Cholesterol Metabolism
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Cholesterol is synthesized primarily where?
in the liver
What are the secondary sites of cholesterol synthesizing?
intestine, adrenal cortex, ovaries, and testes
What do you start with in order to start making cholesterol?
2 Acetyl-CoA
What enzyme fuses the 2 Acetyl-CoA's together to produce Aceto Acetyl CoA?
thiolase
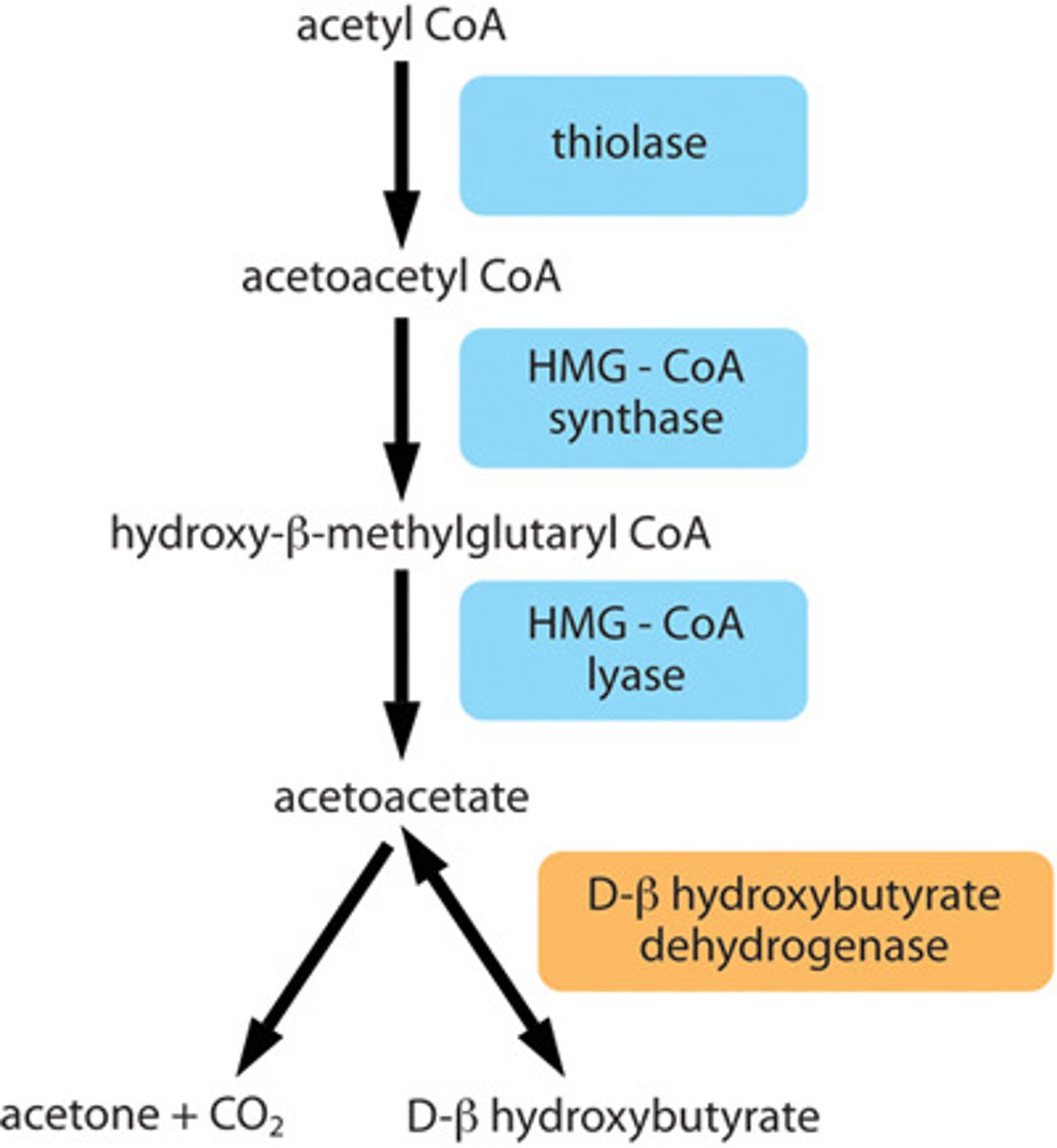
What is the most important enzyme of the body that helps to produce cholesterol?
HMG-CoA reductase
What does the enzyme reductase mainly rely on?
NADPH/NADP+
What is HMG-CoA reductase known to be in this process?
rate limiting/committing step
What are the 3 important functions of Cholesterol in the body?
1. plasma membrane rigidity and fluidity
2. precursor for steroid hormones (testosterone, progesterone, estrogen, corticosteroids)
3. precursor for bile salts (emulsification of lipids)
What is the main function of statin?
a drug that inhibits the production of bodily made cholesterol
What enzyme does the statin inhibit from the cholesterol pathway?
HMG-CoA reductase
What are the 7 FDA-approved statin drugs?
lovastatin
pravastatin
simvastatin
atorvastatin
fluvastatin
rosuvastatin
pitavastatin
What is a type of Bile acids sequestrant?
cholestyramine (questran)
What does cholestyramine (questran) do?
prevent resorption of bile acids from small intestine
What does cholestyramine (questran) treat?
pruritis secondary to increased plasma concentration of bile acids with cholestasis
What are the effects of cholestyramine (questran)?
constipation and bloating
What is a type of Cholesterol Absorption inhibitor?
ezetimibe (zetia)
What are the effects of ezetimibe (zetia)?
allergic reactions
Mechanism of action for Ezetimibe:
- binds to receptor which causes a change in structure where it does not recognize the cholesterol anymore - this causes a decrease in the level of cholesterol
- cholesterol has to be obtained from a different place which is from circulation from the LDL
For the Mechanism of Ezetimibe, what are the sites that get inhibited from change in structure?
NPC1L1 (2 of them)
Where does the mechanism of action for Ezetimibe take place?
enterocytes and also liver (where LDL is)
What is Niacin?
vitamin drug for treating dyslipidemias
What are the effects of Niacin?
vasodilation, flushing, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dry skin
What is Mechanism of Action of Niacin?
Niacin is thought to increase the activity of lipase, which breaks down lipids, and reduces the metabolism of cholesterol and triglycerides.
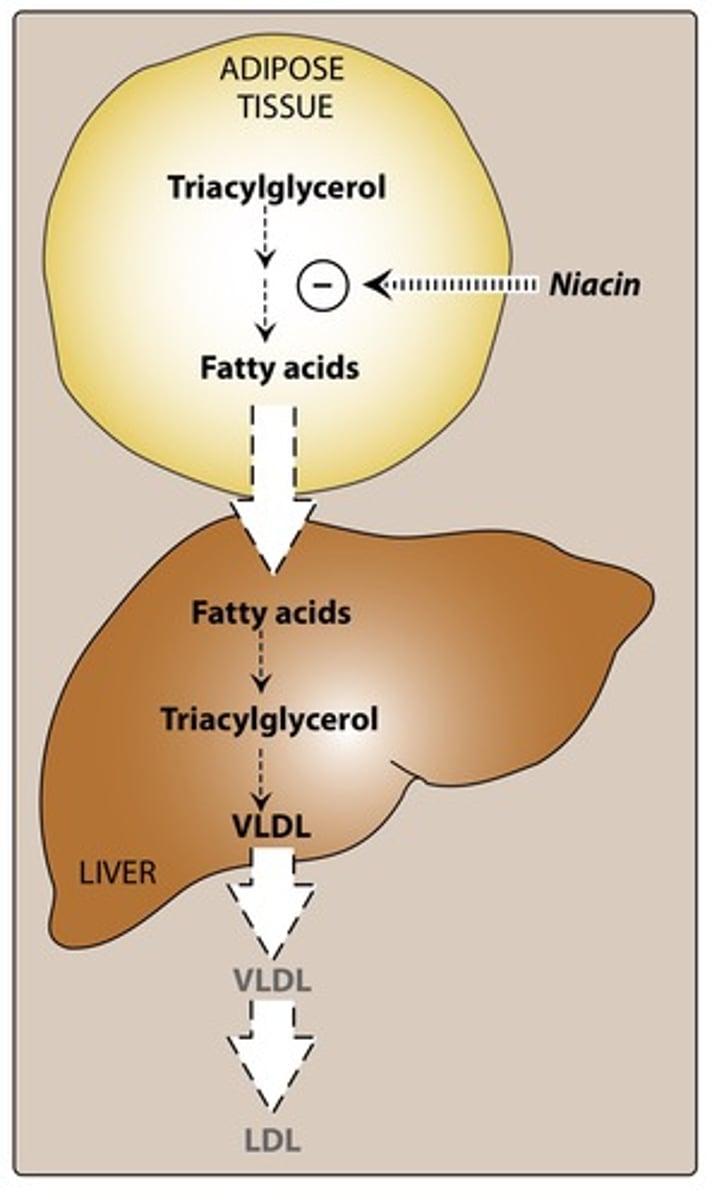
What enzyme does Niacin attack?
hormone sensitive lipase which decreases the amount of fatty acids produced
Emerging Therapeutic Agents
PCSK9 inhibitors
Normally what is the role of LDLR?
it is an LDL receptor in the liver where if you need LDL it will make the receptor to obtain it but when you do not need it anymore it will degrade it
What comes in to degrade the LDLR?
PSCK9
What attaches to the PSCK9 to inhibit degradation of the LDLR?
PSCK9 inhibitor
When the PSCK9 inhibitor binds to the PSCK9 what does this cause?
it causes the LDLR to not be degraded which gives an decrease of LDL from the blood
How does PCSK9 inhibitors promote an decrease in LDL?
because more LDL receptors will stay on the livers surface which helps more LDL to be removed from the circulation in blood
What is Lomitapide?
inhibitor of MTP (microsomal triglyceride transfer protein)
Where is MTP enzyme present?
in ER of hepatocytes and enterocytes
What does the enzyme MTP normally do?
transfer triglyceride to nascent ApoB and helps in synthesis of VLDL in liver and chylomicron in intestines
What does Lomitapide directly bind to?
MTP
When Lomitapide directly binds to MTP what happens?
it inhibits the transfer of triglycerides to Apo B48 and Apo B100 = inhibiting the synthesis of chylomicron and VLDL
What is Lomitapide treat?
homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia
Homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia
genetic disease that prevents LDL receptors from working right
What are the effects of Lomitapide?
nausea, dyspepsia, vomiting, and diarrhea which is seen in 93% of patients