Case 1: Celia + Maria
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
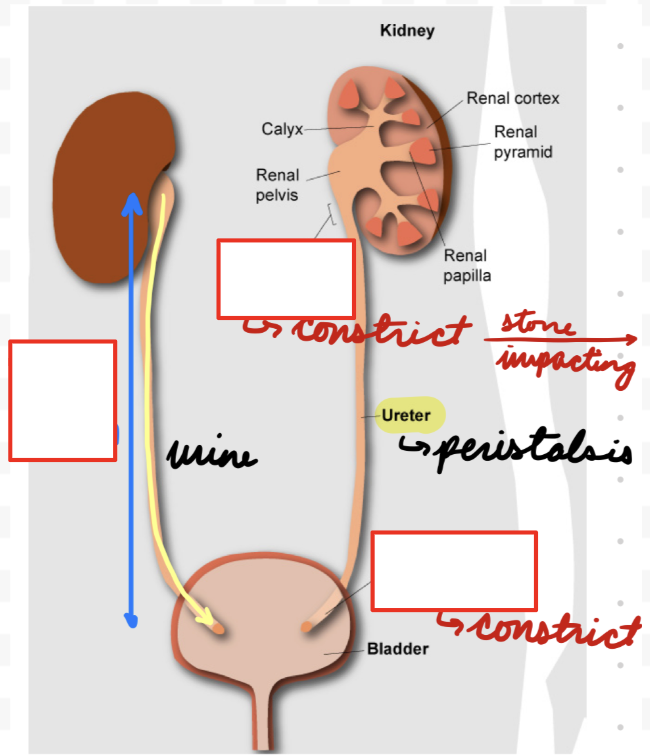
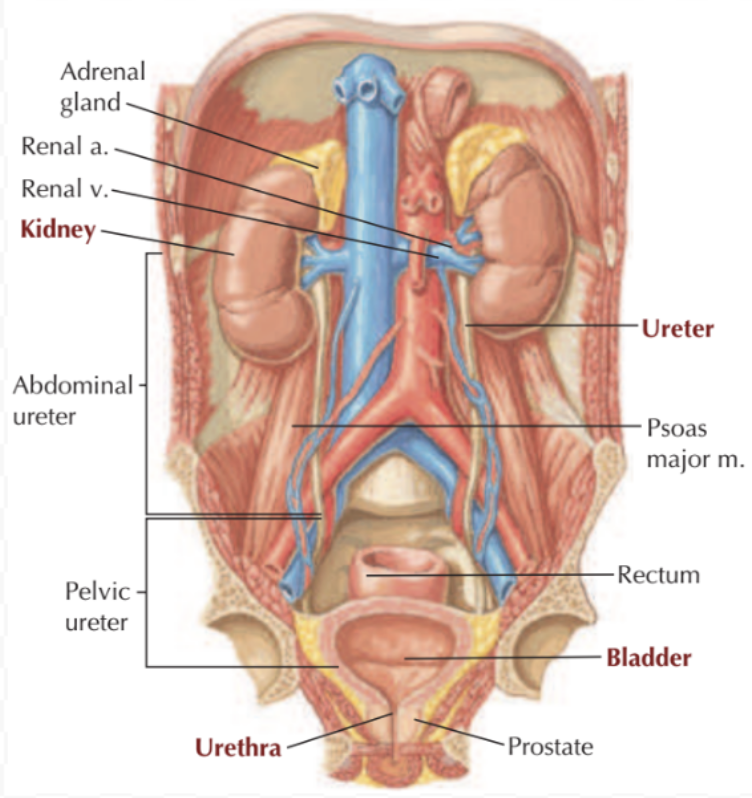
Urinary Tract: Kidneys
Paired “bean” organs in posterior abdominal wall (under ribs)
Kidneys: Capsule
Fibrous outer layer
Kidneys: Layers
Inside capsule
Cortex: Outer
Contain nephrons (filtration unit)
Medulla: Inner
Outer and inner medulla
Contain renal pyramids
Papilla: Inner medulla
Project into renal pelvis
Connected to calyces (ureter extensions) at hilum
Minor calyces → Major calyces → Pelvis → Ureter
Hilum: Contain blood vessels, nerves and ureter


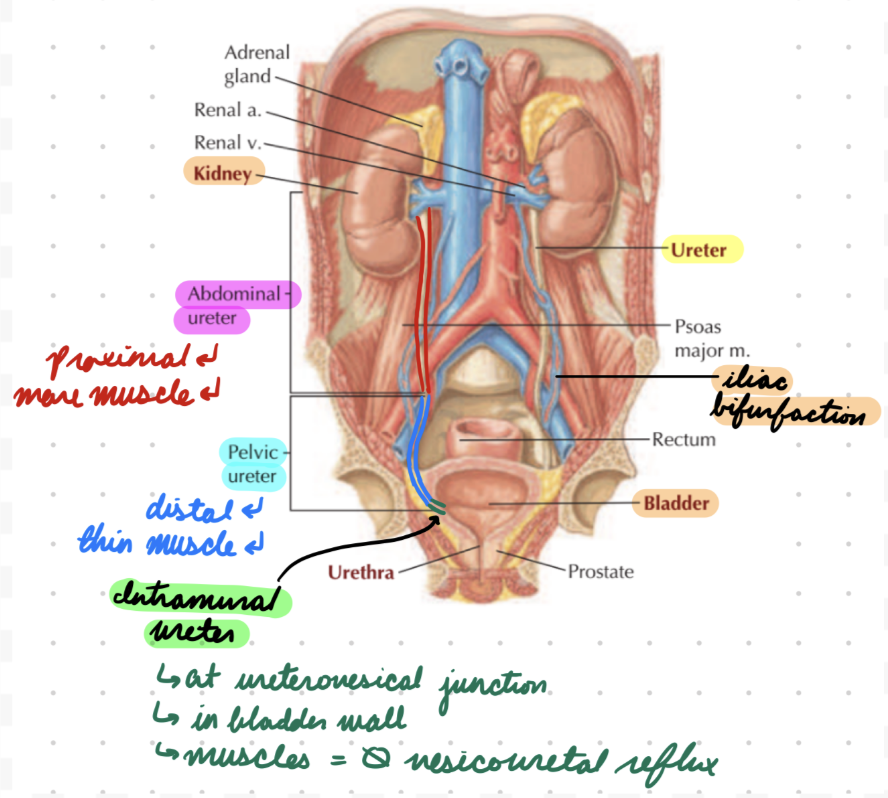
Urinary Tract: Ureters
Connect kidneys to pelvis
Unitary smooth muscle wall
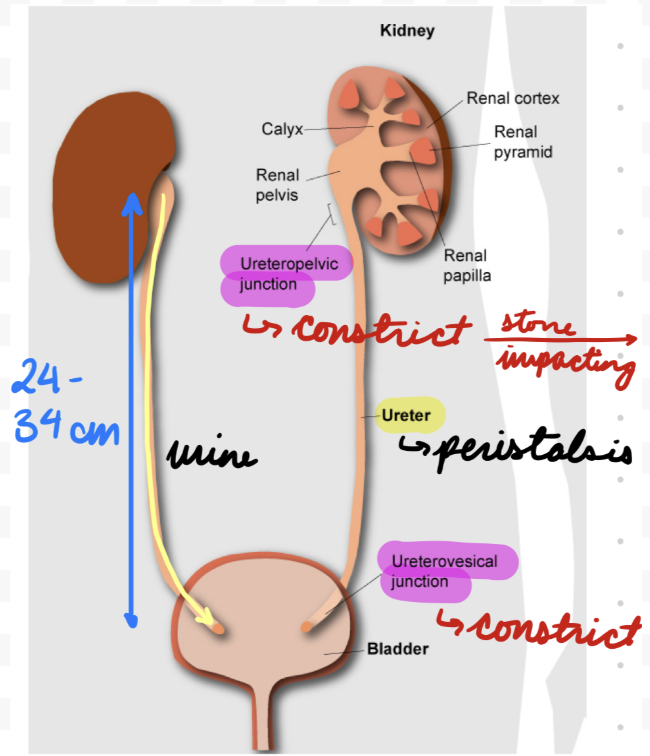
Ureters: Length
24-34 cm
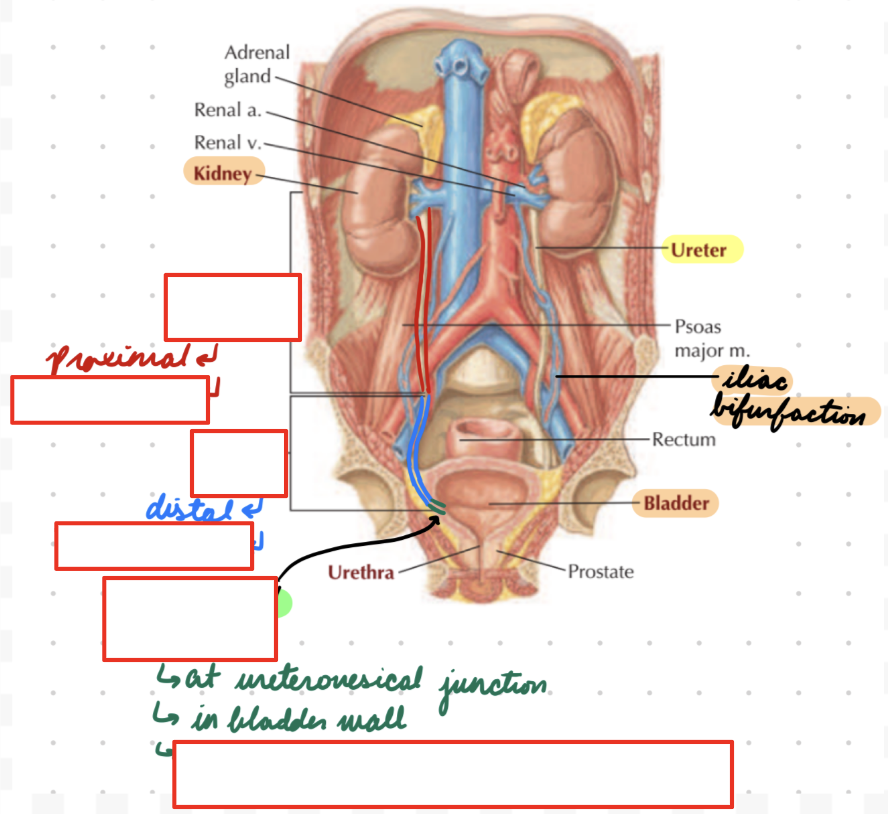
Ureters: Divisions
Proximal (Abdominal): Renal pelvis to iliac bifurcation (iliac artery from aorta splitting)
Upper portion
Muscle layers
Circular and longitudinal
Mucosal folds
Distal (Pelvic): Iliac bifurcation to bladder
Lower portion
Dense fibrovascular and neural tissue
Muscle layer
Less organized
Thin
Intramural: At ureterovesical junction (UVJ)
2 cm
In bladder wall
Ureters: Sites Constriction
Ureteropelvic Junction (UPJ): Connection with kidneys
Posterior to renal vein and artery in hilum
UVJ: Connection with bladder
Ureters: Innervation
SNS: Lumbar splanchnic nerve
PNS: Pelvic splanchnic nerve and vagus nerve
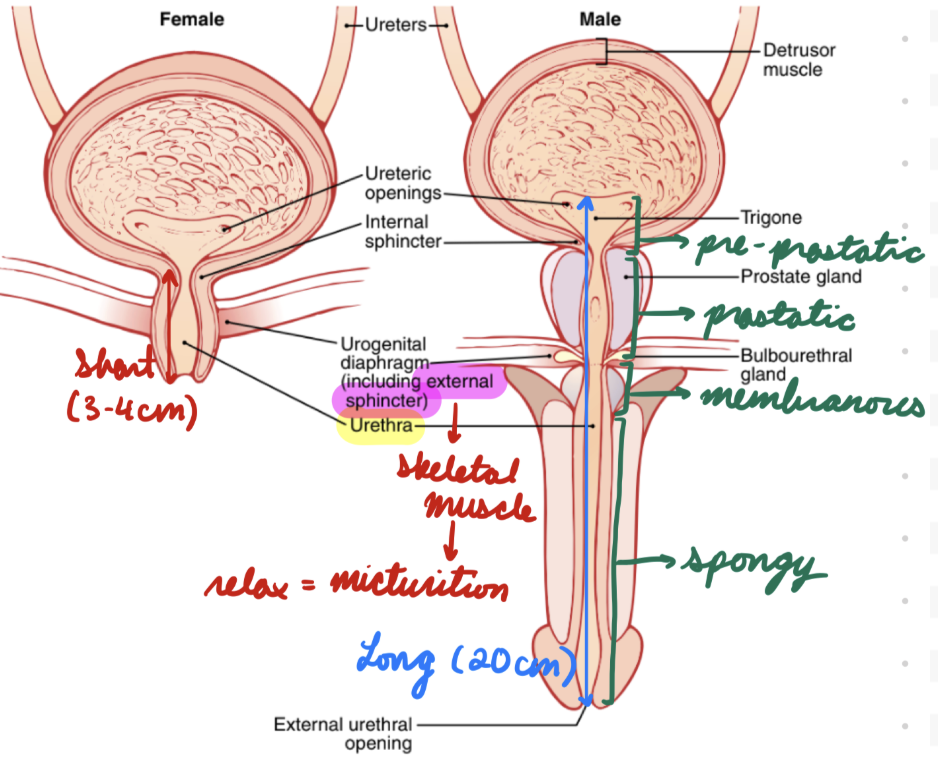
Urinary Tract: Bladder
In anterior pelvis
Body: Smooth muscle (detrusor)
Neck (Posterior Urethra): Funnel-shaped detrusor muscle extension from body
Connect to urethra
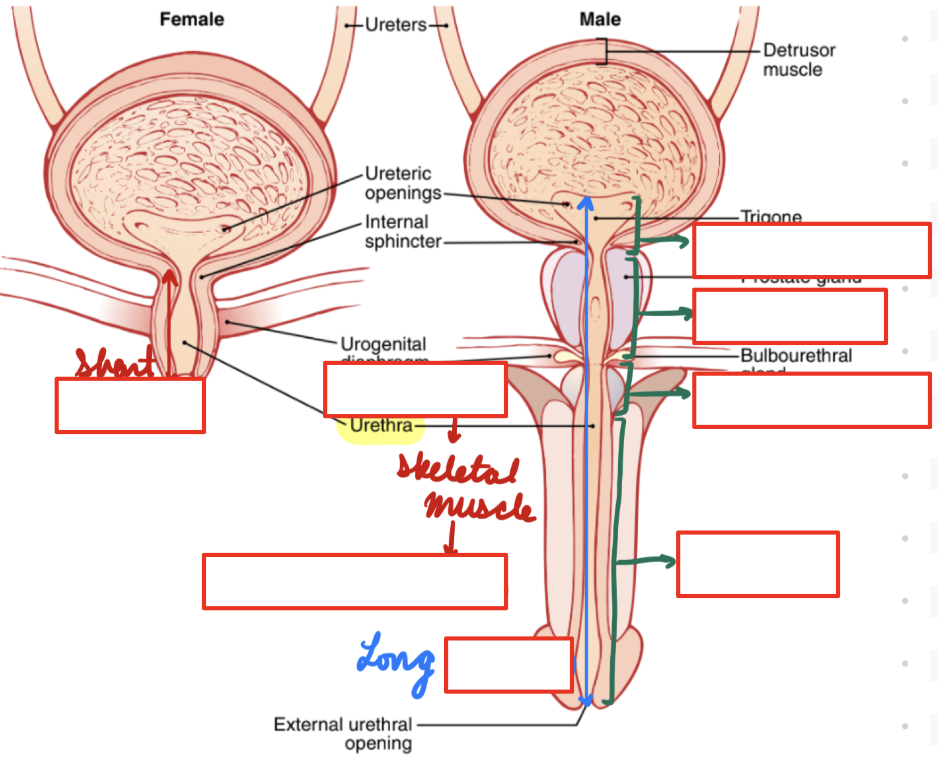
Contain internal sphincter
Bladder: Females
Anterior to uterus and colon
Smaller
Bladder: Males
Superior to prostate
Anterior to colon
Larger
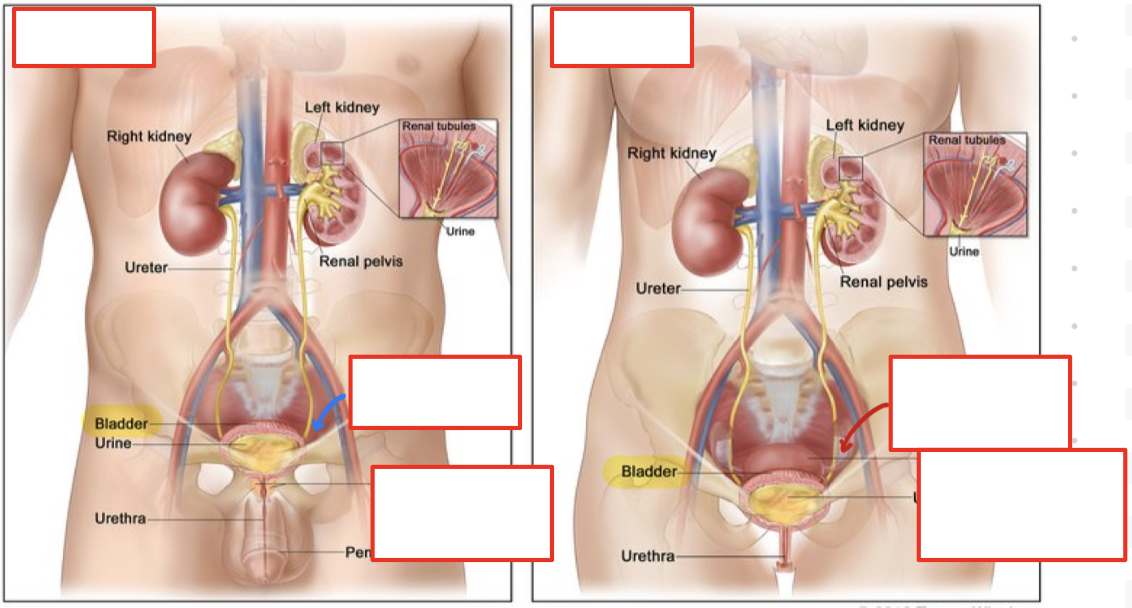

Urinary Tract: Urethra
Connect urinary bladder to exterior (exit body)
Contain external sphincter
Skeletal muscle
Urethra: Males
Long (20 cm)
Pass through prostate gland, external urethral sphincter, and corpus spongiosum
Male Urethra: Regions
Pre-Prostatic: In bladder wall
Prostatic: Through prostate gland
Membranous: Through perineum and deep muscles
Spongy: Through penis in corpus spongiosum
Urethra: Females
Short (3-4 cm)
Urinary Tract Physiology: Kidneys
Filter plasma
Reabsorb electrolytes, molecules, vitamins, and water
Excrete metabolic waste and chemicals (drugs)
Regulate fluid volume, composition, and pH
Hormone secretion
Regulate BP, erythropoiesis, and Ca2+ metabolism
Produce urine
Empty into calyces (Stretch = Initiate peristaltic contractions)
Push urine into ureters
Urinary Tract Physiology: Ureters
Transport urine from kidneys to bladder
Peristaltic smooth muscle contraction
Gap junctions between cells = Simultaneous action potential propagation = Synchronized contraction
Urinary Tract Physiology: Proximal Ureter
Muscle layers form functional sphincter
Regulate urine outflow from renal pelvis
Initiate peristaltic waves
Urinary Tract Physiology: Distal Ureter
Increased pain sensation
Peristaltic coordination
Urinary Tract Physiology: Intramural Ureter
Prevent vesicoureteral reflux (VUR)
Urine backflow from bladder → Kidneys
Increase pressure on ureters = Dilation + Lengthening = Tortuous (twisted) appearance
Urinary Tract Physiology: Sites of Constriction
Increased risk of calculi (stones) lodging + obstructing urinary flow
Urinary Tract Physiology: Bladder
Body:
Store urine
Normal tone of detrusor muscles compress ureters to prevent urine backflow
Peristaltic contractions open ureters for urine entry
Neck:
Internal sphincter
Natural tone (constricted) = Prevent bladder emptying
Bladder: Micturition
Empty urine into urethra
Bladder filling = Increase wall tension > Threshold level = Activate mechanoreceptors
CNS sends somatic signals to bladder = Open internal sphincter
Activate micturition reflex (autonomic from spinal cord) = Detrusor muscle contraction = Empty into urethra
Inhibited or facilitated by cerebral cortex or brain stem
Urinary Tract Physiology: Urethra
External sphincter
Voluntary control
Contraction = Prevent bladder emptying
Urinary Tract Infections (UTI): Description
Urinary system infection
Lower: Bladder (cystitis) or urethra infection
Most common
Upper: Kidney (pyelonephritis) or ureter infection
Recurrent:
≥ 3 episodes in 1 year
≥ 2 episodes in 6 months
UTI: Epidemiology
Risk factors:
Structural/functional urinary tract abnormalities
Ex: Benign prostatic hyperplasia, VUR
Metabolic conditions
Genetic predisposition
Previous UTI
Antibiotic use
Female
Shorter urethra
Anal and genital regions in close proximity
UTI: Etiology
Usually bacterial infection ascending from urethra to bladder
E. coli: Most common
By Population:
Adults:
Female: Most common
Male: Low before 50, increase with age from benign prostatic hyperplasia obstructing urinary tract
Children: Most common
Female: Increased incidence in girls >1 years
Male: More common than girls (esp uncircumcised)
Transgender:
Incidence depend on current genitourinary anatomy + history of gender-affirming surgery
M → F: Increased risk from lack of commensal vaginal bacteria
UTI: Recurrent Etiology
Bacterial Characteristics:
Virulence factors = Evade host response = Increase adaptation and colonization
Host Factors:
Genetic predisposition
Behavioural Factors:
Disturb vaginal microbiome = Increase colonization
Frequent sexual intercourse
Spermicide use
Hygiene
Wiping back to front
UTI: Pathogenesis
Bacteria from bowel or vagina colonize periurethral mucosa
Ascending Infection: Migrate from urethra → Bladder → Kidneys (sometimes)
Bacteria adapt to urinary tract
Virulence factors
Biofilm formation
UTI: Clinical Presentation
Lower:
Urethra:
Dysuria
Urethra pruritus (itching)
Abnormal urethral discharge
Bladder:
Suprapubic or pelvic pain
Increased during filling
Relieved from voiding
Nocturia
Upper:
Kidney:
Flank pain
Fever
Malaise
Hematuria
Impaired renal function
Edema
Hypertension
UTI: Investigation
Urinalysis
Cultures
Imaging
UTI: Urinalysis
Best initial test
Collection:
Clean-catch midstream sample
Bladder catheterization
Pyuria: WBC in urine
Positive leukocyte esterase (emzyme from WBC)
Bacteriuria: Bacteria in urine
Nitrites: Gram- bacteria converting nitrates to nitrites
Alkaline Urine: Urease-producing organisms
UTI: Cultures
For complicated or recurrent UTI
Bacteriurua: ≥ 10^5 CFU/mL
Organisms from suprapubic aspiration
Needle through abdomen into bladder to collect sample
UTI: Imaging
For suspected urinary tract obstruction (No response to antibiotics)
CT
Ultrasound
UTI Imaging: CT
Abdominal and pelvic
UTI Imaging: Ultrasound
Kidney and bladder
UTI: Treatment/Management
Antibiotics
Increase hydration
UTI Treatment: Antibiotics
Empiric first-line
Nitrofurantoin
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (TMP/SMZ)
Fosfomycin (1 dose)
Complicated Lower: Fluorouinolones (first-line)
Recurrent: TMP/SMZ prophylaxis
UTI: Complications
Pyelonephritis
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Description
Smooth muscle and epithelial cell proliferation in prostate
Increase risk of lower UTIs
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Management
Little to no symptoms: Nonpharmacological therapy (watchful waiting)
Symptomatic: Pharmacotherapy and surgery
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Nonpharmacological Therapy
Drugs: Stop/decrease drugs contributing to symptoms
Ex: Opioids, TCA antidepressants, antihistamines
Diet Changes: Decrease caffeine and alcohol
Bladder-emptying techniques
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Pharmacotherapy
First-line
Alpha Blockers:
Inhibit alpha 1-receptors in bladder neck and urethra = Relax smooth muscles = Decrease urinary outflow resistance
5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors (5-ARIs):
Inhibit 5-alpha reductase = Decrease testosterone → DHT = Decrease prostatic growth + Increase prostatic apoptosis
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Surgery
Second-line
Transurethral resection of prostate (gold standard)
Remove excess prostatic tissue around urethra
Nephrolithiasis: Description
Crystalline mineral deposit form in kidneys and ureters
Uretal or kidney stones (renal calculi)
Nephrolithiasis: Epidemiology
Risk factors:
Male
Older age
Low fluid intake/dehydration
Prolonged immobilization
Diet
High Na+
Low Ca2+
Supplements
Family history
Nephrolithiasis: Etiology
Calcium Oxalate Stones: Most common
Caused by hypercalciuria, hyperoxaluria, hypocitraturia
Uric Acid Stones:
Caused by
Gout: Uric acid crystals precipitate in joints
Hyperuricemia: High serum uric acid concentration
Hyperuricosuria: High uric acid excretion in urine (ketogenic diet)
High cell turnover
*Struvite Stones:
Caused by urease-producing bacteria
Cysteine Stones:
Caused by cystinuria (hereditary)
Nephrolithiasis: Pathogenesis
For calcium oxalate stones
Dehydration and high Ca2+ diet = Low urine volume + High Ca2+ reabsorption
Increased urine Ca2+ saturation = Crystals deposit in kidney (papillae) and ureters
Cellular injury, oxidative stress, and inflammation increase crystal retention and aggregation
Nephrolithiasis: Clinical Presentation
Depend on location and size
Larger = More symptoms
Severe unilateral flank pain (renal colic)
Radiating (loin to groin)
Paroxysmal or progressive
Tenderness around kidneys
Hematuria
Nausea/vomiting
Dysuria
Increased frequency and urgency
Nephrolithiasis: Investigation
Urinalysis
Microscopy
Blood test
CT
Ultrasound
X-ray
Stone composition analysis
Nephrolithiasis: Urinalysis
First-line
Hematuria
Alkaline/acidic urine
Nephrolithiasis: Microscopy
Determine crystals = Stone composition
Nephrolithiasis: Blood Test
Metabolic panel to determine metabolite (Ca2+, uric acid) concentration in blood
High WBC
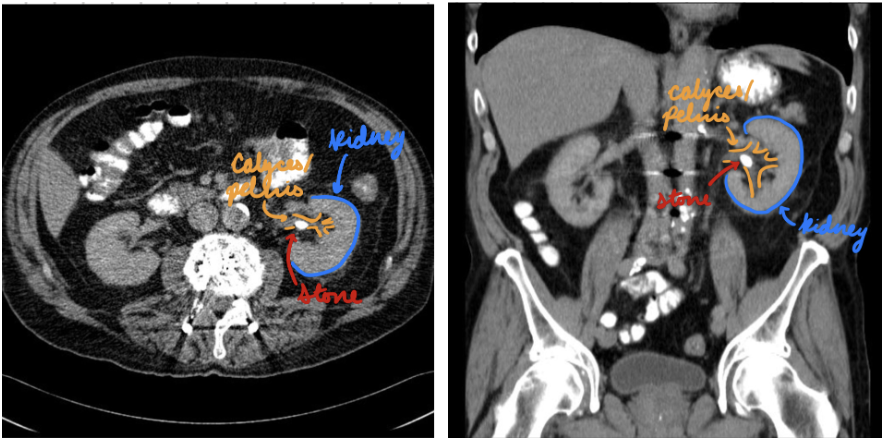
Nephrolithiasis: CT
Gold standard
Stones/calcifications in kidneys and ureters
Determine size, location, density, and degree of obstruction
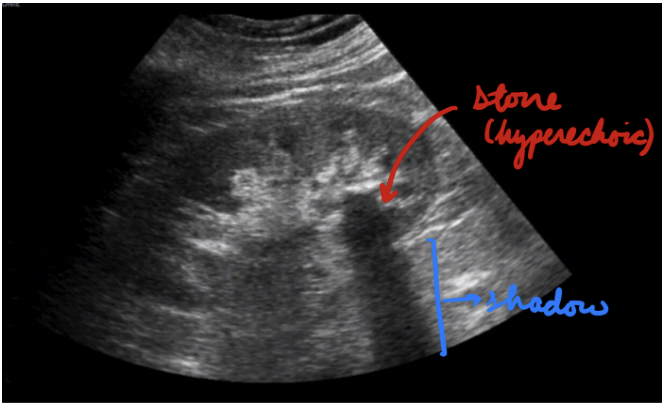
Nephrolithiasis: Ultrasound
Minimize radiation exposure (pregnant, pediatric)
Hyperechoic stones + Shadowing
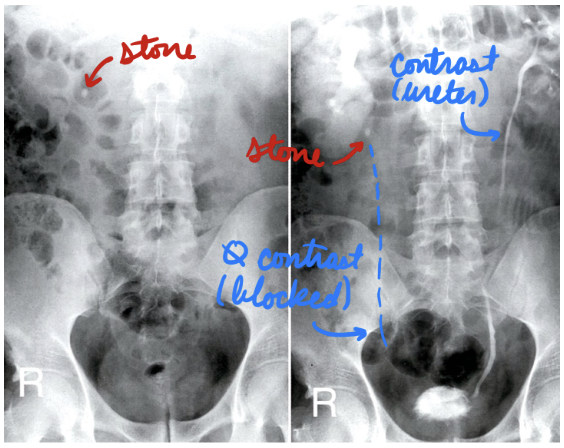
Nephrolithiasis: X-Ray
Intravenous pylogram (IVP)
X-ray + contrast
Rare → Use CT instead
Nephrolithiasis: Stone Composition Analysis
In first stone
Nephrolithiasis: Treatment/Management
Manage symptoms
Non-interventional
Interventional
Nephrolithiasis Treatment: Manage Symptoms
Analgesia
First-line: NSAIDs
Second-line: Opioids
Antiemetics
IV fluids (dehydration)
Nephrolithiasis Treatment: Non-Interventional
Medical expulsive therapy (MET)
First-Line: Tamsulosin (alpha blocker)
Prevent ureter muscle spasms to promote stone passing
Antibiotics for UTIs
Diet modifications
Low Na+ and oxalate
Supplement vit C
Nephrolithiasis Treatment: Interventional
Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL): Acoustic shockwaves breakdown stones
Noninvasive
*Ureteroenoscopy: Endoscope insertion to remove stone
Invasive
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL): Puncture renal pelvis calyx + insert endoscope to remove stone
Invasive
For larger stones
*Ureterolithotomy: Ureteral incision to remove stone
Invasive
Nephrolithiasis: Prognosis
Small Stones (≤ 5 mm): Pass spontaneously
Larger Stones (≥ 10 mm) : Unlikely to pass spontaneously
Recurring stones within 10 years = 50%
Cause or caused by UTIs