test 2: study guide 5
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Glycolysis – cytosolic pathway
Glycolysis takes place in the cytosol of a cell, and it can be broken down into two main phases:
Energy-______ phase (uses 2 ATP). In this phase, the starting molecule of glucose is rearranged, and two phosphate groups are attached. The phosphate groups make the modified sugar—now called fructose 1,6-bisphosphate—unstable, allowing it to split in half and form two phosphate-bearing three-carbon sugars. The three-carbon sugars formed when the sugar is cleaved by aldolase B are: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and DHAP. Only glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is directly oxidized; DHAP is readily converted into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate.
Energy-_____ phase (produces 4 ATP and 2 NADH). In this phase, each three-carbon sugar is converted into another three-carbon molecule, pyruvate, through a series of reactions. In these reactions, two ATP molecules and one NADH molecule are made. Because this phase takes place twice, it makes four ATP and two NADH overall.
requiring
releasing
______ pathway: Glucose is oxidized to pyruvate and oxidation continues in the mitochondria to generate acetyl-CoA
-NAD+ is regenerated by transport of reducing equivalents across the mitochondrial membrane using one of two shuttles
- Glycerolphosphate shuttle (week 3)
- Malate shuttle (week 3)
______ pathway: Glucose is oxidized to lactate
This will occur either in the absence of oxygen
In cells that lack mitochondria (red blood cells)
Skeletal muscle oxidation of glycogen under anaerobic conditions
Impaired activity of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
NAD+ is regenerated by the reduction of pyruvate to lactate
Review glucose uptake (Week 4)
aerobic
anaerobic
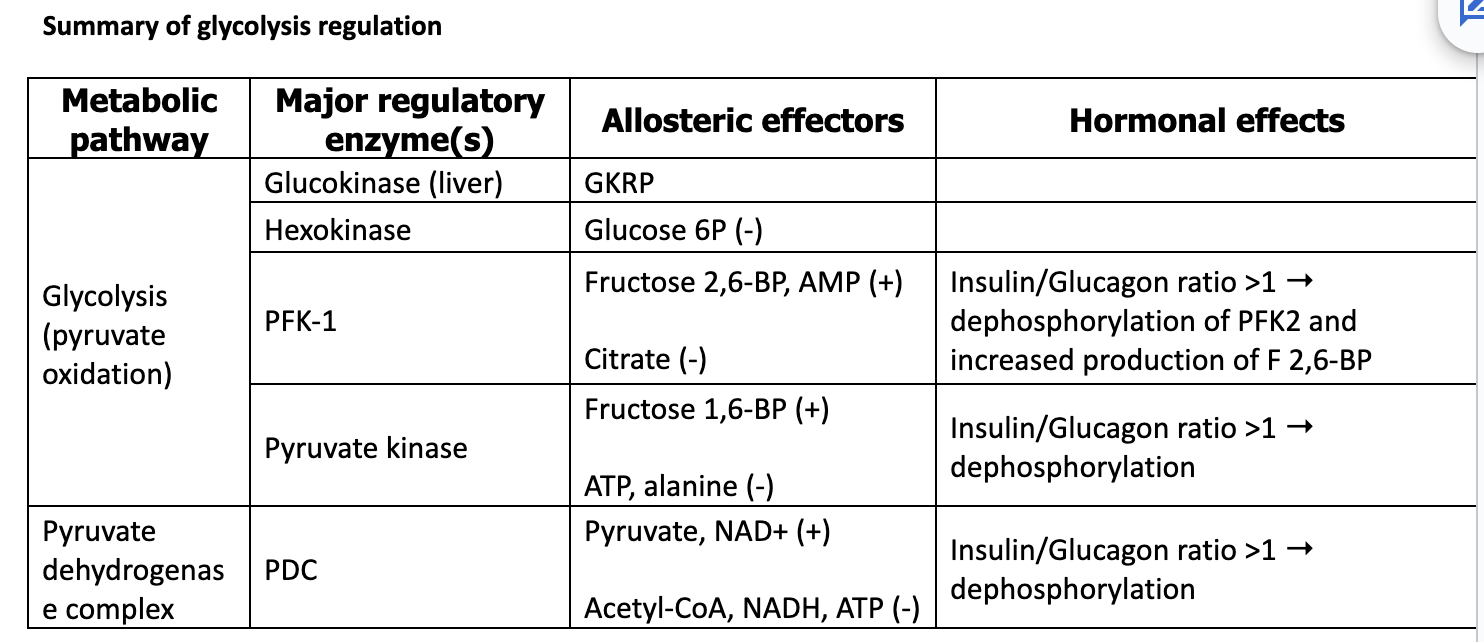
Focus on the three regulatory steps:
1. Conversion of Glucose to Glucose 6-phosphate
- Uses ____
Enzymes: Glucokinase or Hexokinase (Compare the locations and activity of these two enzymes)
Glucokinase vs. hexokinase
- Glucokinase and hexokinase are ______. They catalyze the same enzymatic reaction. Isozymes are enzymes that differ in amino acid sequence but catalyze the same chemical reaction.
- Hexokinase has a ____ Km for glucose and is found in tissues other than the liver. It is rapidly saturated.
- Glucokinase has a ____ Km for glucose and is found liver or pancreas. It is not rapidly saturated and can remove glucose steadily from the bloodstream as a means of allowing for excess glucose to be stored as glycogen (triacylglycerol).
ATP
isozymes
low
high
Focus on the three regulatory steps:
2. Conversion of Fructose 6-phosphate to Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
- Uses ___
Enzyme: Phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK1)
Fructose 6-phosphate can also be converted to fructose 2,6-bisphosphate by Phosphofructokinase-2 (PFK2) – NOTE: this is not considered part of glycolysis but is a shunt of the pathway.
-PFK2 is regulated through phosphorylation.
- When PFK2 is dephosphorylated, it is ACTIVE as a ____
Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate enhances the activity of PFK1 (allosteric activator)
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate is a _______ _____of Pyruvate kinase (See week 2)
ATP
kinase
feedforward activator
Focus on the three regulatory steps:
3. Conversion of phosphoenolpyurvate (PEP) to pyruvate
Enzyme: Pyruvate Kinase (PK)
Catalyzes the ______ reaction of PEP to pyruvate
Regulated by ______ regulation
Allosterically activated by fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
irreversible
feedfoward
Pyruvate generated through this process can either:
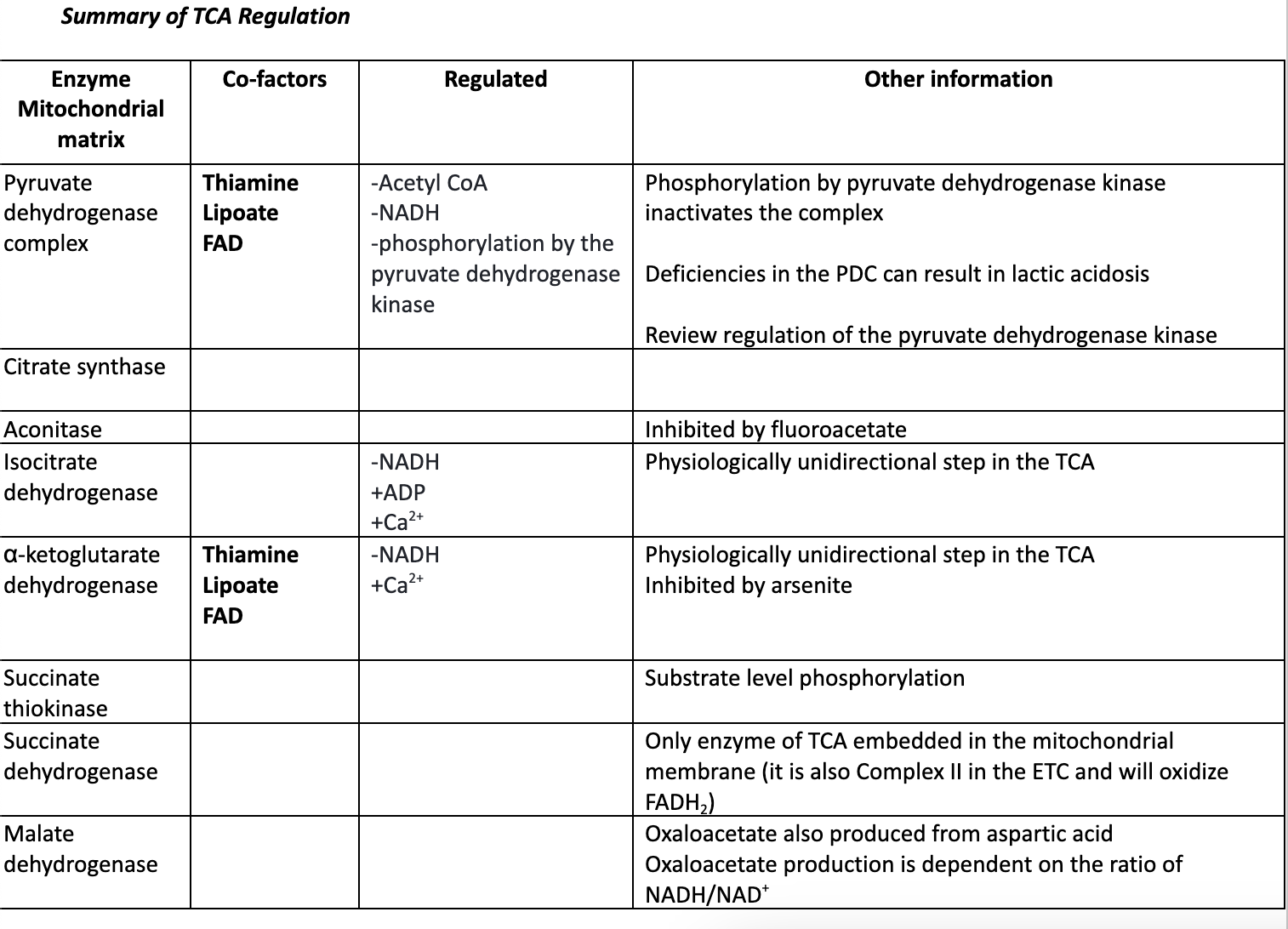
Enter the TCA cycle through the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
Be converted to ____ under anaerobic conditions
Be transaminated to ____
lactate
alanine
Connections to other pathways
____ _____ synthesis
Citrate is shuttled out of the TCA
In the cytosol it is cleaved by citrate lyase to generate: acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate (OAA)
Acetyl-CoA is used as a substrate for fatty acid synthesis
OAA is reduced to malate → malate is decarboxylated back to pyruvate which can reenter the TCA
This conversion by malic enzyme produces _____
fatty acid
NADPH
Connections to other pathways
_______ reactions
Reactions that transfer net carbon into the TCA cycle
Carboxylation of pyruvate → oxaloacetate (by pyruvate carboxylates)
Transamination reactions (specifics of this reaction are covered in Unit 4)
Glutamate → alpha-ketoglutarate
Alanine → pyruvate
Aspartate → oxaloacetate
Products metabolized to propionyl-CoA
anaplerotic
Review shuttles from week 2
Shuttle systems
1) _________ shuttle (Glycerol 3-phosphate shuttle)
Moves reducing equivalents of NADH from the cytosol to an FAD in the mitochondrion
FAD is a required cofactor glycerol-3 phosphate dehydrogenase
FAD is tightly or covalently bound to the dehydrogenase.
Cytosolic dihydroxyacetone phosphate is reduced to glycerol 3-phosphate -->glycerol 3-phosphate moves into the mitochondria and transfers the e- to FAD bound to the dehydrogenase
Glycerophosphate
Review shuttles from week 2
Shuttle systems
2) _____-_____ shuttle
Oxaloacetate DOES not move across the mitochondrial membrane!
Starting in the cytosol:
Oxaloacetate is REDUCED to malate by cytosolic malate dehydrogenase
The shuttle moves malate (reduced form of oxaloacetate) into the mitochondria
Once in the mitochondria:
Malate can be OXIDIZED back to oxaloacetate by mitochondrial malate dehydrogenase
The resulting oxaloacetate can undergo a TRANSAMINATION REACTION (See week 1) with glutamate
The reaction transfers the NH3+ from glutamate TO oxaloacetate to generate
→ alpha-ketoglutarate and aspartate
Aspartate can move in / out of the mitochondria
Aspartate can be converted to oxaloacetate.
For each NADH equivalent → 2.5 molecules of ATP are generated
Malate-Aspartate
Which of the following metabolic shifts would reduce the activity of the glycolytic pathway?
a)Decreased alanine
b)Increased glucose
c)Increased ATP
d)Decreased ATP
c)Increased ATP
A deficiency in which of the following cofactors would result in decreased activity of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex?
A)Thiamine
B)Biotin
C)Vitamin C
D)Folate
A)Thiamine
Alcohol metabolism increases the production of NADH, increasing the ratio of NADH/NAD+ in the cell.
How would you expect increased consumption of alcohol to impact the activity of the TCA cycle?
decreased activity of the TCA cycle