1.6 Sensation
1/385
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
386 Terms
Sensation begins when _____ reach our ______
Environmental stimuli; sensory organs
The environmental stimuli that reaches our sensory organs are converted into ______
Neural signals
The process of converting environmental stimuli into neural signals requires the stimuli to ______ before being detected and processed by the brain
Meet certain thresholds
Absolute threshold is the:
Minimum stimulus intensity detected 50% of the time
The minimum sugar in a gallon of water you can taste 50% of the time is one teaspoon
Which concept is demonstrated above?
Absolute threshold
The just-noticeable difference is the:
Smallest detectable change in stimulus intensity
Joseph tells his father to turn up the volume of the TV, one notch at a time, until he notices a slight volume increase on the radio
Which concept is demonstrated here?
Just-noticeable difference
Sensory adaptation refers to:
Decreased sensitivity to constant stimulation
After staying for 10 minutes in a bakery, the initial strong smell of cookies in the bakery fades
Which concept is demonstrated above?
Sensory adaptation
Our senses rarely work:
Alone
Senses team up through:
Cross-modal processing, sensory interaction, and synesthesia
Cross-modal processing combines:
Multiple senses
A visual input (lip movement for "ga") alters auditory perception (sound of "ba"), resulting in hearing "da"
Which concept is demonstrated above?
Cross-modal processing
Food flavor is largely determined by smell; block your nose, and a jelly bean tastes like sugar water
Which concept is demonstrated here?
Sensory interaction
Sensory interaction enhances:
Overall perception
Synesthesia is when senses:
Overlap
When Tom imagines the letter A, he always imagines it in the red color
Which concept is demonstrated above?
Synesthesia
If an observer responds to a present signal, then it is a:
Hit
If an observer responds to an absent signal, then it is a:
False alarm
If an observer does not respond to a present signal, then it is a:
Miss
If an observer does not respond to an absent signal, then it is a:
Correct rejection
A tumor is present, and the doctor correctly identifies it on the scan
Which concept is demonstrated above?
Hit
A tumor is not present, but the doctor still identifies it as present on the scan
Which concept is demonstrated here?
False alarm
A tumor is present, but the doctor does not identify it on the scan
Which concept is demonstrated above?
Miss
A tumor is not present, and the doctor does not identify it on the scan
Which concept is demonstrated above?
Correct rejection
Our sensory systems are attuned to detecting:
Changes in stimulation
Our sensory systems are not attuned to detecting:
Constant levels of stimulation
Our sensory systems being attuned to detecting changes in stimulation helps us to notice:
Important environmental changes
Our sensory systems being attuned to detecting changes in stimulation helps us to conserve:
Energy
Our sensory systems being attuned to detecting changes in stimulation helps us to conserve energy by:
Reducing responses to ongoing stimulation
Weber’s law governs how we:
Detect differences
The just-noticeable difference is proportional to:
Stimulus intensity
______ are needed to detect differences in stronger stimuli
Larger changes
Weber’s law applies across:
Different sensory modalities
Enoch easily notices a gram added to an empty bag but not to a 50-pound bag
Which concept is demonstrated above?
Weber’s law
Adaptation helps us to tune out:
Constant background noise
Adaptation helps us to stay sensitive to:
New or changing stimuli
Sensory adaptation allows us to adjust to:
Different environments
Adaptation allows us to optimize sensory processing for:
What’s happening now
The brain ______ to create coherent experiences
Integrates information from multiple senses
Integration of info from multiple senses happens:
Automatically and continuously
Integration of information from multiple senses enhances our ability to:
Understand and navigate environment
Common sensory interactions include:
Taste (smell + visual), speech comprehension (auditory) + lip movements (visual) , balance (vision + auditory)
Synesthesia is a form of:
Sensory interaction
During synesthesia, one sensory experience ______
Triggers another
Associations during synesthesia are:
Consistent and automatic
Experiences during synesthesia can involve ______ combination of senses
Any
Experiences during synesthesia can boost:
Memory and creativity
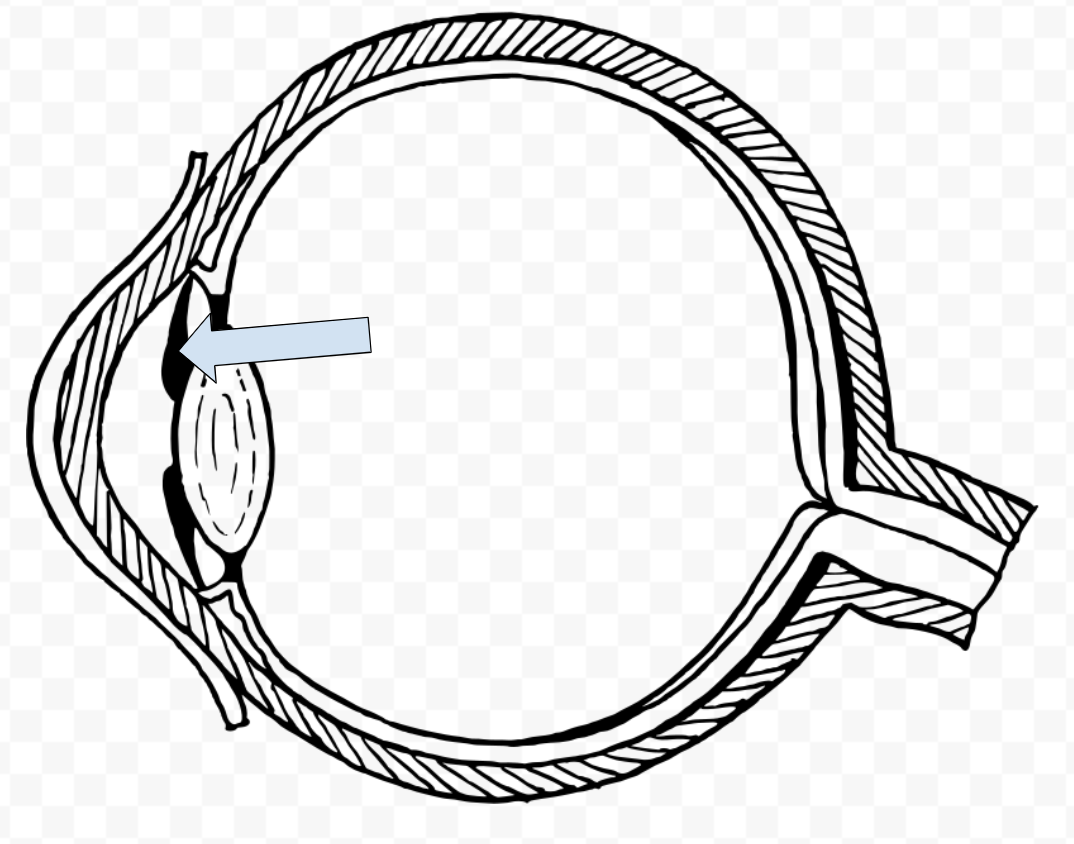
What is this called?
Iris
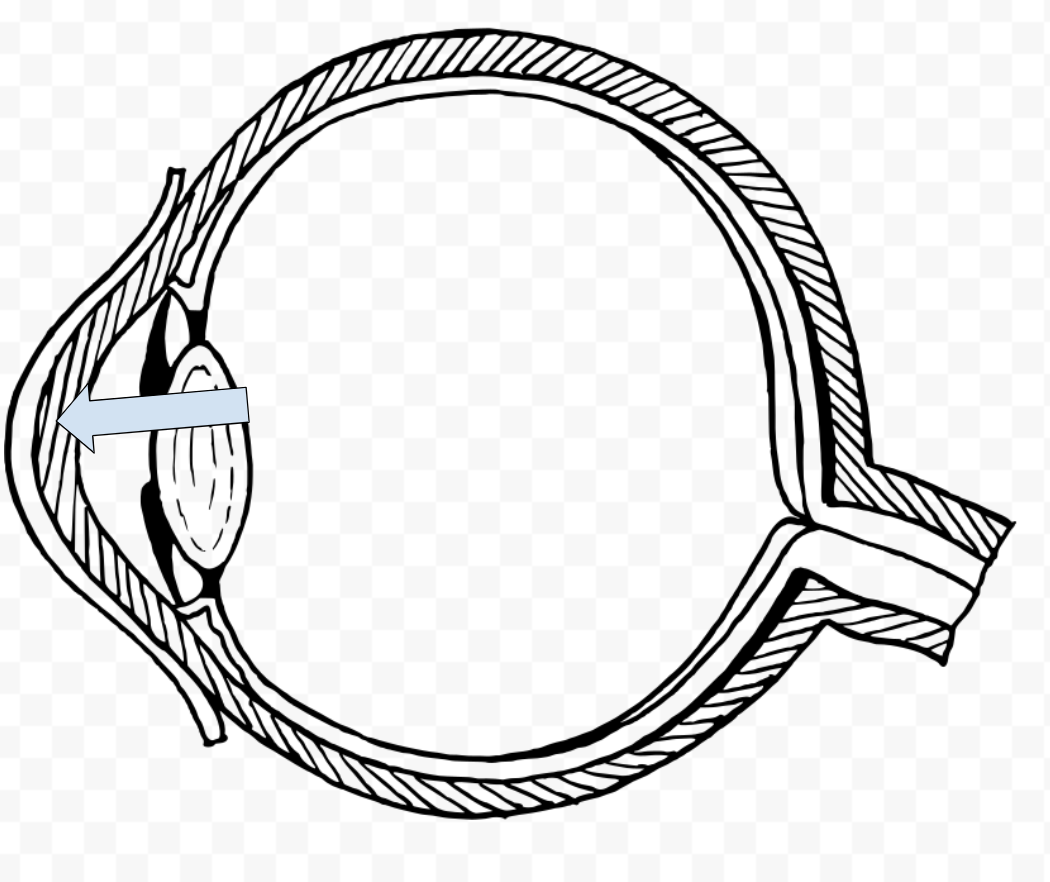
What is this called?
Cornea
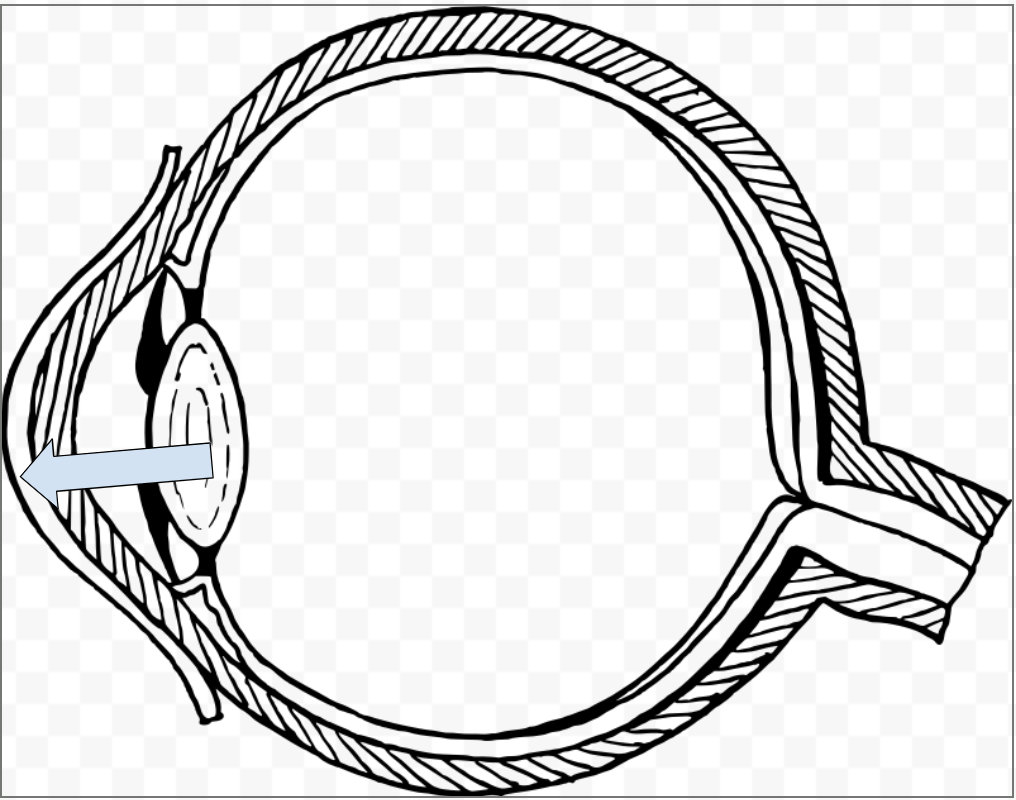
What is this called?
Conjunctiva
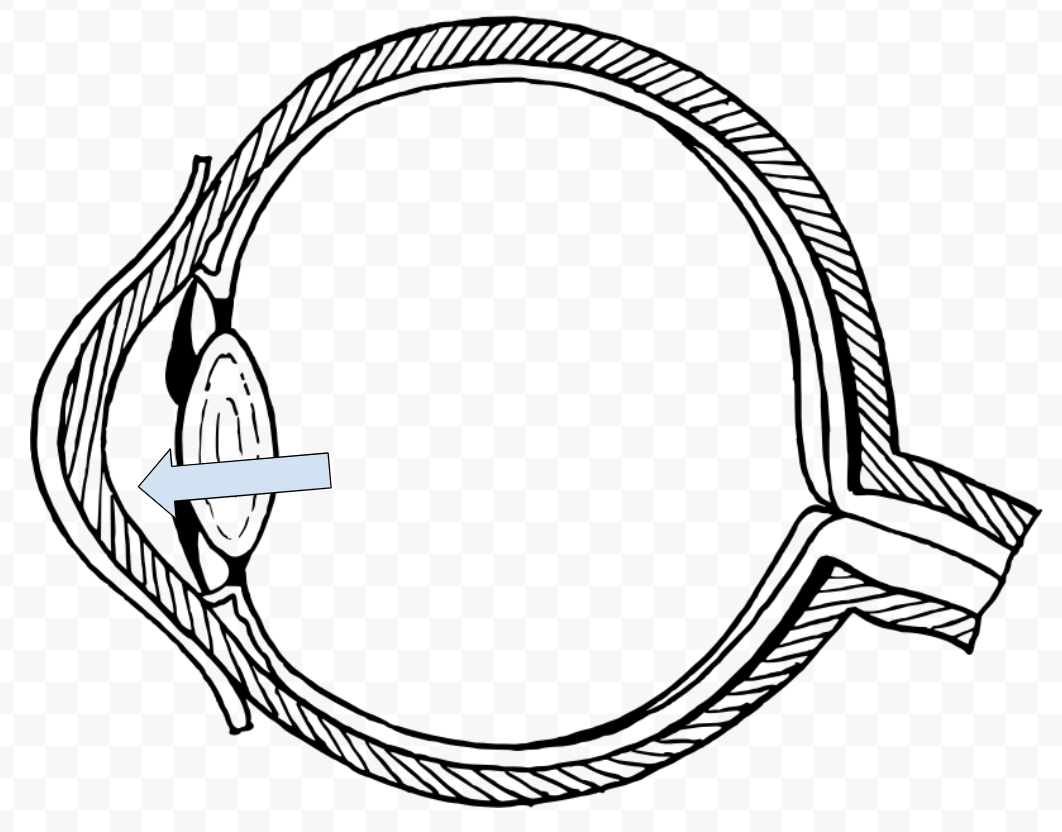
What is this called?
Pupil
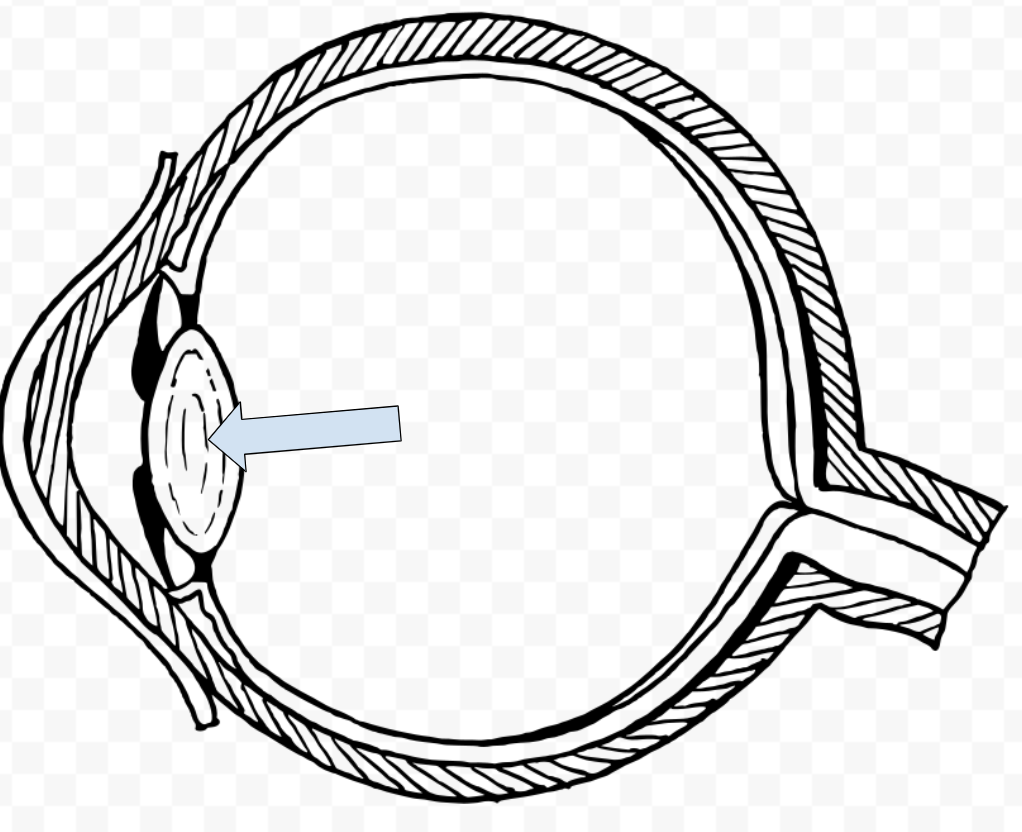
What is this called?
Lens
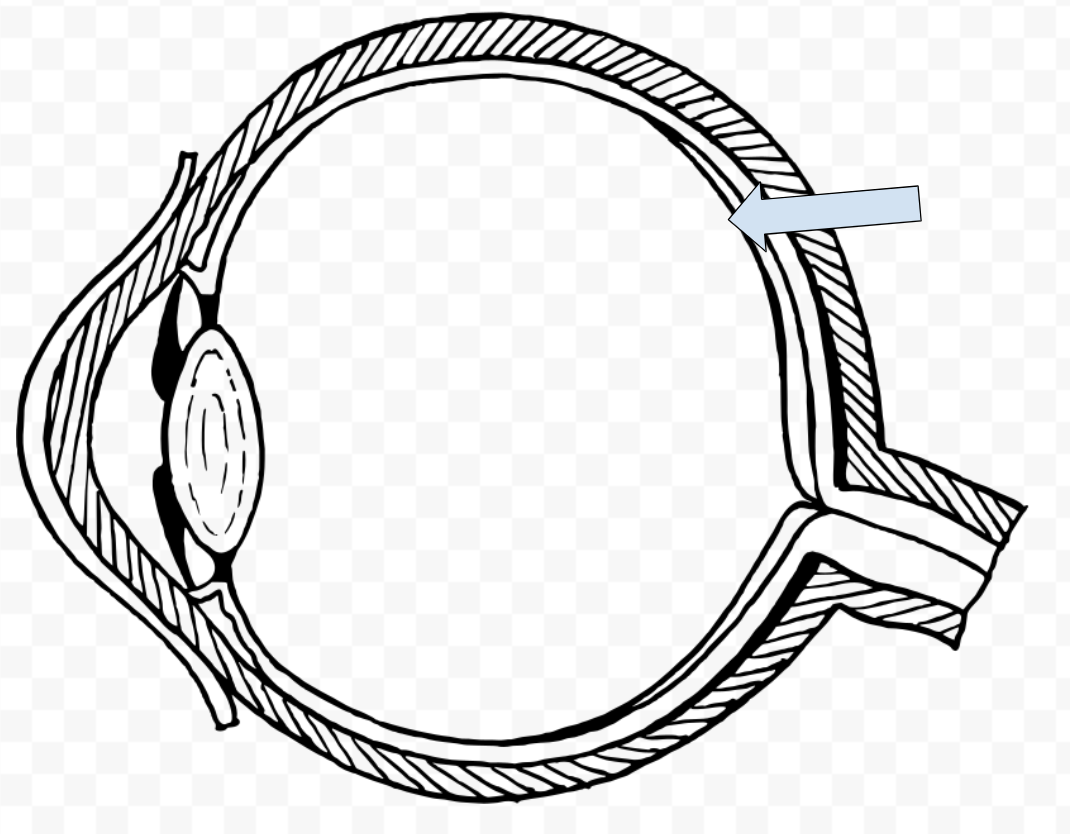
What is this called?
Retina
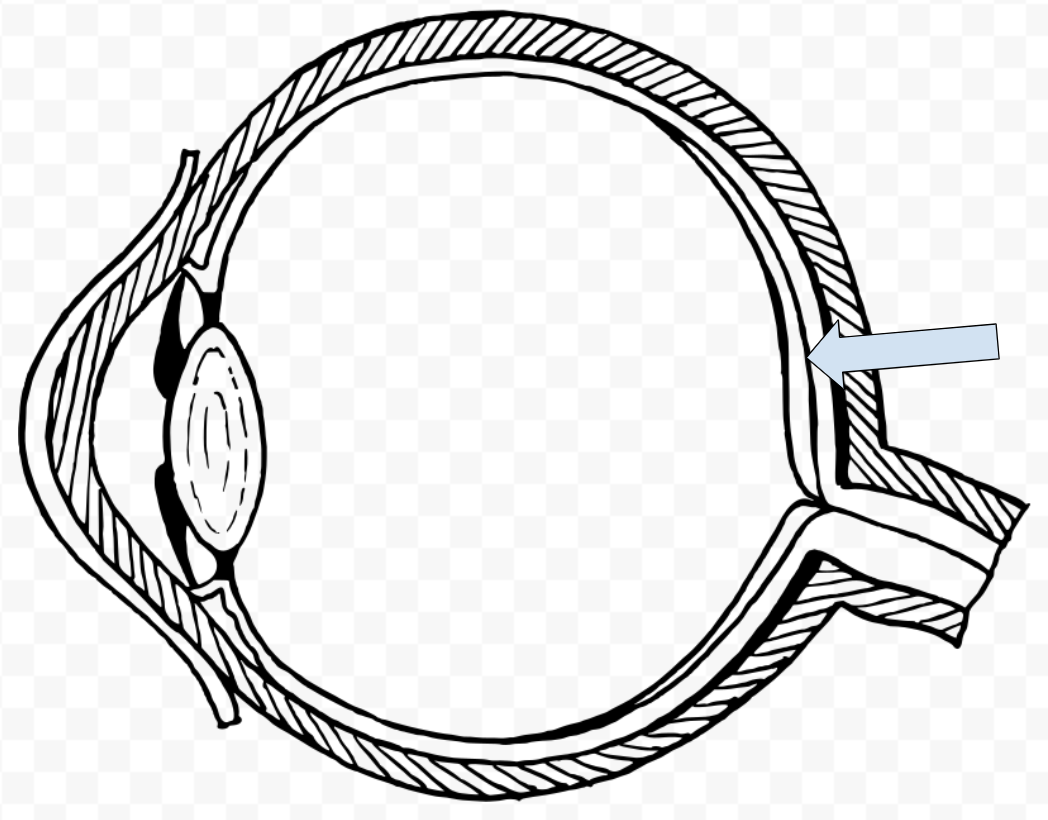
What is this called?
Fovea
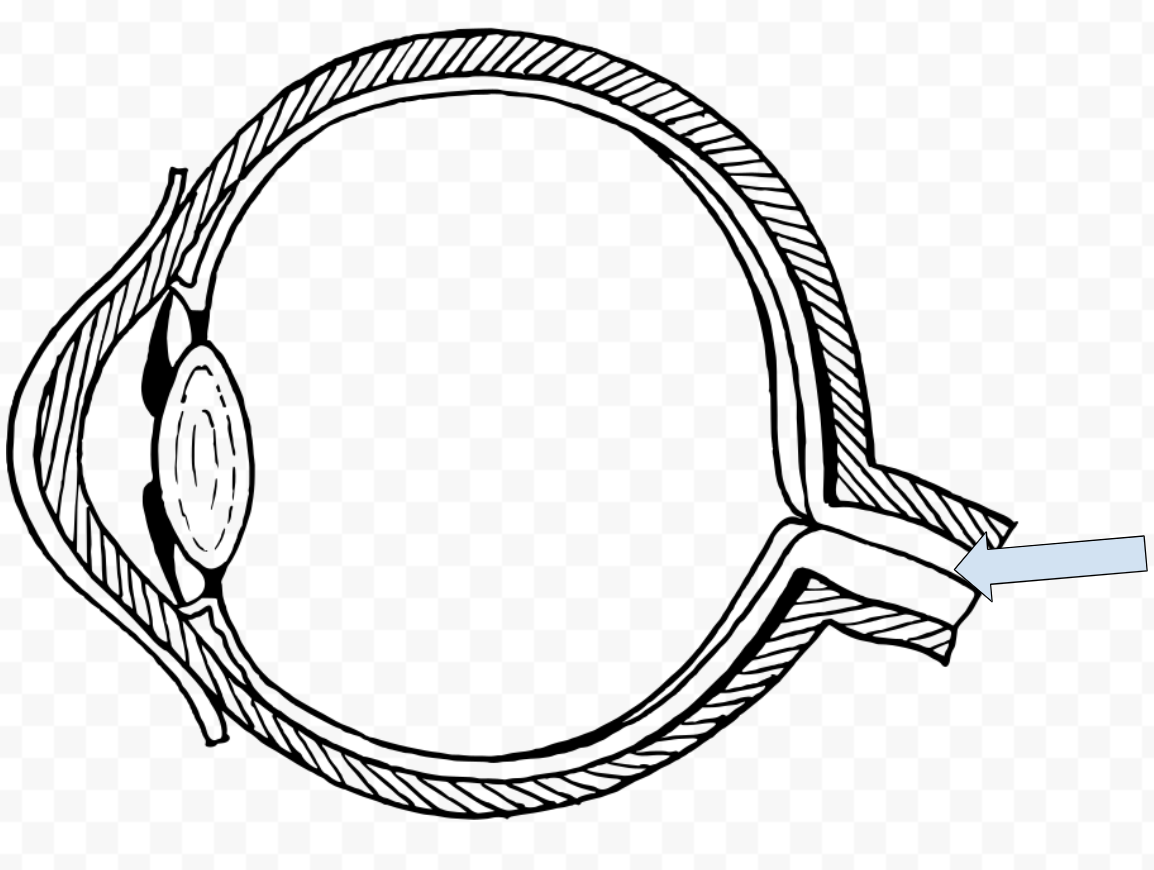
What is this called?
Optic nerve
The retina serves as the:
Primary visual receptor
The retina converts ______ into ______
Light into neural signals
The retina contains:
Multiple cell layers
The cell layers in the retina begin _______ before the visual information reaches the brain
Processing visual information
Initial visual processing includes detecting:
Light intensity, basic edge and motion, and color processing
Color processing happens in _____ areas
Cone-rich
After initial visual processing, the ______ makes up for retinal limitations
Brain
After initial visual processing, the brain makes up for retinal limitations by filling in the:
Blind spot
After initial visual processing, the brain makes up for retinal limitations by maintaing:
Perceptual stability
After initial visual processing, the brain makes up for retinal limitations by integrating information from:
Both eyes
The lens adjust to:
Focus images on retina
The lens focusing images on retina is called:
Accommodation
The lens changes shape for:
Near and far vision
The pupil size adjusts for:
Light intensity
Eye muscle coordinates for:
Binocular vision
Examples of vision problems:
Myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism
Myopia is when images focus:
In front of retina
Myopia is also called:
Nearsightedness
Hyperopia is when images focus:
Behind retina
Hyperopia is also called:
Farsightedness
Astigmatism is caused by:
Irregular cornea shape
An irregular cornea shape causes:
Distortion
Mr. Davis, a 65-year-old high school teacher, has recently noticed that he struggles to read the student essays on his desk. He can see the students at the back of the classroom clearly, but anything up close appears blurred and out of focus. A trip to the ophthalmologist confirms that the structure of his eye responsible for focusing light has become less flexible with age.
Which eye structure is involved here?
Lens
Maria walks from a brightly lit school hallway into a dark theater to watch a play. Initially, she cannot see well because her pupils were constricted (small) to protect her eyes from the bright light. In the darkness, her pupils will soon dilate (expand) to allow more light to enter the eye and reach the retina, which improves her vision in low-light conditions.
Which part of the eye is responsible for this?
Pupil
Sarah closes her left eye and stares at a cross mark on a piece of paper held at arm's length. A few inches to the right of the cross is a small dot. As she slowly moves the paper closer to her face, keeping her right eye fixed on the cross, the dot suddenly disappears from her peripheral vision at a certain distance
Which concept is demonstrated above?
Blind spot
A student watches her school bus approach from a quarter-mile down the street. Although the image of the bus on her retina gets larger and larger as it gets closer, she does not perceive the bus as physically "growing" in size. Instead, she perceives it as a normal-sized bus that is simply getting nearer.
Which concept is demonstrated above?
Perceptual stability
Maria holds her pointer finger out at arm's length. She closes her left eye and notes the position of her finger relative to a distant object. When she opens her left eye and closes her right eye, her finger appears to jump to a different position. The brain uses this difference (disparity) in the two images to calculate how far away her finger is.
Which concept is demonstrated above?
Binocular vision
Fourteen-year-old Sarah is sitting at the back of her history classroom and cannot clearly read the words written on the whiteboard, but she can perfectly read the textbook on her desk
Which concept is demonstrated above?
Myopia
Sarah, a 45-year-old high school teacher, is grading papers one evening. She can see her students at the back of the classroom clearly during the day and has no issues driving. However, when she tries to read the comments she has written on the papers in front of her, the words appear blurry and out of focus. To read them clearly, she has to hold the papers at arm's length. After an hour of grading, she develops a headache and eye strain.
Which concept is demonstrated above?
Hyperopia
Mrs. Thomas is reading a newspaper and notices that some lines of text appear clear while others, particularly those at a different angle (e.g., vertical vs. horizontal), look blurry or smeared. When she looks at a circle of lines radiating like a star some lines look darker and clearer than others
Which concept is demonstrated here?
Astigmatism
Rod cells give us vision in:
Low light
Rod cells are crucial for detecting movement in our:
Peripheral vision
Rod cells ______ as lighting conditions change
Adapt significantly
Light adaptation happens ______ when entering bright areas
Fast
When entering bright areas, rod sensitivity:
Decreases
When entering bright areas, cone cells become:
More active
When entering bright areas, the pupil ______
Constricts
When entering bright areas, the pupil constricts to:
Reduce light entry
Dark adaptation is ______ than light adaptation
Slower
Dark adaptation involves ______ rod senstivity
Increased
Dark adaptation involves ______ cone activity
Reduced
Dark adaptation involves pupil ______
Dilation
Dark adaptation involves ______ regeneration
Rhodopsin
Sarah is walking home late at night. The streetlights are dim, and the environment is mostly dark.Sarah can still see the general shapes of trees and buildings along the street. When a cat darts across the path in her peripheral vision, she immediately notices the movement
Which part of the eye is responsible for these sights?
Rod cells