hormones
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
hormones
organic signaling molecules
produced by cells
signal to other cells (or to the same cell)
autocrine
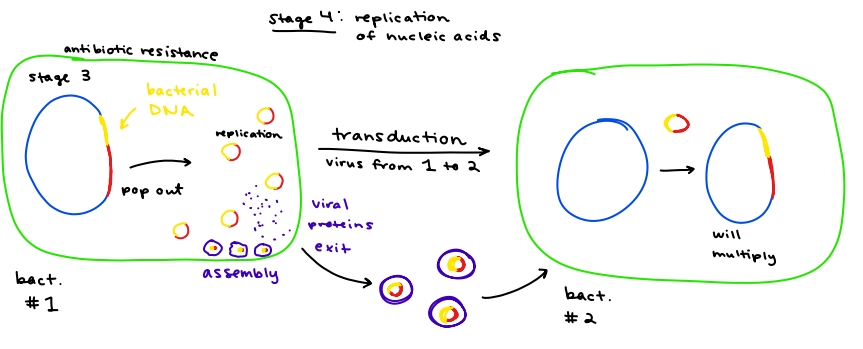
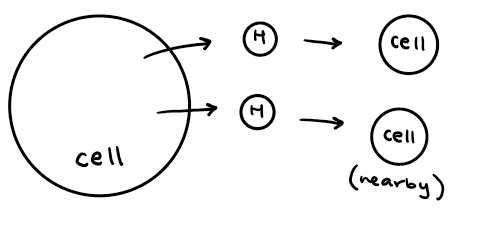
paracrine
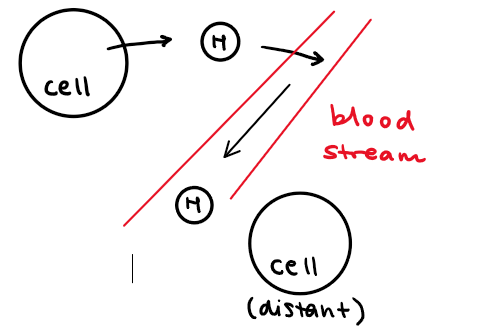
endocrine
peptide hormones
insulin (51 amino acids)
vasopressin / ABH (9 amino acids)
amino acid derivatives
epinephrine / adrenaline - modified to tyrosine
serotonin - chemically modified tryptophan
steroid-base
made up from cholesterol
testosterone - male sex characteristic
aldosterone - Na+ / water balance
cortisol - anti-stress hormone
fatty-acid derivatives
arachidonic acid (20C) - prostaglandins (pain)
water-soluble except for thyroxine (A.A.D)
peptide hormones and amino acid derivatives
water-insoluble plus thyroxine
steroid-base and fatty acid derivatives
hormones must…
bind their receptors on target cells
can open or close membrane ion channels
can affect or change membrane voltage
effect of hormone on receptor signaling
can activate or inhibit enzymes in cell
effect of hormone on receptor signaling
can turn on certain gene
express new / more proteins
effect of hormone on receptor signaling
can stimulate cell cycle
effect of hormone on receptor signaling
can stimulate another cell to produce and secrete hormone
effect of hormone on receptor signaling
transport
either water soluble or water insoluble
water soluble
travel freely dissolved in solution
water insoluble
bound to carrier proteins
albumins and globulins
potency
very potent, e.g. nM
onset
secs - mins - hrs
duration
mins - hrs - days
half life (t 1/2)
amount of time to go from a measure a value of hormone level / concentration to ½ of that volume of level / concentration
permissive hormones
one hormone needs another particular hormone present in order to signal
ex: testosterone requires thyroxine
synergism
where the whole is greater than the sum of the parts
antagonism
hormones have opposing effects
blood sugar low…
stimulates alpha cells
makes glucagon (hormone)
raises blood glucose levels
blood sugar high…
stimulates beta cells
makes insulin (hormone)
lowers blood glucose level
2 types of feedback regulation
negative and positive feedback
negative feedback
reverses a change
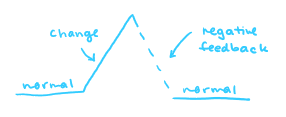
positive feedback
amplifies a change

TRH
thyrotropin-releasing hormone
TSH
thyroid stimulating hormone