Coastal Landforms Formation - Vocabulary Flashcards
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key coastal landforms and the processes that form them, based on the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Headland
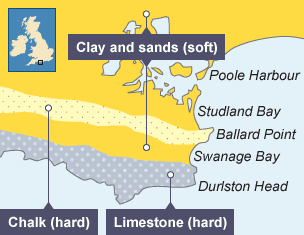
A projection of resistant rock that sticks out into the sea on a discordant coastline; formed where less resistant rock erodes, leaving the headland, with energy concentrated on it by wave refraction. Ballard Point(Dorset)
Bay
A curved inlet formed where softer rock erodes more quickly between headlands on a discordant coastline. Swanage Bay
Differential erosion
Unequal erosion rates between rock types, creating features such as headlands and bays.
Discordant coastline
A coastline with rock bands running at right angles to the shoreline, producing alternating hard and soft rock that erodes at different rates. creating headlands and Bays
Additional Information -
The soft rock is made of clay and sands, and the hard rock is chalk and limestone. As erosion processes take place, the clay erodes away quicker than the limestone and chalk. This forms headlands and bays, creating Swanage Bay and two headlands - Ballard Point and Durlston Head.
Wave refraction
The bending of waves as they approach an irregular coast, concentrating energy on headlands and dispersing it in bays.
Cliffs
Steep rock faces formed by coastal erosion (hydraulic action and abrasion) at the base, often retreating over time. Example-The White Cliffs of Dover
Wave-cut notch
A hollow eroded at the base of a cliff by wave action, leading to eventual cliff collapse.
Wave-cut platform
A flat rocky shelf left at the foot of a retreating cliff, exposed at low tide.Example Flamborough Head, Holderness.
Cave
A hollow formed by erosion of joints/faults in rock.
Arch
A natural opening formed when a cave is enlarged until it breaks through to the other side.
Stack
A vertical rock column left after the roof of an arch collapses.
Stump
A small, eroded remnant of a former stack near sea level. Example Old Harry Rocks-Dorset
Beach
A gently sloping accumulation of sand or shingle deposited by constructive waves; features include berms and ridges. eg Chesil Beach
Constructive waves
Low-energy waves that deposit sediment and build beaches.
Berm
A ridge of sand or shingle deposited at the edge of the beach, marking the high-tide line.
Longshore drift
The movement of sediment along the coast driven by waves hitting the coast at an angle.
Spit
A long narrow ridge of sand/shingle extending beyond a headland due to longshore drift; often with a recurved end and salt marsh behind. Example- Spurn Head-Holderness
Tombolo
A spit that connects a mainland to an offshore island by deposition under wave refraction. Example-Chesil Beach linking Isle of Portland, Dorset.
Offshore bar
A submerged ridge formed by deposited material just offshore.
Barrier beach
A beach formed when a spit grows across a bay, creating a sheltered lagoon behind. Chesil Beach
Barrier island
A detached ridge running parallel to the coast, forming a separate island. Scolt Head Island
Sand dune
A wind-formed accumulation of sand that develops through stages—embryo dune, foredune, yellow dune, grey dune—followed by dune slacks and eventual heath/woodland. Studland Bay-Dorest
Embryo dune
The first stage of dune formation where sand begins to accumulate and vegetation starts.
Foredune
The dune formed as wind-blown sand builds up on the beach.
Yellow dune
A mature dune with yellow, dry sand indicating stabilization.
Grey dune
A stabilized dune with organic matter and vegetation.
Dune slack
A damp hollow between dunes, often in wet conditions.
Estuarine mudflat
Low-energy estuaries where silt/clay is deposited where Flocculation encourages settlement and then trapped by halophytes, forming creeks/channels.Blackwater-Estuary, Essex.
Saltmarsh
Coastal wetland formed by sediment accumulation and halophytic vegetation (e.g., Spartina) in sheltered areas.
Spartina
A salt-tolerant grass that helps trap sediment in saltmarshes.
Flocculation
The clumping of fine particles (clay/silt) in water, aiding deposition.
Ria
A drowned river valley with a deep, narrow upper course and a wider lower course due to sea-level rise. Kingsbridge Estuary, Devon
Fjord
A drowned glacial U-shaped valley with steep sides and a deep basin, often with a shallow threshold from terminal moraine.Loch Torridon- Scotland
Dalmatian coast
A drowned concordant coastline where parallel ridges of resistant rock are submerged, leaving long islands; Isles of Scilly and Croatia.
