Malignant epithelial neoplasms + PE
1/94
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CHECK REVISED PP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
what are the three malignant epithelial neoplasms
basal cell carcinoma (BCC)
squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)
verrucous carcinoma
what is basal cell carcinoma also known as
rodent ulcer
is BCC a low, medium, or high grade epithelial malignancy
low grade
cause of BCC
sun exposure
common age assocIated w BCC
> 40 yrs
common location for BCC
80% H&N
mid face most common
prevalence of BCC
most common skin cancer and most common of all cancers
tx for BCC
surgical excision
order these from most to least common:
BCC
melanoma
SSC
BCC > SCC > melanoma
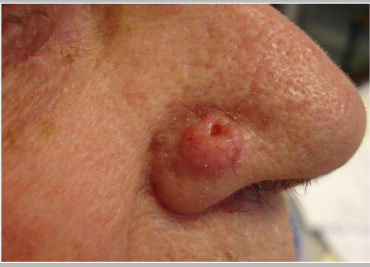
dx
BCC
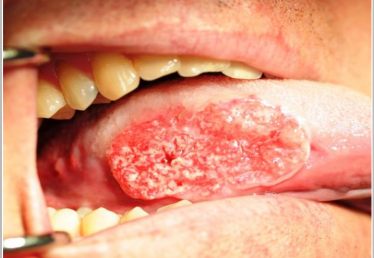
dx
SCC
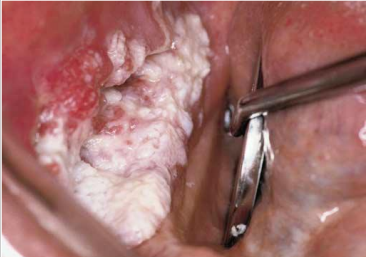
dx
verrucous carcinoma
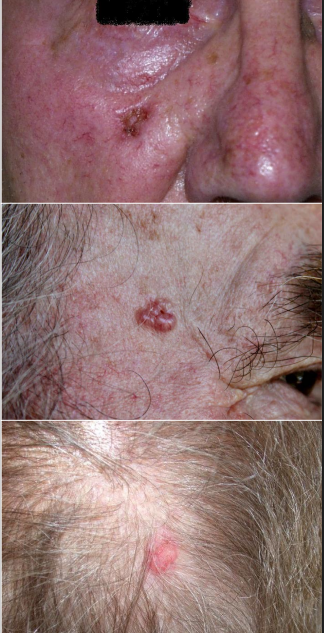
dx
SCC
OKC + multiple BCC + <30-40 yrs =
nevoid basal cell carcinoma; gorlin-goltz or gorlin syndrome
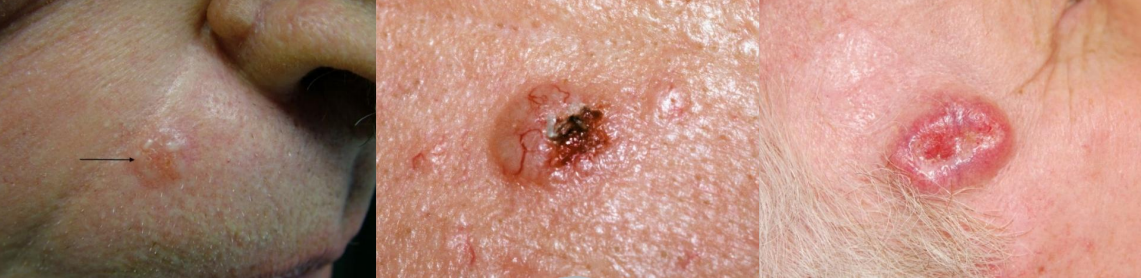
dx
BCC
clinical description of BCC
begins as a firm, painless papule
will slowly enlarges and gradually develops a central depression
rolled borders usually present
one or more telangiectatic blood vessels are seen
metastasis association w BCC
is extremely rare; locally destructive
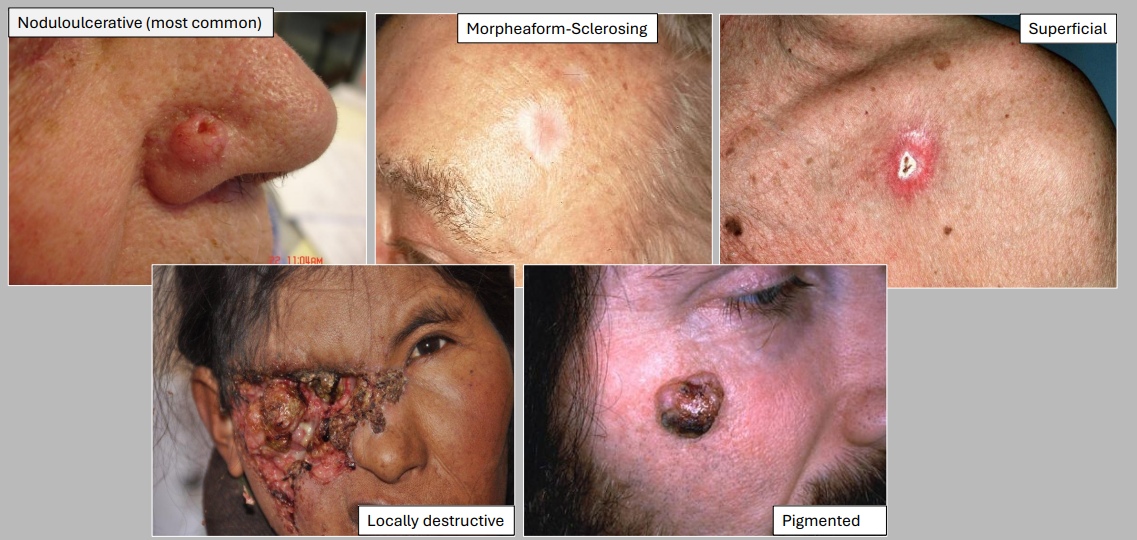
BCC can have clinicopathological varieties, what is most common
noduloulcerative
what can cause cutaneous SCC
chronic sun exposure
actinic keratosis
radiation therapy
common location of cutaneous SCC
70% head and neck region
clinical presentation of cutaneous SCC
non-healing ulcer
slowly growing
plaque, papule, or nodule variable degree of scale, ulcer, or crest
often erythematous base
what is the prevalence and survival rate of oral cancer
1 in 3 americans will develop
2/3 survive
oral cancer accounts for ____% of deaths in the US
20%
oral cancer accounts for ___% of all cancers
3%
___% of oral cancers are what type…
95% are SCC
what is the cause of SCC
multifactorial
what is verrucous carcinoma also known as
snuff dipper’s cancer / Ackerman’s tumor
clinical presentation of verrucous carcinoma
diffuse, well-demarcated, painless, thick plaque w papillary or verruciform surface projections
verrucous carcinoma is a _____ (high or low)- grade variant of oral SCC
low-grade (90% disease-free survival)
what can cause verrucous carcinoma
smokeless tobacco or from PVL
common location for verrucous carcinoma
mandibular vestibule and gingiva
20% verrucous carcinoma have ____ developing within
SCC
tx for verrucous carcinoma
surgical excision
which of the following is true about BCC:
it commonly affects individuals under 30
it frequently metastasizes to distant organs
common location in FOM
typically has central depression w rolled borders
typically has central depression w rolled borders
which habit is strongly associated w verrucous carcinoma:
cigarette smoking
chewing betel quid
alcohol consumption
using smokeless tobacco
using smokeless tobacco
which is the most common type of skin cancer:
BCC
SCC
melanoma
verrucous carcinoma
BCC
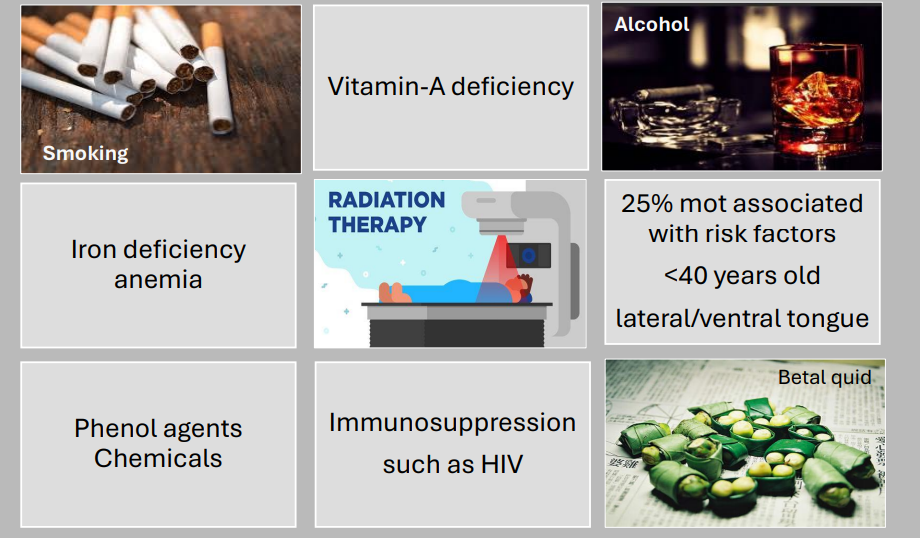
etiology for oral cancer
smoking
alcohol
radiation therapy
betel quid
gender most affected by OSCC
caucasian men- this is changing
age affected by OSCC
older age group- this is changing
common location of OSCC
FOM, posterior lateral ventral tongue, lower lip
why is there a delay in seeking care in OSCC
bc the early stages are painless
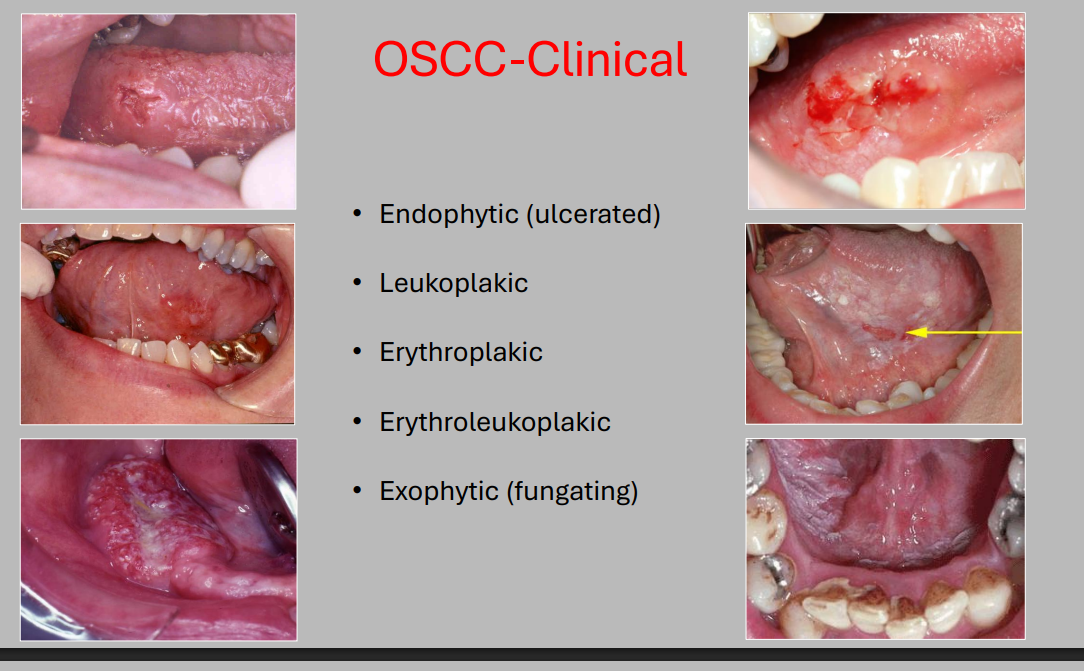
OSCC clinical presentation (5)
endophytic (ulcerated)
leukoplakic
erythroplakic
erythroleukoplakic
exophytic (fungating)
rank the following in order from most to least high risk sites for oral cancer:
tongue
lip
FOM
soft palate
FOM > tongue > lip > soft palate
OSCC association w metastasis
spread largely via lymphatics; tends to spread to ipsilateral cervical lymph nodes
how will lymph nodes present in OSCC metastasis
firm to stony hard
painless
enlarged
fixed- cells have perforated the capsule of the nodes and invaded into surrounding tissue
what is sentinel lymph node
the first lymph node to which cancer cells are most likely to spread from a primary tumor
what is local metastasis in OSCC
lymph nodes in neck
what is distant metastasis in OSCC
below the clavicle
where are the common sites of metastasis in OSCC
lungs and bones
what dictates the tx and is the best indicator of pt prognosis
TNM:
T- size of primary tumor in cm
N- involvement of local lymph nodes
M- distant metastasis
how many stages are there in TNM classification, how does prognosis change
4; prognosis will worsen as you inc in stage
stage I in TNM classification
T1 N0 M0
stage II in TNM classification
T2 N0 M0
stage III in TNM classification
T3 N0 M0 OR any T, N1, M0
stage IV in TNM classification
lymph node involvement and metastasis: any M or T4 or N1
is clinical grading or staging a better prognostic indicator
staging is better than histological grading
how many grades are there in OSCC
3
grade 1 in OSCC
low grade
well-differentiated
resemble their parent tissue
grade II OSCC
tumors less resemble parent tissue
moderately-differentiated
intermediate grade
grade III OSCC
tumors have v little resemblance of their parent tissue; tend to enlarge
poorly differentiated
high grade
metastasize early
what distinguishes OSCC of the lip from intraoral OSCC:
lip OSCC metastisizes more frequently
intraoral OSCC has a better prognosis
lip OSCC often arises from actinic cheilitis
lip OSCC can’t be tx surgically
Lip OSCC often arises from actinic cheilitis
which of the following has the best prognosis for oral cancer
T4 N1 M1
T2 N0 M0
T3 N1 M0
T1 N1 M0
T2 N0 M0
which of the following is NOT true of metiastatic disease
painless lymphnodes
spread through lymphatics
lymph nodes are mobile and soft
enlarged lymph nodes
lymph nodes are mobile and soft
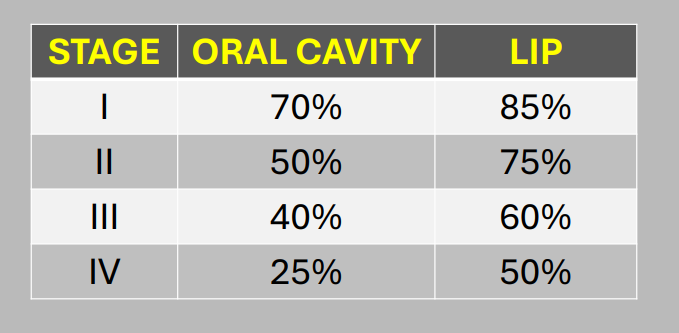
OSCC v lip SCC 5 yr survival rate
lip has higher survival rate overall
which lip is more common in SCC
lower lip; upper lip is rare
causes of lip SCC
chronic sun exposure
arises in a setting of actinic cheilitis
clinical presentation of lip SCC
slow, non-healing ulcer
rough and scaly
can be mistaken for an ulcer
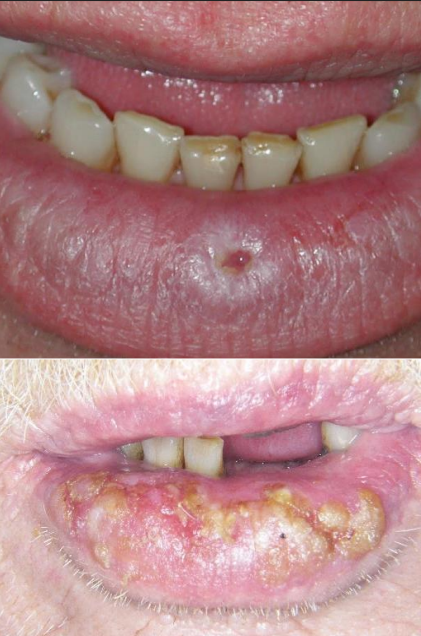
dx
lip SCC
cutaneous SCC tx
surgical excision- good prognosis if detected early
lip carcinoma tx
wedge resection w excellent results
OSCC clinical stage guide txs
wide surgical excision and/or radiation therapy
chemo is sometimes administered
does NOT improve survival rate
pts w intraoral tumors that have a 4 mm depth of invasion recieve…
radical neck dissection
pts w one carcinoma of the mouth or throat are at an inc risk for…
additional SCC
concurrently
pt can synchronously develop an additional SCC
metachronous
pt can develop additional SCC at a different time, usually within 3 yrs
what is field cancerization
tendency toward development of multiple mucosal cancers
gorlin syndrome is most commoly associated w which type of neoplasm:
BCC
verrucous carcinoma
SCC
merkle cell carcinoma
BCC
which is the highest risk factor for OSCC:
smoking cigs
radiation therapy
chewing tobacco
alcohol consumption
smoking cigs
which clinical appearance is NOT typically associated w OSCC:
leukoplakia
generalized ulcers
erythroplakia
exophytic mass
generalized ulcer (not generalized)
what is the most common site for OSCC to metastasize:
kidney
brain
liver
lung
lung (or bone)
which of the following is FALSE regarding SCC:
most common intra-oral cancer
HPV+ has worse prognosis
stage III includes lymph node involvement
cutaneous SCC resembles BCC
HPV+ has a worse prognosis
what is high risk type of HPV w OSCC
HPV 16 is most common
what are the common sites of HPV + OSCC
oropharyngeal: soft palate or tonsillar area or base of the tongue
________ is NOT the cause of HPV + OSCC, __________ is
tobacco is not the cause; inc in sexual partners is
is there a male or female predilection for HPV + OSCC
male
what is the clinical presentation of HPV + OSCC
a mass or an erythroplakia
is there a better or worse prognosis of HPV+ OSCC compared to just OSCC
better prognosis of HPV+ OSCC than just OSCC
primary clinical feature of OSCC
leukoplakia, erythroplakia, erythroleukoplakia, ulcer
primary clinical feature of HPV+ OSCC
enlarged lymph node in neck, dysphagia, very subtle, asymptomatic initially
is the incidence of HPV+ OSCC inc or dec
inc
is the incidence of OSCC inc or dec
dec
list the prognosis of these cases from best to worse:
HPV-, nonsmoker
HPV+, smoker
HPV-, smoker
HPV+, nonsmoker
HPV+ nonsmoker → HPV+ smoker → HPV- nonsmoker → HPV- smoker
tx for HPV+ OSCC in early disease
platinum-based chemoradiotherapy
surgery
tx for HPV+ OSCC in late disease
surgery
chemotherapy
radiation
what does the vaccine GARDASIL target
HPV types: 16, 18