2.1 SI Units and the Metric System
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
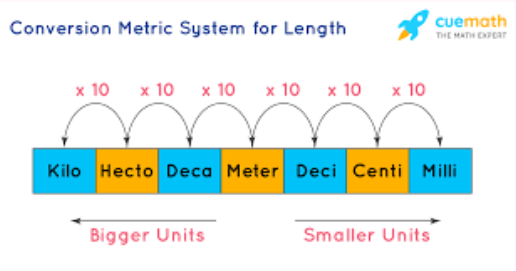
Metric System
A decimal-based measurement system built on powers of ten and used worldwide by scientists.
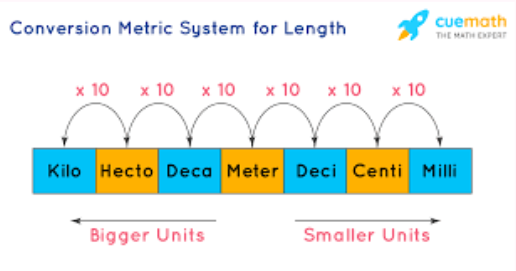
Base-10 Structure
The feature of the metric system in which each unit is related by factors of ten, making conversions simple.
Meter (m)
The base metric unit of length equivalent to 1/10,000,000 of the distance from the equator to the North Pole.

Gram (g)
The basic metric unit of mass; one thousand grams equal one kilogram.

Liter (L)
The metric unit of volume commonly used for liquids; equivalent to 1,000 cubic centimeters.
Length
A measurement of distance between two points, typically expressed in meters, centimeters, or millimeters in science.

Mass
The amount of matter in an object; typically measured in grams or kilograms in science.
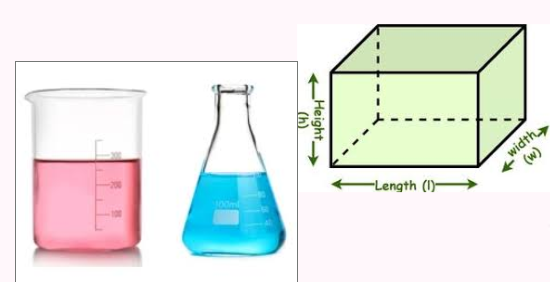
Volume
The amount of space an object occupies; typically measured in liters or cubic units in science.

Kilometer (km)
A metric unit of length equal to 1,000 meters; useful for large distances.

Centimeter (cm)
A metric unit of length equal to one-hundredth of a meter (0.01 m). Equal to about the width of your finger.

Millimeter (mm)
A metric unit of length equal to one-thousandth of a meter (0.001 m). Equal to about the thickness of your fingernail.

Conversion factor
A ratio that expresses how many of one unit are equal to another unit, used to switch between measurement units.
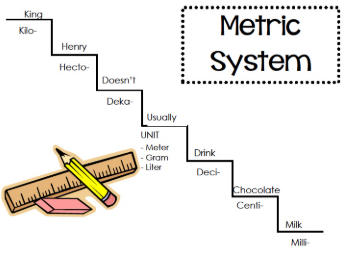
Mnemonic device
A memory aid—such as “King Henry Died By Drinking Chocolate Milk”—that helps recall metric prefixes and their order.
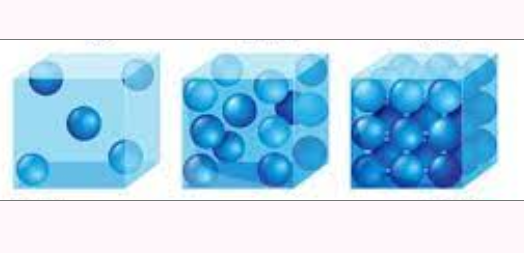
Density
The mass per unit volume of a substance, often expressed in g/cm³.
Standardization in science
Using the same measurement system (SI/metric) globally to allow clear communication and consistent data comparison.
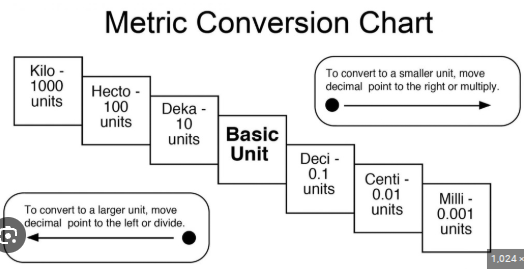
Prefix
A letter or group of letters placed before a metric base unit; used to make the base unit either bigger or smaller; indicates a specific multiplier in the metric system, such as kilo- (1000), centi- (100) or milli- (0.001).
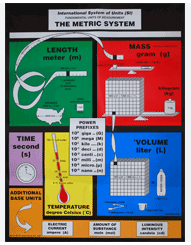
Base Unit
A unit in the metric system that defines a standard for measurement of physical quantities, including meter (length), kilogram (mass), second (time), ampere (electric current), kelvin (temperature), mole (amount of substance), and candela (luminous intensity).

International System of Units (SI)
The modern form of the metric system, which is a comprehensive system of units used for scientific and technical measurements, providing a standardized approach to quantify and compare physical properties.