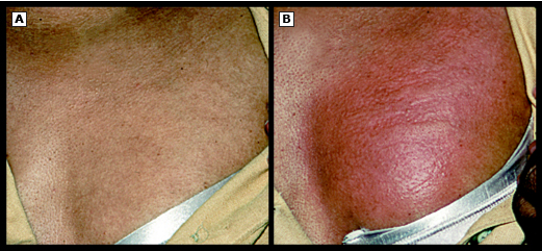
what is cholinergic urticaria?
exercise and sweating → small, papular, highly pruritic urticarial lesions; special test- treadmill test
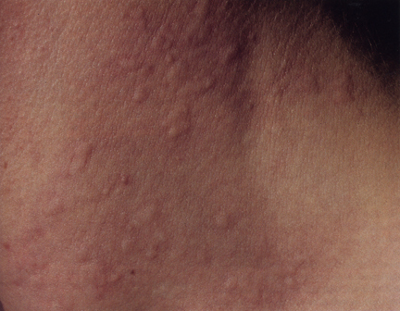
what is contact urticaria?
contact with water → eruption similar to cholinergic urticaria
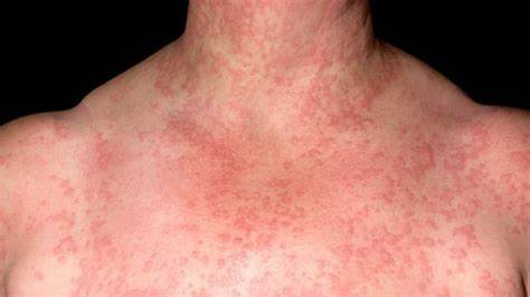
What are autoimmune dz that urticaria is assoc. w/?
SLE, sjogrens dz, thyroid disorders, RA, DMT1
lesions persist for 12-24 hrs
what is urticarial vasculitis?
2 elements: urticaria (> 24 hrs) and histopathology confirming leukocytoclastic vasculitis of small vessels
assoc. w/ hypocomplementemia
what is tx for urticaria?
H1 receptors
1st gen: hydroxyzine (atarax), diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
2nd gen: loratadine (Claritin), cetirizine (zyrtec), fexofenadine (allegra) *less sedating
oral glucocorticoids- i.e prednisone
what is angioedema?
acute, self limited, localized SC or submucosal swelling, which results from extravasation of fluid into interstitial tissues
location: face, lips, larynx, bowel, genitalia
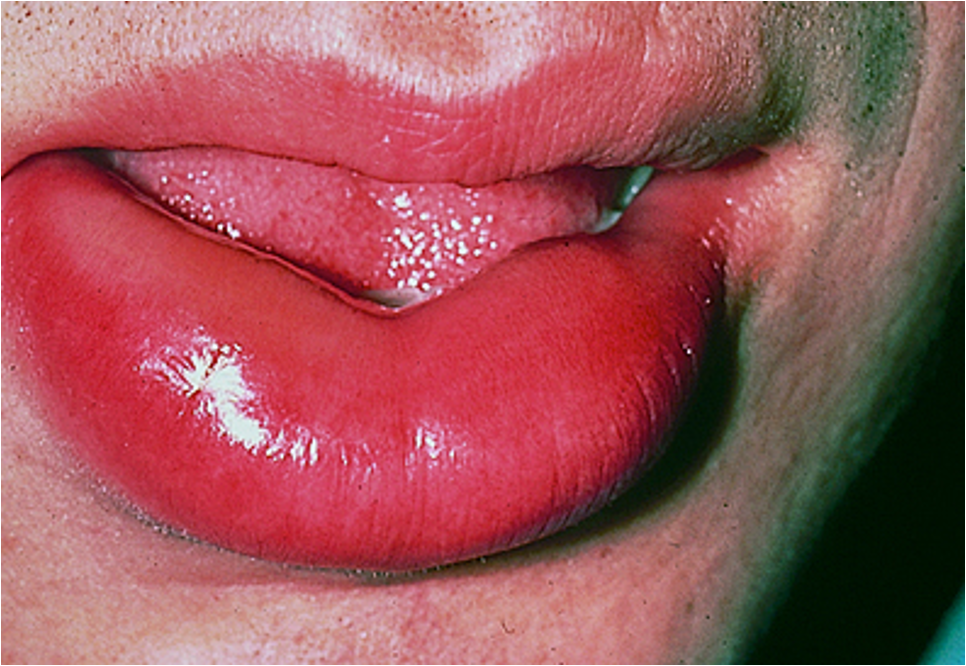
what are clinical features of angioedema?
large edematous area ± pruritus
deep and ill defined areas
occurs w/in hrs and resolves w/in 1-3 days
pressure: delayed, painful, erythematous swelling induced by sustained pressure
vibratory: caused by vibrating stimulus
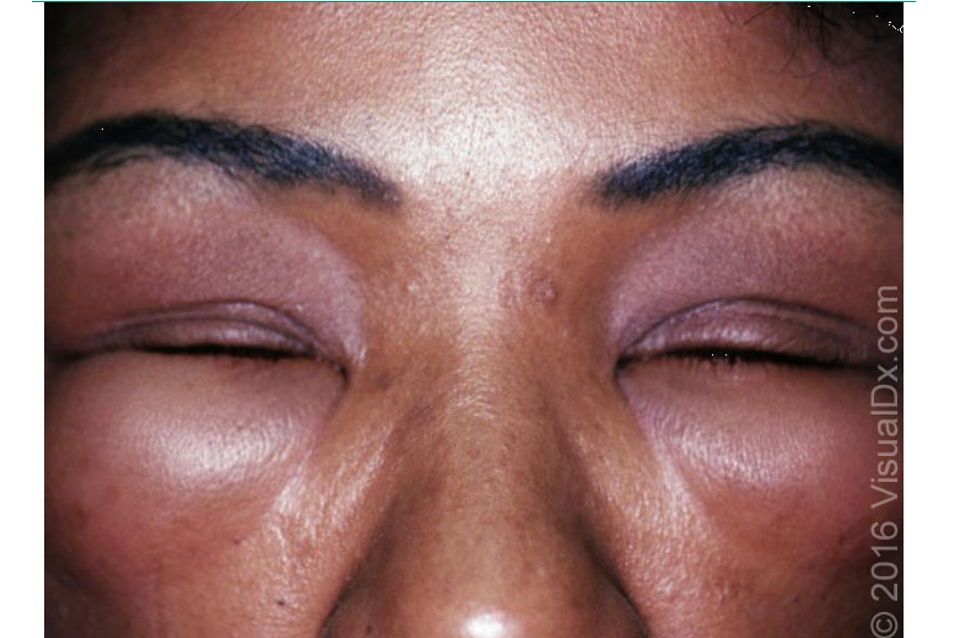
what are classifications of angioedema?
histaminergic (allergic): assoc. w/ anaphylaxis
non-histaminergic: can present w/ urticaria
drug induced: ACE inhibitors
C1 inhibitor deficiency: autosomal dominant hereditary; affects face, extremities, laryngeal edema, angioedema of bowel
idiopathic
what is the pathophysiology of angioedema?
mast cell mediated: release of mast cells derived mediators that inc vascular permeability
assoc. w/ pruritus and urticaria
begins w/in mins and resolves over 24-48 hrs
bradykinin mediated: overproduction or inhibition of bradykinin degradation resulting in vascular permeability and vasodilation
pruritus and urticaria are absent
frequently involves GI muse → bowel wall edema
develops over 24-36 hrs and resolves over 2-4 days
what is tx of angioedema?
evaluate in ER
w/ airway involvement → protect airway
w/ anaphylaxis → epi IM or IV, IVFs, oxygen
allergic → antihistamines and glucocorticoids are mainstay, ex- methylprednisolone (solumedrol) 600-80mg IV bolus
What is behcet syndrome?
rare vasculitis characterized by recurrent aphthous ulcers of mouth, eyes, skin, GI dz, CNS involvement, and arthritis
exact cause unknown, linked to genetics and infectious exposure
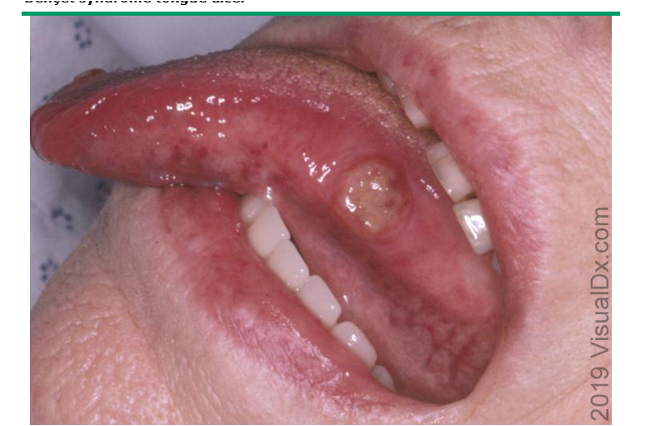
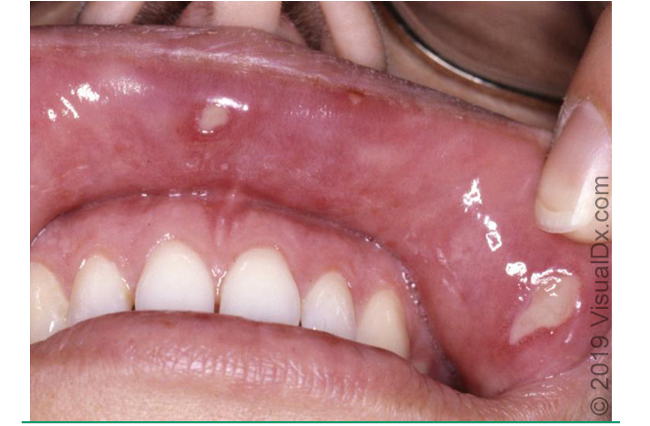
what are clinical features of behcet syndrome?
recurrent, mucocutaneous aphthous ulcers
genital ulcers- found ons scrotum In men and vulva in women
cutaneous lesions- acneiform, papulovesicular eruptions, nodules, thrombophlebitis, palpable purpura
location: mouth, genital, ocular, GI, CNS, vascular, arthritis
what are risk factors for behcet syndrome?
M > F
what are complications of behcet syndrome?
pulmonary artery aneurysms
CNS dz
vasculitis including all arteries and veins
ocular dz → uveitis → blindness
How do you dx behcet syndrome?
clinical; recurrent oral aphthae atleast 3x in 1 yr) plus 2 of the following
recurrent genital aphthae (aphthous ulceration or scarring)
eye lesions (including anterior/posterior uveitis
skin lesions
positive pathergy test
what is tx for behcet syndrome?
aphthous and genital ulcers: 1st line→ TCS ± topical sucralfate
recurrent ulcers: colchicine 1-2mg/day divided BID
refractory lesions: prednisone or azathioprine
what is dermatomyositis?
idiopathic inflammatory myopathy that commonly presents w/ progressive, symmetric, proximal muscle weakness and a group of cutaneous findings
unknown cause
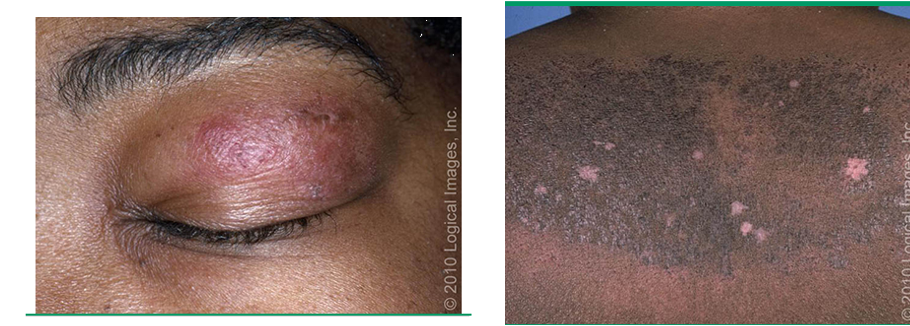
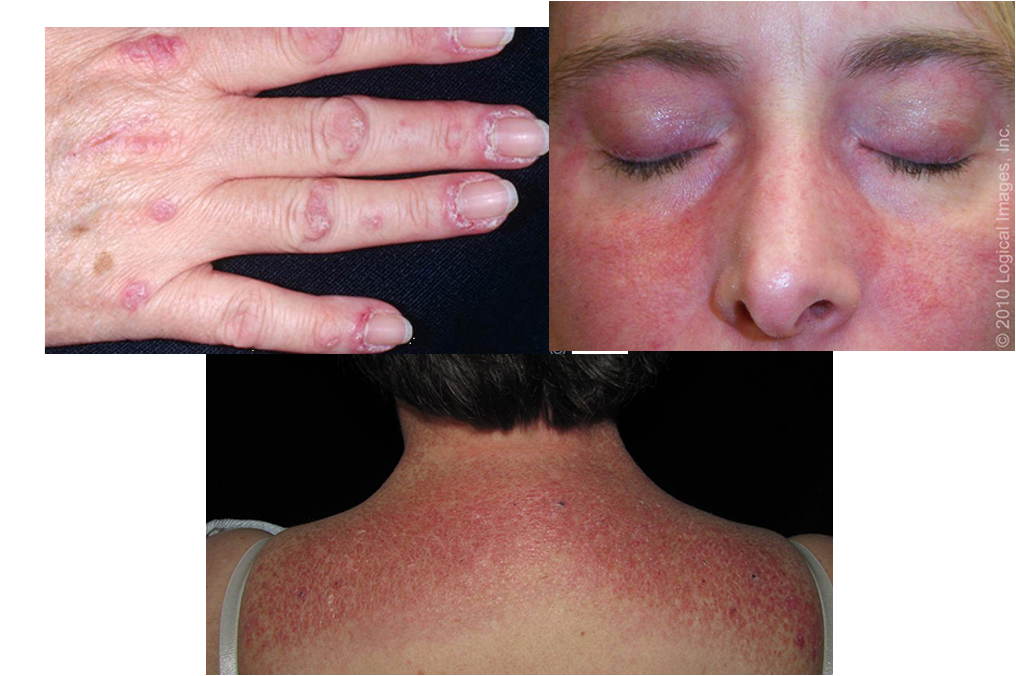
what are clinical features of dermatomyositis?
progressive, symmetric proximal muscle weakness
gottrons papules: pink violaceous papules overlying interphalangeal and metacarpophalangeal joints
heliotrope eruption: pink violaceous erythema, ± edema, involving periorbital skin
shawl sign: confluent, violaceous erythema on posterior neck, upper back, and shoulders
rash is photosensitive
what is the pathophysiology of dermatomyositis?
thought to be result of humoral mediated attack against muscle capillaries and arteriole endothelium
hypoxic injury to muscle fibers ensues, leading to atrophy of muscle fibers
what are risk factors of dermatomyositis?
age < 55, genetics, viral exposure (coxsackie, parvovirus, HIV), meds
how do you dx dermatomyositis?
skin bx: vacuolar changes of basal layer, inc lymphocytic infiltrate, and inc mucin deposition in dermis
muscle bx: perivascular inflammatory infiltrate, atrophy of muscle fibers in perifascicular region, IG and complement deposits on intramuscular blood vessels
creatine kinase
aldolase levels
LDH
ANA, anti-mi-2, anti-jo antibodies
what is 1st line tx for dermatomyositis?
systemic glucocorticoids (ie prednisone) ± DMARD (ie MTX)
alt for skin dz: hydroxychloroquine plus MTX
what is 2nd line tx of dermatomyositis?
rituximab, mycophenolate, IVIG
what is patient education for dermatomyositis?
educate on using SPF
for pruritus→ antihistamines, TCS, or calcineurin inhibitors
all pts should have screening CXR to eval for interstitial lung dz
maintain high protein diet and physical exercise to inc muscle strength
what is cutaneous lupus erythematous?
chronic autoimmune dz that encompasses a wide range of dermatologic manifestations and may or may not be assoc. w/ systemic dz
what are the 3 subsets of cutaneous lupus erythematous?
acute (ACLE): transient erythematous patches
subacute (SCLE): small erythematous scaly papules
chronic (CCLE): subtypes discoid (DLE) and lupus panniculitis
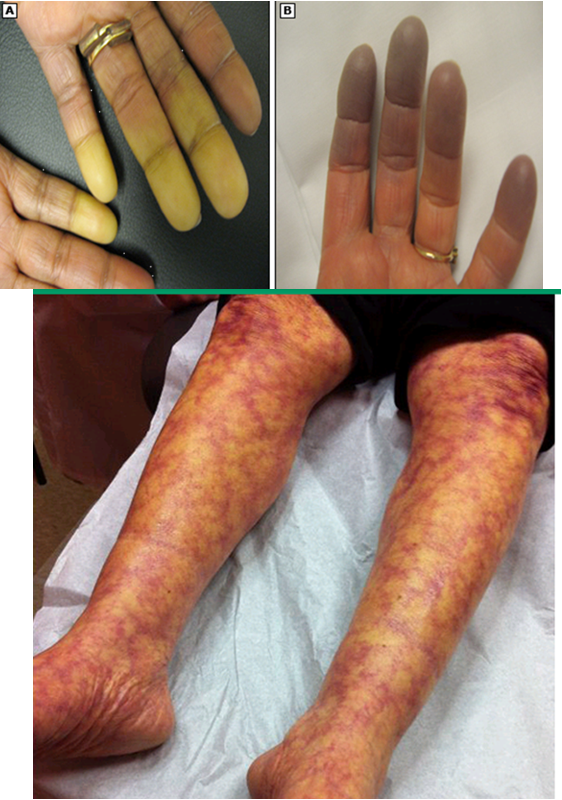
what are vascular manifestations of CLE?
periungual erythema: dilated tortuous loops of caps and prominent sub cap venous plexus along base of nail
livedo reticularis: reddish-cyanotic, reticular pattern on skin- arms, legs, torso (exacerbated by cold temps)
Raynaud phenomenon: vasospastic process of fingers/toes → blanching
vasculitis: urticarial vasculitis → painful petechial or purpura that may heal w/ hyperpigmentation
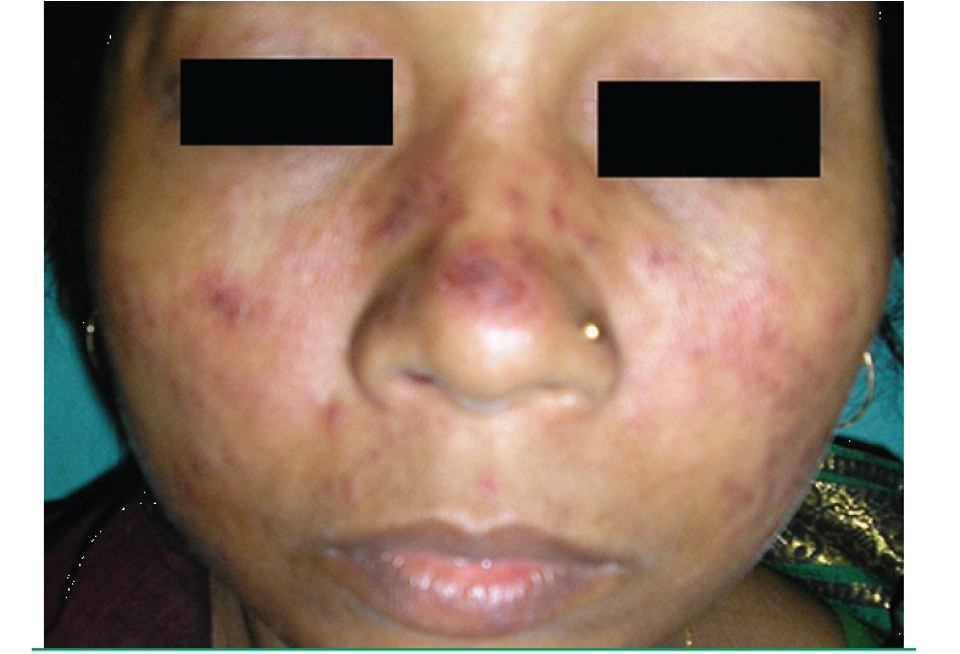
what is acute cutaneous lupus erythematous (ACLE)?
malar or butterfly rash: erythema along cheeks and bridge of nose; spares nasolabial folds; may last hrs-wks; exacerbated by sun exposure
morbilliform rash: erythematous maculopapular eruption on sun exposed areas
histology: apoptotic keratinocytes, vascuolization of basal cell layer; lymphohistiocytic infiltrate in superficial dermis and dermic mucin deposition
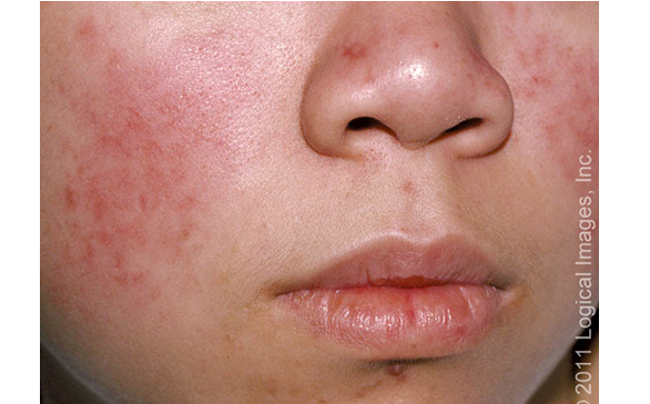
What is subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosis (SCLE)?
small, erythematous, slightly scaly papules that evolve into either psoriasiform or annular plaques
location: shoulders, forearms, neck, upper torso
risk: sun exposure, drug induced (anticonvulsants, ACEI, BBs, immune modulators)
histology: superficial perivascular and appendageal lymphocytic infiltration; vascuolization of basement membrane and mucin deposition in dermis
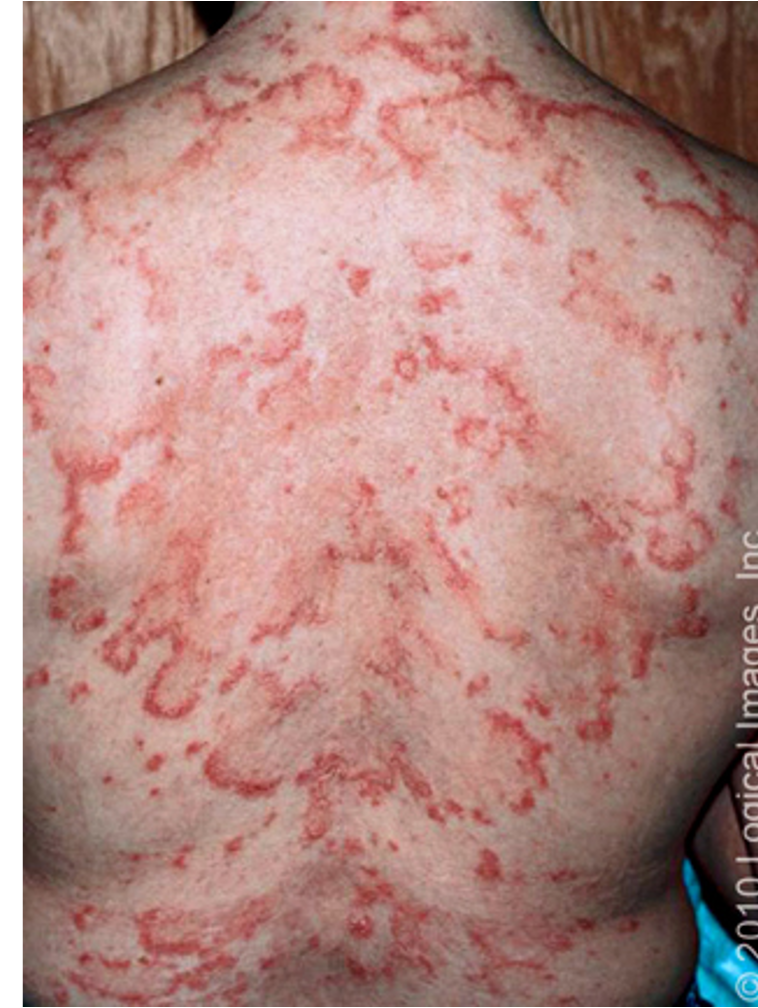
what is the MC type of CCLE?
discoid lupus
what is chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CCLE?)
discrete, erythematous, indurated plaques covered by well-formed adherent scale that extends into dilated hair follicles
plaques heal leaving depressed central scars, atrophy, telangiectasis, and hyper or hypopigmentation
location: face, neck, scalp, ears, upper torso
histology: hyperkeratosis, follicular plugging, basal layer vacuole changes and mononuclear cell infiltrate at DEJ
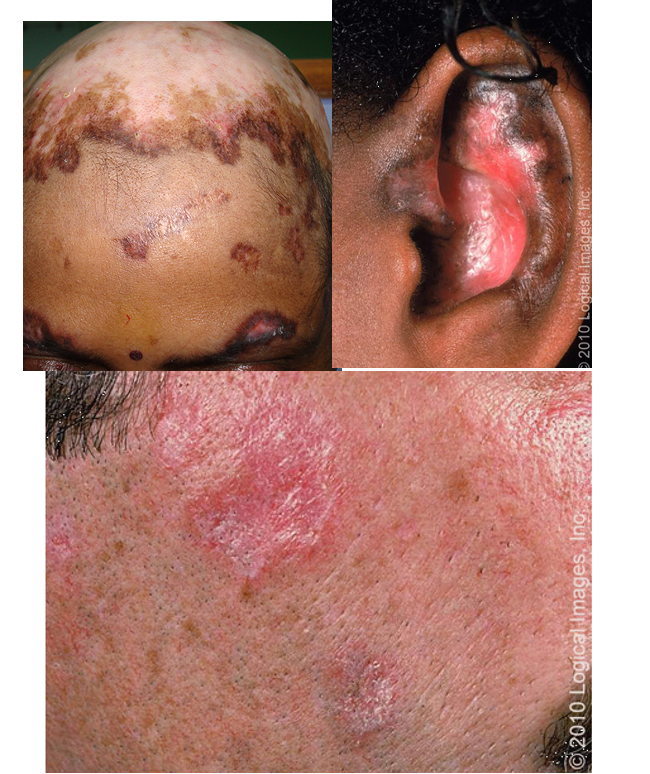
what is lupus panniculitis / lupus profundus?
presents as painful indurates plaques or firm SC nodules
upon resolution → SC atrophy and scarring
location: scalp, face, upper arms, chest, breasts, lower back, flank, upper thighs, or buttocks
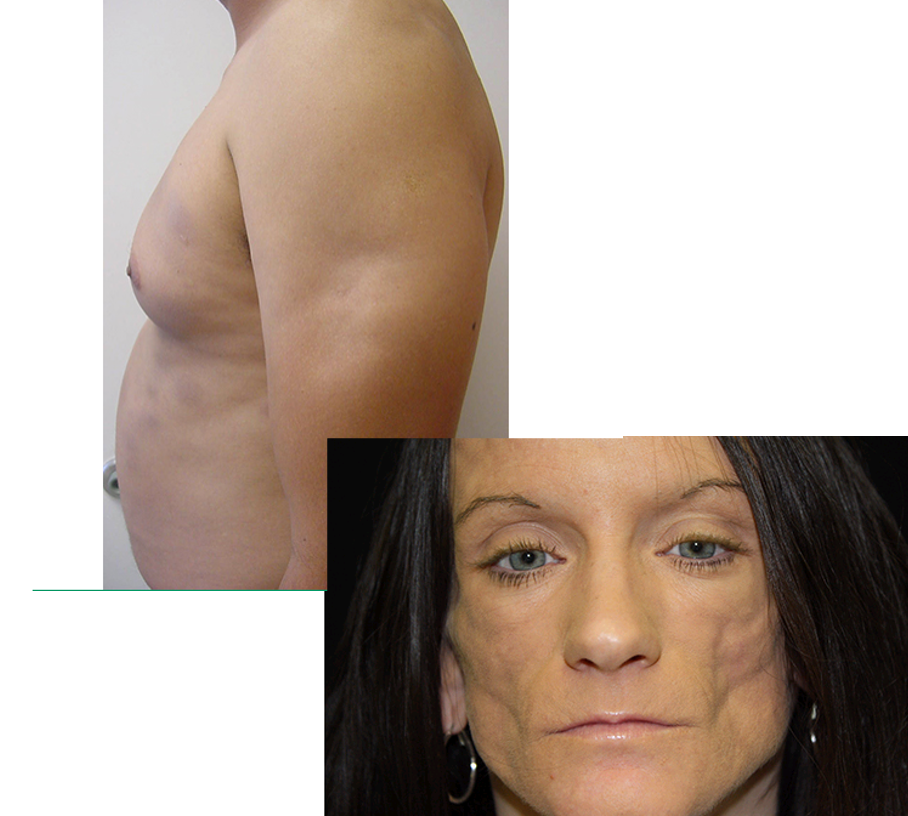
what are risk factors for CLE?
African American; F > M
how do you dx CLE?
biopsy, labs, ANA postive (>95%)
what is 1st line tx for CLE?
photoprotection: broad spectrum sunscreen
topical vs intralesional vs oral corticosteroids
refractory: oral antimalarials (hydroxycloroquine or chloroquine)
what is 2nd line tx for CLE?
glucocorticoid-sparing DMARDs→ MTX
what is scleroderma?
hallmark feature of systemic sclerosis; widespread vascular dysfunction and progressive fibrosis of skin and internal organs
what are clinical features of scleroderma?
pruritus and edema in early stages
skin hyperpigmentation or depigmentation
dry skin, skin thickening/hardening
Raynaud phenomenon
painful ulcerations at DIP/PIP ; “rat bite necrosis”
sclerodactyly w/ tapering of fingers→ loss of distal phalanges
loss of sweat glands, anhidrosis
calcinosis cutis
early face changes→ periorbital edema
late face changes → edema and fibrosis result in loss of normal facial line, mask like thinning of lips, beak like sharp nose
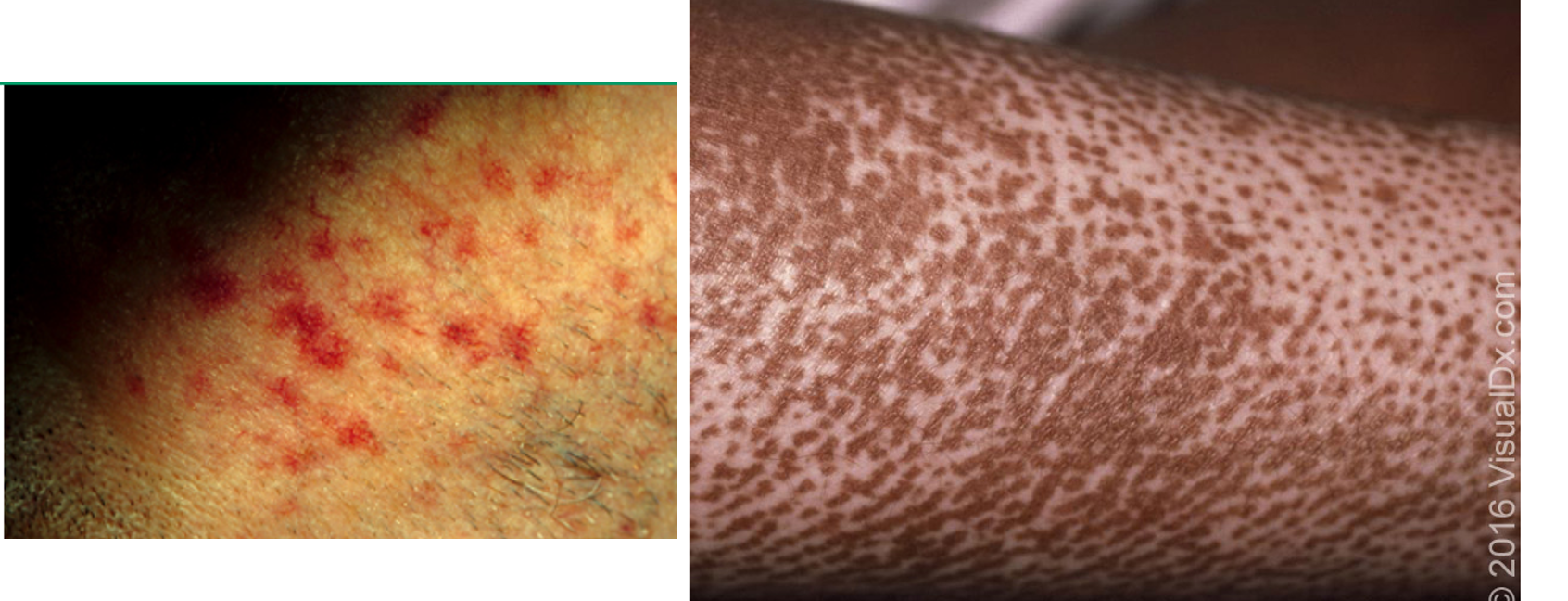
how do you dx scleroderma?
ANA- pos
anticentromere abs (ACA)
anti-Scl-70 abs
extremity plain films- may demonstrate calcinosis
what is tx for scleroderma?
1st line: MTX
refractory: IVIG or Rituximab (Rituxan)
what is the mnemonic for scleroderma associated syndrome?
CREST syndrome
Calcinosis cutis- fingertips, elbows, trochanteric regins
Raynaud phenomenon
Esophageal dysfunction- dysphagia, diminished peristalsis, reflux esophagitis
Sclerodactyly
Telangiectasia- face, upper trunk, handsw
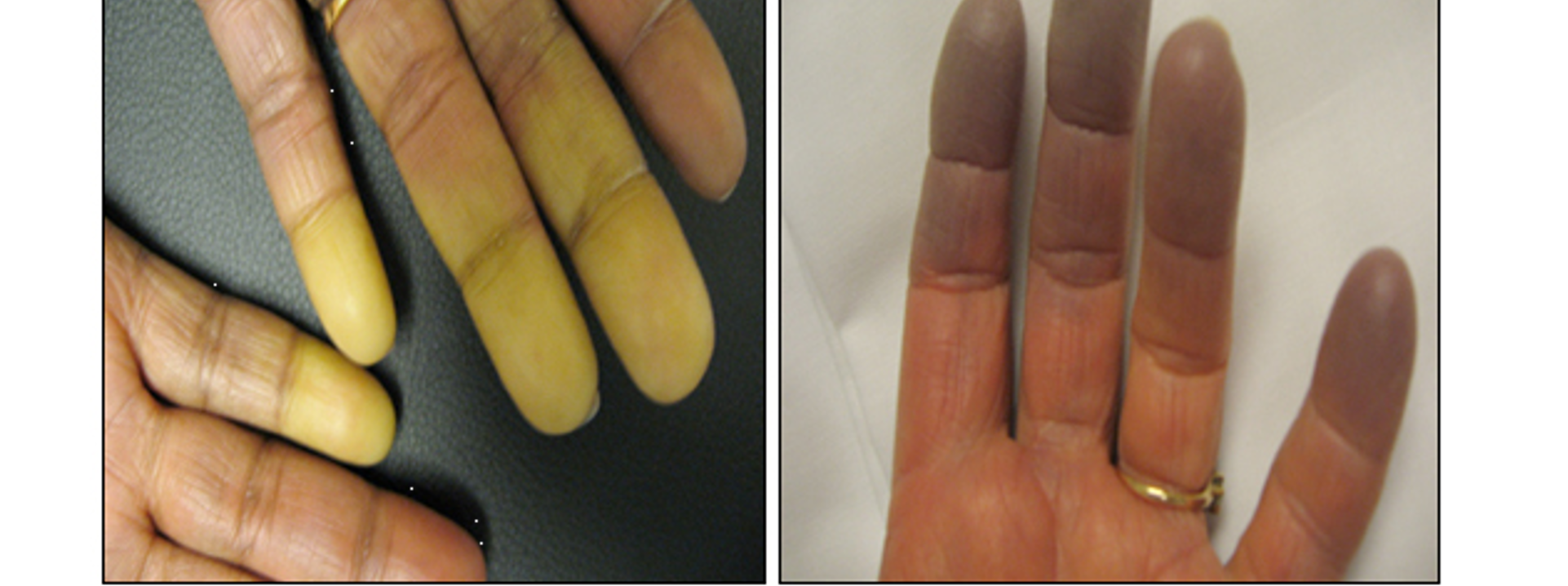
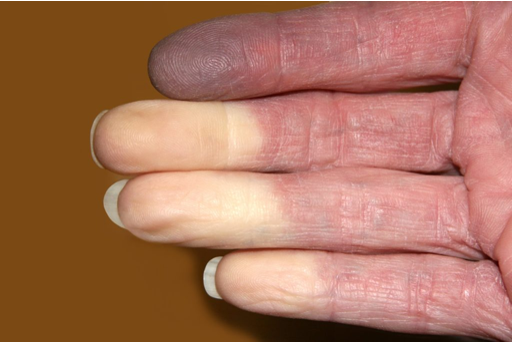
what is Raynaud phenomenon?
exaggerated vascular response to cold temps or emotional stress
what are the subtypes of Raynaud phenomenon?
primary RP: exaggeration of vasoconstriction to cold temp w/o underlying dz; 15-30 y/o and MC in females
secondary RP: vasoconstriction occurs due to underlying dz
what are clinical features of Raynaud phenomenon?
digital color changes
white pallor- vasoconstriction
blue- tissue hypoxia
red- reperfusion after rewarming
numbness/pain
cold induced skin color changes
what are risk factors for RP?
F > M, cold temp, stress, smoking, underlying dz
what is nonpharmacologic management of RP?
smoking cessation, avoid cold exposure, hand warmers, avoid vasoconstrictive meds (pseudoephedrine, amphetamines, sumatriptan)
what is pharmacologic management for RP?
1st line: Ca channel blockers; Amlodipine, Nifedipine
2nd line: PDE5I or topical nitrate; sildenafil PO or nitroglycerin 2% cream
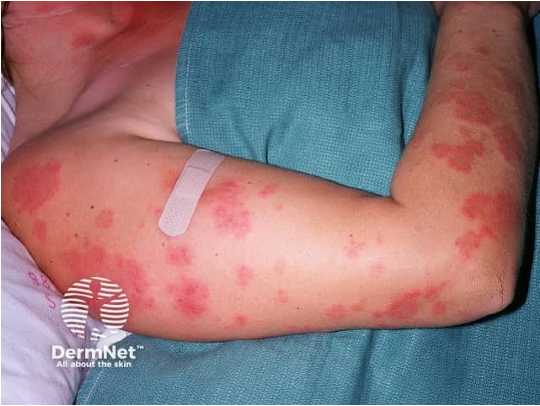
what is IGA vasculitis / henoch schoenlein purpura?
acute IgA mediated vasculitis involving small vessels of skin, GI tract, kidneys, joints, and rarely lungs and CNS
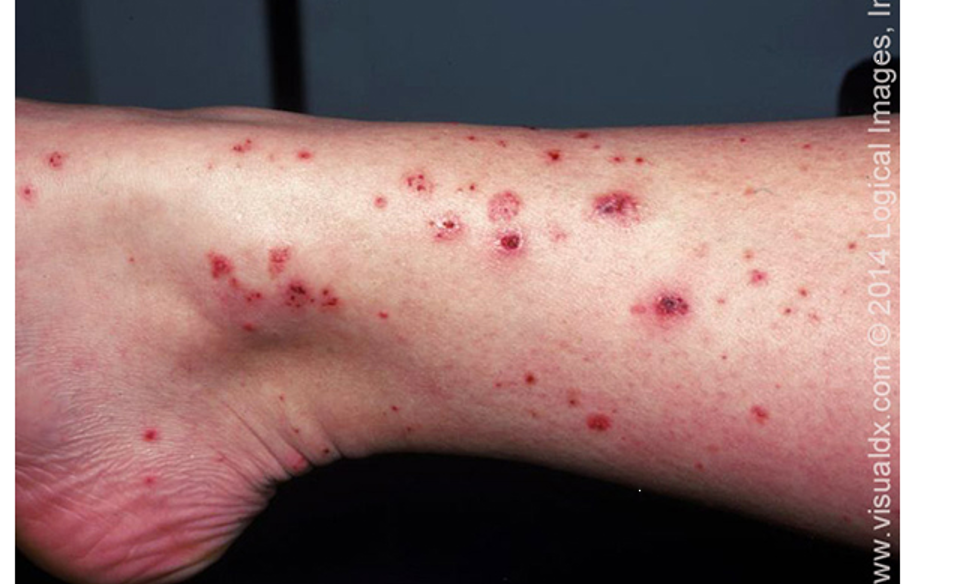
what are clinical features of IgA vasculitis / HSP?
palpable purpura in pts w/ neither thrombocytopenia nor coagulopathy
can be pruritic, rarely painful
rash begins as erythematous macular or urticarial wheals and progresses to petechia and palpable purpura
arthritis/arthralgia
abd pain- can be assoc. w/ GI bleeding
renal dz
location- lower extrem, lesions appear symmetrical in crops
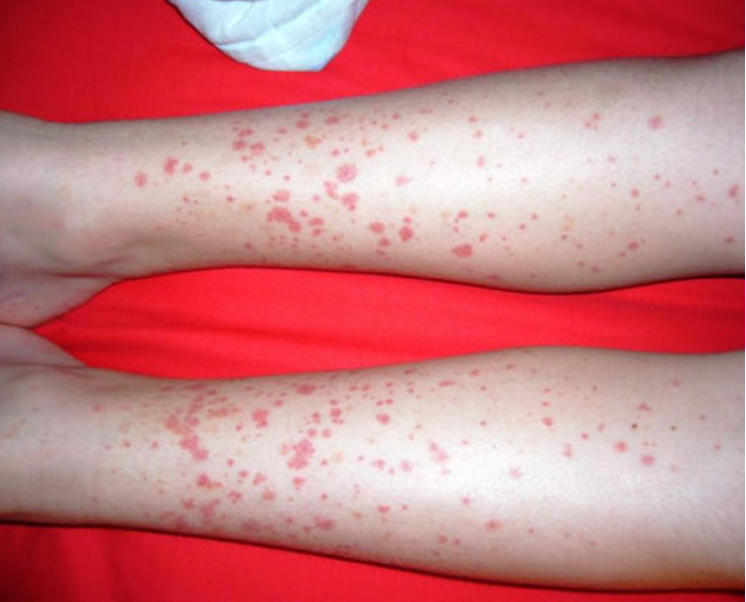
what are risk factors for HSP?
age bt 4-7; infx- s. pyogenes
how do you dx HSP?
labs: CBC, CMP, PT/INR, PTT
skin bx: pathognomic finding- leukocytoclastic vasculitis in post capillary venues w/ IgA deposition
What is tx for HSP?
majority recover spontaneously
supportive- pain control (acetaminophen and NSAIDs)
hospitalization if severe dehydration, GI bleeding, mental status change, elevated BUN/cr
what is polyarteritis nodosa?
systemic necrotizing vasculitis that typically affects medium sized muscular arteries, w/ additional involvement of small arteries
cause- idiopathic
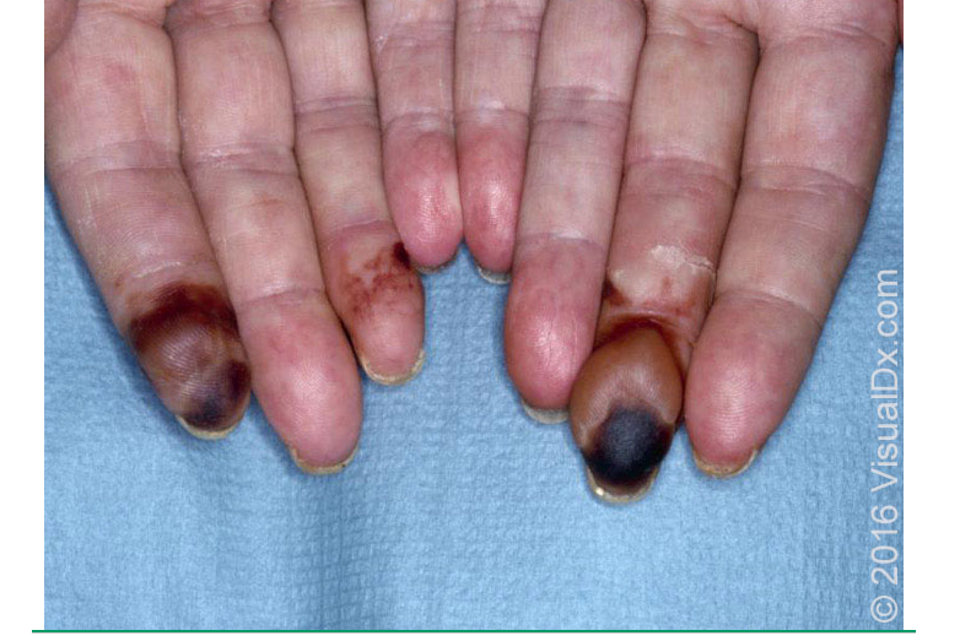
what are clinical features of polyarteritis nodosa?
assoc. w/ constitutional sx- fever, fatigue, malaise, arthralgias, loss of appetite
skin lesions- purpura, livedo reticularis, painful nodules, ulcers follow ischemia of nodules
location: lower legs, thighs, arms, trunk, head, neck, buttocks
risk: male and age
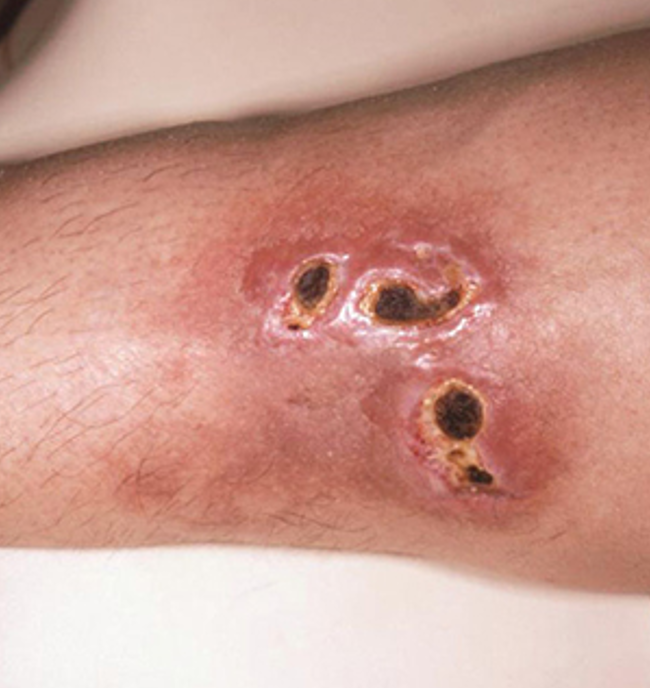
how do you dx polyarteritis nodosa?
ANCA, ANA, complement proteins, skin bx
what is tx for polyarteritis nodosa?
mild: prednisone
moderate-severe: combo therapy- azathioprine or MTX
what is Kawasaki dz?
self limiting vasculitis of childhood
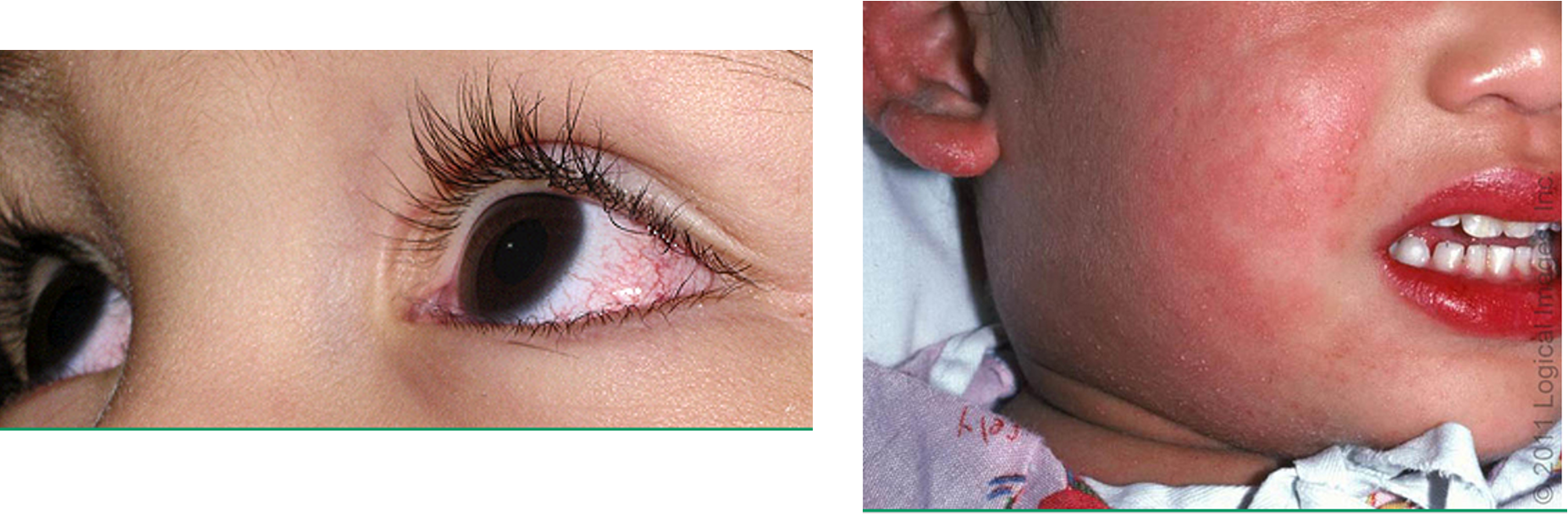
what are clinical features of Kawasaki dz?
fever
cutaneous/mucosal erythema and edema w/ subsequent desquamation
bilateral non exudative conjunctivitis
polymorphous exanthem
cervical LAD
cracked, cherry red lips and oropharyngeal erythema
erythema of palms/soles
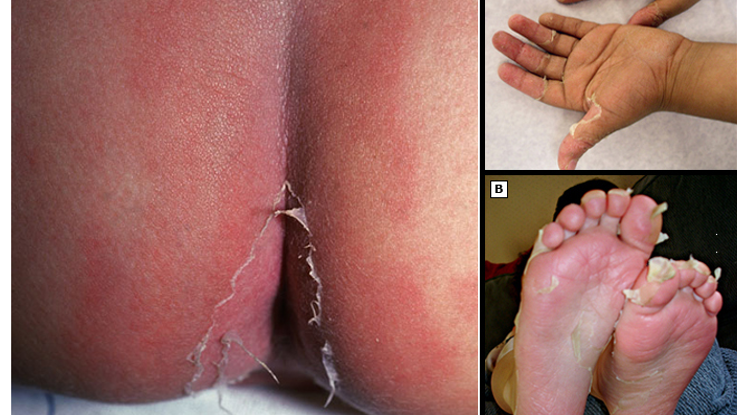
what are risk factors for Kawasaki dz?
age- 2.5 y/o***; winter/spring seasons
what are complications of Kawasaki dz?
coronary abnormalities → coronary artery aneurysm, myocarditis, arthritis, urethritis, aseptic meningitis
how do you dx Kawasaki dz?
presence of fever lasting atleast 5 days w/o explanation PLUS 4 out of the 5 following:
bilateral bulbar conjunctival injection
oral mucous membrane changes, including injected or fissured lips, injected pharynx, or strawberry tongue
peripheral extremity changes including erythema of palms/soles, edema of hands/feet (acute phase), and periungual desquamation (convalescent phase)
polymorphous rash
cervical LAD
what is the dx workup for Kawasaki dz?
LFTs- elevated
CBC- leukocytosis, thrombocytosis, anemia
ESR- elevated or normal
U/A- pyuria
echo- eval for coronary aneurysm
what is tx for Kawasaki dz?
IVIG 2g/kg infused over 8-12 hrs
ASA 30-50 mg/kg/daily divided every 6 hrs
what is sarcoidosis?
systemic granulomatous dz of unknown cause
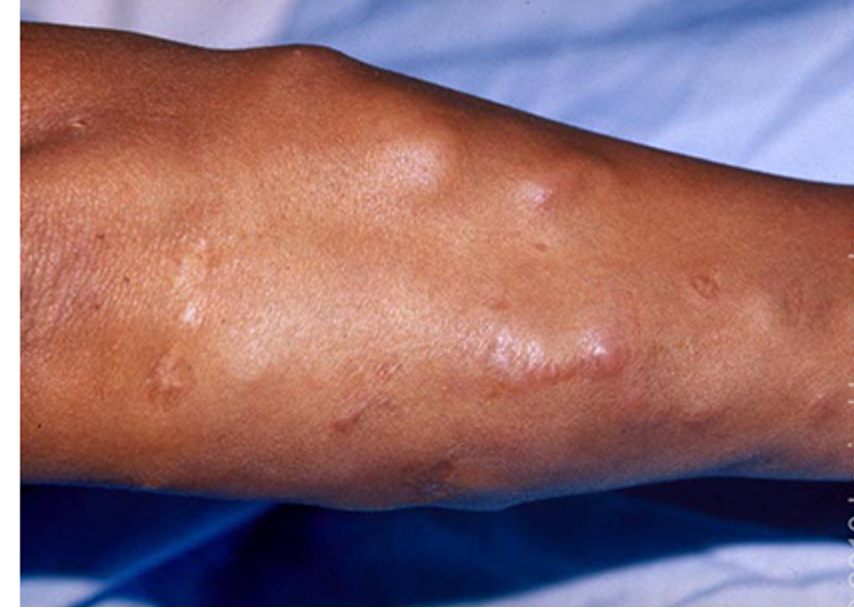
what are clinical features of subtypes of sarcoidosis?
papular: papules, translucent yellow-red w/ apple jelly appearance on diascopy
nodular: erythema nodosum
lupus pernio: diffuse, violaceous, soft doughy infiltrations on nose, cheeks, or earlobes
plaque: brown or purple infiltrated plaques- mainly on extremities, buttocks, and trunk
maculopapular: scattered maculopapular lesions yellow/brow/purple one ace and extremities
subcutaneous: erythematous, flesh colored, violaceous, or hyperpigmented nodules
what are risk factors for sarcoidosis?
African American
how do you dx sarcoidosis?
diascopy: apply jelly semi translucent yellowish brown color
skin or LN bx: noncaseating granuloma
what is tx for sarcoidosis?
localized: intralesional or topical steroids (class I-II)
systemic: oral glucocorticoids
refractory: MTX, hydroxycholorquine
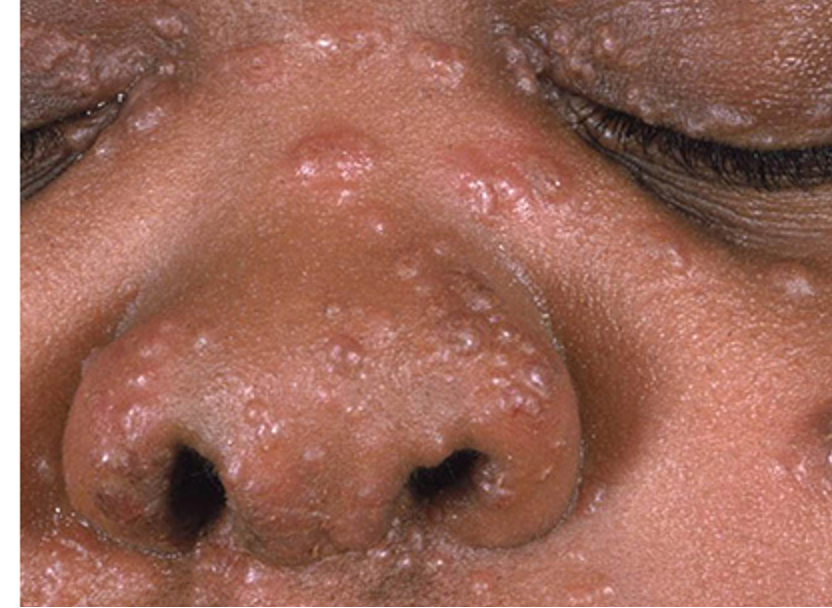
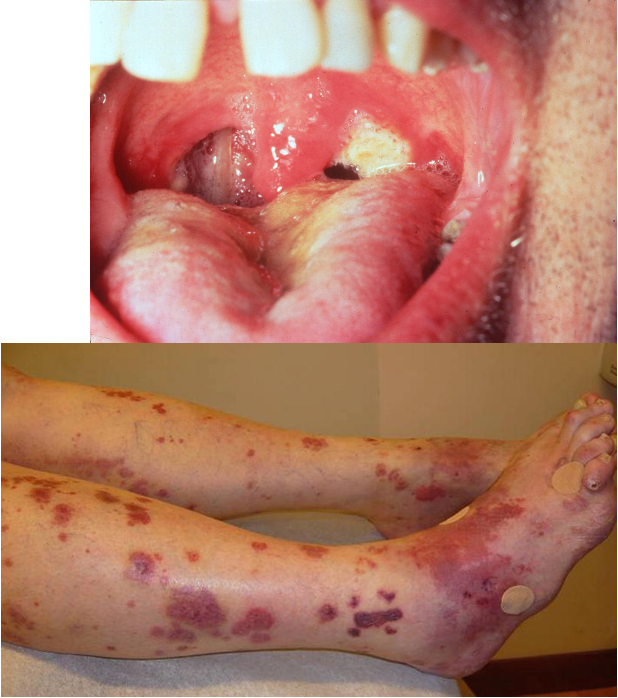
what is another name for granulomatosis w/ polyangiitis (GPA)?
wegener granulomatosis
what is GPA?
rare autoimmune necrotizing vasculitis affecting small sized arteries
unknown cause
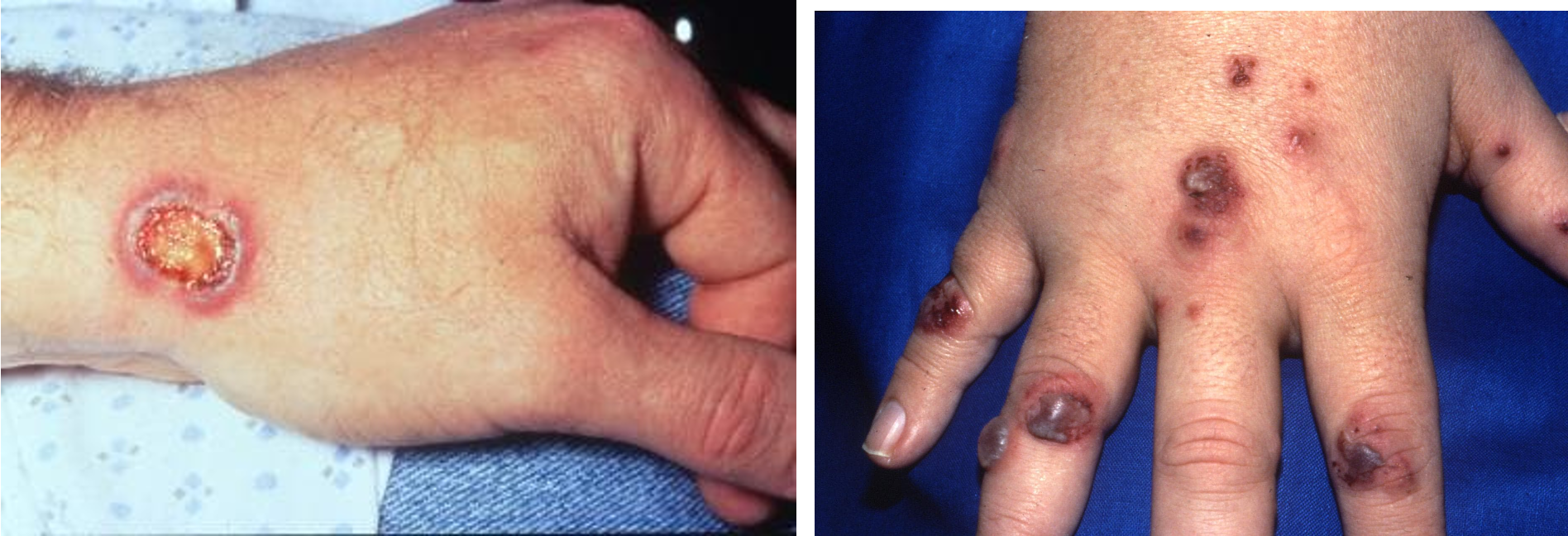
what are clinical features of GPA?
purpura w/ focal necrosis
oral/nasal ulcerations
skin ulcers
papules, vesicles, palpable purpura
triad:
necrotizing granuloma in upper resp. tract and lungs
vasculitis involving both arteries and veins
glomerulitis
location: lower limbs, face, trunk, upper extremities
what are complications of GPA?
renal failure, interstitial lung dz
How do you dx GPA?
CBC: anemia, leukocytosis, ± thrombocytosis
ESR elevated
impaired renal function
urine: RBC casts
antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoabs (ANCA), C3, C4, ANA
skin bx: necrotizing vasculitis of small arteries/vein w/ intra or extravascular granuloma formation
what is tx for GPA?
induction: cyclophosphamide or rituximab PLUS prednisone
maintenance: MTX or rituximab or azathioprine
prevention of opportunistic infx: trimethoprim (Bactrim) 160-800 mg 3x/weekly
what is bullous pemphigoid?
autoimmune chronic inflammatory sub epidermal blistering dz
cause: hypothesized destruction and inflammation caused by IG binding in epithelial basement membrane zone
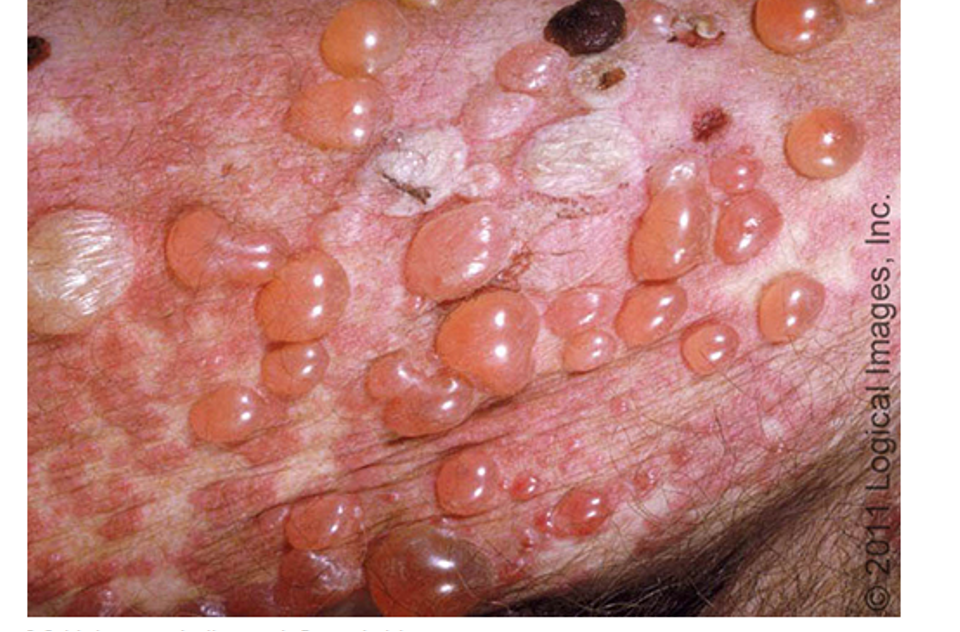
what are clinical features of bullous pemphigoid?
prodromal: wks/mos of pruritic eczematous papular or urticaria like skin lesions
1-3 cm bulla on erythematous, urticarial, noninflammatory base; blisters may be numerous and widespread
pruritus
location: trunk, extremity flexures, axillary/inguinal folds, oral mucosa, larynx, genital and anus
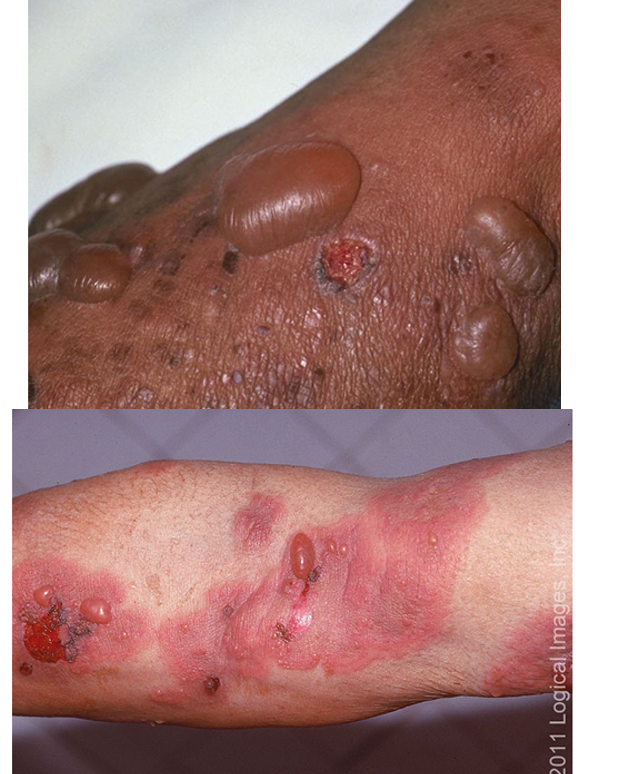
what are risk factors for bullous pemphigoid?
age > 60
how do you dx bullous pemphigoid?
clinical- should be suspected in pts > 60 w/ features of
blistering skind z
desquamative gingivitis or mucositis
unexplained pruritic urticarial plaques
skin bx- definitive
what is tx for bullous pemphigoid?
initial tx: one of the following
high potency TCS- clobetasol
oral glucocorticoids
doxycycline
refractory: biologics- ritximab (rituxan)
what is pemphigus vulgaris?
rare autoimmune dz characterized by painful blisters and erosions on skin and mucous membranes; MC bt ages 40-60
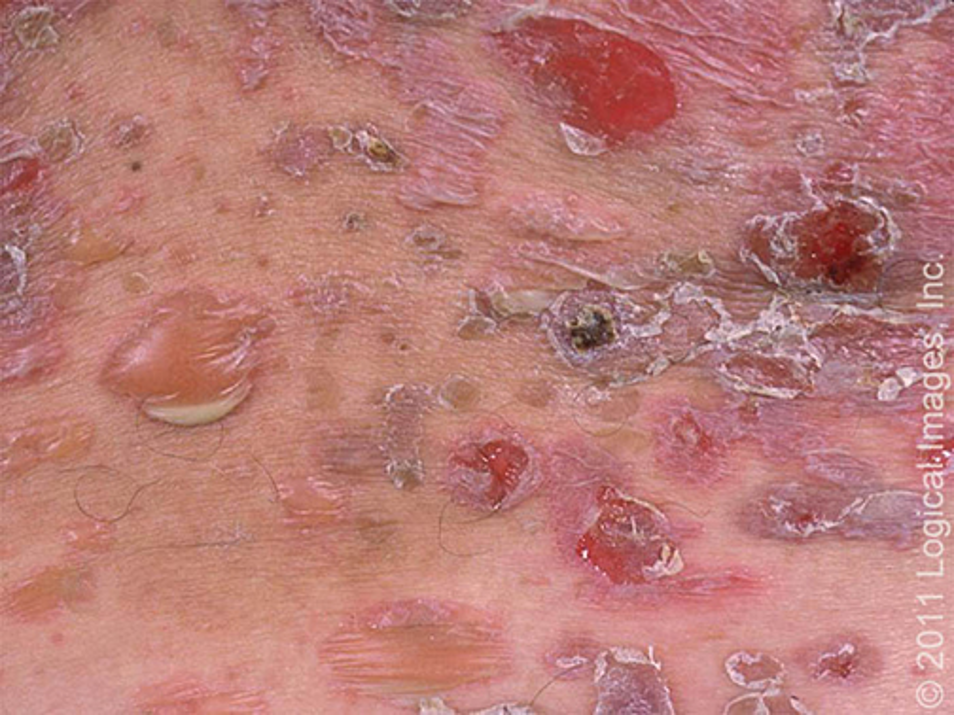
what are clinical features of pemphigus vulgaris?
intraoral blisters and erosions
cutaneous lesions- vesicles, erosions, bullae
pos nikolsky sign
heals w/o scarring
location: mouth (MC), genitalia, face, scalp, trunk, groin, axilla
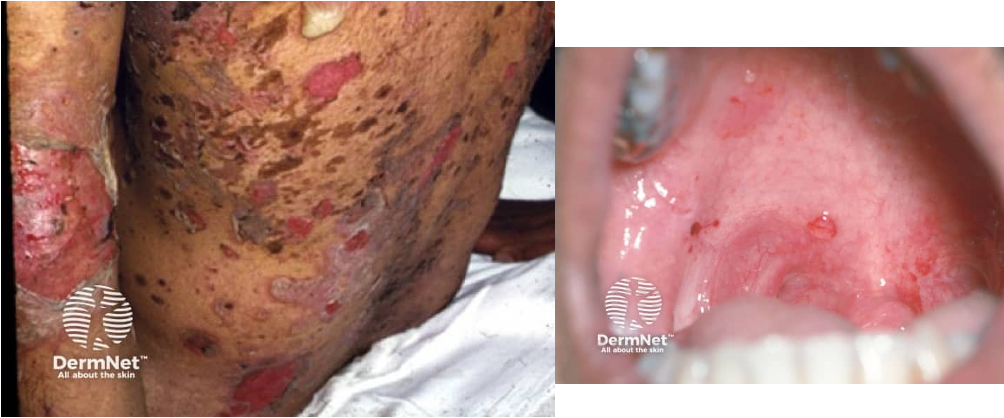
what is pathophysiology of pemphigus vulgaris?
autoantibodies against desmoglzins → disrupts keratinocyte adhesion causing separation → acantholysis
(desmogleins are glycoproteins that are required for cell-cell adhesion)
how do you dx pemphigus vulgaris?
skin bx- acantholytic cells above basal layer of epidermis
ELISA test- look for anti-desmoglein abs
what is tx for pemphigus vulgaris?
1st: systemic corticosteroids (prednisone); add rituximab in mod-severe cases
2nd: immunosuppressive drugs (azathioprine, MMF)
what is erythema nodosum?
delayed type hypersensitivity rxn that most often presents as erythematous, tender nodules on shins
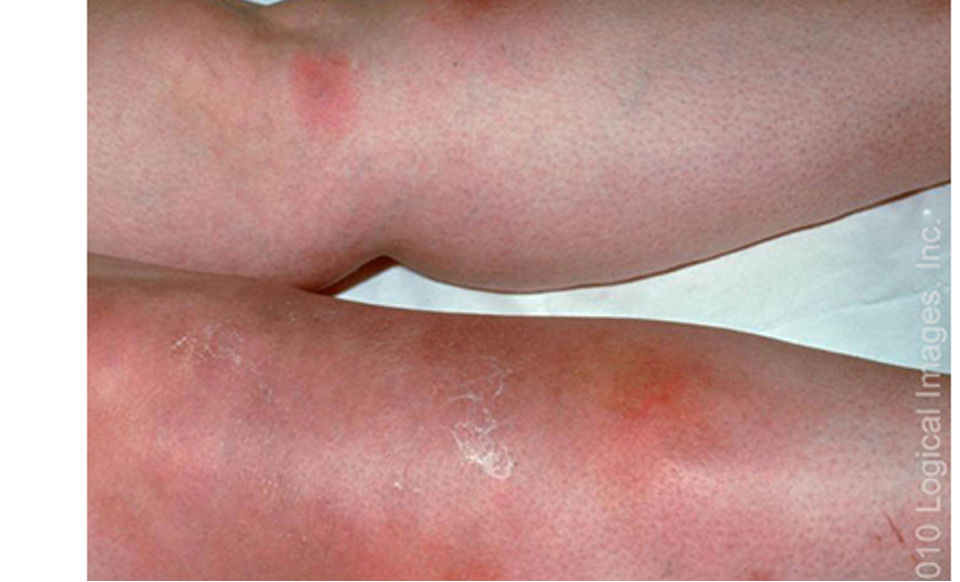
what are clinical features of erythema nodosum?
prodrome: fever, fatigue, malaise, arthralgias may precede nodules 1-3 wks
erythematous, tender, non ulcerated nodules 2-5 cm
location: shins, ankles, thighs, arms, buttocks, calves, face
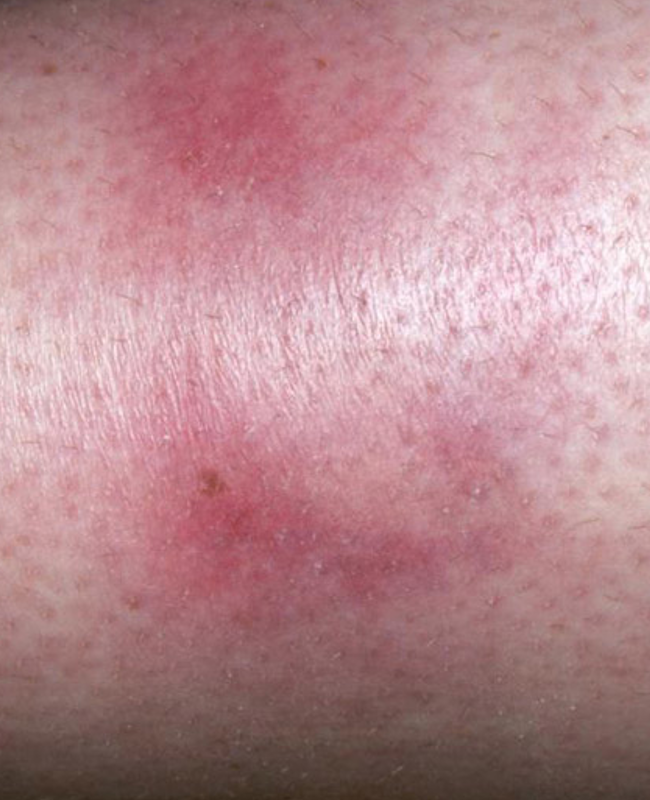
what are risk factors for erythema nodosum?
drugs, pregnancy malignancy, strep infx, inflammatory conditions (sarcoidosis, GI dz, IBD)
how do you dx erythema nodosum?
clinical; assess for underlying cause- CBC, ESR, ASO titer, CXR
what is tx for erythema nodosum?
mild: elevate legs, rest, compression
moderate: NSAID- ibuprofen, naproxen
severe: oral glucocorticoid- prednisone, intralesional steroid injection
what is neurofibromatosis?
multi system genetic disorder most notably characterized by cafe au lait spots and neurofibromas
autosomal dominant inheritance
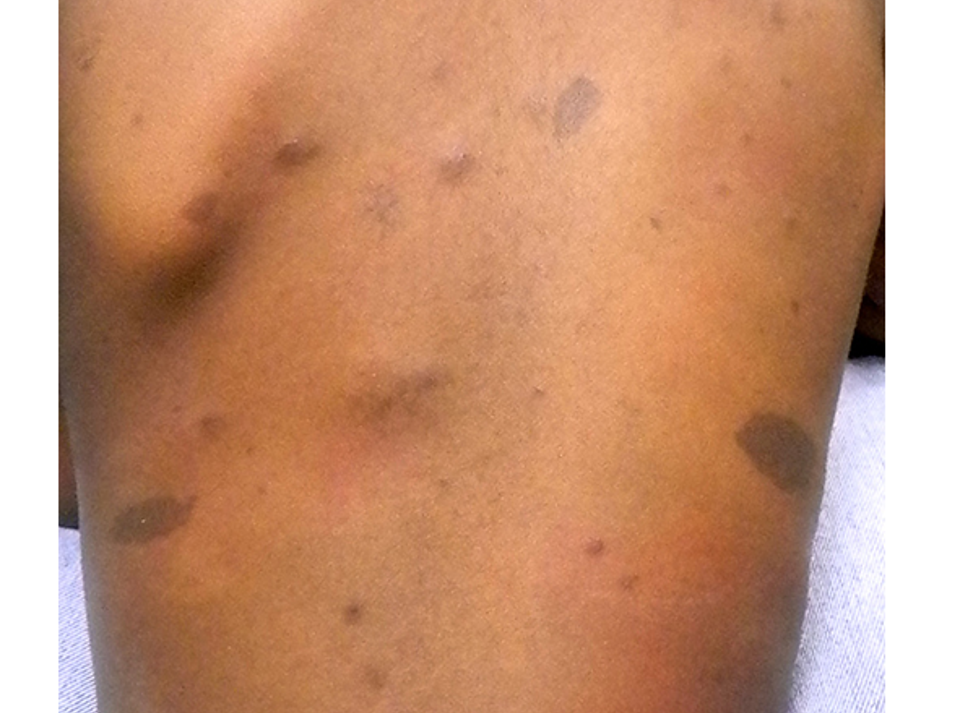
what are clinical features of neurofibromatosis?
multiple cafe au lait spots
soft, fleshy, sessile, pedunculated tumors
freckling- axillary/inguinal regions
Lisch nodules: raised tan colored hamartomas of iris
location: trunk
subtypes
NF1- von recklinghausen
NF2- schwannomatosis